CHAPTER 14 - DEVELOPING PRICING STRATEGIES AND PROGRAMS
1/146
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
147 Terms
Marketing Mix
Product
Price
Place
Promotion
the only one of the 4ps that produce revenue
Price
traditionally a major determinant of buyer choice.
Price
Ways the buyers can discriminate between sellers
get instant price comparisons from thousands of vendors.
name their price and get it
get products for free
the buyer can discriminate the seller by comparing the prices offered by multiple stores.
Get instant price comparisons from thousands of vendors
the buyer can discriminate the seller by stating the price they want and meeting sellers who can meet the price willingly.
Name their price and have it met
the buyer can discriminate the seller by acquiring the initial product for free.
Get products free
ways sellers can discriminate against the buyers
monitor customer behavior and tailor offers to individuals
give certain customers access to special prices
way buyer and seller can discriminate against each other
negotiate prices in online auctions and exchanges or in person
how small companies price
the boss sets the prices
how large companies price
through pricing departments, top management, or finance departments.
based on how consumers perceive prices and what they consider the current actual price to be.
purchase decisions
consumers compare an observed price to an internal reference price they remember or an external frame of reference e.g., SRP
Reference price
consumers use price as an indicator of quality
price-quality inferences
When information about the ____ is unavailable, price acts as a signal of quality.
quality
many sellers believe prices should end in an odd number.
price endings
steps in setting the price
selecting price objective
determine demand
estimate costs
competitor analysis
price method
selecting the final price
the company first decides where it wants to position its market offering.
Setting pricing objectives
Five Major Pricing Objectives
survival
Maximum current profit
maximum market share
maximum market skimming
product-quality leadership
short-run pricing objective for firms to deal with overcapacity, intense competition, and changing customer wants.
Survival
pricing objective where they estimate the demand and costs associated with alternative prices and choose the price that produces [redacted], cash flow, or rate of return on investment.
Maximum current profit
pricing objective wherein they set the lowest price, assuming that the market is price sensitive.
maximum market share
another term for maximum market share
market-penetration pricing
conditions that favor adopting maximum market share
market is highly price sensitive
production and distribution costs fall with acuumulated production experience.
low price discourages competition
pricing objective wherein they price high then slowly drop over time
maximum market skimming
pricing objective wherein they offer brands that are affordable luxuries.
product-quality leadership
pricing objective wherein they provide quality product at a cost lower than expected.
Partial cost recovery
each price will lead to a different level of demand and have a different impact on a company’s marketing objectives.
Determine demand
a measurement of how much the price of goods and services affects customers' willingness to buy them.
Price sensitivity
customers are less sensitive to ____ items or items they buy ___.
low-cost; infrequently.
the purchase price of an asset plus the costs of operation.
total cost of ownership (TCO)
different methods to measure demand curves
surveys
price experiments
statistical analysis
can explore how many units consumers would buy at different proposed prices.
surveys
can vary the prices of different products in a store or charge different prices for the same product in similar territories to see how the change affects sales.
price experiments
can reveal the relationship of past prices, quantities sold, and other factors.
statistical analysis
data over time
longitudinal data
data from different locations at the same time.
cross-sectional
demand changes considerably
elastic demand
demand hardly changes
inelastic demand
the higher the price,______.
the lower the demand
a range of prices within which price changes have little or no impact on customers’ willingness to make a purchase.
price indifference band
the company wants to charge a price that covers its cost of producing, distributing, and selling the product.
estimate costs
sets the price ceiling
demand
sets the price floor
costs
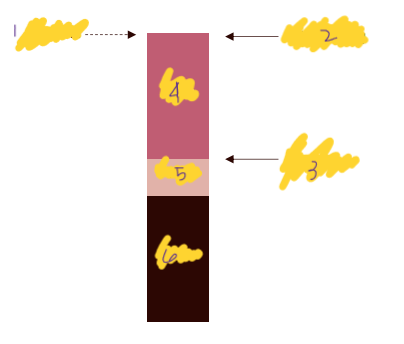
Demand
Price Ceiling
Price Floor
Price
Profit
Costs
types of cost
fixed costs
variable costs
total costs
average costs
overhead
fixed costs
costs that do not vary with production levels or sales revenue
fixed costs
rent is an example of what cost?
fixed costs
vary directly with the level of production.
variable costs
raw materials is an example of what cost?
variable costs
fixed costs + variable costs
total costs
Total costs formula
Fixed costs + variable costs
cost per unit at that level of production
average costs
total costs / production
average costs
average costs formula
total costs / production
the gain a company experiences in producing a product over a period of time
accumulated production
the decline in the average costs with accumulated production experience
experience curve/learning curve
the pricing of a product at a lower than average-cost level on the basis that costs will decrease as production experience increases.
experience curve pricing
examining each cost element and bringing down costs so the final costs projection are in the target range.
target costing
analyzing competitors’ costs, prices, and potential price reactions
Competitor Analysis
three major considerations in price setting
costs
competitors
customers
their prices provide an orienting point
competitors
their assessment of unique features establishes the price ceiling.
customers
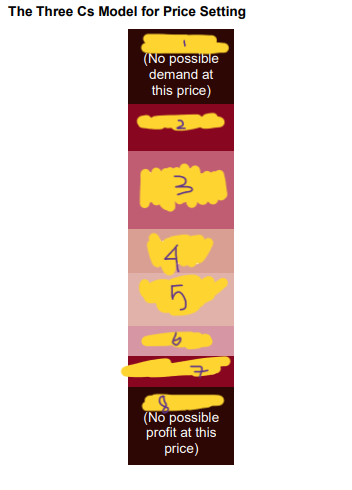
High price
ceiling price
customers’ assessment
orienting point
competitors’ prices
costs
price floor
low price
Price Setting methods
markup pricing
target-return pricing
perceived-value pricing
value pricing
going-rate pricing
auction-type pricing
does not take into account the current demand, perceived value, or competition.
markup pricing
the most elementary pricing method
markup pricing
formula of unit cost
Unit cost = (variable cost) + [(fixed cost) / (unit sales)]
formula of markup pricing
(unit cost) / (1 - desired return on sales)
the firm determines the price that yields its target rate of return on investment.
target-return pricing
pricing method often used by public utilities.
target-return pricing
formula of target-return price
[unit cost] + [(desired return x invested capital) / unit sales ]
the amount of your production that you will need to produce and sell to cover total costs of production.
break-even volume
formula of break-even volume
fixed cost / (price - variable cost)
customer’s perceived value is determined by the buyer’s image of the ____.
product performance
channel deliverables
warranty quality
customer support
supplier’s reputation
companies must deliver the value promised by their value proposition, and the customer must perceive this value.
Perceived-value pricing
a matter of reengineering the company’s operations to become a low-cost producer without sacrificing quality to attract a large number of value-conscious customers.
value pricing
an important type of value pricing where they charge constant low price with little or no price promotions and special sales.
Everyday Low Pricing
charges higher prices on an everyday basis but runs frequent promotions with prices temporarily lower than the EDLP level.
high-low pricing
the firm bases its price largely on comeptitor’s prices.
Going-rate pricing
pricing through auctions and bids
auction-type pricing
a process of buying and selling goods or services by offering them up for bid, taking bids, and then selling the item to the highest bidder.
auction
an offer to pay a particular amount of money for something that is being sold.
bid
three major types of auctions
English auctions
dutch auctions
sealed-bid auctions
ascending bids; highest bidder gets the item
English auctions
1 seller : many buyers
english auctions
descending bids; buyer announces something they want to buy, then potential sellers compete to offer the lowest price.
dutch auctions
one buyer : many sellers
dutch auctions
lets would-be suppliers submit only one bid and they cannot know the other bids.
sealed-bid auctions
the company must consider additional factors like the impact of other marketing activities, company pricing policies, gain-and-risk sharing pricing, and the impact of price on other parties.
Select final price
the final price must take into account the brand’s quality and advertising relative to the competition.
impact of Other marketing activities
the price must be consistent with company pricing policies.
company pricing policies
buyers may resist accpeting a seller’s proposal because of a high-perceived level of risk.
gain-and-risk-sharing pricing
how will distributors and dealers feel about the contemplated price?
Impact of price on other parties
Price-Adaptation Strategies
geographical pricing
price discounts and allowances
promotional pricing
differential pricing
the company decides how to price its products to different customers in different locations and countries.
geographical pricing
offering other items in payment
countertrade
different forms of countertrade
barter
compensation deal
buyback arrangement
offset
buyer and seller directly exchange goods; no money; no third party involved.
barter