Biol 200 Unit 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/112
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:34 AM on 3/3/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
113 Terms
1
New cards
3 basic plant organs
Roots, stems, and leaves
2
New cards
Roots
collect/ store nutrients (water & minerals), and provide structural support
3
New cards
Stems
transport water and nutrients up, sugars and nutrients down, structural support
4
New cards
Leaves
synthesizing sugars, cellular respiration
5
New cards
Modded Roots
Prop
Storage
Pneumatophores
Storage
Pneumatophores
6
New cards
Prop Roots
Stabilize, better anchoring, aerial roots
7
New cards
Storage Roots
Stored energy that would be used for flowering, but we eat before it can
8
New cards
Pneumatophores
Enable roots to obtain oxygen, “air roots”
9
New cards
Reproductive shoot
Flowers
10
New cards
Apical bud
where vertical growth of the stem occurs
11
New cards
Node
intersection of anything growing out
12
New cards
Internode
sections in between extensions coming off of the stem
13
New cards
vegetative shoot
outgrowth of plant that supports many leaves
14
New cards
axillary bud
growth to fill in extra capacity (leaves prevent plant from becoming top heavy)
15
New cards
petiole
supports a single leaf
16
New cards
blade
the leaf
17
New cards
stem
provides structure, contains minerals and water for transportation between roots and shoots
18
New cards
Apical bud functions
growth of shoot allows for vertical growth, on top of stem
19
New cards
Axillary bud functions
can grow into branches or flowers, at the base of leaves
20
New cards
Modified Stems
Rhizomes
Tuber
Stolons
Tuber
Stolons
21
New cards
Rhizomes
Horizontal shoot below surface
22
New cards
Tuber
Enlarged ends of rhizomes, specialized food storage
23
New cards
Stolons
Horizontal shoot on surface. maximize photosynthesis opportunity
24
New cards
3 different leaf shapes
Simple
Pinnate compound
Palmate compound
Pinnate compound
Palmate compound
25
New cards
Simple
single blade (can be lobed)
26
New cards
Pinnate compound
blade consists of multiple leaflets
27
New cards
Palmate compound
leaflets arise from common point
28
New cards
Modified leaf
Tendrils
Spines
Storage leaves
Spines
Storage leaves
29
New cards
Tendrils
Clings for support, vertical growth for sunlight
30
New cards
Spines
Protection
31
New cards
Storage leaves
Storage of food Short underground stem and modified leaves store food underground
32
New cards
Phyllotaxy
The arrangement of leaves on a stem
Alternate
Opposite
Whorled
Alternate
Opposite
Whorled
33
New cards
Alternate
staggered, maximizes exposure to sunlight
34
New cards
Opposite
opposite of each other
35
New cards
Whorled
take advantage of heavy resources, sunlight may be limited
36
New cards
3 tissue systems
Dermal
Vascular
Ground
Vascular
Ground
37
New cards
Dermal
outer protective covering.
First line of defense against physical damage/pathogens.
Barrier between inside and outside of the plant.
First line of defense against physical damage/pathogens.
Barrier between inside and outside of the plant.
38
New cards
Vascular
xylem and phloem (nutrient and water transport)
39
New cards
Ground
everything else (photosynthesis
40
New cards
5 structures of the dermal system
Epidermis
Cuticle
Root hairs
Trichomes
Periderm
Cuticle
Root hairs
Trichomes
Periderm
41
New cards
Epidermis
outer layer of tightly packed cells
42
New cards
Cuticle
waxy layer reducing water loss
43
New cards
Root hairs
extensions of epidermal cells
44
New cards
Trichomes
hair-like extensions of shoot epidermis (can deter insects (defense) and prevent/reduce water loss)
45
New cards
Periderm
replaces epidermis in woody plants
46
New cards
General function of the vascular system
Transporting materials between roots and shoots (water/ sugar/ nutrients)
47
New cards
2 basic components of the vascular system
Xylem
Phloem
Phloem
48
New cards
Xylem
moves water and minerals from roots to shoot
49
New cards
Phloem
moves sugars from site of synthesis/storage to where sugars are needed (fruits or roots) (both directions)
50
New cards
What is the ground system?
Everything else; storage, photosynthesis, support
51
New cards
difference between the primary and secondary cell wall
Primary cell wall: relatively thin and flexible, all cells have this
Secondary cell wall: strong, between cells plasma membrane and primary cell wall, only some cells have this
Secondary cell wall: strong, between cells plasma membrane and primary cell wall, only some cells have this
52
New cards
Cell types
Parenchyma
Collenchyma
Sclerenchyma
Collenchyma
Sclerenchyma
53
New cards
Parenchyma
Primary Wall - Yes
Secondary Wall - No
Structure - Thin, flexible
Function - Metabolic functions like storage and photosynthesis (synthesize/store products)
Secondary Wall - No
Structure - Thin, flexible
Function - Metabolic functions like storage and photosynthesis (synthesize/store products)
54
New cards
Collenchyma
Primary Wall - Yes
Secondary Wall -No
Structure - Thicker primary cell wall than parenchyma, grouped in strands
Function - Provides flexible support
Secondary Wall -No
Structure - Thicker primary cell wall than parenchyma, grouped in strands
Function - Provides flexible support
55
New cards
Sclerenchyma
Primary Wall - Yes
Secondary Wall - Yes
Structure - Thick 2˚ wall. Dead at maturity
Function - Rigid support
Secondary Wall - Yes
Structure - Thick 2˚ wall. Dead at maturity
Function - Rigid support
56
New cards
Indeterminate growth
throughout life, doesn’t stop, plants have indeterminate growth
57
New cards
Determinate growth
organisms stop growing when they reach a critical size (humans, associated with sexual maturity)
58
New cards
3 different plant life cycles
Annuals
Biennials
Perennials
Biennials
Perennials
59
New cards
Annuals
complete life-cycle in under a year
60
New cards
Biennials
complete life cycle in 2 growing seasons
61
New cards
Perennials
live many years
62
New cards
Meristems
Perpetually dividing, unspecialized tissues, found in areas of growth (root/shoot tips)
63
New cards
Primary growth
growth in length. Roots through soil, shoots towards light. Apical meristems at shoot/root tips
64
New cards
Secondary growth
Not all plants, only woody plants. Growth in width and thickness
65
New cards
3 zones in a longitudinal section of a root tip
Zone of cell division
Zone of elongation
Zone of cell differentiation
Zone of elongation
Zone of cell differentiation
66
New cards
Zone of cell division
cell division occurs here → apical meristem located here
67
New cards
Zone of elongation
cells are 10x original size
68
New cards
Zone of cell differentiation
cells become distinct types, contain root hairs
69
New cards
What is the function of the root cap
protects apical meristem, produces mucus making it easier for the root to slide into the soil
70
New cards
Monocots
1 cotyledon
leaf veins are parallel
fibrous root system
leaf veins are parallel
fibrous root system
71
New cards
Dicots
2 cotyledons
leaf veins in net-like pattern
tap root system
leaf veins in net-like pattern
tap root system
72
New cards
Monocot root
Vascular tissue arrangement - Cylinder
Xylem/phloem arrangement - Xylem forms an O, phloem all around w/i stele
Core of parenchyma cells/Pith - Yes
Xylem/phloem arrangement - Xylem forms an O, phloem all around w/i stele
Core of parenchyma cells/Pith - Yes
73
New cards
Dicot root
Vascular tissue arrangement - Cylinder
Xylem/phloem arrangement - Xylem forms X, phloem around it in stele
Core of parenchyma cells/Pith - No
Xylem/phloem arrangement - Xylem forms X, phloem around it in stele
Core of parenchyma cells/Pith - No
74
New cards
Monocot stem
Vascular tissue arrangement - Bundles
Xylem/phloem arrangement - Bundled together scattered throughout
Core of parenchyma cells/Pith - No
Xylem/phloem arrangement - Bundled together scattered throughout
Core of parenchyma cells/Pith - No
75
New cards
Dicot stem
Vascular tissue arrangement - Bundles
Xylem/phloem arrangement - Bundled together around outside border
Core of parenchyma cells/Pith - Yes
Xylem/phloem arrangement - Bundled together around outside border
Core of parenchyma cells/Pith - Yes
76
New cards
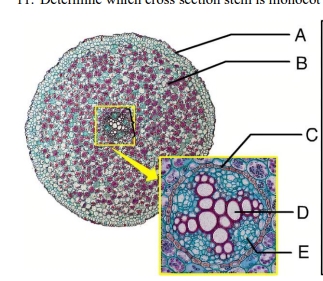
dicot
A-epidermis
B-cortex
C-endodermis
D-xylem
E-phloem
B-cortex
C-endodermis
D-xylem
E-phloem
77
New cards
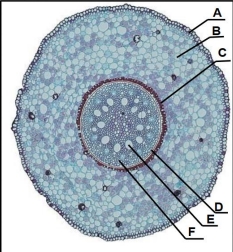
monocot
A-epidermis
B-cortex
C-endodermis
D-vascular cylinder
E-xylem
F-phloem
B-cortex
C-endodermis
D-vascular cylinder
E-xylem
F-phloem
78
New cards
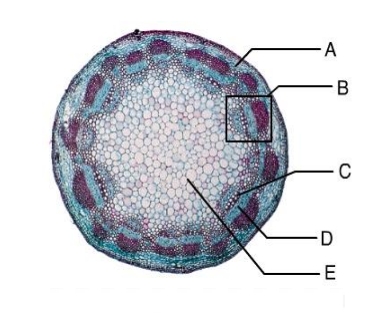
dicot
A-ground tissue
B-vascular bundle
C-xylem
D-phloem
E-pith
B-vascular bundle
C-xylem
D-phloem
E-pith
79
New cards
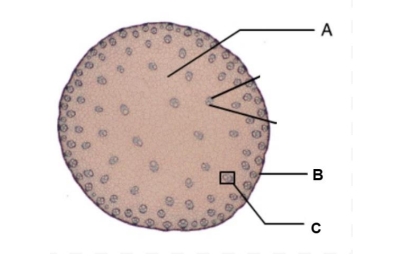
monocot
A-ground tissue
B-epidermis
C-vascular bundle
B-epidermis
C-vascular bundle
80
New cards
Apical dominance
inhibition of axillary buds by apical bud
Is an evolutionary adaptation that focuses plant’s energy on elongation to increase light exposure
Is an evolutionary adaptation that focuses plant’s energy on elongation to increase light exposure
81
New cards
Pruning
removal of apical buds, allows for growth out
If apical bud is removed, the axillary bud develops into a branch that takes over growing towards light
If apical bud is removed, the axillary bud develops into a branch that takes over growing towards light
82
New cards
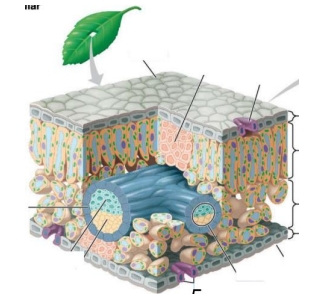
Label: palisade mesophyll, spongy mesophyll, guard cells, stoma, vein, cuticle, upper/lower epidermis, xylem, phloem, sclerenchyma fibers.
Top going around clockwise
Cuticle
Sclerenchyma fibers
Guard cell
Upper epidermis
Palisade mesophyll
Spongy mesophyll
Lower epidermis
Vein
Stoma
Xylem
Phloem
Bundle sheath
Cuticle
Sclerenchyma fibers
Guard cell
Upper epidermis
Palisade mesophyll
Spongy mesophyll
Lower epidermis
Vein
Stoma
Xylem
Phloem
Bundle sheath
83
New cards
Mesophyll
specialized for photosynthesis
84
New cards
Cuticle
waxy outer layer reducing water loss
85
New cards
Stoma
openings/pores on the surface of leaves that allow for transfer of gasses (oxygen, carbon dioxide) and water
86
New cards
Spongy mesophyll
Allows gasses to circulate cells
Allows for gas exchange in diffusion (CO2 in, O2 out).
Contains chloroplasts for photosynthesis
Allows for gas exchange in diffusion (CO2 in, O2 out).
Contains chloroplasts for photosynthesis
87
New cards
Vascular cambium
adds secondary xylem and secondary phloem (located between xylem and phloem)
88
New cards
Cork cambium
creates thick, rough covering (develops from cortex), produces cork cells
89
New cards
What do cork cells do?
replaces the epidermis with the periderm
cork cells are filled with a hard wax that protects the tree
cork cells are filled with a hard wax that protects the tree
90
New cards
Periderm
mainly cork cambium and cork cells
91
New cards
Bark
everything outside vascular cambium (periderm + phloem)
92
New cards
Heartwood
The oldest part of the tree is the middle of the tree
made up of secondary xylem
made up of secondary xylem
93
New cards
Sapwood
secondary xylem that does still conduct water/minerals.
94
New cards
order from the most central to the outermost layer
Heartwood
Sapwood
Vascular cambium
Secondary phloem
Layers of periderm
Sapwood
Vascular cambium
Secondary phloem
Layers of periderm
95
New cards
Passive transport
diffusion across a membrane, no metabolic energy, moving down its concentration gradient
96
New cards
Active transport
pumping a solute across a membrane against its concentration gradient (ATP)
97
New cards
Transport proteins
embedded in membrane, help substances pass through membrane
98
New cards
Osmosis
diffusion of water across a membrane (moves lower to higher solute concentration - water chases solutes)
99
New cards
Aquaporins
Transport proteins that facilitate water transport across the plasma membrane of plant cells.
Channels open/close, affecting rate water moves osmotically across membranes.
Channels open/close, affecting rate water moves osmotically across membranes.
100
New cards
3 cell-to-cell transport routes
Apoplastic route
Symplastic route
Transmembrane route
Symplastic route
Transmembrane route