Chemistry Exam
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/48
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
1
New cards
Boyles Law
P1V1= P2V2
* inversely proportional
* inversely proportional
2
New cards
Charles Law
* directly proportional
* temperature must be in Kelvin (Celsius + 273)
* temperature must be in Kelvin (Celsius + 273)

3
New cards
Amonton’s Law (Gay-Lussac)
P 1/T 1 = P 2/T 2
* directly proportional
* temperature must be in Kelvin (Celsius + 273)
* directly proportional
* temperature must be in Kelvin (Celsius + 273)
4
New cards
Combined Gas Law
* directly proportional

5
New cards
Ideal Gas Law
PV = nRT
* P = pressure (ATM)
* V= volume (L)
* n = number of moles
* R= 0.0821 L \* atm / Mol k
* T= temperature (K)
* both direct and inverse
* P = pressure (ATM)
* V= volume (L)
* n = number of moles
* R= 0.0821 L \* atm / Mol k
* T= temperature (K)
* both direct and inverse
6
New cards
The Kinetic Molecular Theory
Kinetic molecular theory states that gas particles are in constant motion and exhibit perfectly elastic collisions.
● Gas molecules move in straight lines \n ● Gas molecules have no volume \n ● Gas molecules do not attract or repel each other \n ● Gas molecules move at the same speed at a given \n temperature \n ● Gas collision are elastic
● Gas molecules move in straight lines \n ● Gas molecules have no volume \n ● Gas molecules do not attract or repel each other \n ● Gas molecules move at the same speed at a given \n temperature \n ● Gas collision are elastic
7
New cards
Pressure Conversions
1 atm = 760 mm Hg = 760 torr = 101.3 KPa = 14.7 Psi = 101300 Pa
\
* Sea Level Pressure = 1 atm
\
* Sea Level Pressure = 1 atm
8
New cards
Solution
solute dissolved in a solvent
9
New cards
Solvation
the process of surrounding solute particles with solvent particles to form a solution
10
New cards
Solute
stuff being dissolved
11
New cards
Solvent / Universal Solvent
\
able to __dissolve__ other substances.
* Water
* capable of dissolving more substances than any other liquid
able to __dissolve__ other substances.
* Water
* capable of dissolving more substances than any other liquid
12
New cards
Miscible
two liquids that are soluble to each other
13
New cards
Solubility
maximum amount of solute that will dissolve in a given amount of solvent at a specified temperature and pressure
14
New cards
What affects solubility?
Temperature
* increase in the temperature of the solution increases the solubility of a solid solute.
* the solubility of the gas in a liquid solution decreases with increase in temperature
Pressure
* solubility of gas increases as external pressure increases
* Changes in pressure have essentially no effect on the solubility of solids and liquids.
Polarity
* If the solvent is polar, like water, then a larger dipole moment, indicating greater molecular polarity, will tend to increase the solubility of a substance in it.
Stirring
* allows the solute to dissolve faster.
Molecular size
* Solubility decreases as the molecular size increases.
* increase in the temperature of the solution increases the solubility of a solid solute.
* the solubility of the gas in a liquid solution decreases with increase in temperature
Pressure
* solubility of gas increases as external pressure increases
* Changes in pressure have essentially no effect on the solubility of solids and liquids.
Polarity
* If the solvent is polar, like water, then a larger dipole moment, indicating greater molecular polarity, will tend to increase the solubility of a substance in it.
Stirring
* allows the solute to dissolve faster.
Molecular size
* Solubility decreases as the molecular size increases.
15
New cards
What are the 4 colligative properties of solutions?
* vapour pressure lowering, boiling point elevation, freezing point depression and osmotic pressure. (the minimum pressure that must be applied to a solution to halt the flow of solvent molecules through a semipermeable membrane)
16
New cards
Consumer (Percent Soln, Percent Sol)
mass of solute/ mass of solution \* 100
vol of solute/ vol soln \* 100
vol of solute/ vol soln \* 100
17
New cards
Morality
* the number of moles of solute dissolved in one liter of solution
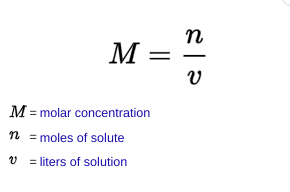
18
New cards
Acids
any species with an H+ proton
* sour
* little pH (less than 7)
* lithmus paper test turns red/ pink
* sour
* little pH (less than 7)
* lithmus paper test turns red/ pink
19
New cards
Bases
any substance with an OH-
* bitter
* slimy
* Big pH (greater than 7)
* lithmus paper turns blue
* bitter
* slimy
* Big pH (greater than 7)
* lithmus paper turns blue
20
New cards
pH
The pH scale is logarithmic, meaning that an increase or decrease of an integer value changes the concentration by a tenfold
* pH = -log \[H+\]
* pOH= -log \[OH-\]
* pH +pOH = 14
* pH = -log \[H+\]
* pOH= -log \[OH-\]
* pH +pOH = 14
21
New cards
Six Strong Acids
* HBr
* HCl
* HI
* HNO3
* H2SO4
* HClO4
* HCl
* HI
* HNO3
* H2SO4
* HClO4
22
New cards
Acid Nomenclature
acids are named using the anion because the cation is always H+
* if anion ends with “ide” then say “hydro” + anion root + “ic” acid
* if anion ends with “ate” then say anion root + “ic” acid
* if anion ends with “ite” then say anion root + “ous” + “acid”
* if anion ends with “ide” then say “hydro” + anion root + “ic” acid
* if anion ends with “ate” then say anion root + “ic” acid
* if anion ends with “ite” then say anion root + “ous” + “acid”
23
New cards
Amphoteric
able to react both as a base and as an acid.
24
New cards
Bronsted/ Lowry Acid
* A Brønsted-Lowry acid is any species that can donate a proton (H+) to another molecule.
* acid is a proton donor
* A Brønsted-Lowry base is any species that can accept a proton from another molecule
* proton acceptor
* acid is a proton donor
* A Brønsted-Lowry base is any species that can accept a proton from another molecule
* proton acceptor
25
New cards
Arrenhius Acid
is any substance that produces hydrogen ions when dissolved in water.
26
New cards
IMFs
attraction etween molecules
* LDF - when the electrons in two adjacent atoms occupy positions that make the atoms form temporary dipoles.
* Dipole- Dipole: all polar molecules
* Hydrogen Bonds: polar molecules with hydrogen bonded with N, O, F
* LDF - when the electrons in two adjacent atoms occupy positions that make the atoms form temporary dipoles.
* Dipole- Dipole: all polar molecules
* Hydrogen Bonds: polar molecules with hydrogen bonded with N, O, F
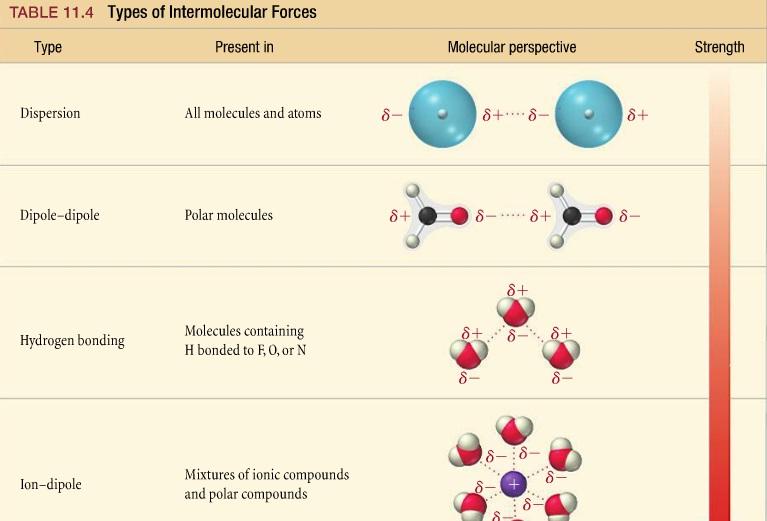
27
New cards
Phase Changes
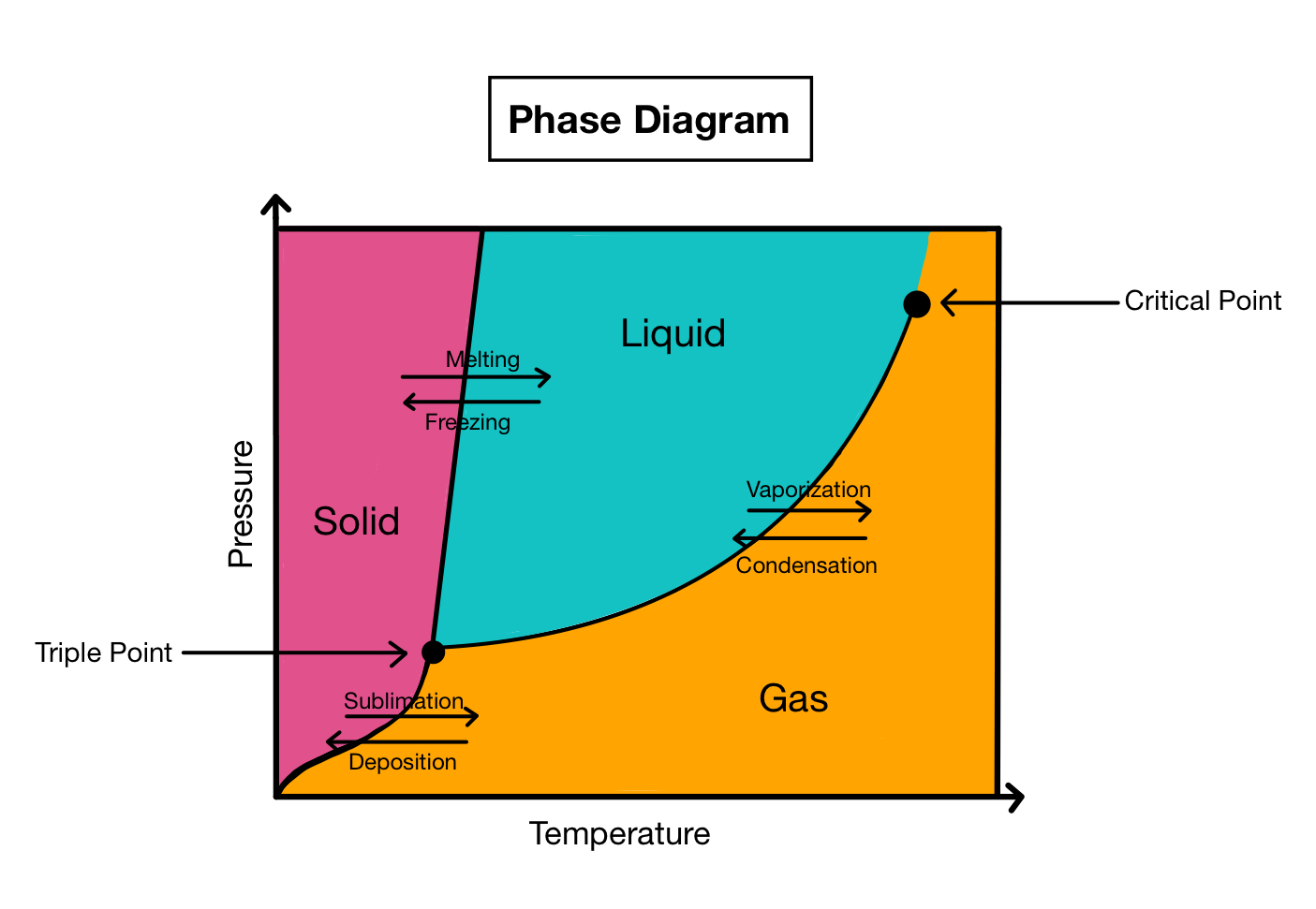
28
New cards
Autoionization
a process by which an excited atom becomes ionized and goes to a lower energy state by emitting one of two or more excited electrons that together possess energy exceeding the atom's ionization energy.
29
New cards
What are the 4 ways to decrease solubility?
decrease surface area (larger chunks), decrease \n temperature, decrease pressure (gas), don’t stir or shak
30
New cards
A 2.50 L flask is filled with propone gas, C3H8, at a pressure of 760 torr and at a temperature of -26 C. How many moles of propane gas are contained in the tank?
0.12 mol
31
New cards
A weather balloon is filled with helium that occupies a volume of 52000 L at 101 kPa and at 32 C. After is it is relased, it rises to a location where the pressure is 71.7 kPa and the temperature is -23 C. What is the volume of the balloon at the new location?
6000 L
32
New cards
The air in a dry, sealed 2-L soda bottle has a pressure of 0.998 atm sea level at temperature of 37.0 C. What will be its pressure if its brought to a higher altitude where the temperature is only 25.0 C?
0.959 atm
33
New cards
Raising the temperature of a gas fixed volume container will most likely change the (Amonton’s)
pressure exerted by the gas in the container
34
New cards
When a sample of a gas is kept at constant pressure, the volume and kelvin temperature of the gas are (Charles’)
directly proportional
35
New cards
If the amount and temperature of a gas are kept constant, the pressure and volume of the gas are (Boyle’s)
inversely proptional
36
New cards
A fixed amount of gas is held in a 1.00 L tank of pressure at 3.00 atm. The tank is connected to an empty 3.00 L tank by a tube with a valve. After this valve has been opened and the gas is allowed to flow freely between the two tanks at a constant temperature, what is the final pressure in the system? (volume of the tube is negligible)
0\.75 atm
37
New cards
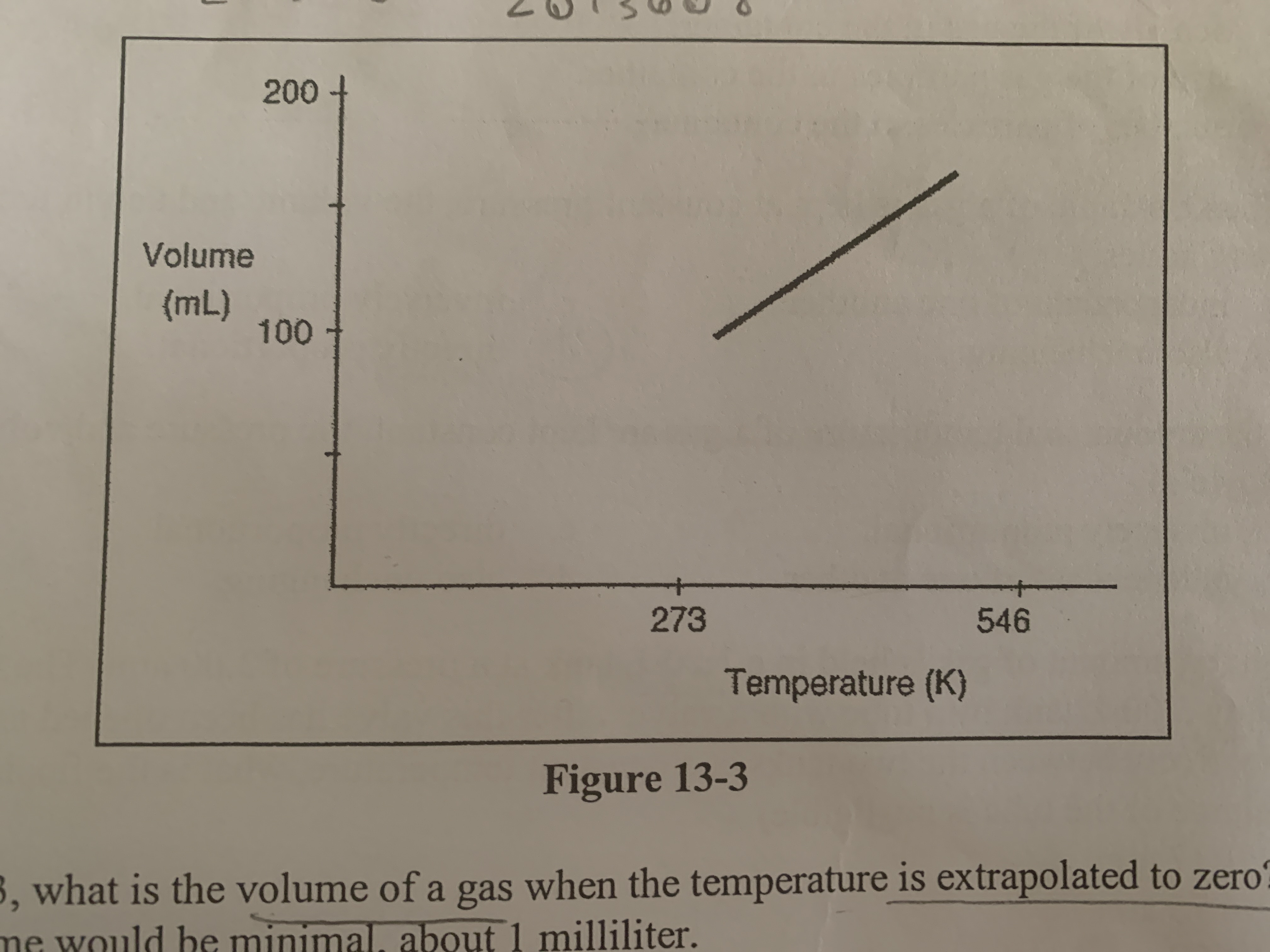
What is the volume of a gas when the temperature is extrapolated to zero?
the volume would be zero
38
New cards
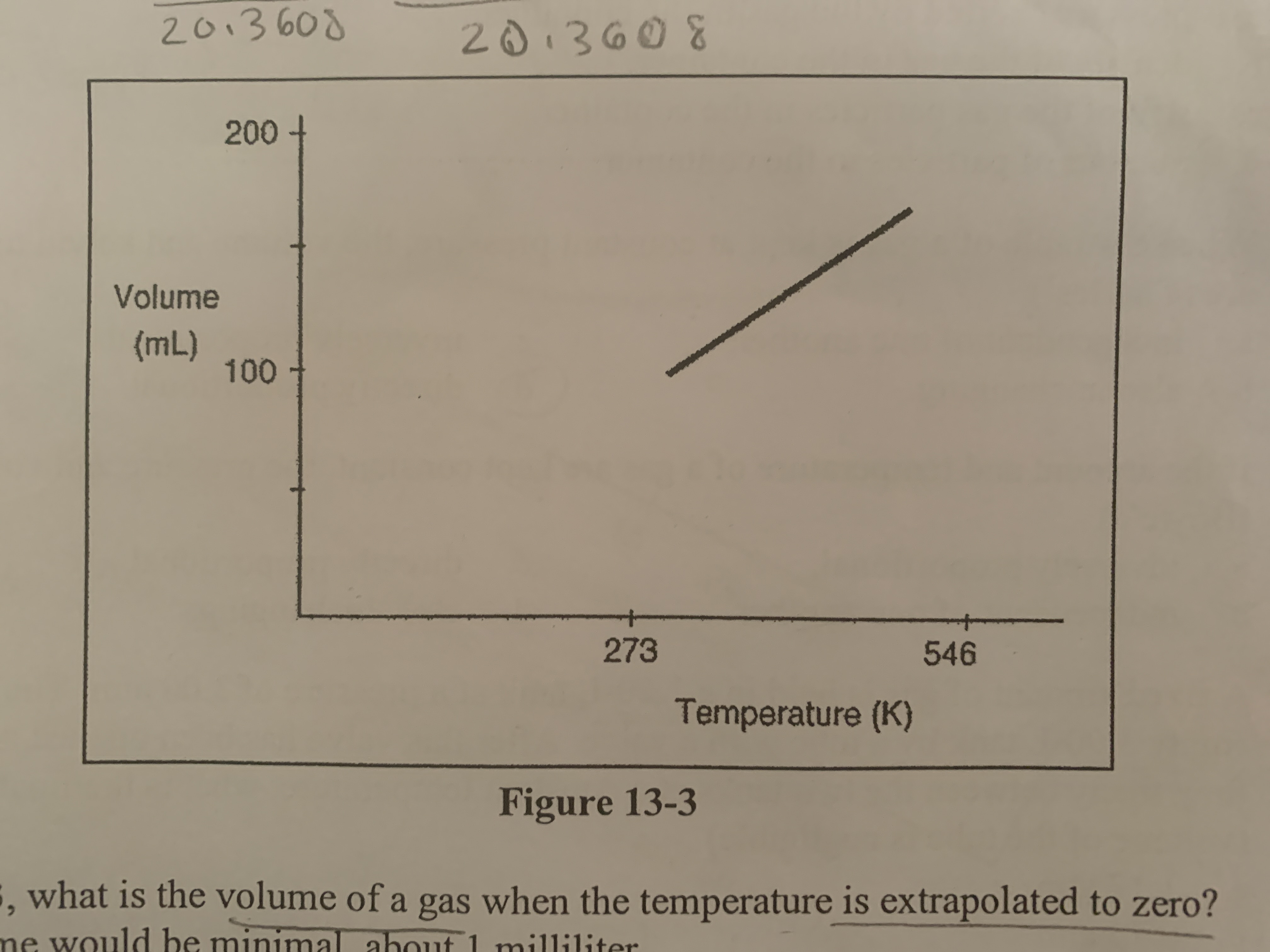
determine how the volume of a gas (at constant pressure) is related to the absolute temperature
they are directly proportional to each other
39
New cards
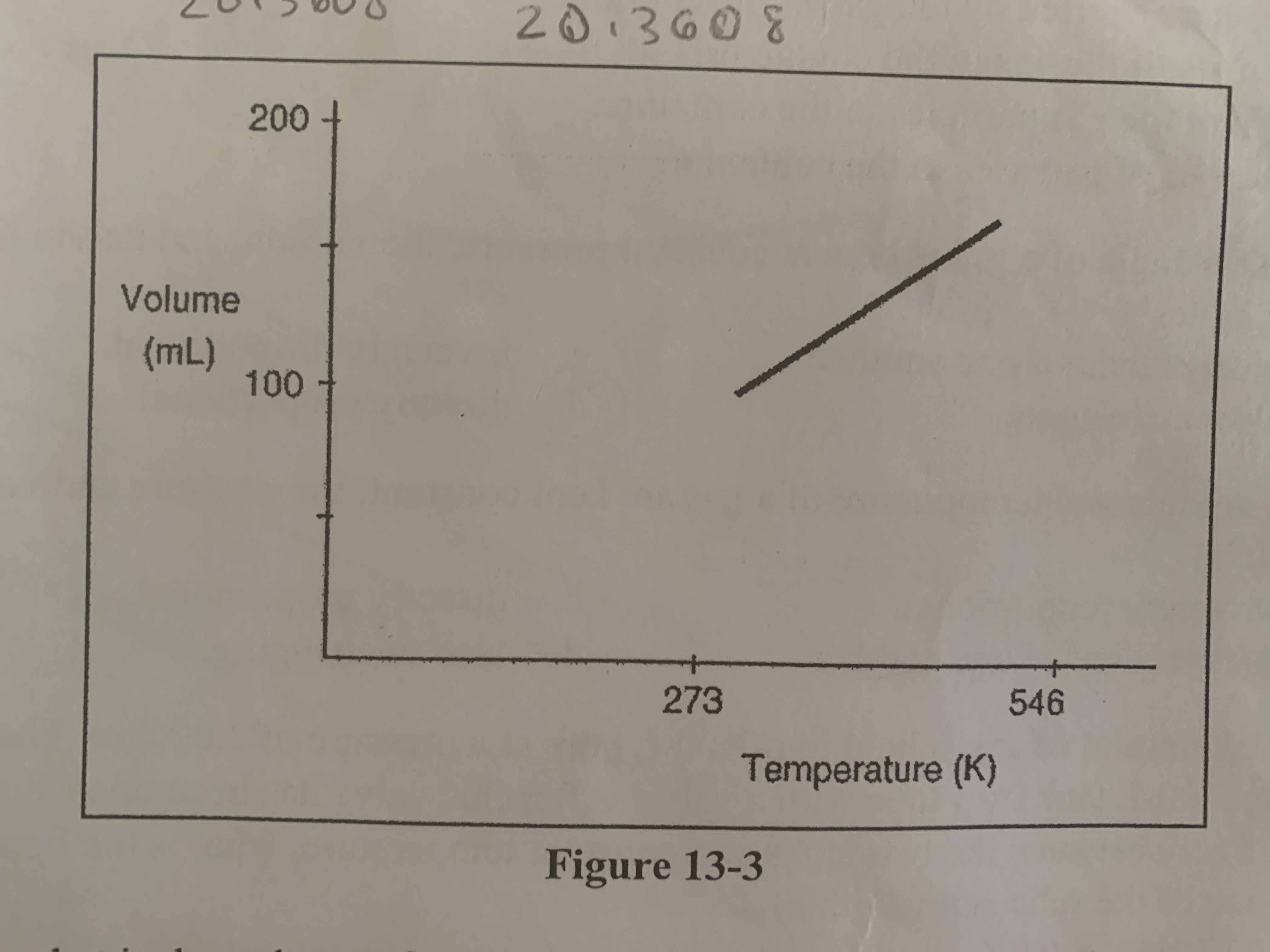
what would be the volume of a sample of has at 600 K if its volume at 300 K was 100 liters
200 Liters
40
New cards
In addition to hydrogen, what other atoms are most common in compounds that have hydrogen bonds?
any of these (N, O, F)
41
New cards
Water has unique and unusual properties because of the
hydrogen bonds between polar water molecules
42
New cards
Dipole- dipole forces would most likely to be found in compounds made up of atoms
different electronegativity
43
New cards
Which of the following would indicate the strongest intermolecular forces in a liquid?
high boiling point
44
New cards
The state in which a substance exists at room temperature depends on
strength of the attractive forces between particles
45
New cards
A liquid that has a high viscosity measure of a fluid's resistance to flow.) would likely have
strong intermolecular forces
46
New cards
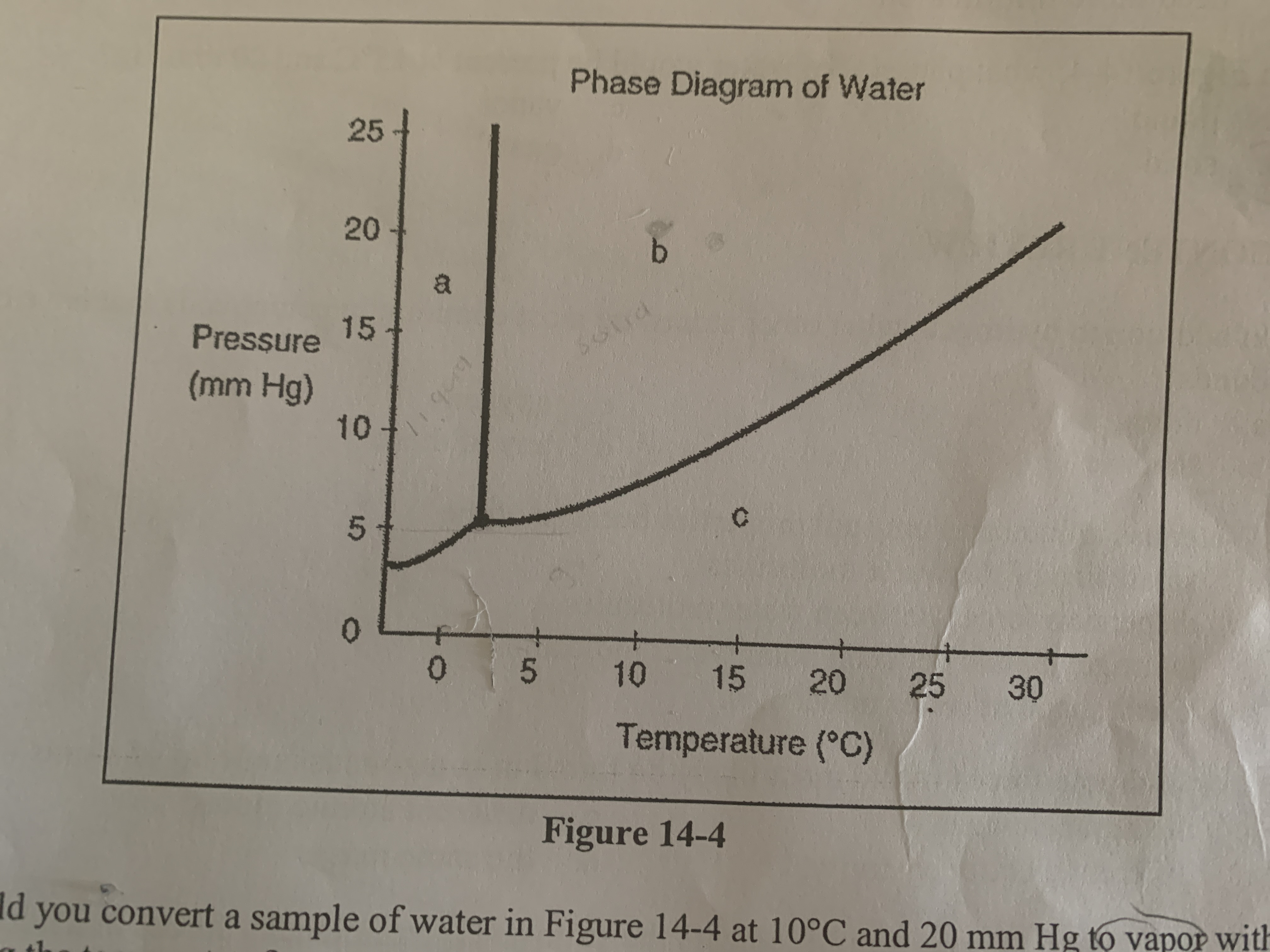
What phase(s) of water would be present at 15 C and 200 mm Hg?
liquid
47
New cards
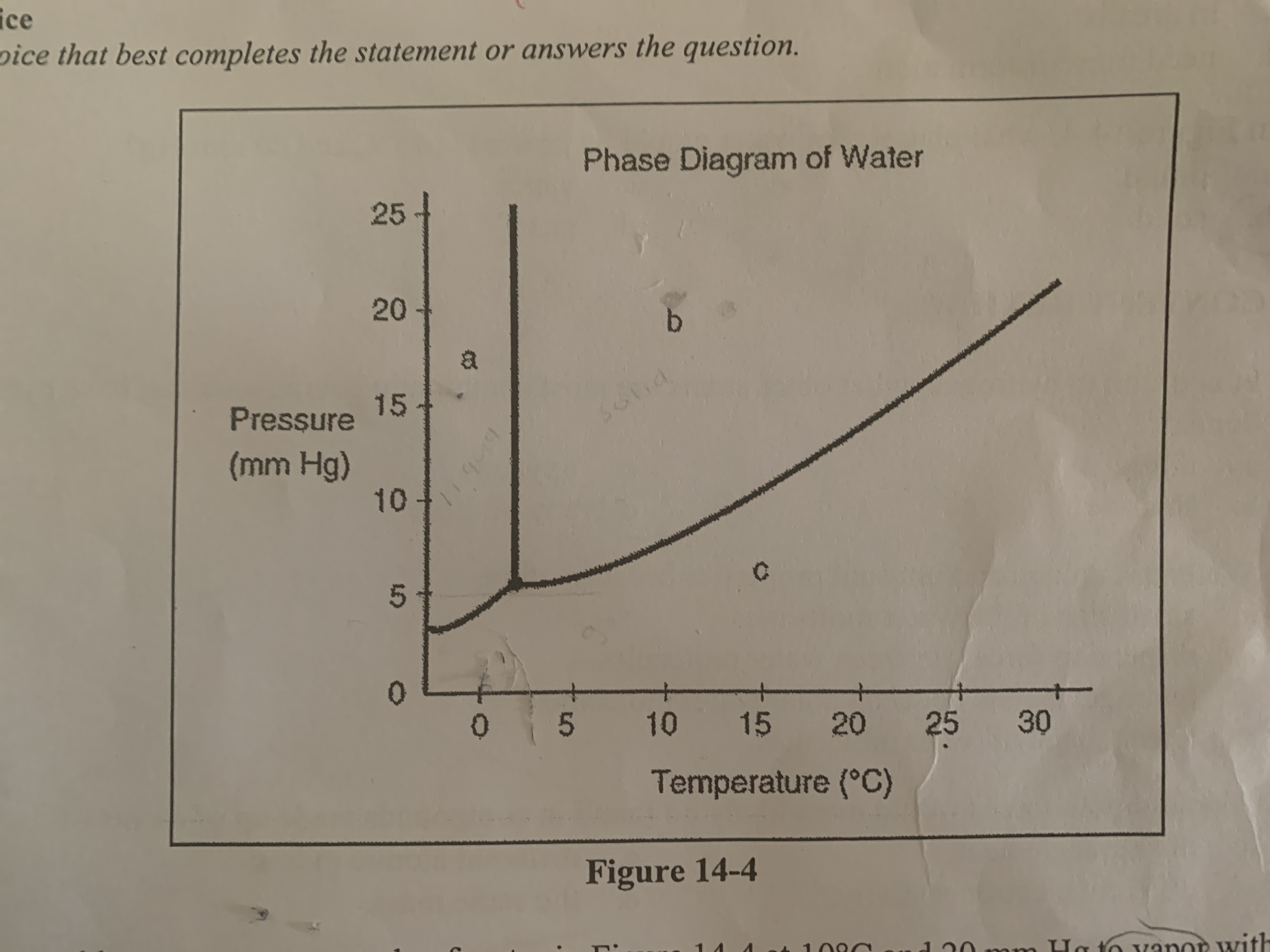
Where would you find boiling water?
at any point along the line separating regions b and c
48
New cards
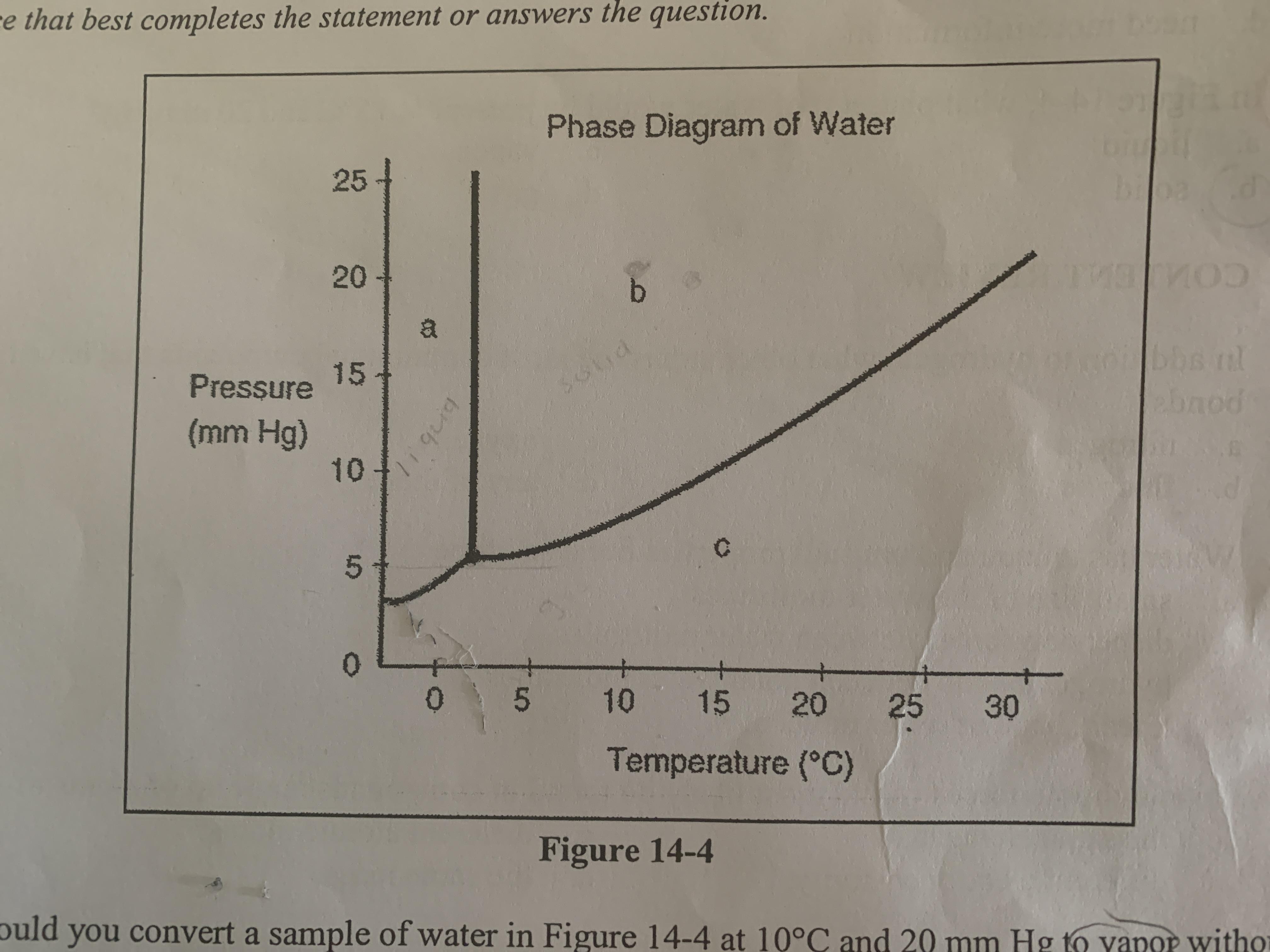
If the temperature of a sample at 0 C and 25 mm Hg is reduced at constant pressure, what would happen to the sample?
the sample would not change
49
New cards
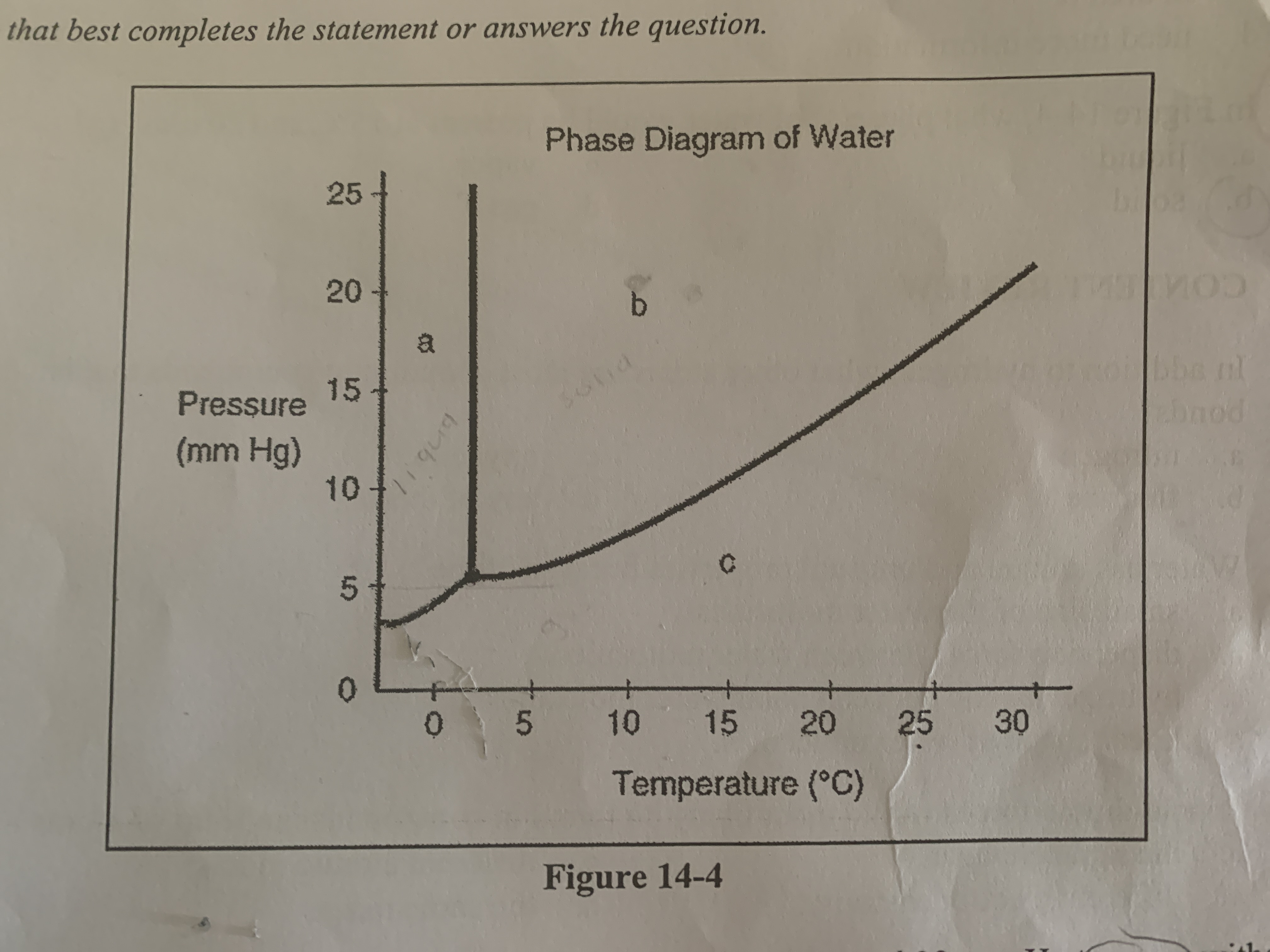
How could you convert a sample of water at 10 C and 20 mm Hg to vapor without decreasing the temperature?
decrease the pressure to 5 mm Hg so conditions for the sample fall below the solid line