Inorganic 1 Topic 11
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Metallic Bonding and Crystallography
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
In the absence of … , electrically … metal … will pack as efficiently as possible in space
directional covalent bonds, neutral, atoms
Hard, non-… spheres of identical … form … layers
deformable, radii, close-packed
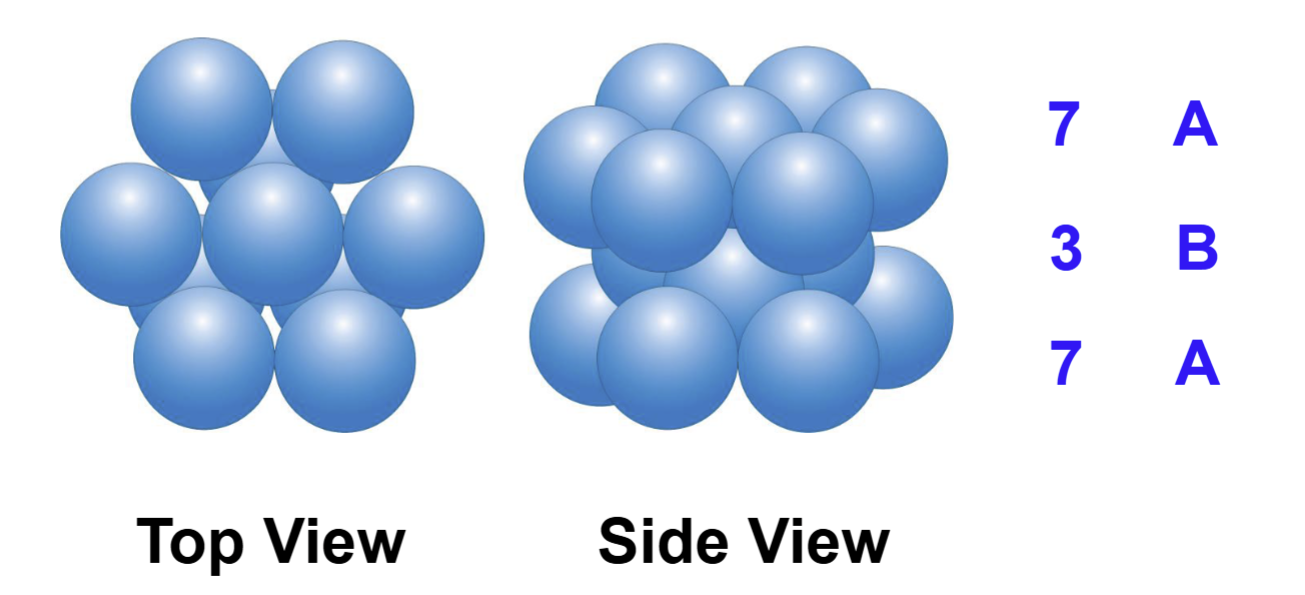
In hexagonal close packing, the third layer sits …
directly over the first layer
The HCP arrangement is usually referred to as an … layer repeat
ABA
Top and side view of HCP layers:
HCP unit cell:
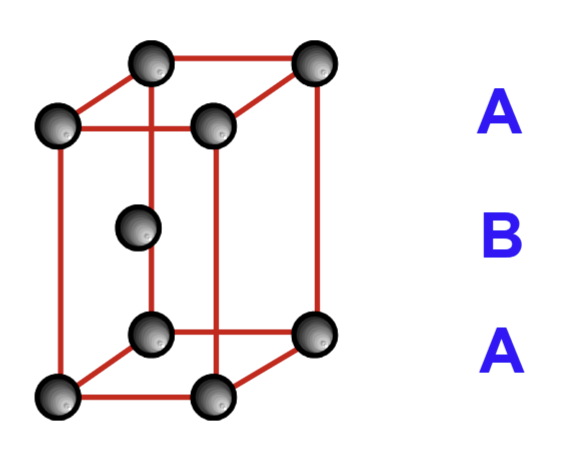
What is the definition of a unit cell?
the smallest repeating unit (group of atoms) in a crystalline substance which has the overall symmetry of the crystal and from which the entire lattice can be built by repetition in three dimensions
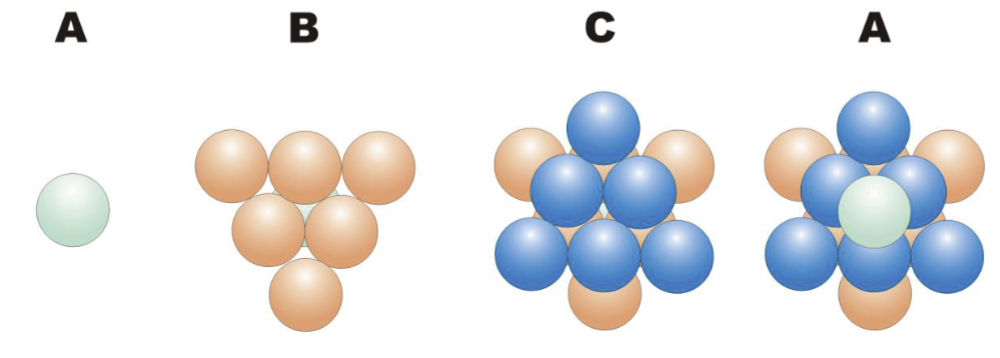
In cubic close packing, the third layer sits …
over holes in the first layer
In cubic close packing, the fourth layer sits …
directly over the first layer
The CCP arrangement is usually referred to as an … layer repeat
ABC or ABCA
What is the arrangement of layers in a CCP arrangement?
CCP unit cell:
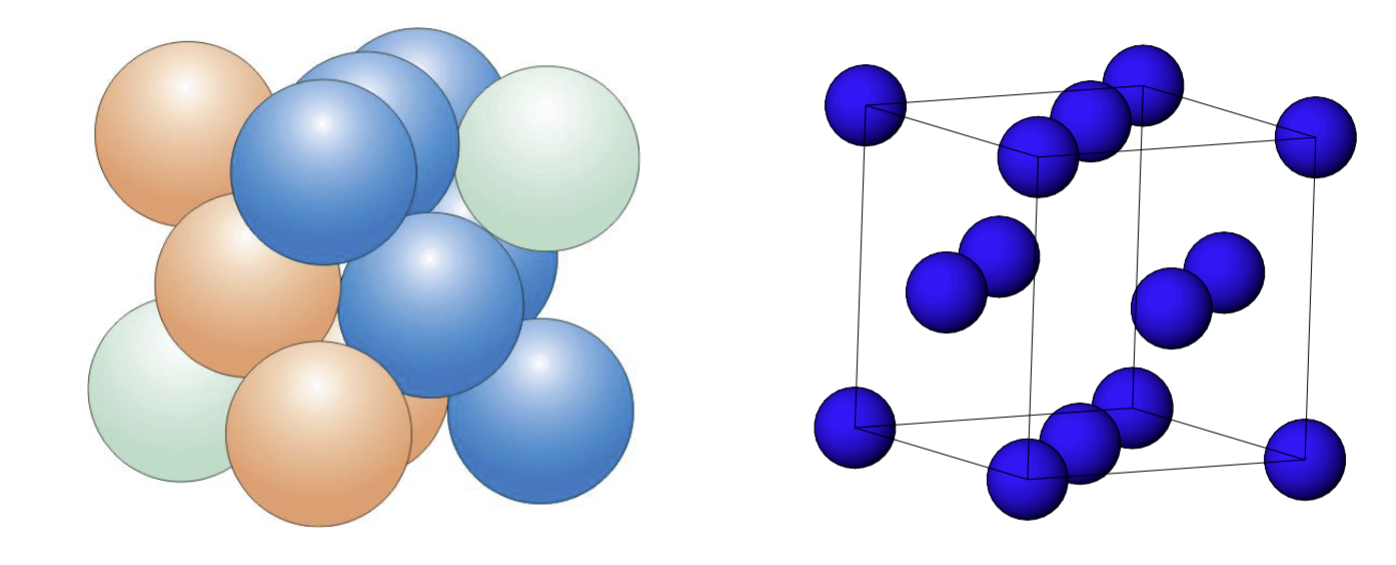
Cubic close packing is also known as …
face-centred cubic
What is the coordination number of an atom in a close packed arrangement (hexagonal or cubic)?
12
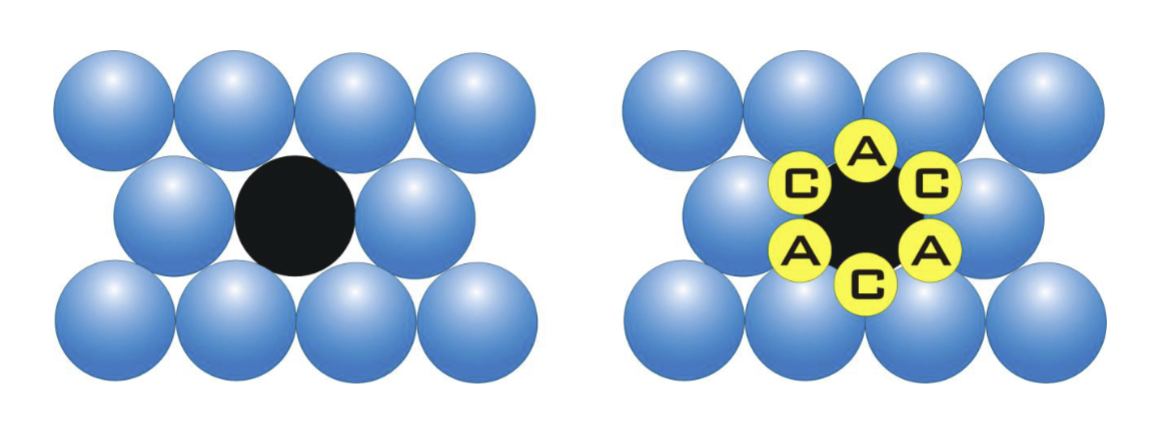
What percentage of the total volume is occupied by spheres in a close-packed arrangement (hexagonal or cubic)?
74%
What percentage of the total volume is occupied by spheres in a body-centred cubic arrangement?
68%
In a BCC arrangement, the spheres are arranged in layers based on … rows, rather than … rows, as in a close-packed arrangement
square, triangular
In BCC, the third layer sits …
directly over the first
BCC unit cell:
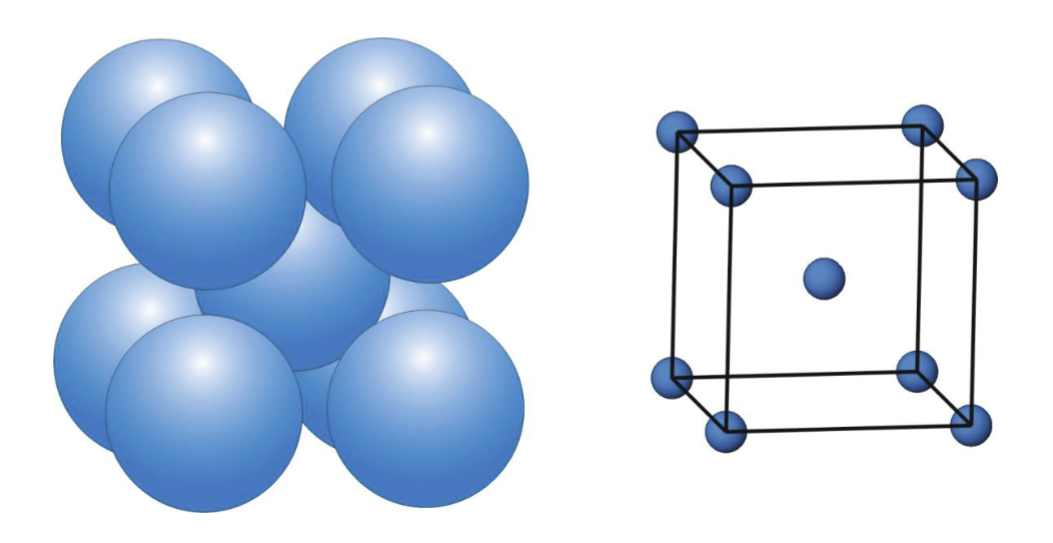
What is the coordination number of an atom in a BCC arrangement?
8
… solids are have a highly ordered shape, whereas … solids are less ordered
crystalline, amorphous
In crystalline solids, the atoms are in an … called a …
orderly array, lattice
Crystalline solids have a … internal arrangement
regular
Amorphous solids have their atoms in a … arrangement, or a …
random, mixture
Amorphous solids have structures which are similar in character to …
liquids
Properties of atomic crystalline solids:
individual atoms held together by weak dispersion forces
noble gases are the only examples
low melting and boiling point reflects weak forces between atoms
Properties of molecular crystalline solids:
held together by intermolecular forces (dispersion, dipole-dipole, hydrogen)
lattice points are occupied by individual molecules
Properties of ionic crystalline solids:
ionic bonding
electrons are transferred between atoms to form cations and anions
solid is held together by electrostatic forces between the ions
Properties of metallic crystalline solids:
metals conduct electricity freely, via motion of electrons
metals can be considered as a sea of electrons surrounding an array of cations
held together by electrostatic interactions between electrons and cations
interactions are maximised when the cations are close packed
Properties of network covalent crystalline solids:
atoms are joined by strong covalent bonds which extend throughout the solid forming a network
hard, rigid materials
In metallic bonding, … electrons lead to … bonding
delocalised, non-directional
Non-directional bonding in metals leads to which properties?
malleability and ductility
The mobility of delocalised electrons results in which properties?
electrical and thermal conductivity
What is an alloy?
a blend of metals (or a metal and another element) that is prepared by mixing the molten components and then allowing to cool
In an alloy, the elements have been mixed at an … level
atomic
What does the term “solid solution” mean?
a term for a solid with elements mixed at the atomic level
homogeneous mixture of two compounds in solid state and having a single crystal structure
What is a substitutional alloy?
atoms of the solute metal randomly occupy sites in the solvent metal lattice (shown in orange)
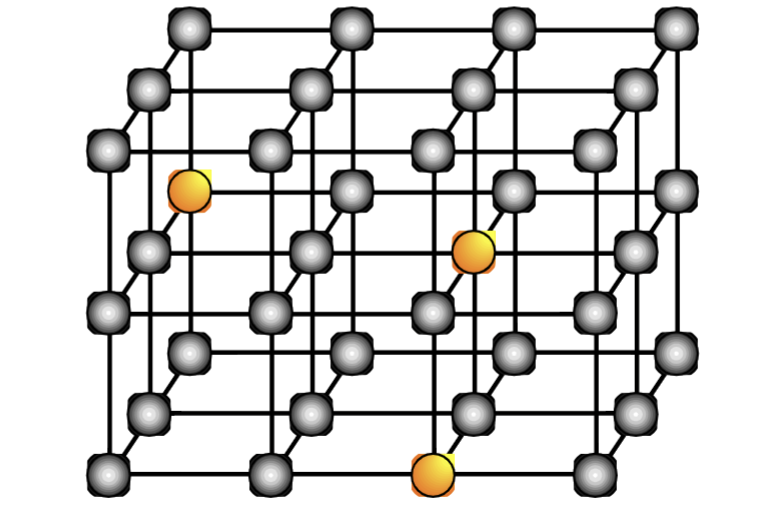
In order for a substitutional alloy to form, the metal radii must be …, normally within … of each other
similar, 15%
In order for a substitutional alloy to form, the … metal must tolerate the … environment of the … lattice
solute, coordination, host
In order for a substitutional alloy to form, the … characteristics of the two metals must be similar, otherwise … may occur and the formation of an … compound is more likely
electropositive, charge transfer, ionic
What is an interstitial alloy?
some holes between the metals in the lattice are occupied by another element
What is a crystal structure?
the name given to the unit cell and the particular arrangement of atoms within it (e.g. HCP, CCP, BCC)
What is a structure type?
a defined arrangement of atoms, for example the NaCl structure type is common for many AX atom combinations
Unit cells are defined by three … (a, b, c) and three … (α, β, γ)
vectors, angles
Cubic unit cells are defined by which vectors and angles?
a = b = c, α = β = γ = 90
Hexagonal unit cells are defined by which vectors and angles?
a = b ≠ c, α = β = 90, γ = 120