unit 3 - energy changes and rates of reaction chem
1/167
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
168 Terms
define the following and give an example:
a) open system
b) closed system
c) isolated system
a) energy and matter may flow in and out of the system (ex: water bottle with cap removed)
b) energy may enter or leave the system, but not matter (ex: sealed water bottle)
c) ideal system where energy nor matter can move out (ex: oven mitts, sealed water bottle with styrofoam all over it)
Define:
a) exothermic
b) endothermic
a) releases heat
b) absorbs heat
Calculate the heat transferred when 15.0 grams of aluminum undergoes a temperature change from 120°C to 30°C
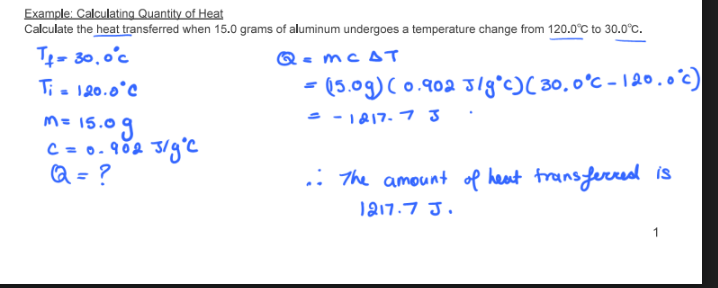
if:
a) ΔH < 0 → _____________
b) ΔH > 0 → _____________
a) exothermic
b) endothermic
During a combustion experiment, 5 grams of methane (CH4) produces 277.26 kJ of heat. Calculate the molar enthalpy of methane.

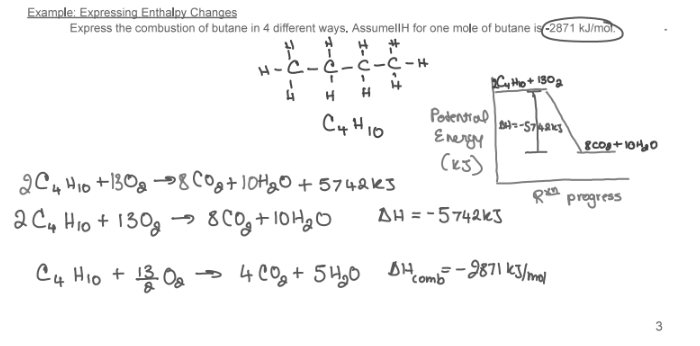
Express the combustion of butane in 4 different ways. Assume ΔH for one mole of butane -2871 kJ/mol
A 10g piece of aluminum, initially 96.0°C, is placed into 500g of water. If the initial temperature of the water was 25.0°C, what was the final temperature of the system?

A 0.100 moles of solid ionic compounds is dissolved into 450g of water. If the water’s temperature increased by 15.0°C, what was the molar enthalpy of the solution?

10.0g of a substance is dissolved in water in a calorimeter. The calorimeter is calibrated and its heat capacity is 550 J/°C. If the temperature change was 27.0°C, what amount of heat was evolved

When heating water on the stove, the heat from the element causes the water to become hotter, until it reaches 100°C. What is this called?
boiling point of water
Calculate the heat required (in Joules) to change 16g of ice at 0°C to liquid water at 25°C

When white phosphorus burns in air, it produces phosphorus(V) oxide:
P4 (s) + 5 O2 →P4O10 (s) ΔH = -2940 kJ
What is the ΔH for the following equation:
P4O10 (s) →P4 (s) + 5 O2
2940 kJ
Carbon disulfide burns in air, producing carbon dioxide and sulphur dioxide:
CS2 (l) + 3 O2 (g) →CO2 (g) + 2 SO2 (g)
ΔH = -1075
What is the ΔH for the following equation:
½ CS2 (l) + 3/2 O2 (g) → ½ CO2 (g) + SO2 (g)
-537.5 kJ
Phosphoric acid, H3PO4, can be prepared by the reaction of phosphorus(V) oxide, P4O10, with water.
¼ P4O10 (s) + 3/2 H2O (l) →H3PO4 (aq)
ΔH = -113.2kJ
What is the ΔH for the following equation:
P4O10 (s) + 6 H2O (l) →4 H3PO4 (aq)
-452.8 kJ
With platinum catalyst, ammonia will burn in oxygen to give nitric oxide, NO:
4NH3 (g) + 5 O2→ 4 NO (g) + 6 H2O
ΔH = -906 kJ
What is the ΔH for the following equation:
NO (g) + 3/2 H2O (g) →NH3 (g) + 5/4 O2 (g)
226.5 kJ
Hydrogen gas is used as a rocket fuel. The hydrogen is burned in oxygen to produce water vapor:
2 H2 (g) + O2 →2 H2O (g)
ΔH = -484 kJ
What is the enthalpy change for 1.00g of hydrogen?
-1.20 × 102 kJ/g
Colourless nitric oxide, NO, combines with oxygen to form nitrogen dioxide, NO2, a brown gas:
2 NO (g) + O2 (g) →2NO2 (g)
ΔH = -114 kJ
What is the enthalpy change per gram of nitric oxide?
-1.90kJ/g
Ammonia burns in the presence of a copper catalyst to form nitrogen gas:
4 NH3 (g) + 3 O2 (g) →2 N2 (g)+ 6 H2O(g)
ΔH = -1267 kJ
What is the enthalpy change to burn 25.6g of ammonia?
-476 kJ
Hydrogen sulphide, H2S, is a foul-smelling gas. It burns to form sulphur dioxide:
2 H2S (g) + 3 O2 (g) →2 SO2 (g) + 2 H2O (g)
ΔH = -1037 kJ
Calculate the enthalpy change to burn 36.9g of hydrogen sulphide
-561 kJ
A solid substance has a mass of 0.250kg. It is cooled by 25.0°C and loses 4937.50 J of energy. What is its specific heat capacity? What is the substance?
790 J/g°C
Calculate the enthalpy change that occurs when a 10.4g iron nail is hammered into wood, as it changes from 22.0°C to 38.5°C
76.2 J
If 0.050kg of ethanol at 15°C gains 1050J of energy, what will be its final temperature?
24°C
If some wood gained 4200 J and its temperature went from 25°C to 35°C, what is its mass?
0.24 kg
Aluminum reacts with iron (III) oxide to yield aluminum oxide and iron. The temperature of 1.00kg of water in a calorimeter increases by 3.00°C during the reaction. Calculate the energy released in the reaction
12.6kJ
In an experiment, dissolving 2.00g of NaOH in water results in an energy change of 110.4 kJ. What is the molar enthalpy for the process?
2.21 × 103 kJ/mol
Burning 1.5g of methanol results in 3.0 × 10 kJ of energy. What is the molar enthalpy of the reaction?
6.4 × 102 kJ/mol
If 1.00 moles of benzene is burned, 3.133 × 103 kJ is produced. If 5.60g of benzene was burned how much energy will be involved?
225kJ
A 24.7g sample of metal is heated to 115°C and then placed in a calorimeter containing 120g of water at a temperature of 23.0°C. After the metal cools, the final temperature of the system is 24.83°C. Assuming no energy is lost, calculate the specific heat capacity of the metal.
0.413J/g°C
0.180g piece of magnesium ribbon was placed into 100.0g of hydrochloric acid in a calorimeter, and the temperature changed from 11.20°C to 20.00°C. How much energy was released by the reaction? Assume the specific heat capacity of the acid is the same as that for water
3.68kJ
When 15.3g of sodium nitrate were dissolved in 256g of water in a calorimeter, the temperature fell from 25.00°C to 21.56°C. What is the enthalpy change for the reaction?
3.68 kJ
When 21.5g of KNO3 were dissolved in water in a calorimeter, the temperature fell from 25.00°C to 14.14°C. The heat capacity of the calorimeter and its contents is 682 J/°C. What was the amount of energy involved in the reaction?
7.41 kJ
When 23.6g of calcium chloride was dissolved in water in a calorimeter, the temperature rose from 25.0°C to 38.7°C. If the heat capacity of the solution and the calorimeter is 1258 J/°C, what is the enthalpy change of the reaction?
-17.2 kJ
A 2.84g sample of ethanol was burned completely in a bomb calorimeter (used to measure heat for reactions involving gases). The temperature of the calorimeter rose from 25.0°C to 33.7°C. If the heat capacity of the calorimeter and contents was 9.63 kJ/°C, what is the ΔH value when 1.00 mol of ethanol is burned? Write your answer as a thermochemical equation
The reaction is:
C2H5OH (l) + 3 O2 (g) → 2 CO2 (g) + 3 H2O (l)
ΔHcomb = -1.36 × 103 kJ
A 3.51g sample of benzene was burned in a bomb calorimeter. The temperature of the calorimeter rose from 25.0°C to 37.2°C. If the heat capacity of the calorimeter and its contents was 12.05 kJ/°C, what is the ΔH for burning 1.00 mol of benzene? Write your answer as a thermochemical equation
ΔHcomb = -3.27 × 103 kJ
A 6.48g sample of LiOH was dissolved in water in a calorimeter. The temperature of the calorimeter rose from 25.0°C to 36.7°C. The heat capacity of the calorimeter and its contents is 547 J/°C. What is the ΔH for the solution process if 3.50mol was dissolved?
ΔH = -82.8 kJ
Given the following two equations:
2 Al(s) + 3/2 O2 (g) → Al2O3 ΔH= -1676 kJ
Mn (s) + O2 (g) → MnO2 (s) ΔH= -521
Calculate ΔH for the reaction:
4 Al (s) + 3 MnO2 (s) →2 Al2O3 (s) + 3 Mn (s)
ΔH = -1789 kJ
Given the following two equations:
H2O2 (l) →H2O + ½ O2 ΔH= -98.0 kJ
2 H2 (g) + O2 →2 H2O ΔH= -571.6 kJ
Calculate the ΔH for the reaction:
H2 + O2 → H2O2
ΔH = -187.8 kJ
Given the following equations:
N2H4 + O2 → N2 + 2 H2O ΔH= -622.2 kJ
H2 + ½ O2 → H2O ΔH= -285.8 kJ
Calculate ΔH for the reaction:
N2 + 2 H2 → N2H4
ΔH = 50.6 kJ
Given the following three equations:
2 W + 3 O2 →2 WO3 ΔH= -1680.6 kJ
C + O2 →CO2 ΔH= -393.5 kJ
2 WC + 5 O2 →2 WO3 + 2 CO2 ΔH= -2391.6 kJ
Calculate ΔH for the reaction:
W + C → WC
ΔH = -38.0 kJ
Given the following three equations:
2 NH3 →N2 + 3 H2 ΔH = 46.0 kJ
2 NO2 + 7 H2 → 2 NH3 + 4 H2O ΔH= 57.0kJ
2 NO2 → N2 + 2 O2 ΔH = 16.5 kJ
Calculate ΔH for the reaction:
H2 + ½ O2 → H2O
ΔH= 21.625 kJ
Given the following three equations:
CO2 →C + O2 ΔH= 295.1 kJ
H2O → H2 + ½ O2 ΔH= 214.3 kJ
CH4 → C + 2 H2 ΔH= 56.1 kJ
Calculate ΔH for the reaction:
CO2 + 2 H2O →CH4 + 2 O2
ΔH = 667.6 kJ
Find the enthalpy change for the formation of 1 mole of butane. You are given the following information:
(I) 2 C4H10 + 13 O2 → 8 CO2 + 10 H2O
ΔH = -5314.8 kJ
(II) C + O2 → CO2 ΔH = -393.5 kJ
(III) 2 H2 + O2 → 2 H2O ΔH = -483.6 kJ
In other words, find ΔH using Hess’s Law when butane is formed from its elements
What process is it
4 C + 5 H2 →C4H10
ΔH = -125.6 kJ
exothermic
Calculate the amount of heat needed to just melt 40.0g of ice at 0°C
13.4kJ
How much heat is required to change 50.0g of water at 100°C to steam at 100°C?
113 kJ
Calculate the enthalpy change when 500g of steam at 100°C condenses and cools to 25.0°C
-1.29 × 103 kJ
Calculate the amount of heat needed to change 0.20kg of ice at -10.0°C to water at 20.0°C
88 kJ
Calculate the amount of heat needed to convert 0.100kg of ice at -5.00°C to steam at 110.0°C
305 kJ
Using bond energies, calculate ΔH for each chemical reaction. Watch out for multiple bonds. Show ur work
2 CH3OH + 3 O2 → 2 CO2 + 4 H2O
-1286 kJ
Using bond energies, calculate ΔH for each chemical reaction. Watch out for multiple bonds. Show ur work
C2H5OH + 3 O2 → 2 CO2 + 3 H2O
-1250 kJ
Using bond energies, calculate ΔH for each chemical reaction. Watch out for multiple bonds. Show ur work
C2H4 + HBr →C2H5Br
-56 kJ
Using bond energies, calculate ΔH for each chemical reaction. Watch out for multiple bonds. Show ur work
C2H4 + H2O → C2H5OH
-41 kJ
Using bond energies, calculate ΔH for each chemical reaction. Watch out for multiple bonds. Show ur work
H2 + O2 → H2O2
-134 kJ
Using bond energies, calculate ΔH for each chemical reaction. Watch out for multiple bonds. Show ur work
2 H2 + N2 → N2H4
95 kJ
Using bond energies, calculate ΔH for each chemical reaction. Watch out for multiple bonds. Show ur work
N2F2 + F2 → N2F4
-160 kJ
Using bond energies, calculate ΔH for each chemical reaction. Watch out for multiple bonds. Show ur work
HCN + 2 H2 →CH3NH2
-148 kJ


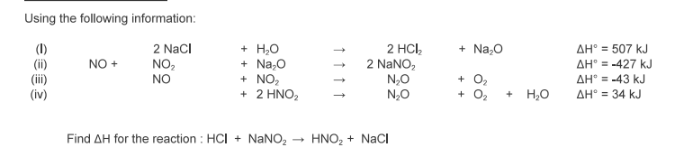
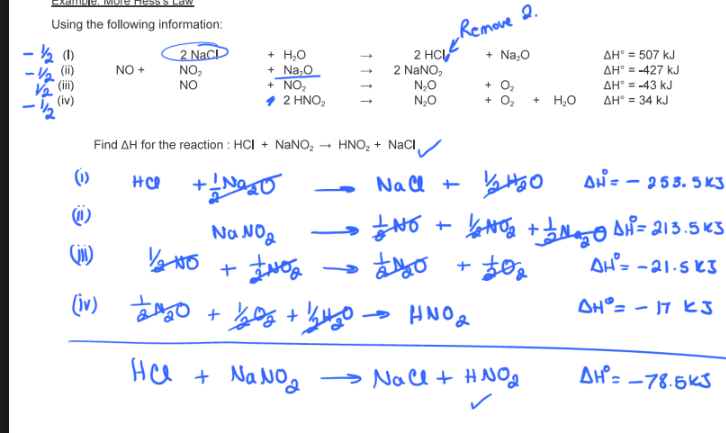
What is the standard heat of reaction when carbon tetrachloride, CCl4, condenses
-43 kJ
Calculate the standard heat of reaction as methanol evaporates
38.1 kJ
Calculate the standard heat of reaction for the following reaction:
2 H2S(g) + 3 O2(g) →2 H2O(l) + 2 SO2(g)
-1124 kJ
Carbon disulfide is a colourless liquid. When pure, it is nearly oudourless, but the commercial product smells vile. Carbon disulfide is used in the manufacture of rayon and cellophane:
CS2(l) + 3 O2(g) → CO2(g) + 2 SO2(g)
-1076.1 kJ
The first step in the preparation of lead from its ore consists of resting the ore:
2 PbS(s) + 3 O2(g) → 2 SO2(g) + 2 PbO(s)
calculate the standard heat of reaction
-835 kJ
Iron is obtained from iron ore by reduction with carbon monoxide:
Fe2O3(s) + 3 CO(g) → 2 Fe(s) + 3 CO2(g)
Calculate the standard enthalpy change for the reaction
-24.8 kJ



why is water a good cooking substance in related to specific heat capacity?
takes longer to get rid of heat since it takes long to boil
Why does pavement (concrete) heat up fast and cool down fast
its specific heat capacity is low so it heats up faster and cools down faster
what are the types of chemical systems
open
closed
isolated
what are the types of thermal energy
endothermic → absorbsheat (+)
exothermic → releases heat (-)


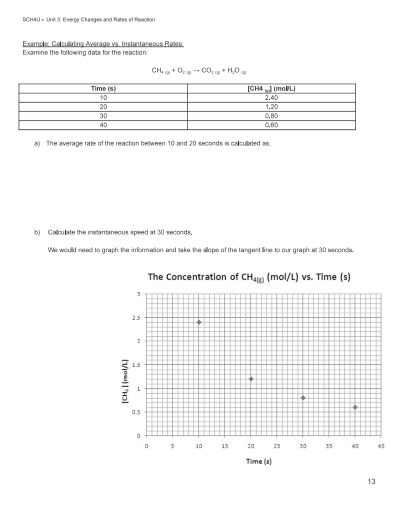
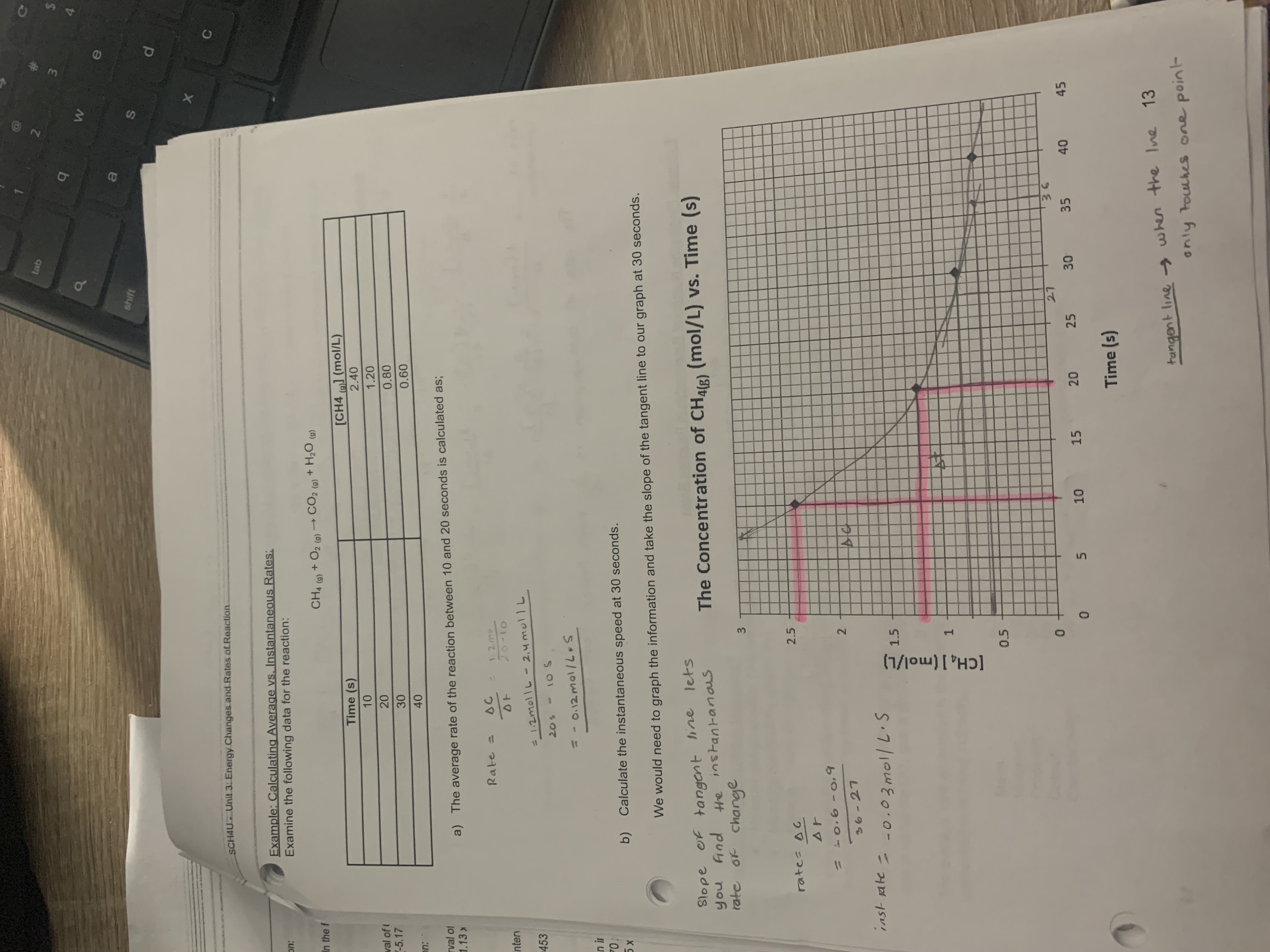





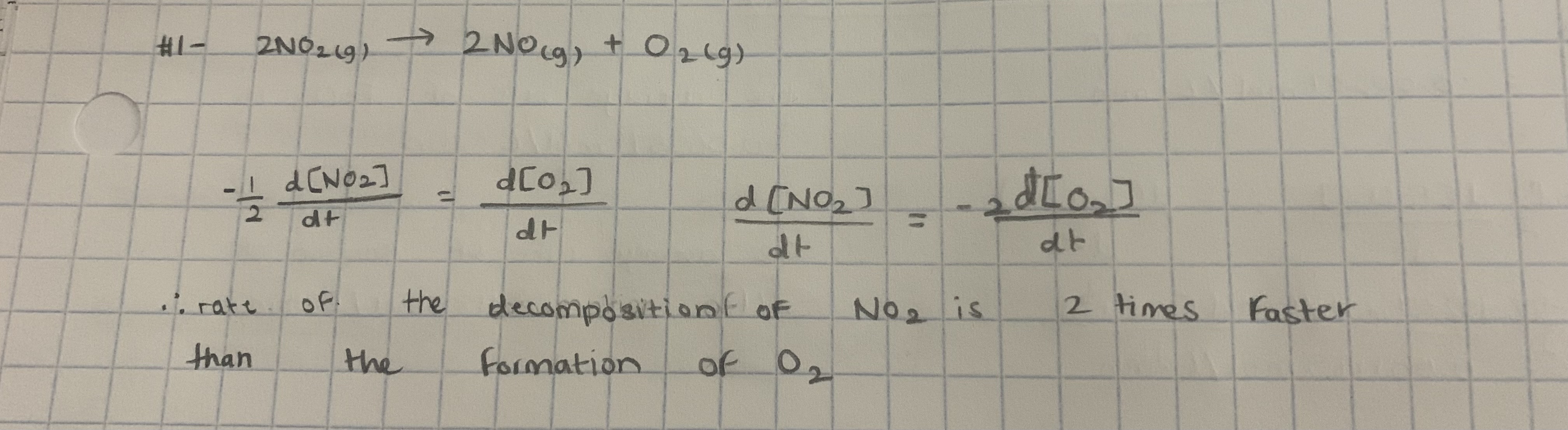
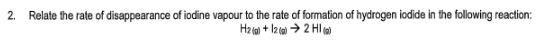


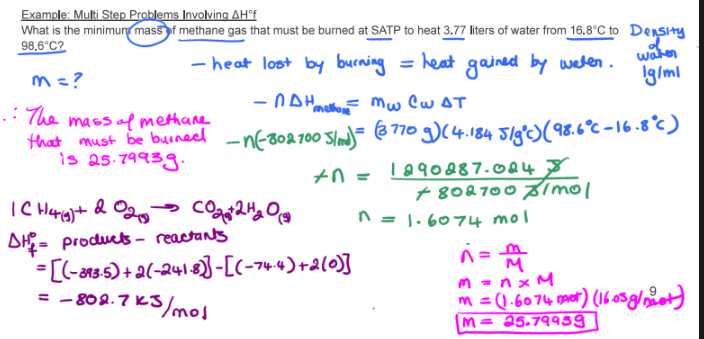
-5.17 × 10-6 mol/L.s
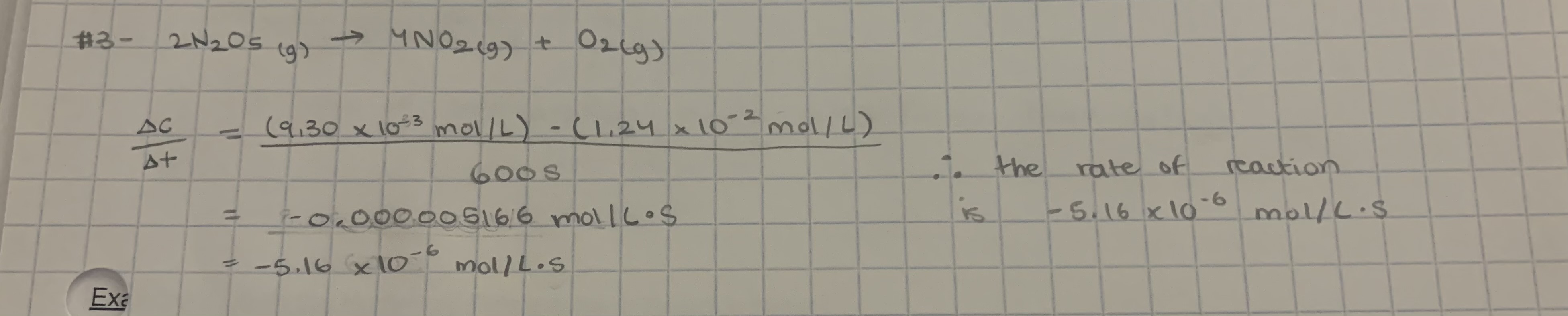

-1.13 × 10-4 mol/L.s

a) -0.0227 mol/L.hr
b) 0.0453 mol/L.hr


a) -2.370 × 10-3 mol/L.min
b) 1.185 × 10-3 mol/L.min


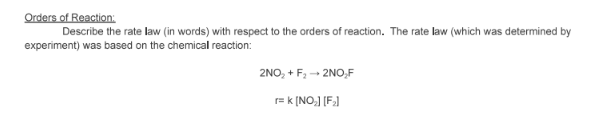
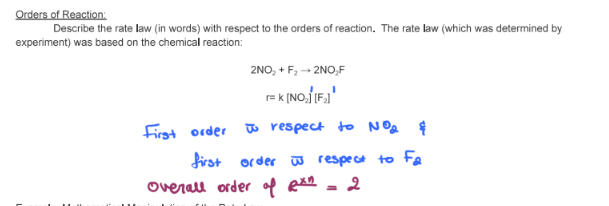
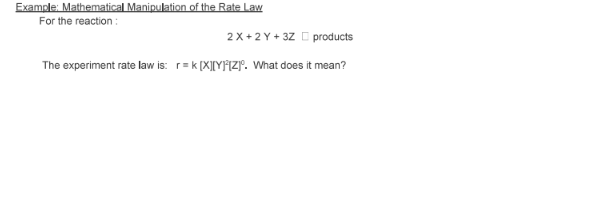


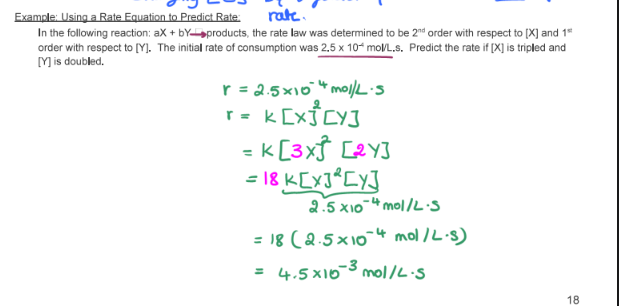
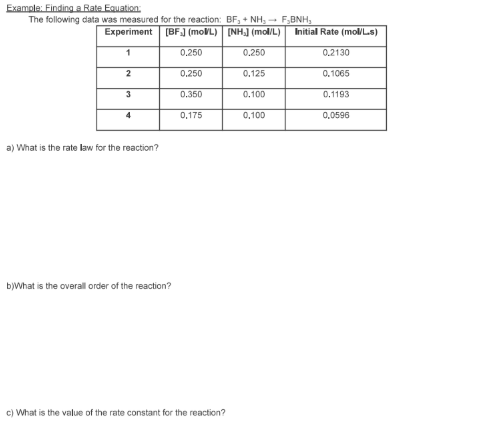

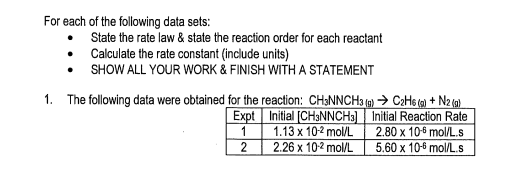
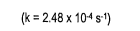

- State the rate law and state the reaction order for each reactant
- calculate the rate constant (include units)
- finish with a statement

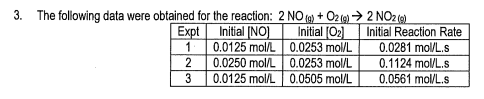
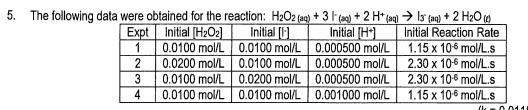
- State the rate law and state the reaction order for each reactant
- calculate the rate constant (include units)
- finish with a statement
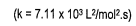

- State the rate law and state the reaction order for each reactant
- calculate the rate constant (include units)
- finish with a statement
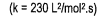
- State the rate law and state the reaction order for each reactant
- calculate the rate constant (include units)
- finish with a statement
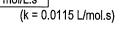
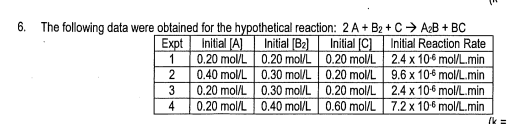
- State the rate law and state the reaction order for each reactant
- calculate the rate constant (include units)
- finish with a statement

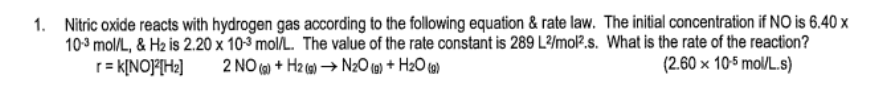





What does the first law of thermodynamics state
total energy of the universe is constant
energy cannot be created or destroyed
energy can only be transferred into different forms
what is the second law of thermodynamics state
also known as law of entropy →chaos/disorder
all changes, whether it be direct or indirect, increases the entropy of the universe
What are the five ways that a system will experience an increase in entropy
increase in volume of a gaseous system
increase of temp of a system
when there is a state change from solid to liquid to gas
when there are more moles of products then of reactants in a system
complex molecules break down into simpler ones
What are the ways we can determine if a reaction is spontaneous or not
ΔH < 0 and ΔS > 0 it is spontaneous
ΔH > 0 and ΔS < 0 it is not spontaneous
if ΔH < 0 and ΔS < 0 then it depends on temp
if ΔH > 0 and ΔS > 0 then it depends on temp
ΔG = ΔH - TΔS
If ΔG = 0 =, it is at equilibrium (phase change)
if ΔG < 0, it is spontaneous towards the forward reaction
if ΔG > 0, it is not spontaneous, or it is spontaneous towards the reverse reaction