Intro to genetics and human genetic diseases
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Mutation
Permanent alteration of a gene
Allele
An alternative form of a gene
Homozygous
Two identical alleles for the same gene
Heterozygous
Two different alleles for the same gene
Genotype
The alleles carried by the individual
Phenotype
The observable traits of an individual
True-breeding
Organism that possess a phenotype that is always transmitted to the off spring
Haploid
A genome that contains a single set of chromosomes
Example of Haploid
Prokaryotes, meiotic simple eukaryotes like yeast, germ cells, gametes
Locus
A location of a particular gene
Diploid
A genome that contains paired chromosomes
Example of diploid
Most somatic cells of most animals and some plants like garden peas, human zygotes.
Law of Dominance
In a cross of parents that are true-breeding for contrasting phenotypes, only one phenotype is expressed in the offspring- the dominant phenotype.
F0 generation
Parents
F1 generation
Hybrids
If parents are true-bred homozygous all F1 hybrids are heterozygous or homozygous?
Heterozygous as well as having the same genotype. All their phenotype are dominant.
Do all phenotypes follow the dominant/recessive pattern?
No
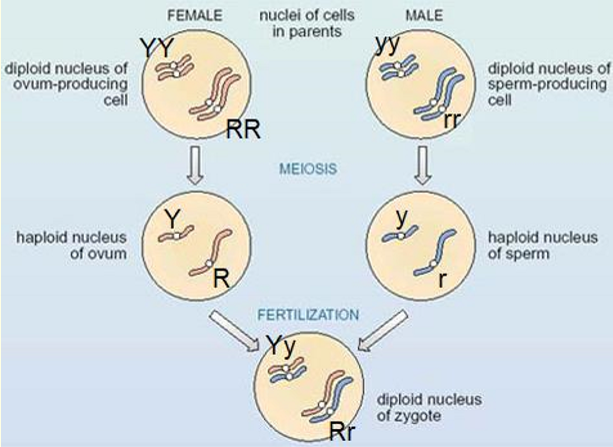
Law of segregation
Parental alleles are segregated into different haploid gametes with equal probability.
In F1 self-fertilization occurs, what is the ratio of dominant to recessive allele being expressed?
The recessive phenotype is expressed in F2 generation, 3:1
Frequency of genotypes in F2 generation? (F1 are all heterozygous)
¼ Homozygous dominant
2/4 Heterozygous
¼ Homozygous recessive
Frequency of phenotypes in F2?
¼ recessive
¾ dominant
Mendelian ratio of a hybrid cross is 3: 1
Law of independent assortment (4 letters)
Genes for different phenotypes are sorted separately from one another so that the inheritance of one phenotype is not dependent on the inheritance of another.
In independent assortment the gametes have how many alleles? To make zygotes with how many alleles?
2 alleles in a gamete to make 4 alleles in a zygote.
What is the phenotypic ratio of independent assortments?
9:3:3:1
What causes dependent assortment?
When recombination does not occur between the two genes located very close to each other during meiosis.
What causes Human Mendelian (monogenic) diseases.
A mutation in a single gene and can be present on one or both chromosomes.
Autosomal dominant
If one parent have the disease, the offspring will have the disease. If both parents do not then disease is NOT dominant. (Huntington’s disease)
Autosomal recessive
Both parents needs to be heterozygous carriers for offspring to have disease.
Disease can skip generations. (Cystic fibrosis)
X-linked recessive
Mother must be at least a carrier for offspring to have disease.
Sex bias in the preference of disease: more frequent in males. (Duchenne muscular dystrophy)
Polygenic diseases
Several alleles acting together contribute to occurrence and severity of the disease
Genetic heterogeneity
Many mutations may result into the same disease (ie. retinitis pigmentosa caused by mutations in any one of 60 diff genes)
Mechanism of Law of segregation
Parental alleles are randomly separated, sex cells contain only one allele of the pair
Offspring inherit 1 genetic allele from each parent in a zygote
parental alleles are segregated into different haploid gametes with equal probability
Mechanism of law of independent assortment: Random Chromosome Assortment
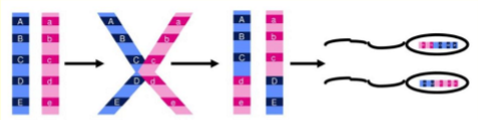
Mechanism of law of independent assortment: recombination
The alleles of genes A, B and C will be inherited independently of the alleles in gene D and E. Notice that the chromosome of each gamete has a different combination of alleles.