Hemoglobinopathies - Clin Med
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
What does this refer to
An 8-year-old African American boy presents with his mother to urgent care for severe pain in his hands and feet.
He reports that he has had on and off pain for as long as he can remember, but this time the pain is unremitting and not responsive to pain medications at home.
He had been playing outside in the snow when the pain started.
His past medical history includes a blood disorder but his parents cannot remember what this was called, as it was diagnosed in a foreign hospital.
On physical exam, he is noted to be pale and he has palpable splenomegaly.
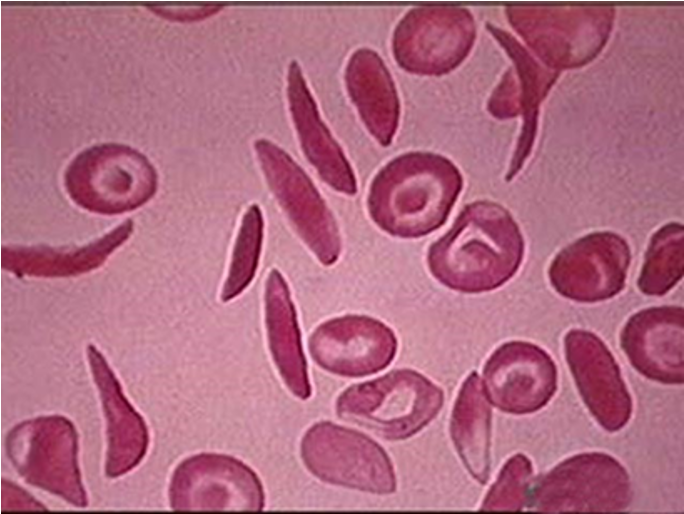
A peripheral blood smear shows sickled red blood cells.
He is started on intravenous pain medications.
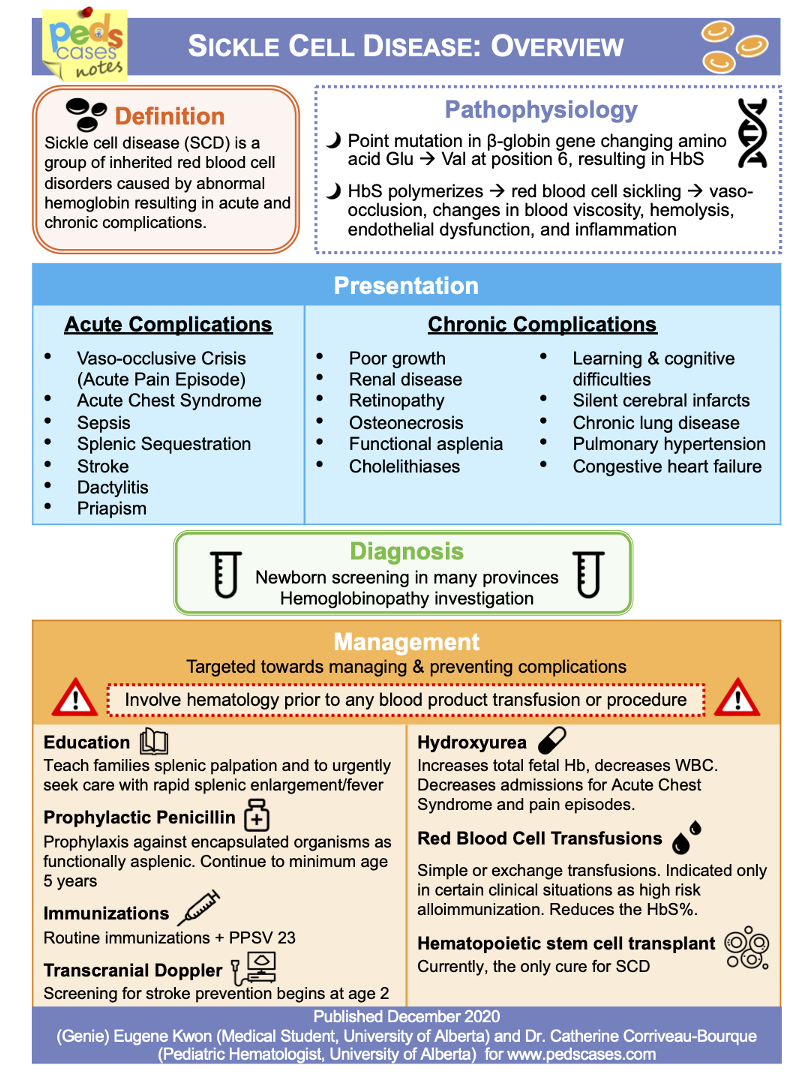
Sickle cell anemia
What does this refer to
Hemolytic anemia
Affects β–globin gene
Genetic defect in synthesis of Hgb S
“Sickled” shape —> hemolysis and vascular occlusion
Includes
Sickle cell disease
Sickle beta thalassemia
Hgb SC disease
Sickle cell trait
Usually asx
Doesn’t usually need tx
Sickle Cell
What does this refer to
Autosomal recessive
Genetic mutation
Chromosome 11
β-globin gene
MC AA
MC inherited blood disorder in US
M = F
Can be dx as early as 10 weeks of age
Epidemiology Sickle Cell
What does this refer to
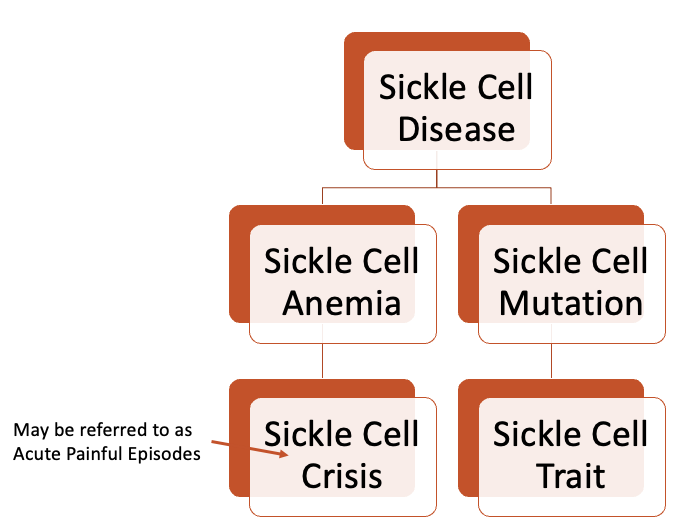
Sickle cell crisis may be referred to as acute painful episodes
What does this refer to
Autosomal recessive
Genetic mutation in HBB gene
Genetically determined defect in synthesis of Hemoglobin S.
Valine at 6th position on Beta globin chain, not glutamine
Etiology Sickle Cell
What does this refer to
Anemia
Shortness of breath
Fatigue
Delayed growth and development in children
Repeated infections
Periodic episodes of pain
MC presenting sx is vaso-occlusive crisis
“Sickle Cell Crisis”
Cold temperatures, stress, alcohol, menses
Clinical history Sickle Cell
What does this refer to
Scleral icterus/jaundice
Pallor
Extremities/joints —> pain
Erythema and edema
Skeletal abnormalities
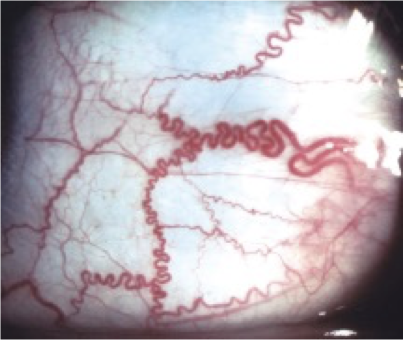
Fundoscopic exam
Corkscrew shaped vessels
Precordial systolic murmur and/or cardiomegaly
Splenomegaly (childhood)
Deficit in growth parameters
Physical exam Sickle Cell
What does this refer to
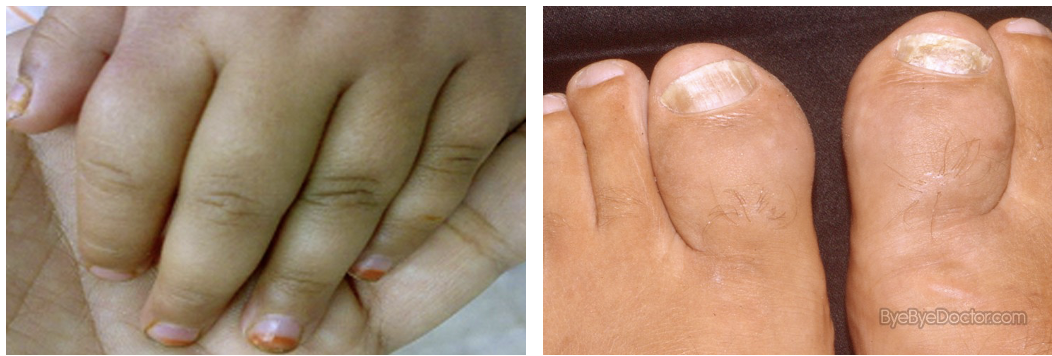
Aseptic Dactylitis (hand-foot syndrome)
Physical exam sickle cell
What does this refer to
Distinguish between the anemias
Hemoglobin C disease
Legg-Calve-Perthes disease
Ophthalmologic manifestations of leukemias
Osteomyelitis
PE
RA
Septic arthritis
Differential diagnosis Sickle Cell
What does this refer to
Workup Sickle Cell
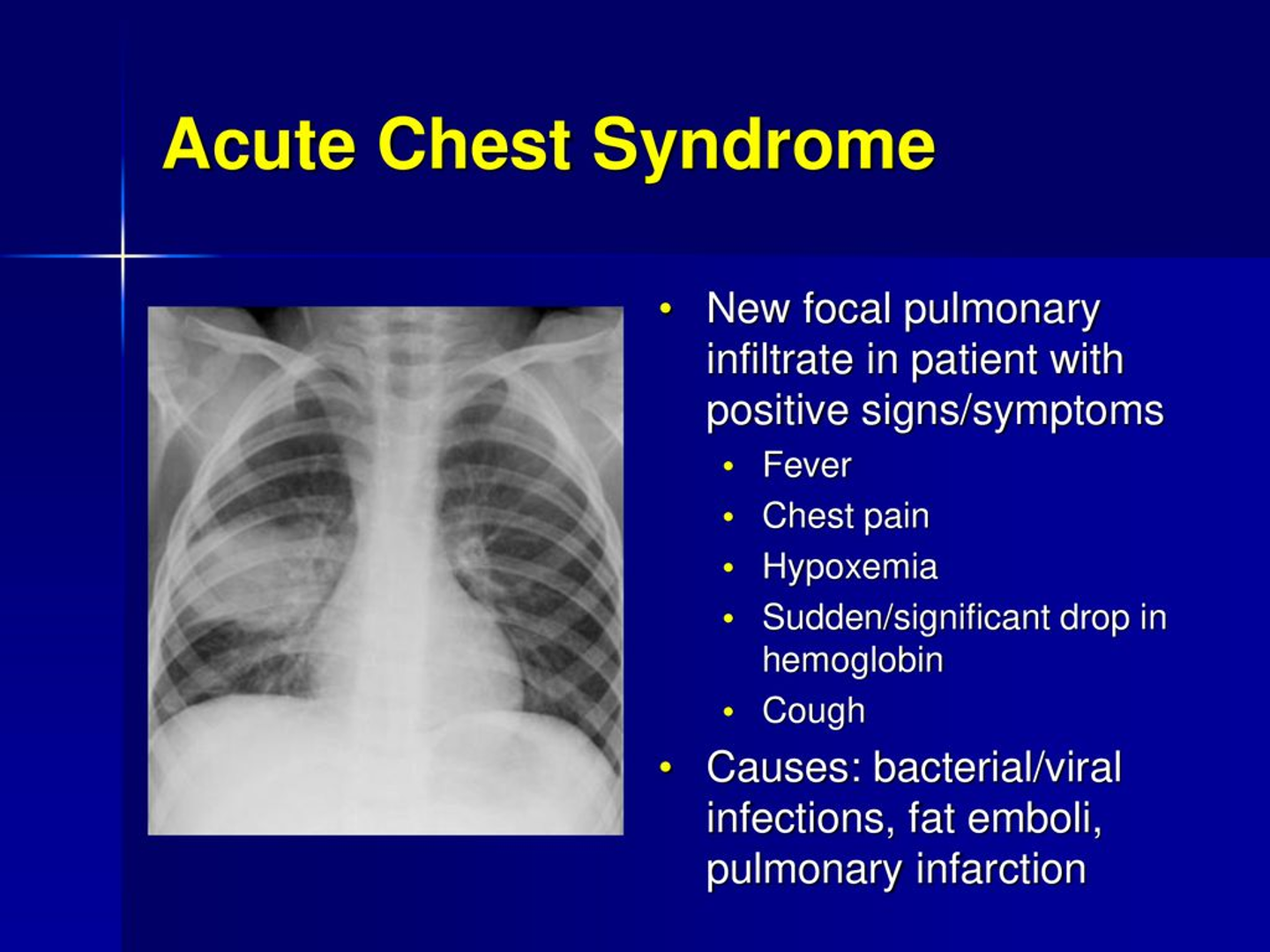
What does this refer to
look at this picture
What does this refer to
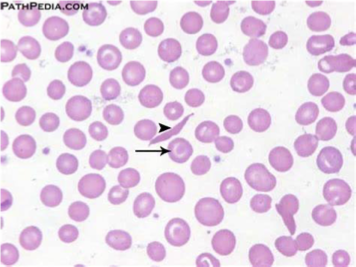
Target cells, elongated cells, and characteristic sickle erythrocytes
Workup Peripheral Blood Smear
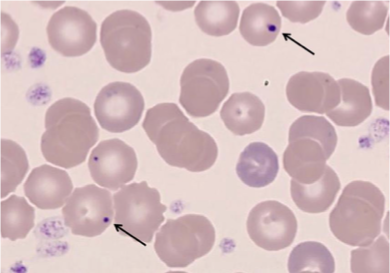
What does this refer to
RBCs with nuclear remnants (Howell-Jolly bodies) = asplenia
Spherical or ovoid eccentrically located granules occasionally observed in the stroma of circulating erythrocytes that occur most frequently after splenectomy or in megaloblastic or severe hemolytic anemia
Workup Sickle Cell

What does this refer to
Remnants of the RBC nucleus
Normally removed by the spleen
Seen in patients with splenectomy or who have functional asplenia (from sickle cell disease).
Target cells (arrows) are another consequence of splenectomy.
Cell Morphology Howell-Jolly bodies
What does this refer to

Clinical intervention Sickle cell
What does this refer to

Treatment Sickle Cell
What does this refer to
Antimetabolites
Hydroxyurea
Opioid analgesics for pain
NSAIDS
Ketorolac (Toradol)
TCA
Amitriptyline
Vitamins
Folic acid
Glutamine amino acid
Clinical pharmacotherapeutics Sickle Cell
What does this refer to

Predictors of adverse outcome
Hand-foot syndrome (dactylitis) in infants younger than 1 year
Hb level of less than 7 g/dL
Leukocytosis in the absence of infection
Prognosis Sickle Cell
What does this refer to
What does this refer to
A 22-year-old Vietnamese female presents for a routine gyn exam. Her menstrual cycle is normal and there is no evidence of other bleeding. Guiac is negative. Her hemoglobin is at 11 (12-16), RBC is 5.8 (3.5-5.5), and an MCV of 70 (80-100) with a normal RDW of 10. WBC and platelets are normal. Hemoglobin electrophoresis shows an increase in amount of Hgb A2 and Hgb F
Alpha (⍺)-thalassemia
What does this refer to
Decreased alpha globin chain production
Sx – ↓ RBC
Reduction in the amount of hemoglobin prevents enough oxygen from reaching the body's tissues
Determined by 4 genes
4 ⍺-genes and 2β-genes = 3 forms of Hgb (A, A2, and F)
⍺-Thalassemia
What does this refer to
MC Southeast Asia followed by Mediterranean, Africa and Middle East
Lowest among Caucasians
⍺-thalassemia is MC Asian Americans
Congenital
M = F
Epidemiology ⍺-Thalassemia
What does this refer to
Decrease in alpha (⍺) chain production
Genetic
Deletions of HBA1 and HBA2 (we have 2 of each)
Determined by 4 genes
1/4 abnormal allele (silent carrier)
2/4 abnormal alleles (minor trait)
3/4 abnormal alleles (intermedia)
4/4 abnormal alleles (hydrops fetalis) —> ⍺-thalassemia major = Hb Bart disease
Fetal demise (total body edema)
Etiology ⍺-Thalassemia
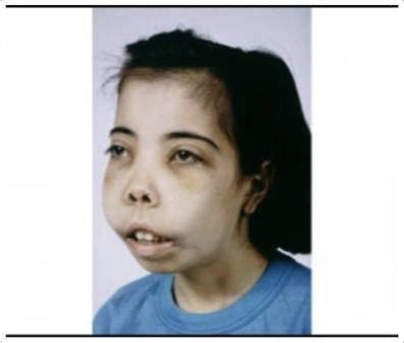
What does this refer to
Mild-moderate anemia
Hepatosplenomegaly
Jaundice
Heart defects
Increased bone marrow hematopoiesis
Frontal bossing
Maxilla overgrowth
Abnormalities of the urinary system or genitalia
Physical exam ⍺-Thalassemia
What does this refer to
Beta thalassemia
Iron – folate deficiencies in pregnancy
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia
Non-immune hemolytic anemia
Sideroblastic anemia
Differential diagnosis ⍺-Thalassemia
What does this refer to
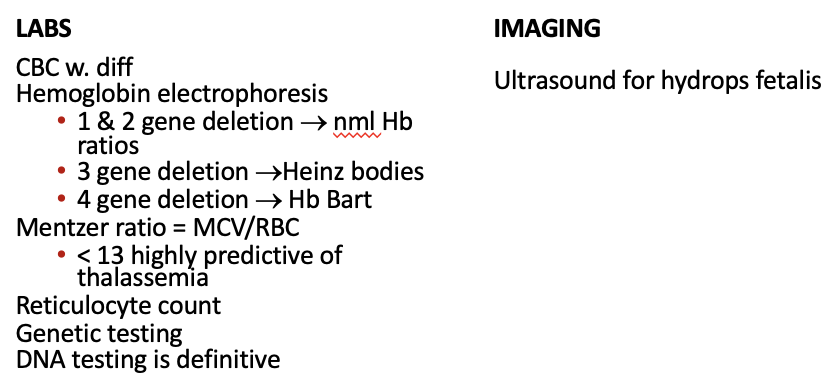
Workup ⍺-Thalassemia
What does this refer to
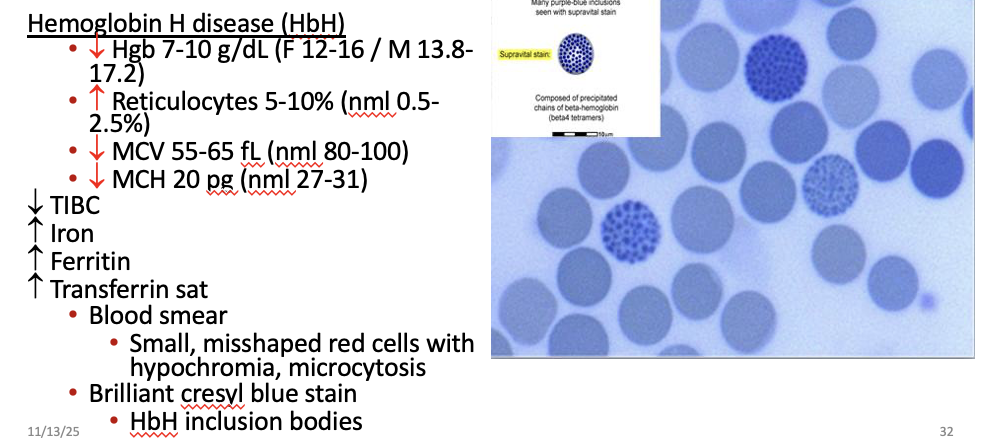
Workup ⍺-Thalassemia
What does this refer to
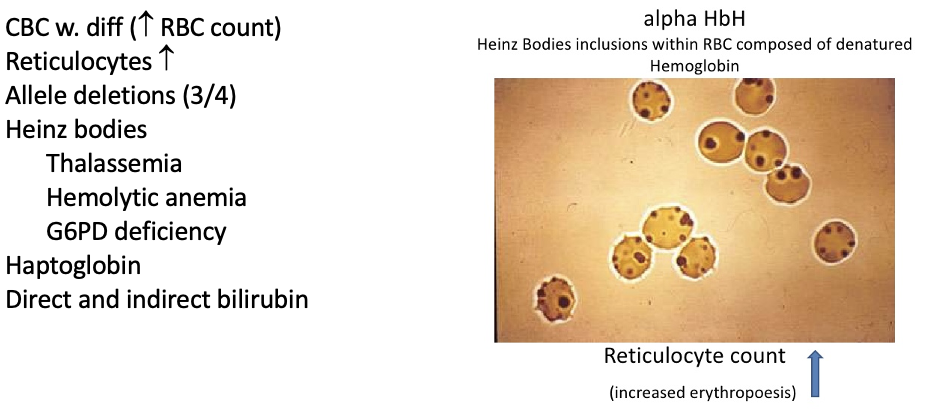
Workup ⍺-Thalassemia
What does this refer to
Mentzer Ratio = MCV/RBC (< 13)
MCV - profoundly decreased
TIBC - decreased
Iron - increased
Ferritin - increased
Reticulocyte count - increased
Transferrin saturation – increased
Unexplained finding is that although there is a decrease in the Hgb concentration and MCV, there is a normal or slightly increased RBC count
How’s it diagnosed? thalassemia
What does this refer to
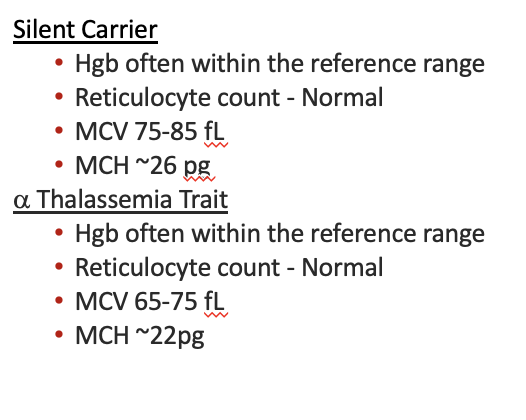
Results of diagnostics by type ⍺-Thalassemia
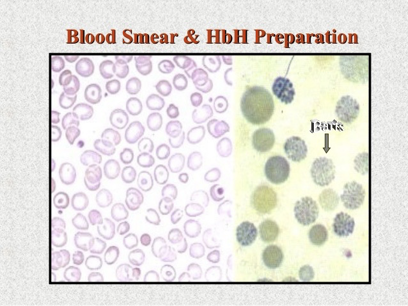
What does this refer to
Hydrops fetalis
Hemoglobin - 4-10 g/dL
MCV - 110-120 fL
Peripheral blood smear - Severe anisopoikilocytosis, severe hypochromia, and nucleated red blood cells (RBCs)
Workup ⍺-Thalassemia
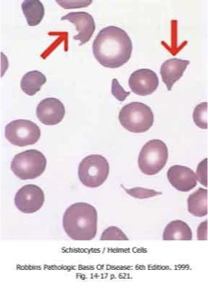
What does this refer to
Schistocytes
Tear drop cells
Increased reticulocytes
Hemolytic anemia ⍺-Thalassemia
What does this refer to
Consult/referral Hematology
Episodic blood transfusions
Vitamin C and folate supplements
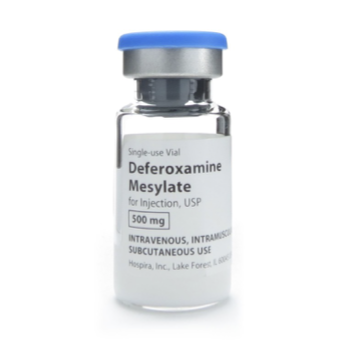
Iron chelating agents (deferoxamine) prevent iron overload
Clinical Management ⍺-Thalassemia
What does this refer to
Silent carriers have excellent prognosis
Outcome deteriorates with HbH disease
Hydrops fetalis is incompatible with life
Prognosis ⍺-Thalassemia
What does this refer to
Microcytic Anemia
Group of hereditary disorders characterized by a genetic deficiency (decreased production) in the synthesis of beta-globin chains
Hb E variant
Homozygous
Heterozygous
β-Thalassemia
What does this refer to
MC Mediterranean and African American populations
Disease may not be detected until about 6 months after birth
Β-thalassemia trait (minor) MC type
Epidemiology β-Thalassemia
What does this refer to
Genetic
Β-thalassemia trait (minor) 1 abnml allele
B-thalassemia major (Cooley’s anemia) 2 abnml alleles
B-thalassemia intermedia mild homozygous form
Etiology of β-Thalassemia
What does this refer to
Varies based on type/severity
Β-thalassemia trait (minor) – asx
B-thalassemia intermedia
Anemia
Hepatosplenomegaly
Bony disease
B-thalassemia major
Ineffective erythropoiesis
Short RBC life span
Clinical history of β-Thalassemia
What does this refer to
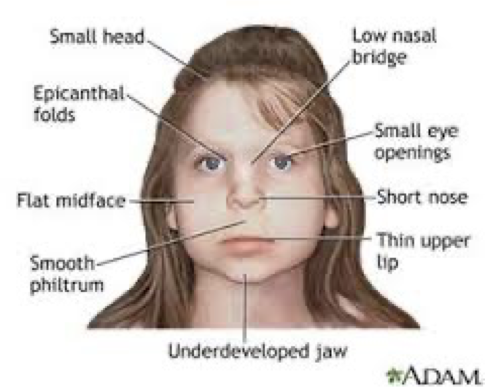
Delayed growth
Severe, chronic anemia
Hemolytic anemia
Hepatosplenomegaly
Bony abnormalities
Osteoporosis
Frontal bossing
Abnormal ribs
Hypogonadism
Physical exam β-Thalassemia
What does this refer to
Alpha thalassemia
Anemia of chronic disease with renal failure
Iron Deficiency Anemia
Lead Nephropathy
Sideroblastic Anemia
Differential Diagnosis β-Thalassemia
What does this refer to
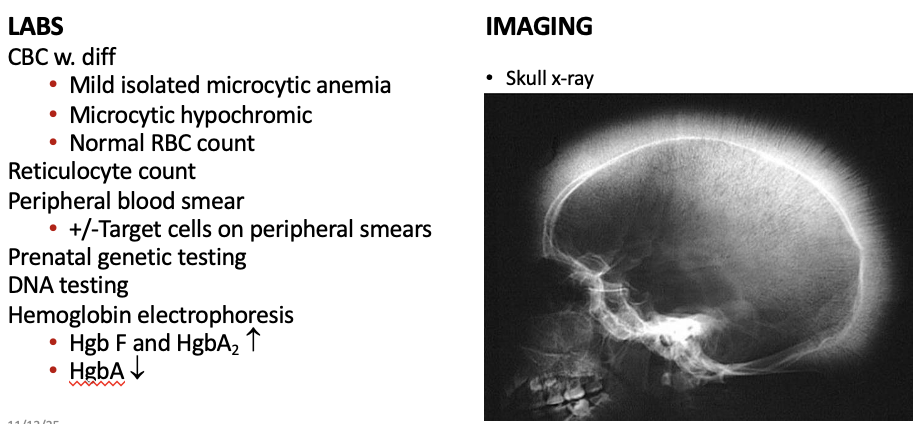
Workup β-Thalassemia
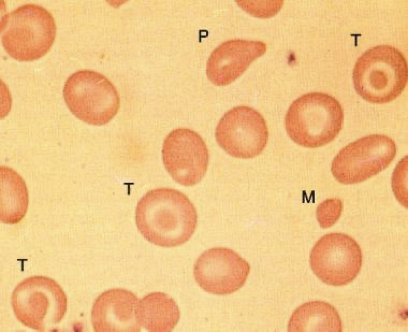
What does this refer to
Peripheral smear in beta-zero thalassemia minor
Microcytes (M)
Target cells (T)
Poikilocytes (P)
Workup for β-Thalassemia
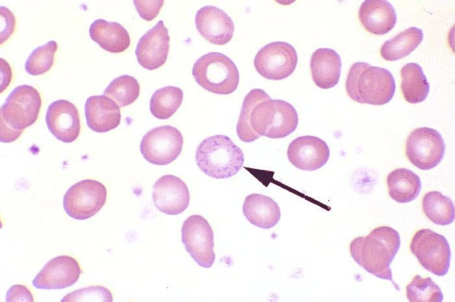
What does this refer to
Basophilic stippling
Work up β-Thalassemia
What does this refer to
Consult/referral hematology
Genetic counseling
Beta thalassemia major requires tx
Long-term transfusion therapy
Iron chelation
Splenectomy
Allogeneic hematopoietic transplantation
Vitamin C and folate supplements
Clinical intervention for β-Thalassemia
What does this refer to
Individuals with thalassemia minor (thalassemia trait) usually have mild, asymptomatic microcytic anemia and does not result in mortality or significant morbidity
Thalassemia major prognosis depends on adherence to long term treatment
The major causes of morbidity and mortality in beta thalassemia are anemia and iron overload
The long-term increase in red-cell turnover causes hyperbilirubinemia and bilirubin-containing gallstones
Onset osteoporosis usually by age 10
Prognosis β-Thalassemia