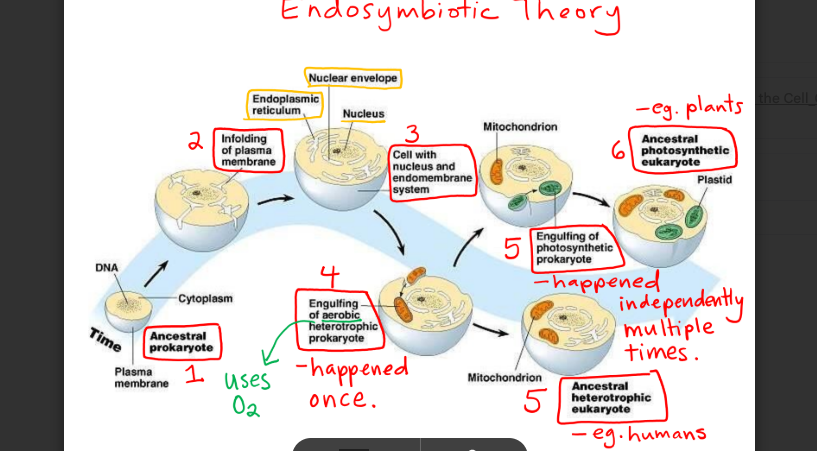
AP bio Ch 4 Flashcards
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
Smooth ER
lipid synthesis
poson detoxification
calcium ion storage
rough ER
protein synthesis
Golgi Apparatus
protien modification and sorting
cisternal maturation
lysosomes
macromolecule digestion
autophagy
Which of the following proteins are synthesized by bound ribosomes?
insulin
lysosomel enzyme
ER protien
path a secretory protein follows from synthesis to secretion.
Protien Systhesis
a. endoplasmic recticulum
b. cis golgi cisternea
c. medical golgi cisternea
d. trans golgi cisternea
e. plasma membrane
extra cellular space
true statements about phagocytosis
Lysosomes fuse with phagosomes formed during phagocytosis.
Phagocytosis occurs when part of the cell’s plasma membrane engulfs a particle, forming a phagosome.
he contents of phagosomes are digested with the help of hydrolytic enzymes in lysosomes.
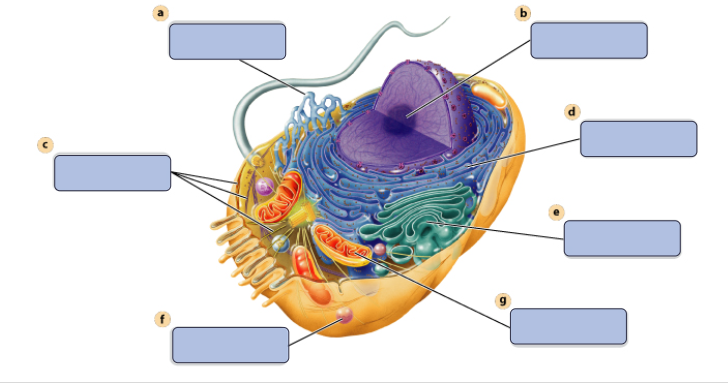
a
synthesises Lipids
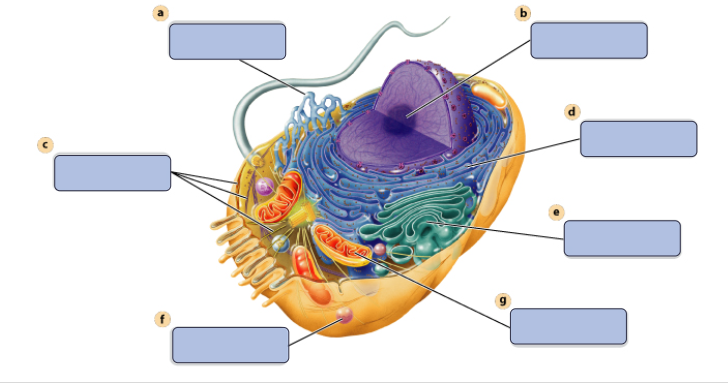
b
assembles ribosomes
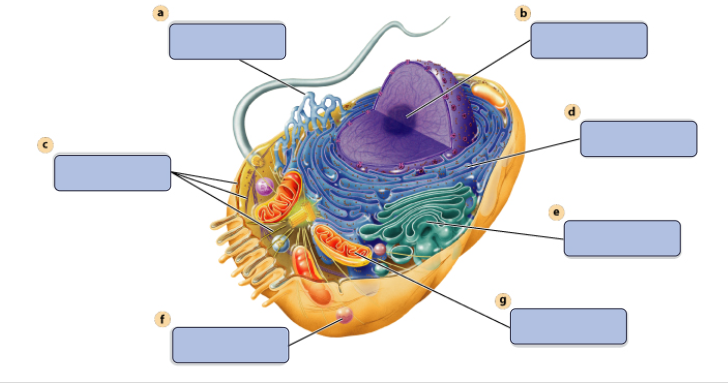
c
defines cell shape
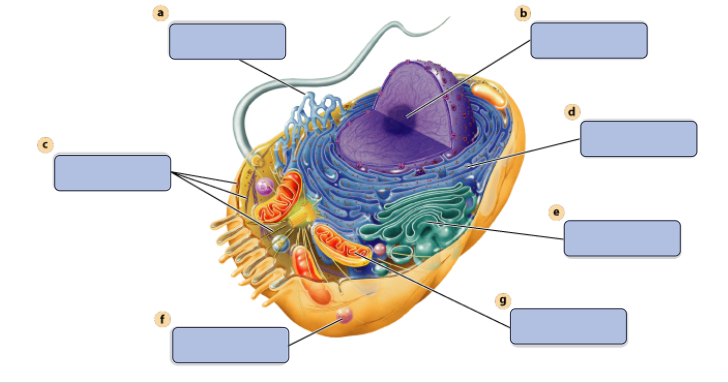
d
produces secretory proteins
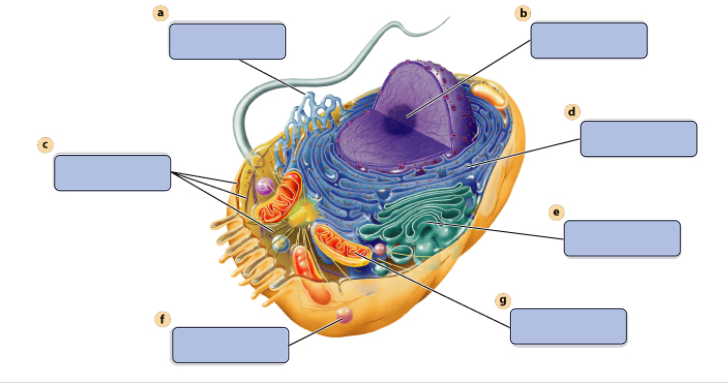
e
modefies and sorts protiens
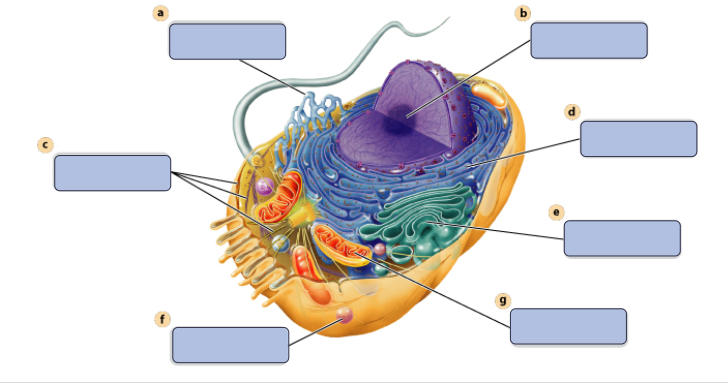
f
digests proteins
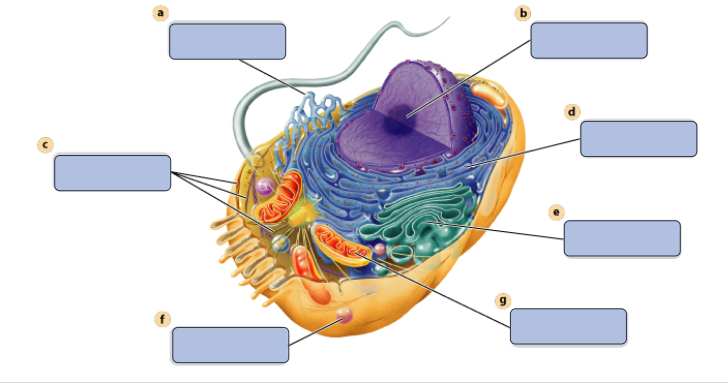
g
generates ATP
prokaryotic only
nucleoid
eykariotic only
lysosome
mitochondria
nucleous
Both (eukaryotic & prokaryotic)
ribosomes
plasma membrane
flagella
1. In eukaryotic flagella, the fibers that slide past one another due to the activity of dynein proteins are ______
microtubules
Many cell organelles, most notably the nucleus, are anchored by _____which are assembled from a diverse class of proteins.
intermediate filaments
Centrosomes are sites where protein dimers assemble into ____
microtubules
The extension of pseudopodia in amoeba is due to the regulated assembly and destruction of______
microfialments
The only cytoskeletal fibers not associated with intracellular movement or whole cell locomotion are the ________
intermediate fialments
During muscle contractions, myosin motor proteins move across tracks of ______
micro filaments
Which of these is the simplest unit of life?
cell
A researcher wants to film the movement of chromosomes during cell division. Which type of microscope should be chosen and why?
light microscope, because the specimen is alive
Cell fractionation __________.
separates cells into their smallest component parts
Plant cell only
chloroplast
cellulose cell wall
central vacuole
animal cell only
centriole
both (plant & animal cell)
mitochondrion
Endoplasmic recticulum
Golgi apparatus
cytoskeleton
nucleus
plasma membrane
Plant cell wall (discription)
strong, protective structure made from cellulose fibrils
central vacuole (discription)
regualtes cytoplasm composition, creates internal pressure, adn stores cell compounds
cholorplast
makes sugar by converting light energy into chemical energy
mitochondrion (discription)
produces chemical energy (ATP) that can power the cell
Golgi apparatus
modfies and pacages proteins
Which statements are true for chloroplasts?
They contain the green pigment chlorophyll.
They have membranous sacs called thylakoids that are surrounded by a fluid called stroma
They are the sites of reactions that convert solar energy into chemical energy.

1
Animal

2
structure: gap juctions

3.
Structure: tight junctions
animal

4
Structure: plasmodesmata
plant

5
structure: cellulose
plant

6
Structure: collagen
animal
Which organelle plays a role in intracellular digestion?
lysosome |
The cilia and flagella of eukaryotic cells are composed of _____.
microtubules
Consider two cells with the same volume but with very different surface areas due to differences in their shapes. The cell with the larger surface area is likely to __________.
be involved in the rapid uptake of compounds from the cell's environment
Which is/are likely to limit the maximum size of a cell?
diffusion time, surface area-to-volume ratio, and shape
Which structure is found in eukaryotic, but not prokaryotic, cells?
mitochondria
A substance moving from outside the cell into the cytoplasm must pass through __________.
the plasma membrane
In terms of cellular function, what is the most important difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Eukaryotic cells are compartmentalized, which allows for specialization.
Bacterial cells are prokaryotic. Unlike a typical eukaryotic cell they __________.
lack membrane-bounded organelles in their cytoplasm
Which feature do prokaryotes and eukaryotes have in common? (Section 4.2)
ribosomes, plasma membrane, cytoplasm
In addition to the fundamental structures required to be defined as a cell, which cell type(s) also has/have a nucleus and chloroplasts? (Section 4.2)
a protist cell and a plant cell
A dish of animal cells was grown in the presence of radioactive phosphorous. The phosphorous largely ended up in nucleotides. In which cellular structure(s) would you predict the majority of the radioactive phosphorous to accumulate? (Section 4.2)
the nucleus
What is the functional connection between the nucleolus, nuclear pores, and the nuclear membrane? (Section 4.3)
Subunits of ribosomes are assembled in the nucleolus and pass through the nuclear membrane via the nuclear pores.
Which group is primarily involved in synthesizing molecules needed by the cell? (Section 4.4)
ribosomes,
rough endoplasmic reticulum,
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Which structures will not necessarily increase in abundance in pancreatic cells that begin to secrete large amounts of digestive enzymes? (Section 4.4)
free cytoplasmic ribosomes
Which category best fits the function of the rough endoplasmic reticulum? (Section 4.4)
manufacturing
You would expect a cell with an extensive Golgi apparatus to ___________. (Section 4.4)
secrete a lot of protein
A researcher made an interesting observation about a protein made by the rough endoplasmic reticulum and eventually found in a cell's plasma membrane. The protein in the plasma membrane was actually slightly different from the protein made in the ER. The protein was probably altered in the __________. (Section 4.4)
Golgi apparatus
Consider a protein that is made in the rough endoplasmic reticulum. When the synthesis of the protein is complete, the protein is located in the ER membrane. Where else in the cell might this protein be found? (Section 4.4)
embedded in the plasma membrane, functioning in the transport of molecules into the cell
Which is/are most likely to be involved in the process of producing proteins for a chloroplast or mitochondrion? (Section 4.4)
free cytoplasmic ribosomes
A protein that ultimately functions in the plasma membrane of a cell is most likely to have been synthesized __________. (Section 4.4)
in the rough endoplasmic reticulum
Which of these membranes are likely to have a lipid composition that is most distinct from the others? (Section 4.5)
mitochondrial outer membrane
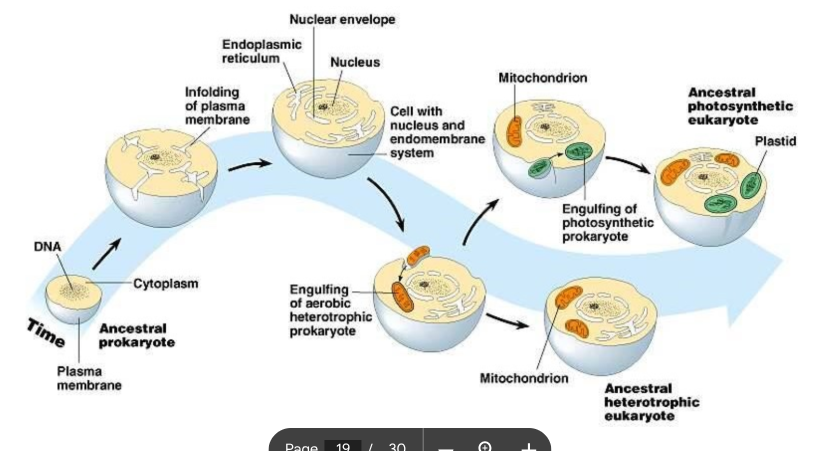
Chloroplasts and mitochondria are thought to have started as prokaryotes. One piece of supports for this hypothesis is these organelles prokaryotic-type ribosomes. These ribosomes are probably most similar to ribosomes found __________. (Section 4.5)
in bacterial cells
Which statement about chloroplasts and mitochondria is true? (Section 4.5)
Chloroplasts and mitochondria synthesize some of their own proteins.
Which is a possible reason for grouping the peroxisomes with chloroplasts and mitochondria? (Section 4.5)
None of these organelles are part of the endomembrane system.
Which type of cell will have have the most mitochondria? (Section 4.5)
muscle cells in the legs of a marathon runner
Which of these is a false statement? (Section 4.5)
Mitochondria contain ribosomes in the intermembrane space.
The observation that chloroplasts and mitochondria each contain their own DNA and synthesize some of the proteins that function in these organelles suggests that chloroplasts and mitochondria __________. (Section 4.5)
must divide each time the cell containing them divides
Which is/are possible site(s) of protein synthesis in a typical eukaryotic cell? (Section 4.5)
cytoplasm
the rough endoplasmic reticulum
in mitochondria
Which organelle might be found inside other organelles? (Section 4.5)
ribosomes
Microtubules and microfilaments commonly work with what to perform many of their functions? (Section 4.6)
motor proteins
Which structure is found in animal cells but not in plant cells? (Section 4.6)
centrioles
Which statement about the cytoskeleton is true? (Section 4.6)
Components of the cytoskeleton often mediate the movement of organelles within the cytoplasm.
Cilia and flagella move due to the interaction of the cytoskeleton with what? (Section 4.6)
motor proteins
Where would you expect to find proteins involved with movement of structures within a cell? (Section 4.6)
cytoskeleton
Basal bodies are most closely associated with which of the following cell components? (Section 4.6)
cilia
Dye injected into a plant cell might be able to enter an adjacent cell through __________. (Section 4.7)
a plasmodesma
Which correctly compares the extracellular matrix (ECM) of animal cells to cell walls of plant cells? (Section 4.7)
Both the ECM and the plant cell wall are composed of varying mixtures of proteins and carbohydrates.
Your intestine is lined with individual cells. No fluids leak between these cells from the gut into your body. Why? (Section 4.7)
The intestinal cells are bound together by tight junctions.
Which statement correctly describes characteristic shared by plant cell walls and an animal cell extracellular matrices? (Section 4.7)
Both are permeable to water and small solutes.
Both are synthesized in the ER and Golgi apparatus.
The walls of plant cells are largely composed of polysaccharides and proteins that are synthesized __________. (Section 4.7)
in the rough endoplasmic reticulum and in the Golgi apparatus
Which structure is NOT part of the endomembrane system?
cholorplasts
Which structure is common to plants AND animal cells?
mitochondrion
which of the following is present in a prokaryotic cell?
ribosomes
Which cell would be best for studying lysosomes?
phagocytic white blood cells
memorize the order ig