Soil, Soil and Vegetation Regions
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
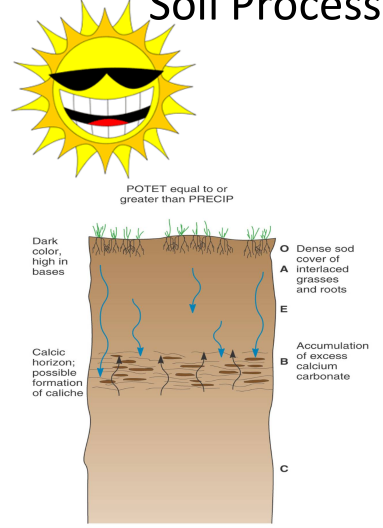
Calcification
When high evaporation pulls moisture up the soil. Many minerals, such as calcium, concentrate in the topsoil making it toxic for plant growth
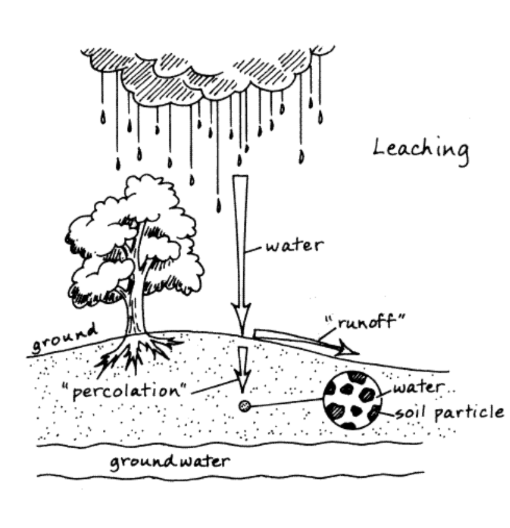
Leeching
Result of heavy precipitation. Rainfall moves the nutrients down the soil column away from the root structure of plants, therefore causing a poor layer of topsoil that is bad for plant growth.
Topsoil
Has a slow formation process. Since the end of the last ice age (6,000-12,000 y.a.), only 15-25 cm of it has formed under Canadian forests. 40-100 cm has formed under the grasslands of the prairies.
Minerals
Parent material (rock) breaks down overtime into small particles of sand, silt, and clay. Common examples of these which are required for plant growth include: calcium, phosphorus and potassium
Humus
Formed when organic matter is broken down by bacteria. This provides nutrients and moisture to growing plants.
Air
Required in order for roots to grow. Passages for this are created by worms, insects, small animals, and high levels of humus/loose decaying matter
Moisture
helps to weather rocks, break down organic matter, and help nutrients dissolve and go into soil.
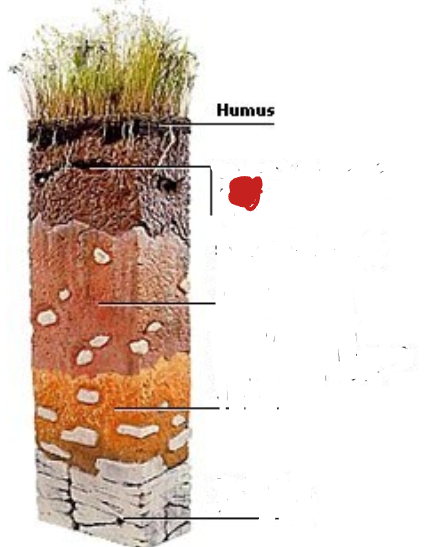
Topsoil. Often rich in humus and minerals.
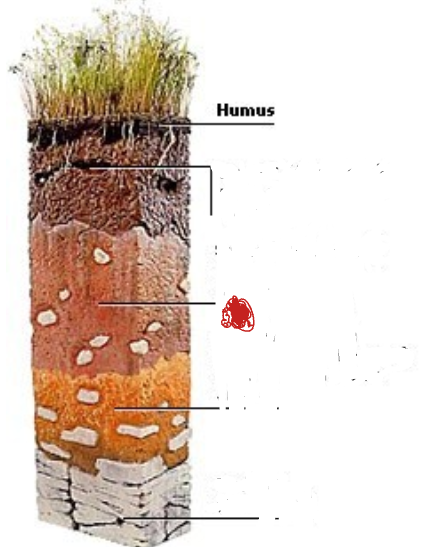
Subsoil. Poor in humus, rich in minerals
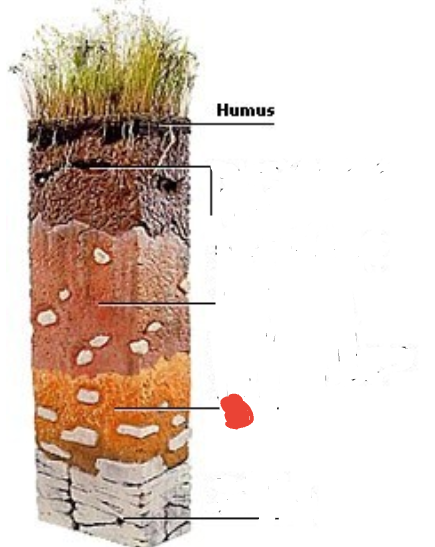
Weathered rock fragments. Little or no plant or animal life.
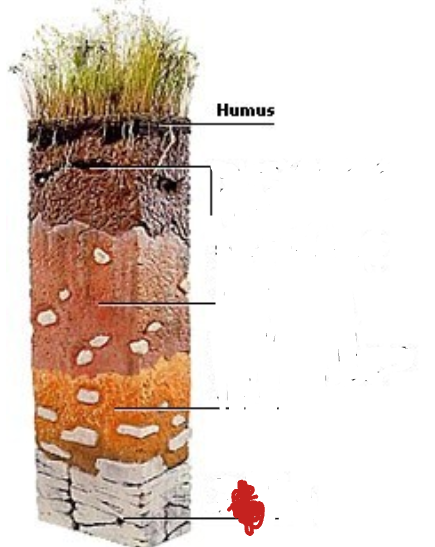
Bedrock
wet-climate soils
soils that develop where leaching is the dominant soil-forming process
dry climate soils
soils that develop where calcification is the dominant soil-forming process
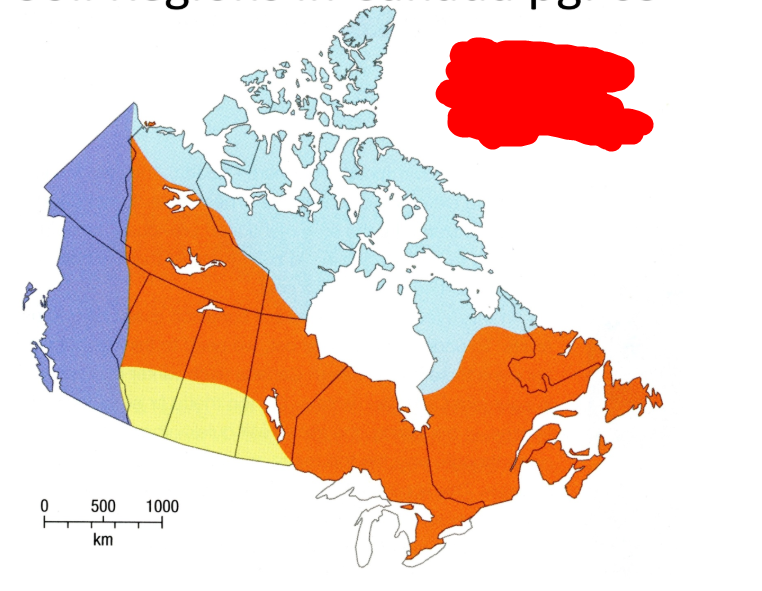
What is the light blue soil region?
Tundra soils
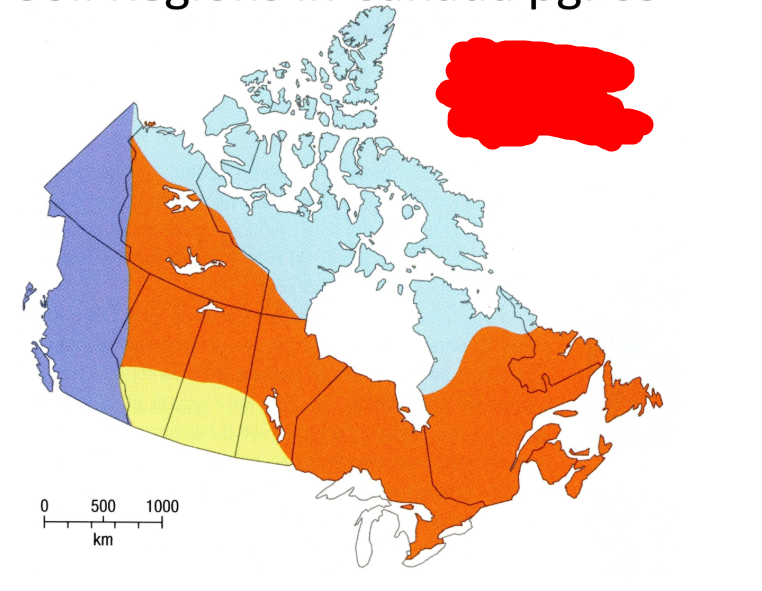
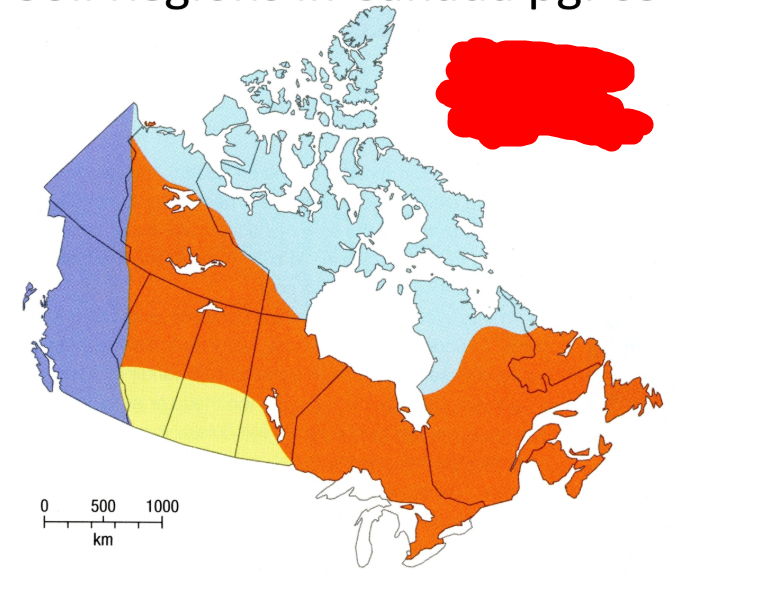
What is the orange soil region?
Wet-climate soils
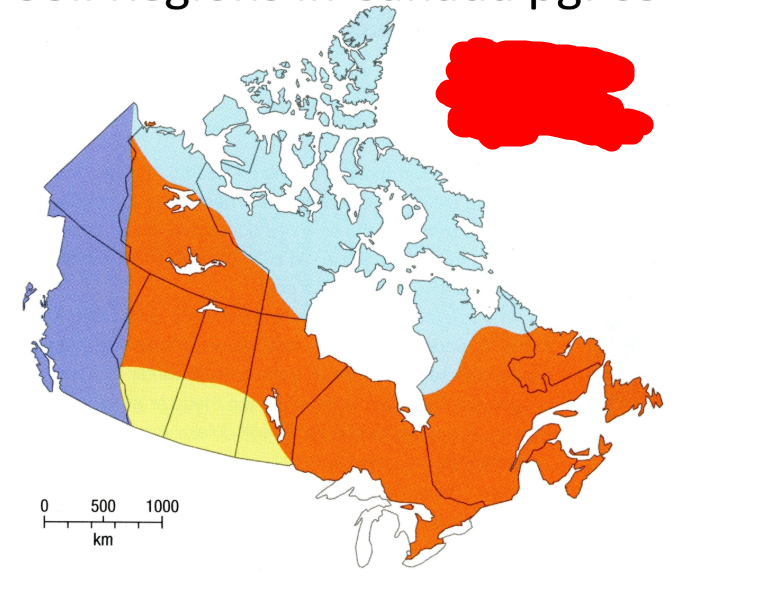
What is the yellow soil region?
Dry-climate soils
What is the purple soil region?
Wide range of soils in the mountainous area
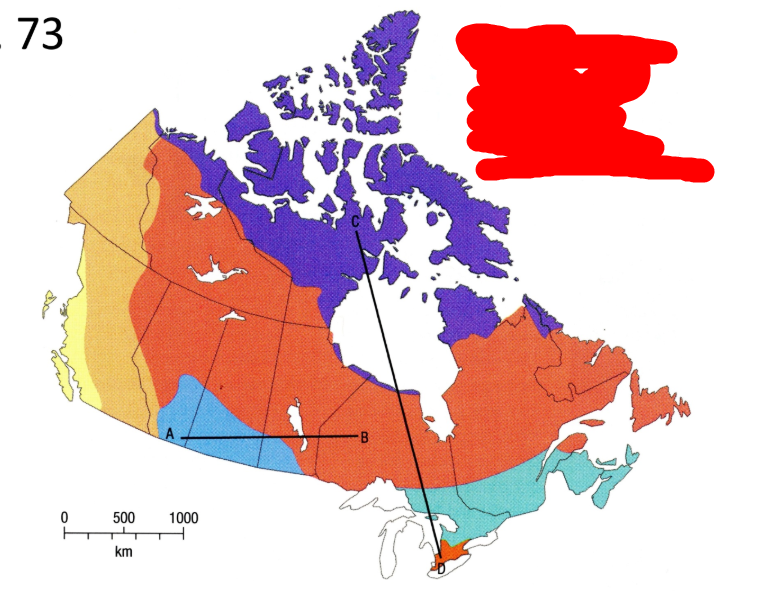
What is the purple vegetation region?
Tundra
What is the very large orange vegetation region?
Boreal and taiga forest
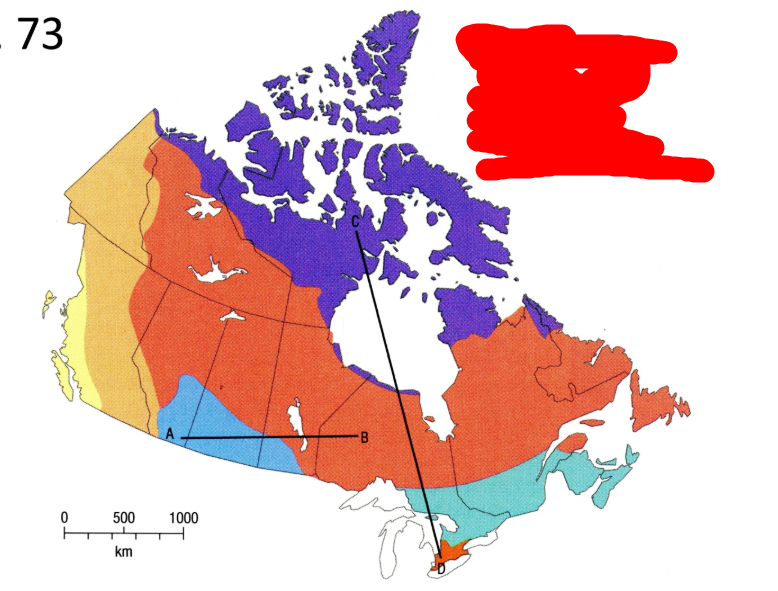
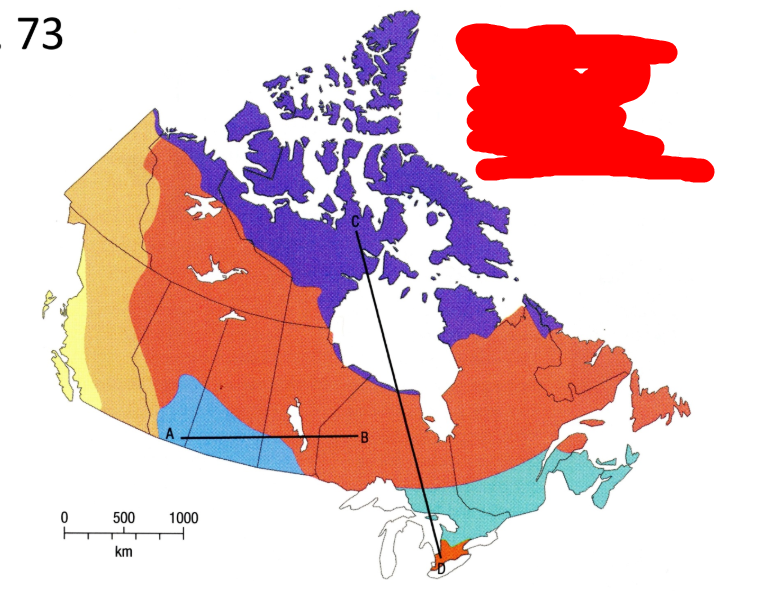
What is the blue vegetation region?
Grassland
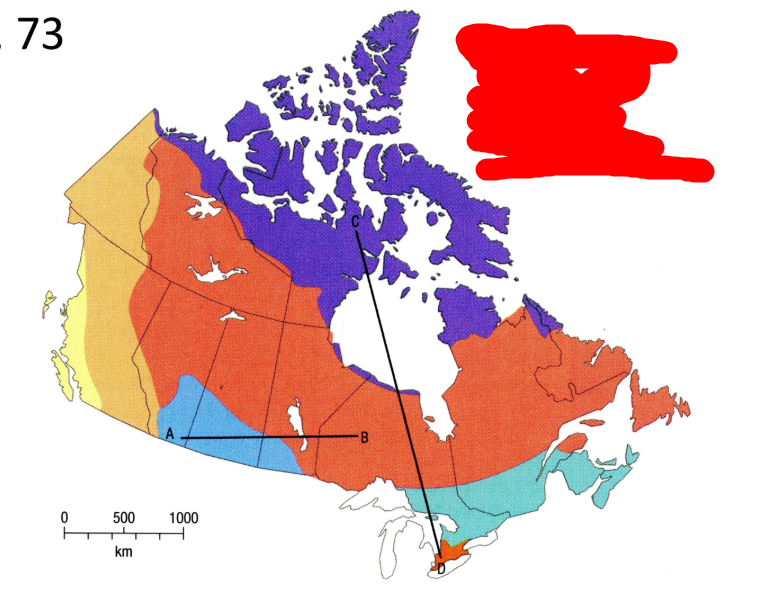
What is the turquoise vegetation region?
Mixed Forest
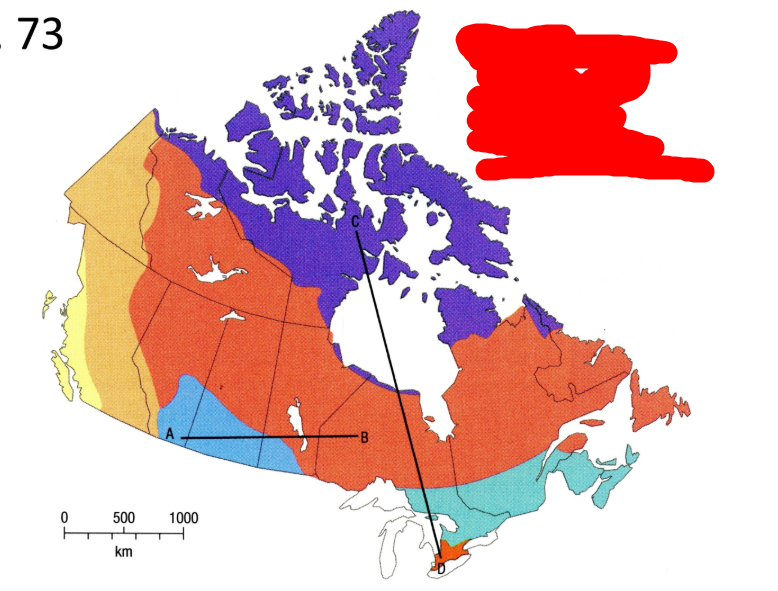
What is the very small orange vegetation region?
Deciduous Forest
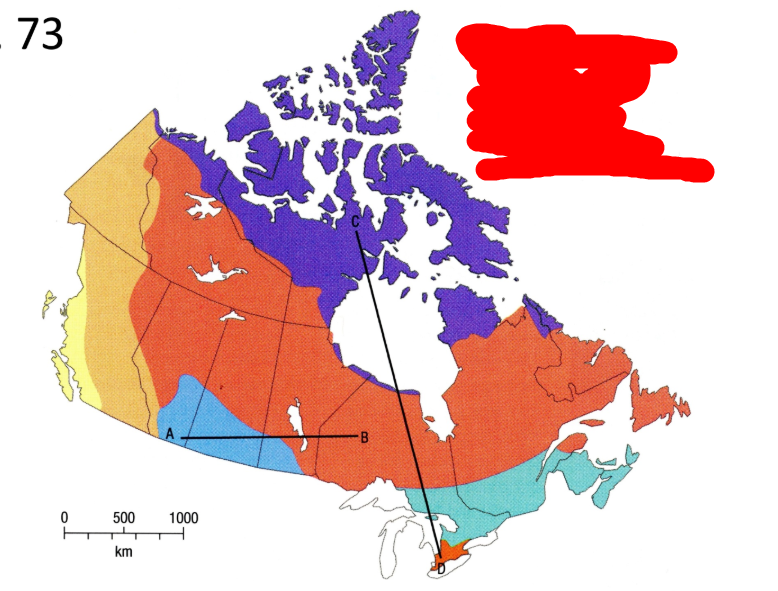
What is the light orange vegetation region? (west side)
Wide range of vegetation types in the mountainous area
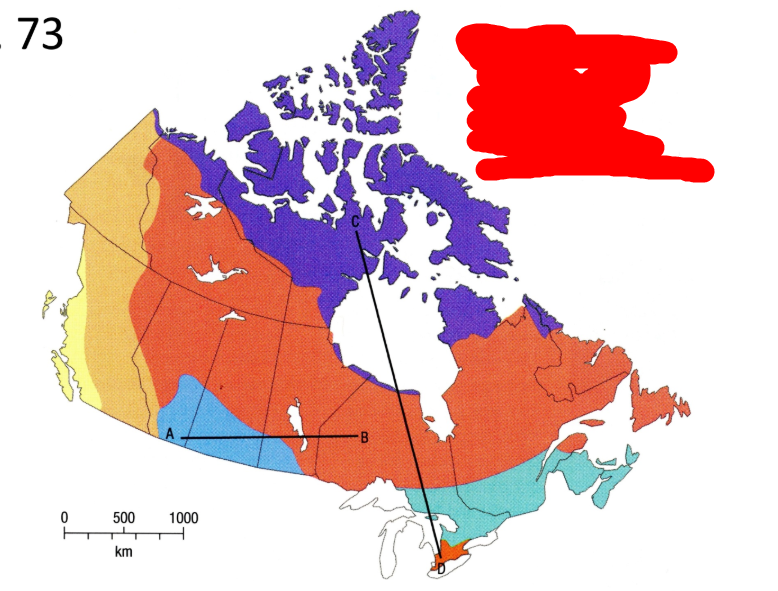
What is the yellow vegetation region?
West coast forest