Unit 0 Properties of Water: Polarity, Hydrogen Bonds, and Surface Tension
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
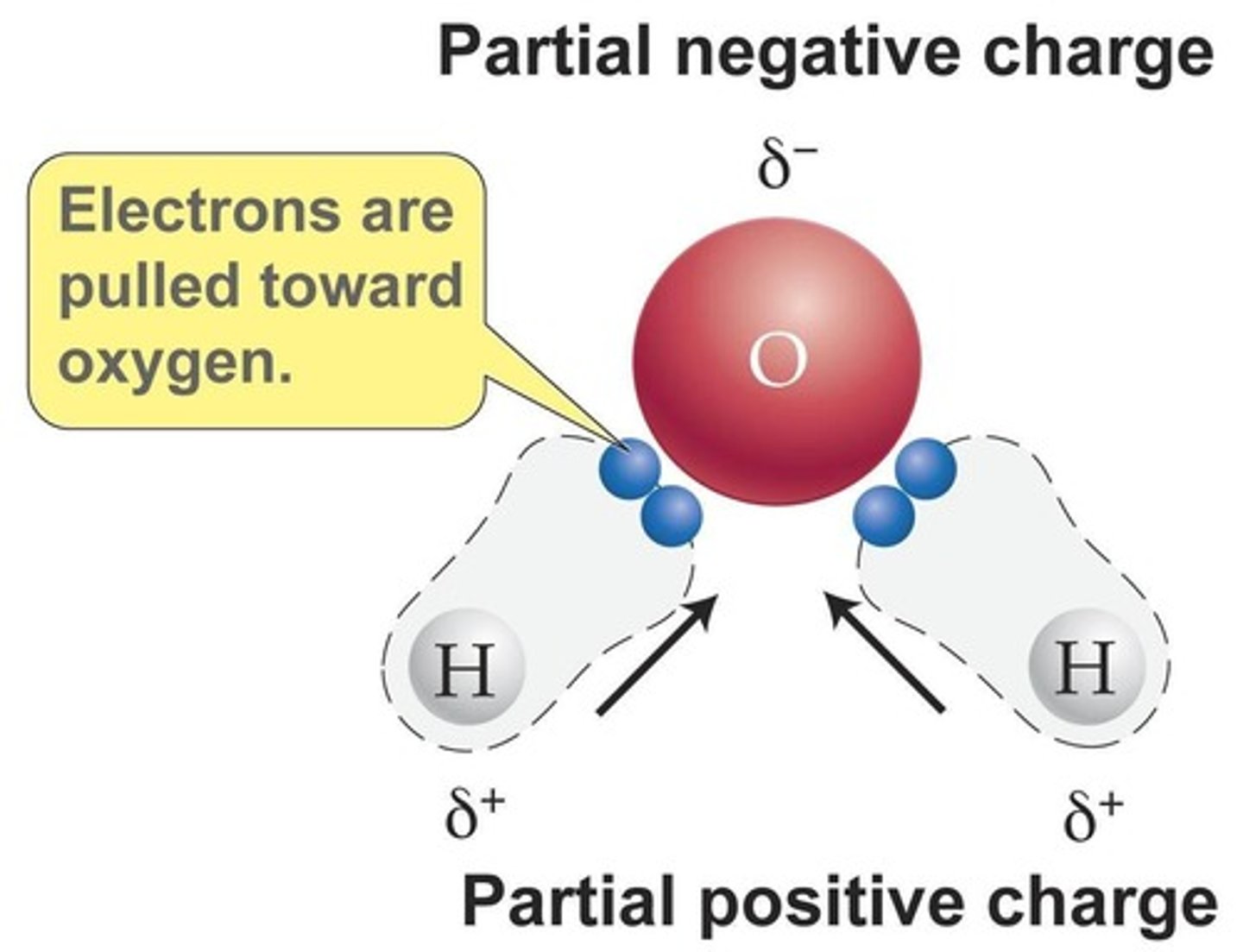
What is the molecular nature of water?
Water is a polar molecule, having a negative region and a positive region.
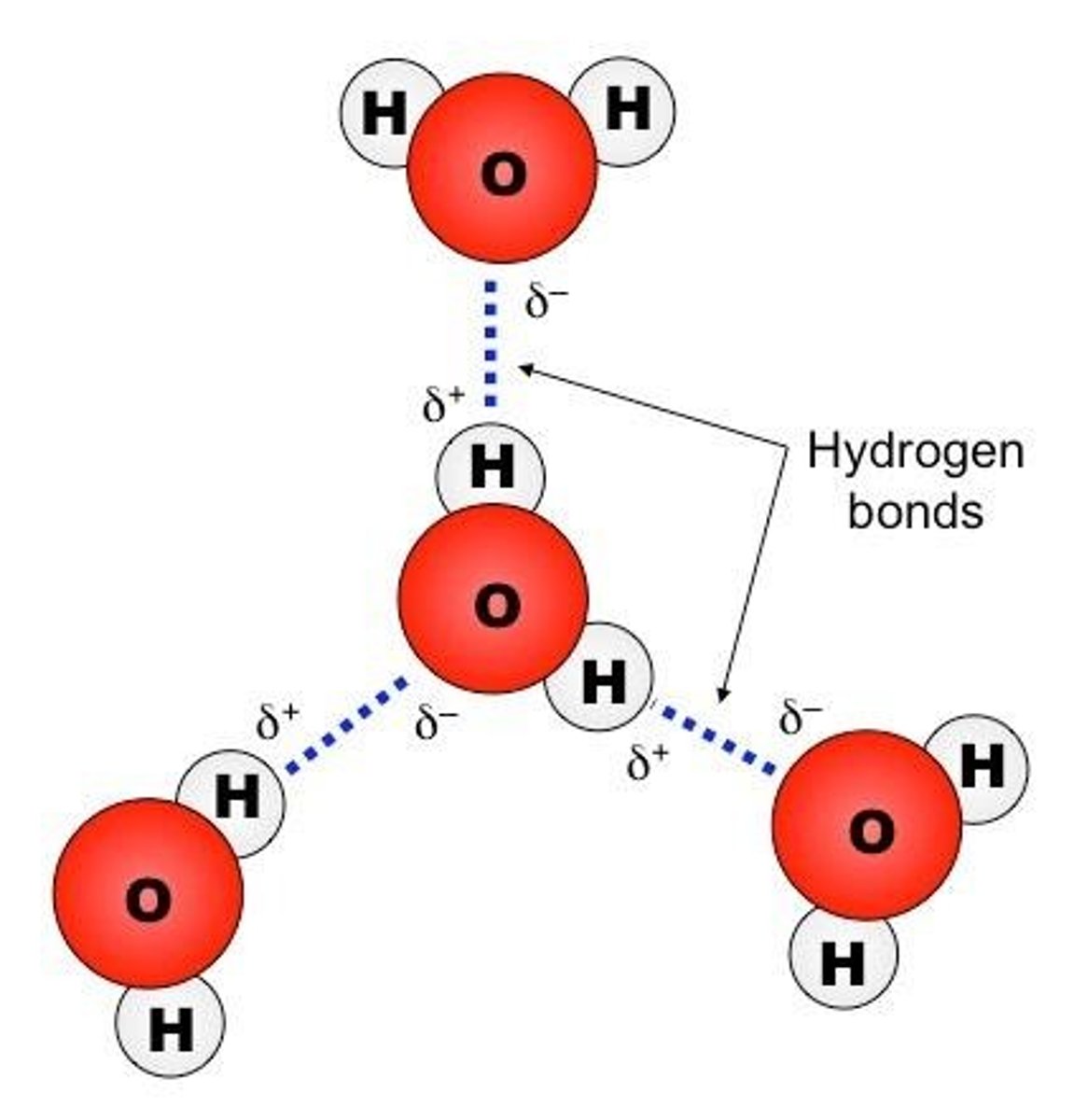
What is a hydrogen bond?
A hydrogen bond is an attraction between a slightly positive hydrogen atom and a slightly negative atom.
What important qualities do hydrogen bonds give to water?
Hydrogen bonds give water a high specific heat, allowing it to resist temperature changes and absorb large amounts of energy without changing temperature.
What is the heat of vaporization?
The heat of vaporization is the energy required to turn a substance into a gas. Water has a high heat of vaporization.
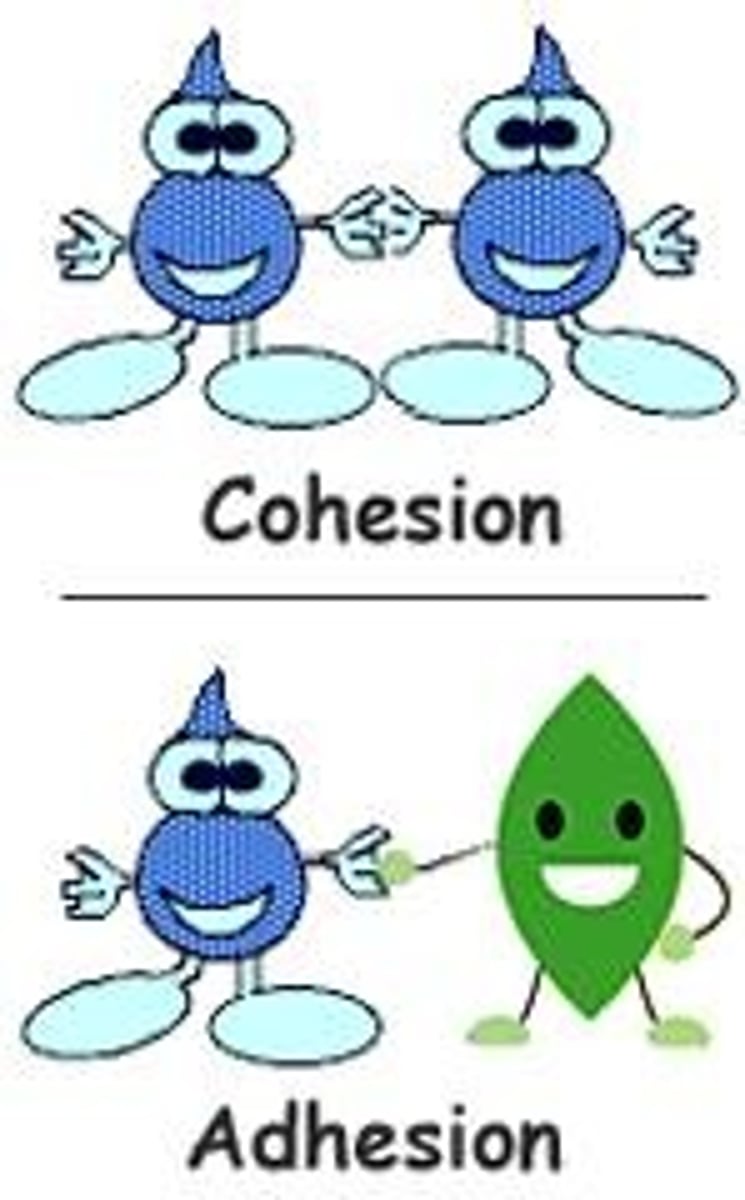
What is adhesion in the context of water?
Adhesion is the attraction between dissimilar molecules, such as water droplets on a plant leaf.
What is cohesion in the context of water?
Cohesion is the attraction between like molecules that causes them to stick together, such as water forming puddles.
What causes the properties of adhesion and cohesion in water?
Both properties are caused by water's hydrogen bonds and polarity.
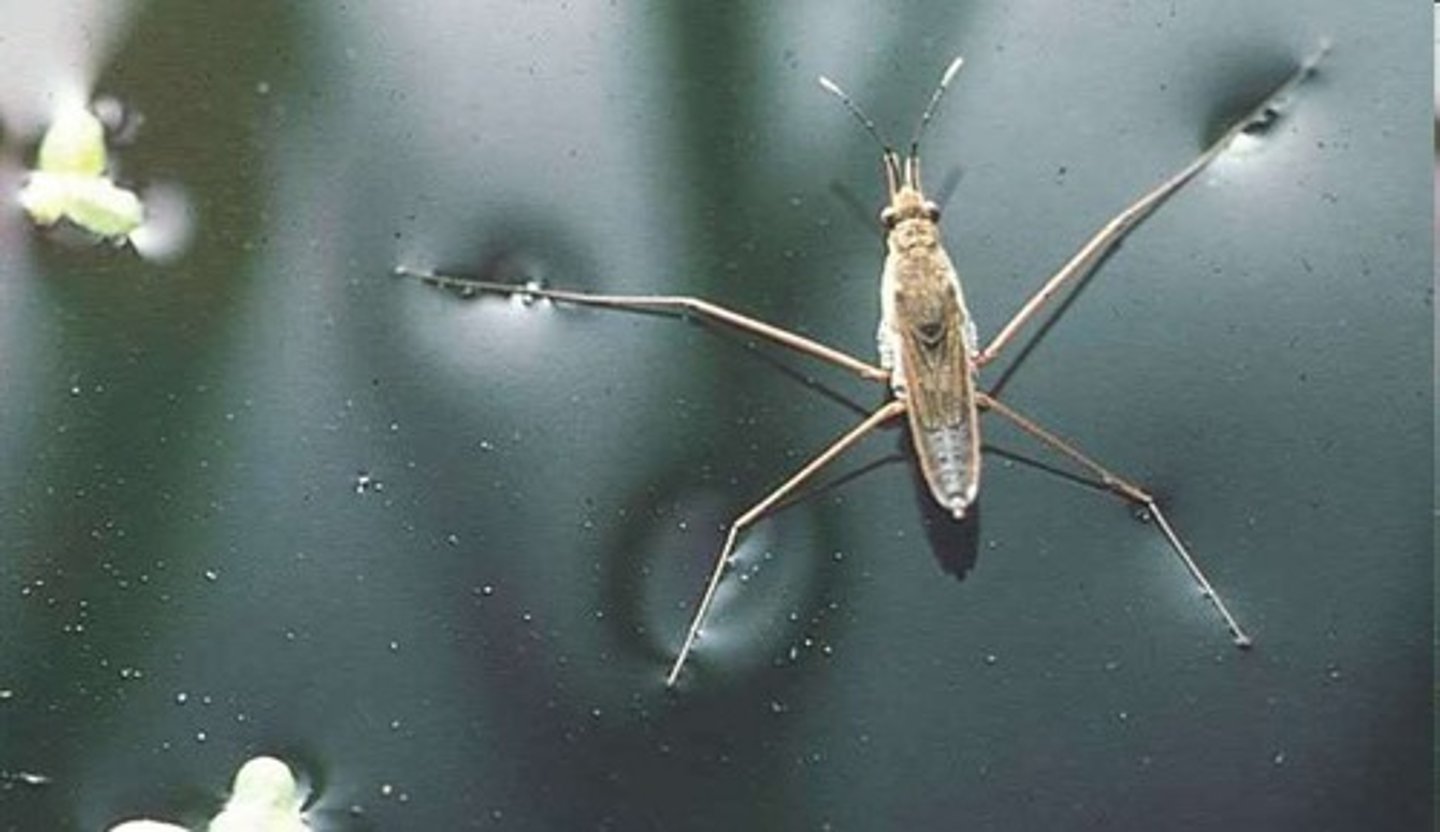
What is capillary action?
Capillary action is the ability of water to move through small tube-like structures against gravity, resulting from the combination of adhesion and cohesion.
What is surface tension?
Surface tension is a property of the surface of a liquid caused by the cohesion of like molecules, allowing them to bond together.
Why does ice float on water?
Ice is less dense than liquid water, which is why it floats.
What is the density of water at 4 degrees Celsius?
Water is most dense at 4 degrees Celsius.
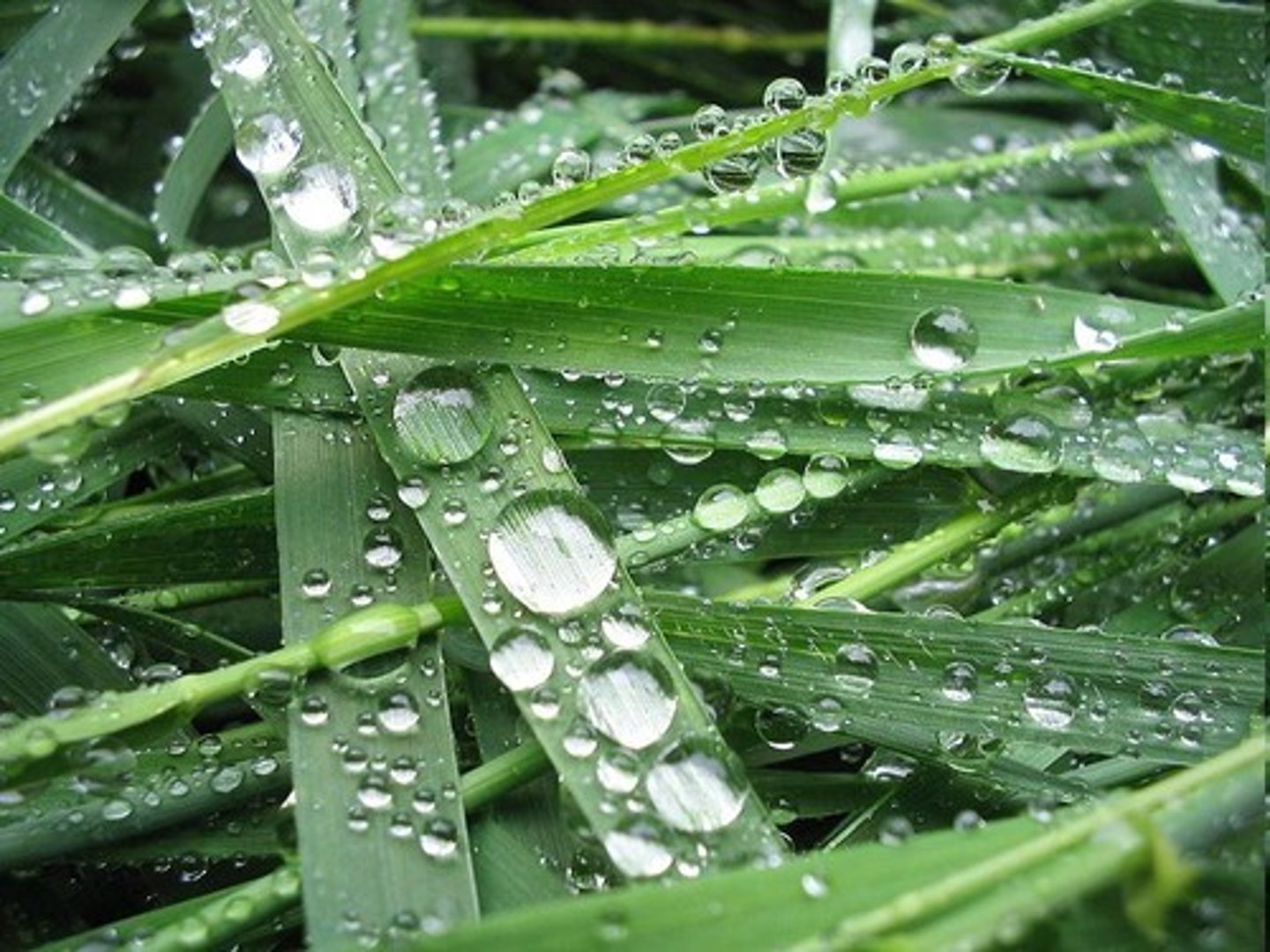
What is an example of cohesion in water?
An example of cohesion is water forming droplets.
What is an example of adhesion in water?
An example of adhesion is water sticking to grass or spider webs.

How does the density of ice compare to liquid water?
Ice is less dense than liquid water.
What happens to water's density as it freezes?
Water expands and becomes less dense when it freezes, resulting in ice.

How does water's high specific heat affect its temperature?
Water resists changes in temperature, allowing it to absorb large amounts of energy without a significant temperature change.
What role do hydrogen bonds play in water's properties?
Hydrogen bonds are responsible for water's high specific heat, cohesion, adhesion, and surface tension.
What is one consequence of water's inability to be compressed?
Water cannot be condensed or compressed from its liquid state, maintaining its density.