Understanding cancer 1 6.4
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Key revision points
the risk factors are: Infection (HPV, H.pylori), geography (UV), social economic status, gene
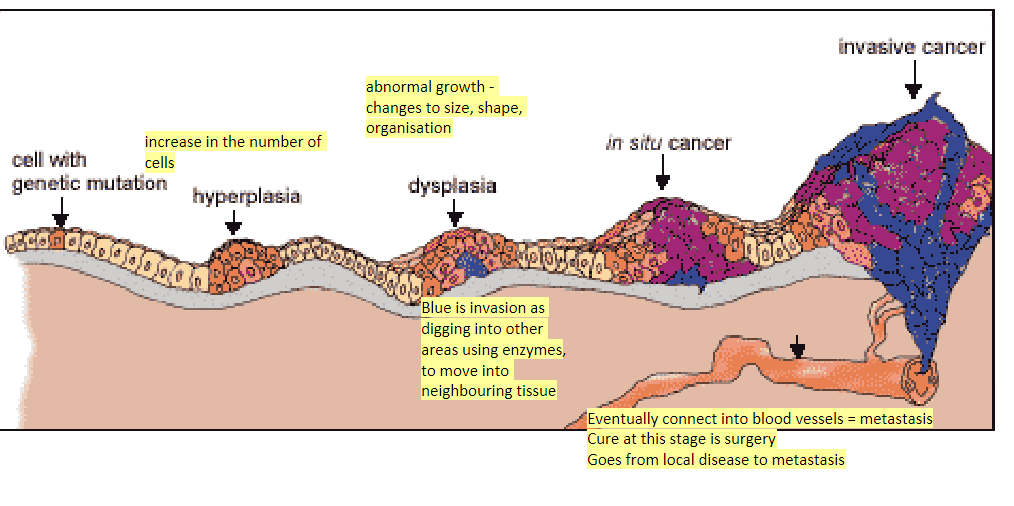
carcinogenic → cancer causing with epi or mutation
mutation→ hyperplasia→dysplasia→in-situ cancer→ invasion
BRAC1: can b triple negative i.e not oestrogen dependent
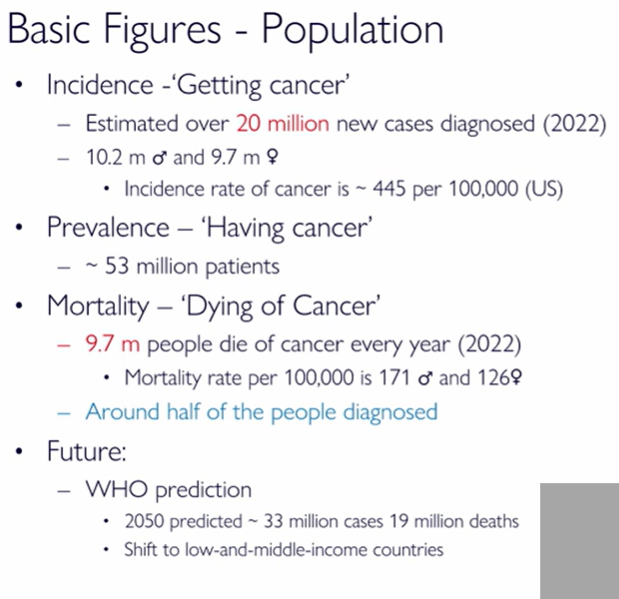
Basic population figures of cancer
20 million diagnosis per year
estimate 33 million cases in 2050 and 19 million deaths
more common in low-and-middle income countries
10.2 male 9.7 female
445 per 100,000 US
prevalence is 53 million - people living with cancer
mortality is close to 50% - prognosis
9.7 m people die every year : 171 male, 126 female per 100,000
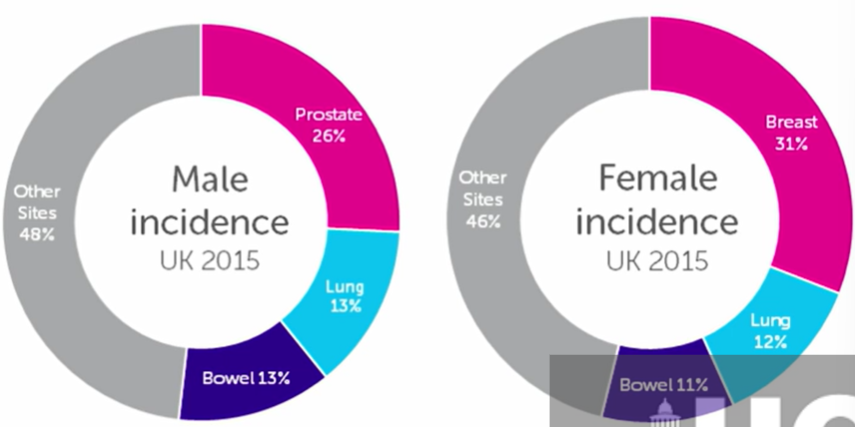
what are the most common cancers?
breast
prostate
lung
bowel
make up 50% of cancers, obi swap the first 2 based on gender
what does cancer from smoking depend on?
how much you smoke
how long you smoke - the longer the worse
if you stop smoking, risk of cancer reduced rapidly, after 15yrs ur like a non-smoker
passive smoking increases risk ~ 25% increased risk to spouse, high exposure 17% risk
what increases women risk of cervical cancer?
HPV virus
90% in developing countries due to less vaccinations (protects 70& against virus)
body often kills the virus - when you have underlying health conditions, less likely to
describe genetic predisposition to cancer and how to reduce it using 1 example
BRAC1 & BRAC2 DNA repair genes mutations
these maintain integrity of DNA and repair damage so are tumour suppressors
mutations increase risk of breast cancer
these are passed on to germ lines and affect all cells bu mother and father
12% → 20-80% risk
also increases risk of other cancers e.g. ovarian, breast
age risk especially after 40/50 as cancer takes years to develop
reduce risk:
screening earlier
mastectomy - remove breast tissue - 90% risk reduction - prophylactic surgert
chemoprevention - selective estrogen receptor modulators e.g. tamoxifen, raloxifen (3-50% risk reduction)
not all cancers from BRAC1/BRAC2 are related to oestrogen modulated drugs - triple negative breast cancer - cancer cells have no oestrogen receptors
Bullet point common risk factors
age
lifestyle
diet
geography - as different risks globally e.g. UV
genetics
infections e.g. h.pylori and stomach cancers, HPV
socio-economic status (higher lung/oral but less breast/cervica/prostate)
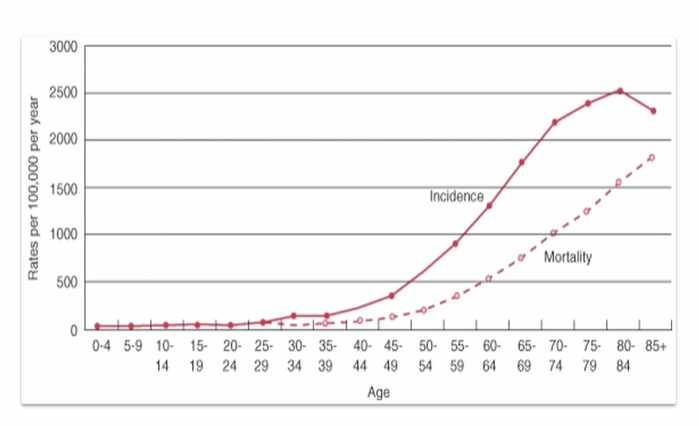
which ages are likely to have cancer
above 20 it starts to increase
this is as we have an ageing population
increases rapidly after 45
of course, mortality will also increase with age, as higher cases
risk factors - intrinsic vs non-intrinisc
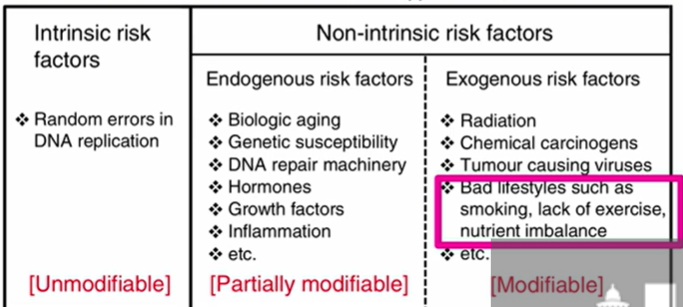
Examples of non-intrinsic exogenous risk factors
these are fully modifiable
breastfeeding: breast tissue gets fully differentiated which provides protection
the earlier you start your period, and the later you go into menopause, the higher the risk due to increased oestrogen (encourages cells to proliferate)
diet: low fruit and veg
e.g. avoid UV - also effects geography risk factor
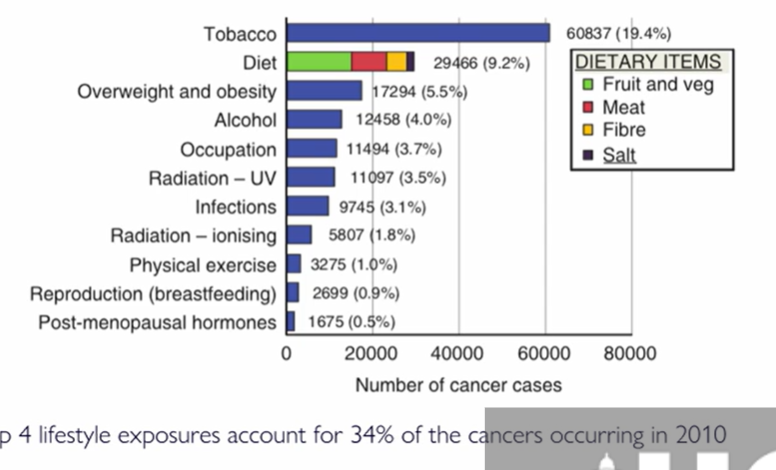
why is smoking such a big risk factor?
50% of smokers will die from smoking-related diseases
90% of lung cancers are from smoking
remember, we said it depends on time and quantity
length of time being the most important
the risk stops when you stop smoking, after 15yrs you are like a non-smoker in risk
25% second hand smokers also have 25% spouds/ 17% increased risk
what other chemicals can cause lung cancer
second most common cancer
asbestos
radon
chemicals
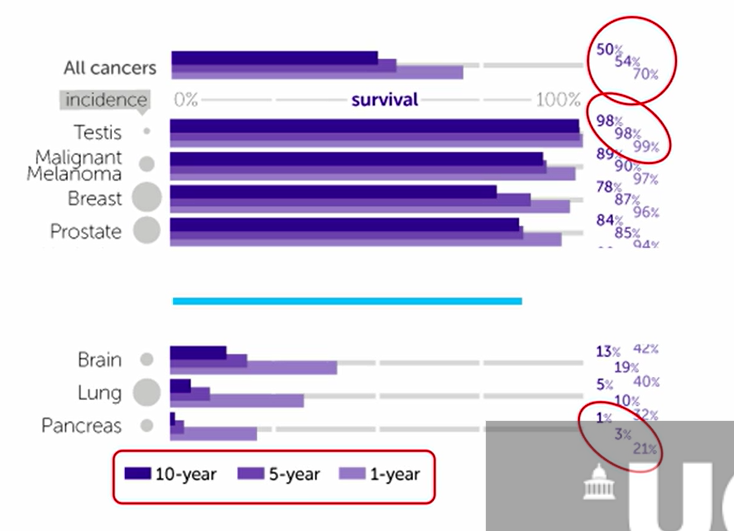
which cancers have the lowest prognosis?
brain 13%
lung 5%
pancreas 1%
after 10 yrs
this is because they are hard to notice as not on the skin, so you wont know until you have have severe symptoms
based on which stage you are on
Order of progression of a tumour - basic
hyperplasia - increase in the number of cells
dysplasia - abnormal growth - changes to size, shape, organisation
describe TNM staging system
T = tumour - how big is it? bigger it is, the longer its been growing
N= nodes - when cancer spreads, it can enter lymphatic vessels which are found all over the body, it can enter lymph nodes and become trapped there, and can grow there too
we check for signs that the cancer has spread there
M- metastasis - often goes from 90%-15% survival rate for breast cancer
What treatment would you use for local or metastasis?
local often radiation
metastasis often surgery
we want to know how we can target cancer cells without targeting human cells
what is a mutagen vs carcinogen?
leads to changes in DNA which increases risk of cancer
a carcinogen will lead to cancer development , can be affected by epigenetics