Psych 257 - Lecture 3
1/9
Earn XP
Description and Tags
An Integrative Approach to Psychopathology
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
Multidimensional integrative approach
Mental illness as system of different reciprocal influences
◦ Complex interactions
◦ Cannot consider any one in isolation
Treating one component of system will likely influence other components
Biological - genetics and neuroscience
Psychological - behaviour and cognitive
Social
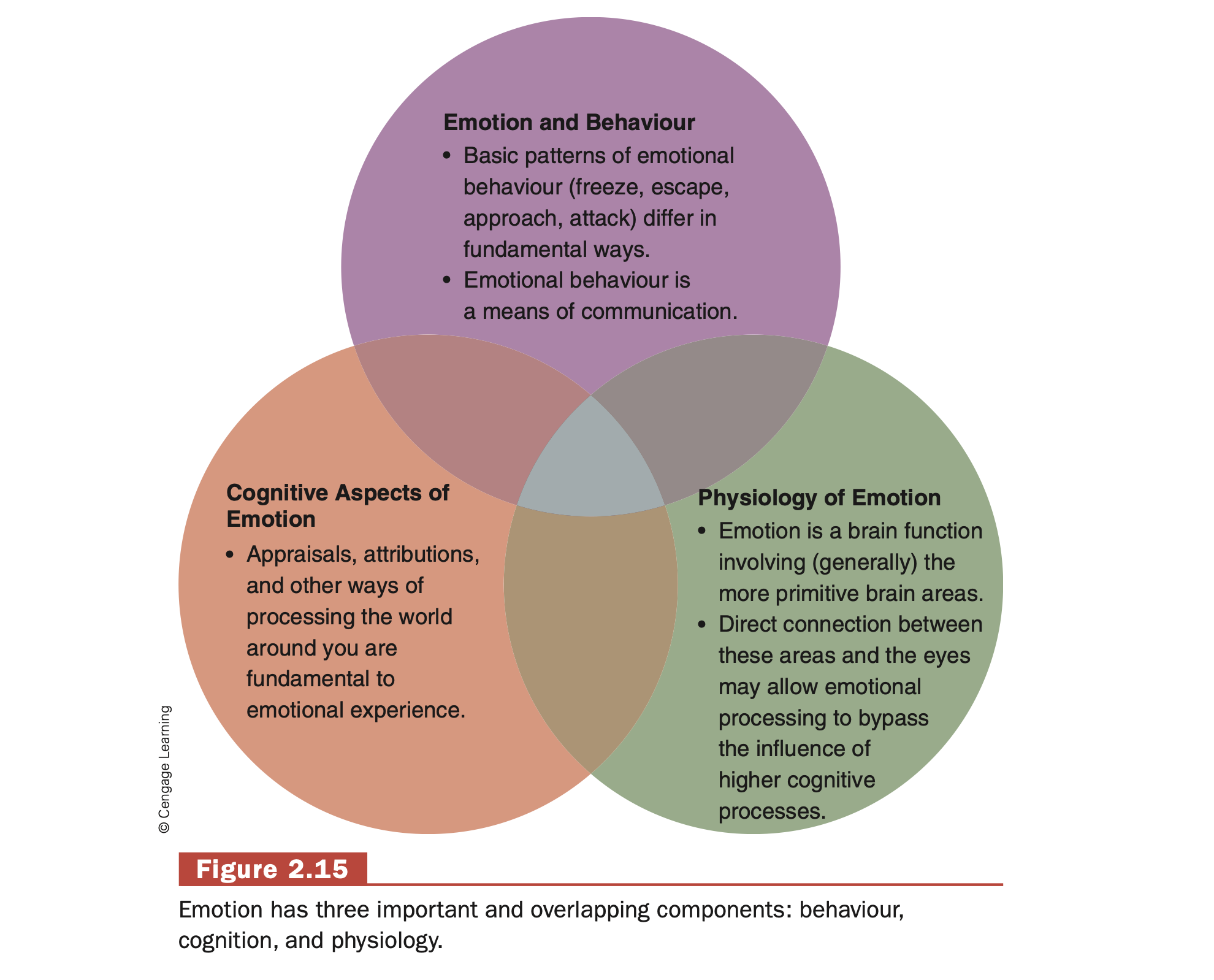
Genetics and Psychopathology
Genes contribute to almost all mental
disorders
◦ 1⁄2 the explanation
Disorder mostly polygenetic
many genes influence illness - mental and physical
Genes - Development of mental disorders
a) Diathesis-stress model
b) Reciprocal gene-environment
c) Epigenetics
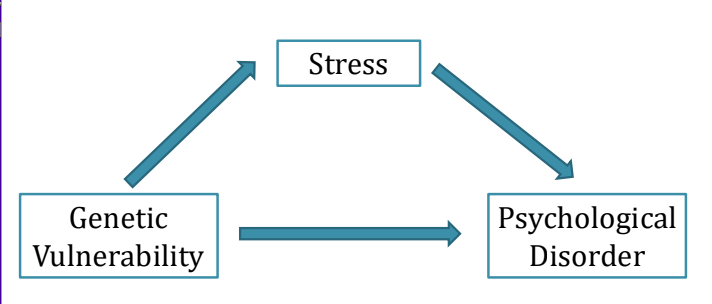
Diathesis-Stress Model
Environmental stress interacts with genetics to predict mental disorders
Genetic Vulnerability (Diathesis) X Stress (Predisposing) (Precipitating) → Psychological Disorder
Predisposing: The underlying vulnerability that increases a person’s risk of developing a disorder. Usually biological, genetic, or psychological.
Precipitating: The external events or triggers that activate the underlying vulnerability. Typically situational or environmental stressors.
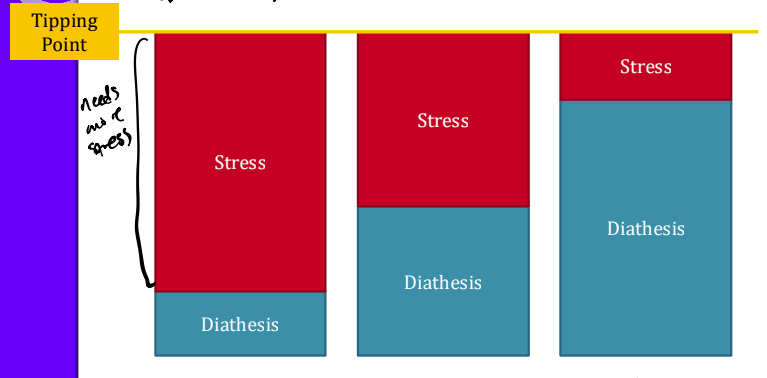
→ Everyone has a tipping point, some people have a lower/higher diathesis (cannot change this) - with enough stress, everyone would get the disorder
Diathesis Stress: Research Support
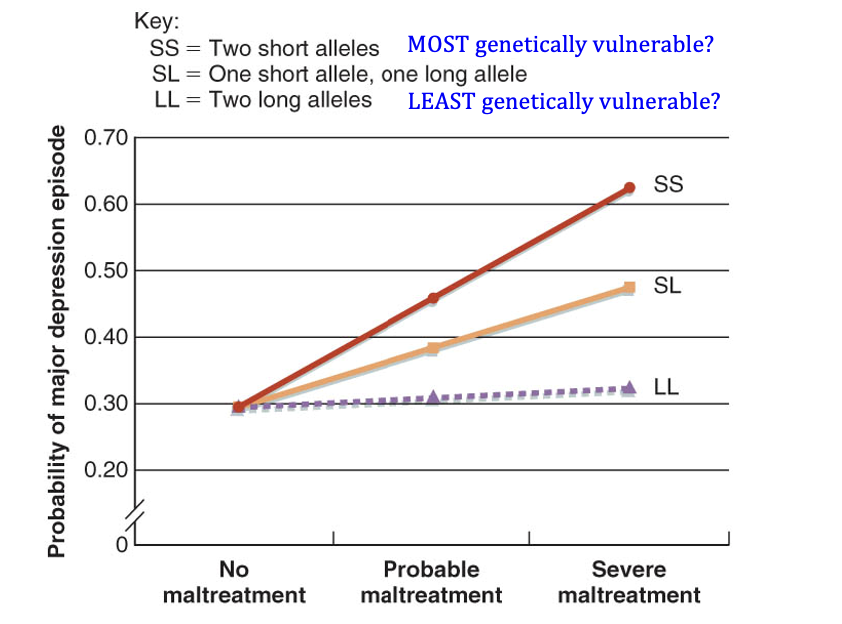
→ Oldest/ simplest model
Serotonin levels (alleles)
ss- even with little stressor could develop
ll- (most proyectes) - even with high maltreatment, might not develop it
Gene-Environment Correlation Model + Research
Environmental stress mediates the effect of genetics on psychopathology
genetic endowment may increase the probability that an individual will experience stressful life events
Divorce Probability: Researchers found that adoptees resembled their biological, not adoptive, siblings in their history of divorce, suggesting that genetic factors contributed to divorce - being hard to get along with, not choosing good partners
Depression and support for stress- generation hypothesis: Unable to replicate any polymorphism or gene effects on depression, or gene-by-environment interactions on depression. They did find, however, that stressful life events increased the risk of depression
Epigenetic
(Environment influence genes) Environment feeding into genome and passed down
Historical record of all your ancestors environment (parents, grandparents, ..)
Genes are turned on/off by cellular material outside of genome (“epi”) - methyl groups
Environmental factors influence epi-genome (instruction for DNA - tags on genome)
Passed down to next generation
Epigenetic - Research
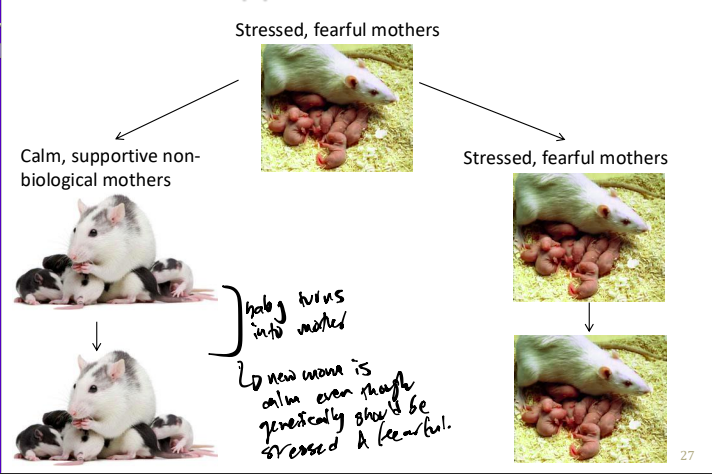
Baby turns into the adoptive mom behaviour
The researchers demonstrated that calm and supportive behaviour by the mothers could be passed down through generations of rats independent of genetic influences, because rats born to easily stressed mothers but reared by calm mothers grew up calmer and more supportive.
Early environment can modify the traits we pass along to our offspring, even if the genome does not change
env that are supportive/positive early on is the best way to not develop these disorders
The brain and psychosocial functioning
All disorders → the main focus and target is usually biological
Brain structures and neurotransmitters influence psychosocial functioning
Psychological treatments and factors can modify brain (CBT)
◦ NEUROPLASTICITY - biological and also experiences
→ Experience and therapy can change brain structure and function
Major neurotransmitters relevant to psychopathology
Norepinephrine (also known as noradrenaline), serotonin, dopamine, gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA - inhibitory), glutamate (the most common neurotransmitter - excitatory).
Initially:
reduced levels of GABA were initially thought to be associated with excessive anxiety,
linked increases in dopamine activity to schizophrenia.
found correlations between depression and high levels of norepinephrine and low levels of serotonin
However, more recent research, described later in this chapter, indicates that these early interpretations were much too simplistic
The stress hormone cortisol. This system is called the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical axis, or HPA axis; it has been implicated in several psychological disorders. There is good evidence showing that a dysregulation of the HPA axis and other endocrine systems are linked to depression