BIS 2C Midterm 1
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/128
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 10:10 PM on 3/23/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
129 Terms
1
New cards
tree of life
refers to the concept that all living organisms are related to one another through a shared ancestry
2
New cards
phylogeny
a unifying principal: all organisms are linked to one another through their shared evolutionary history
3
New cards
tree
a simplified model of the genealogy of life
4
New cards
taxon
any organism, or species, or group of species that we designate or name
5
New cards
taxa
what is the plural of taxon
6
New cards
speciation
the process whereby one species gives rise to two descendent species
7
New cards
speciation events
Phylogenies are the result of multiple what?
8
New cards
internal node
1
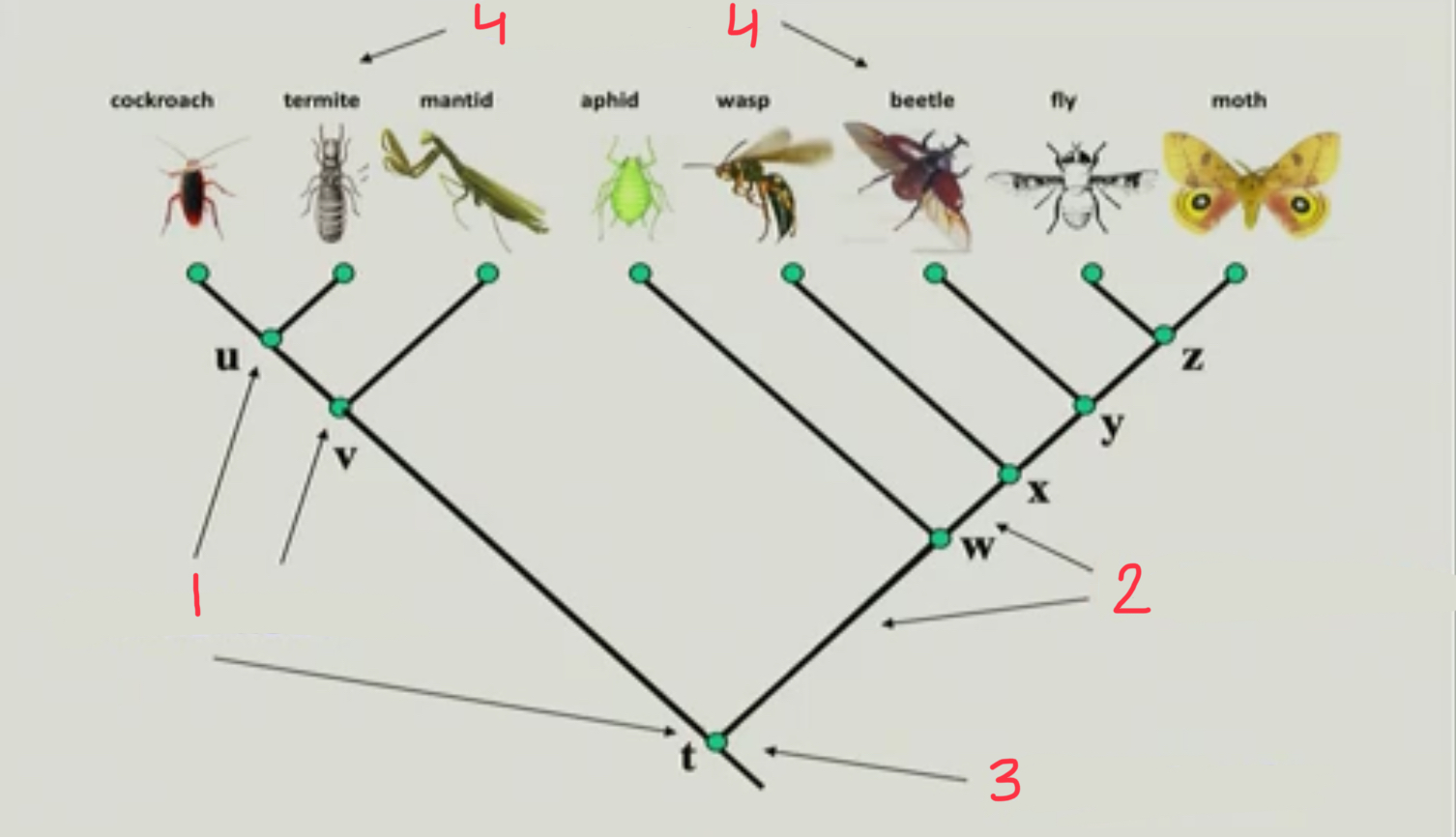
9
New cards
root node
3
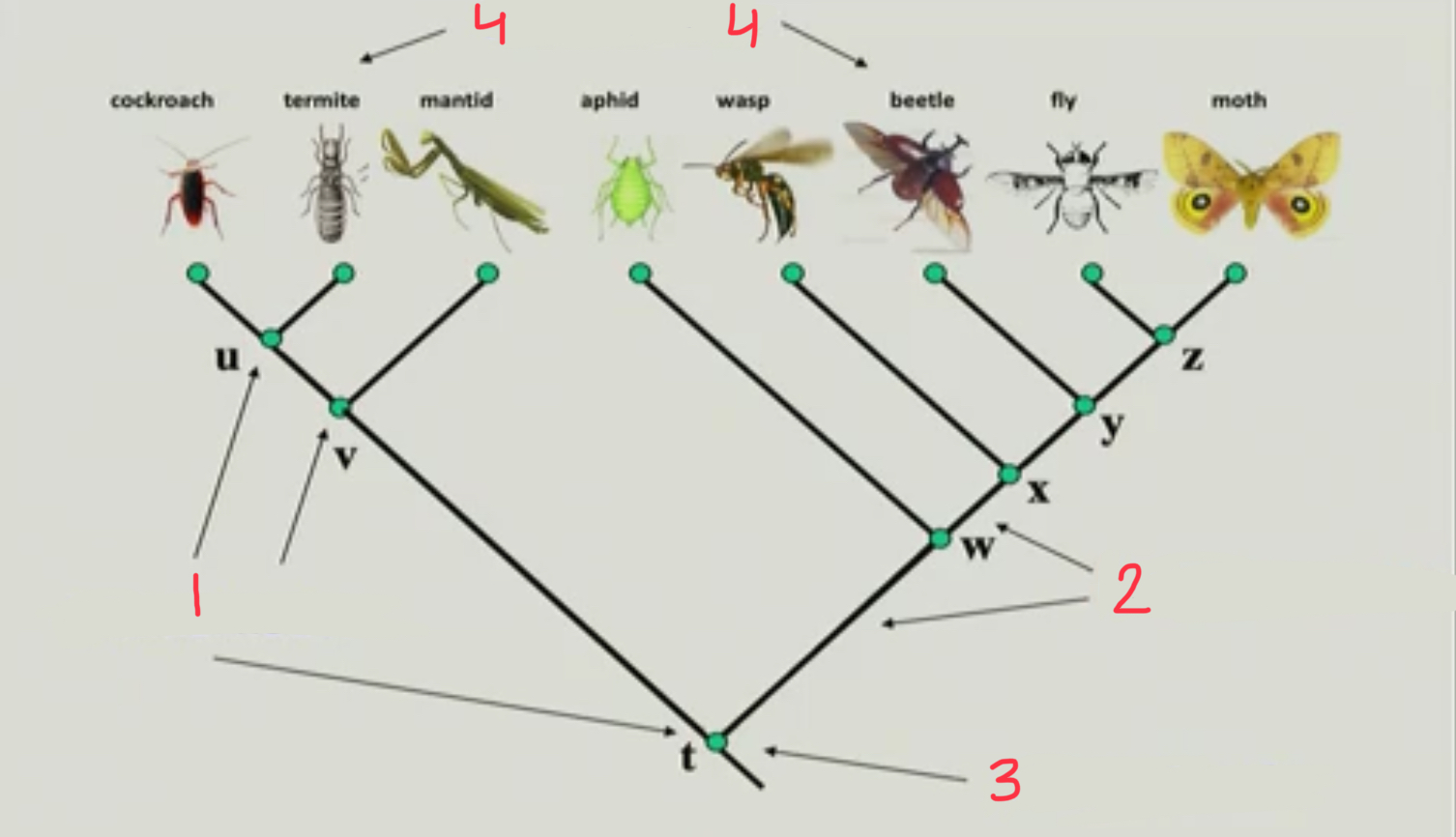
10
New cards
internal branches
2
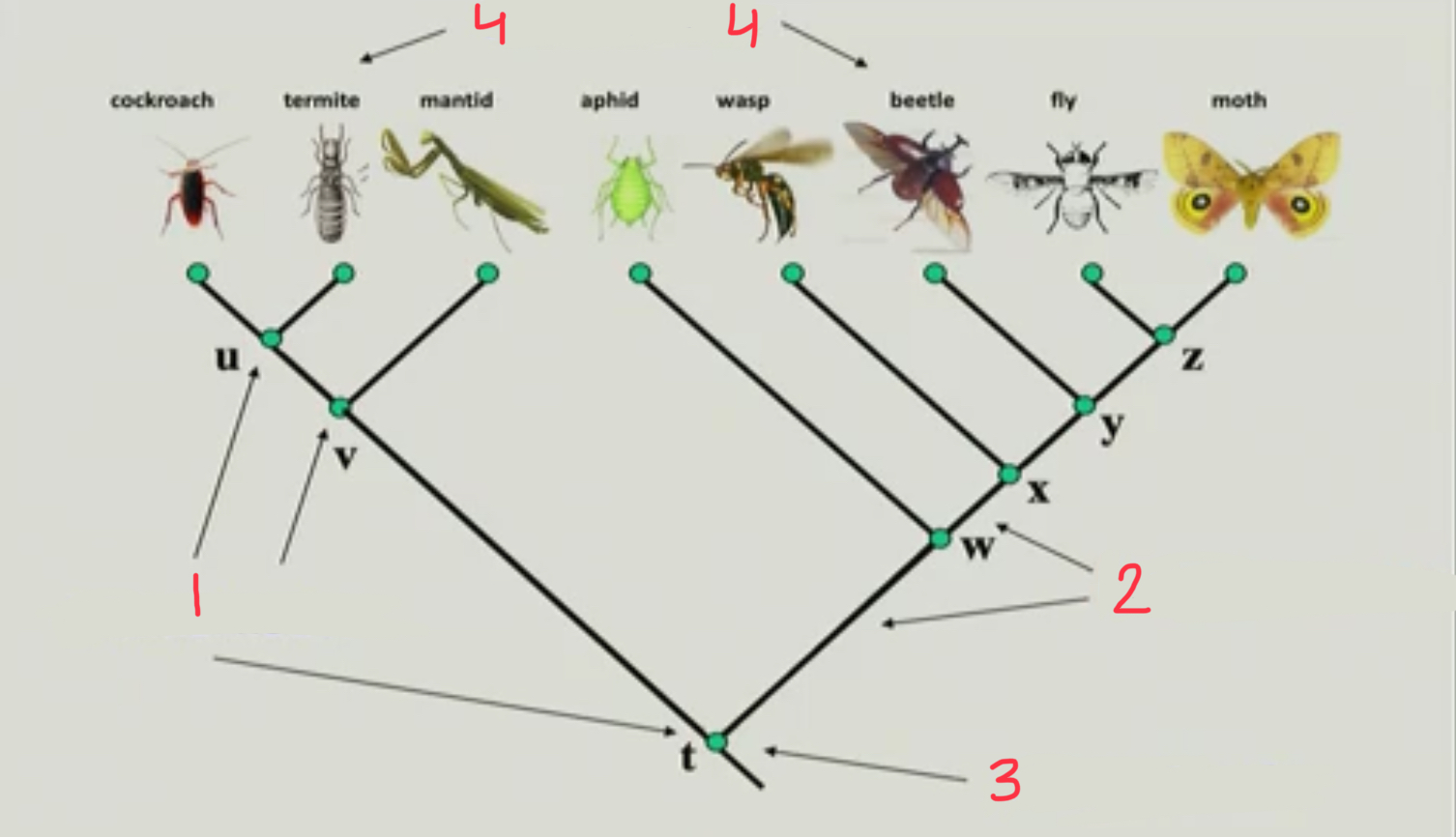
11
New cards
Terminal node
4
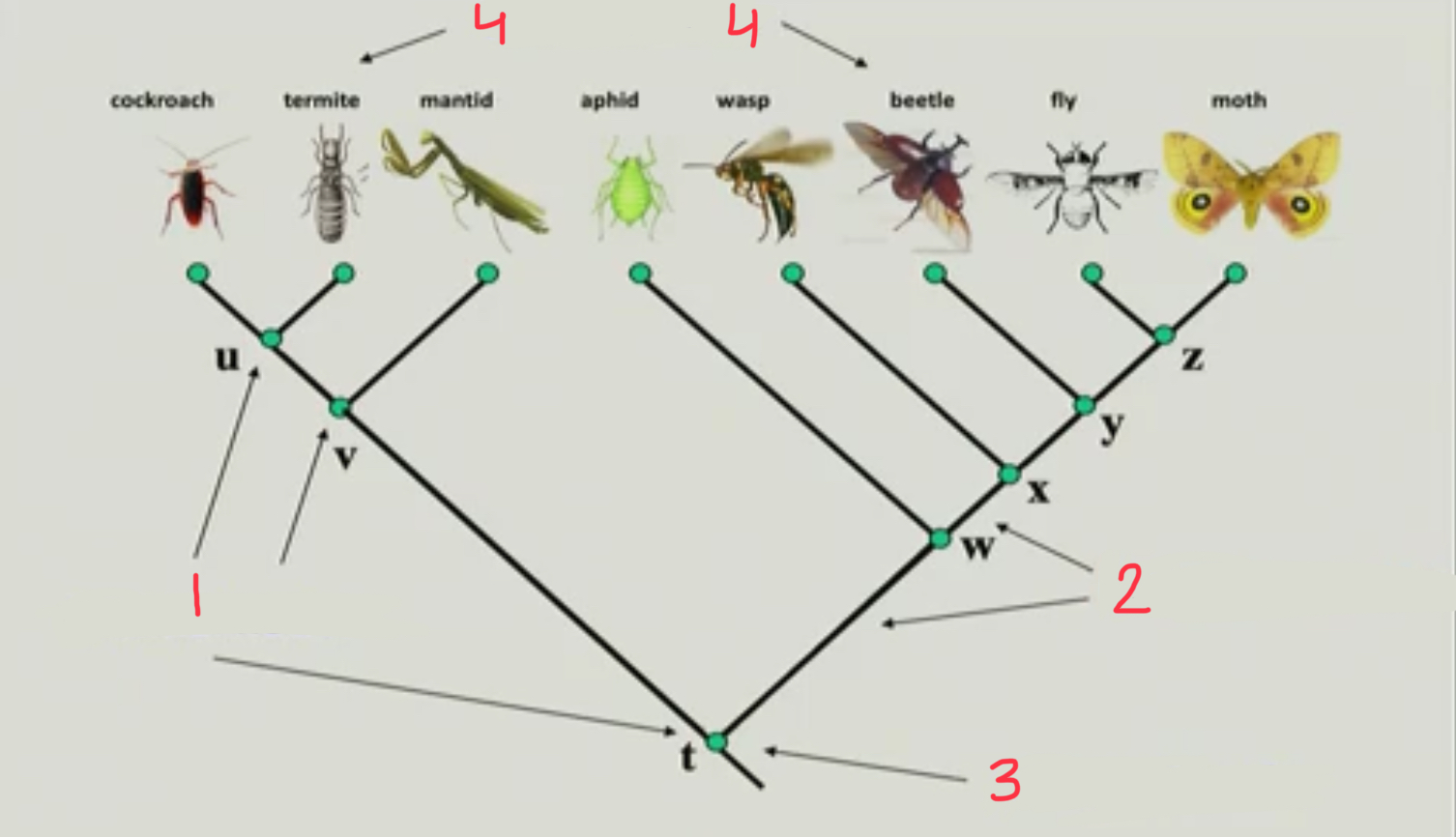
12
New cards
bifurcating trees
these are trees in which each internal node gives rise to two descendent branches, the photo is an example of one
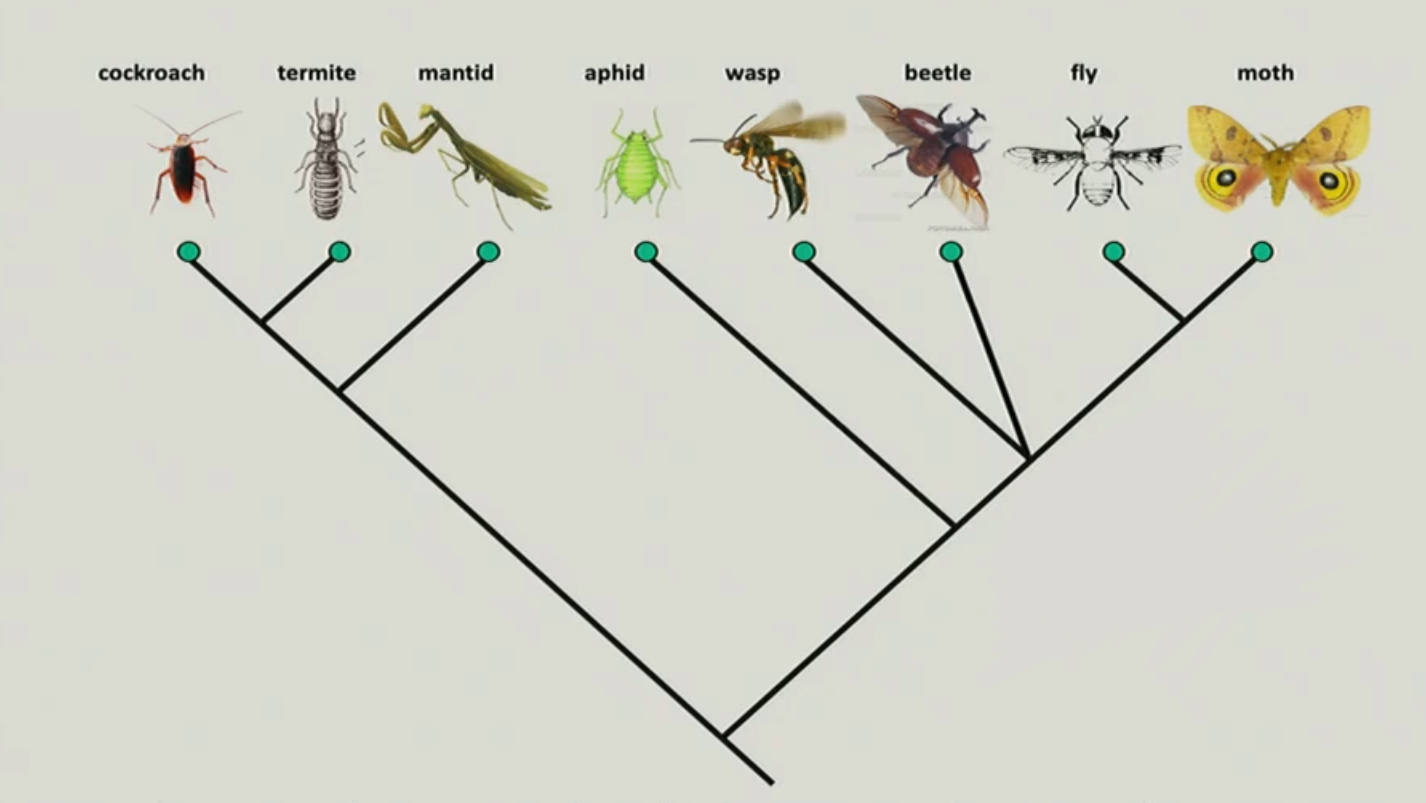
13
New cards
polytomy
Trees with nodes that have three or more descendent branches, they usually reflect uncertainty about phylogenetic relationships
14
New cards
monophyletic group
a group of organisms consisting of the MCRA and all its descendants
15
New cards
clade
a monophyletic group
16
New cards
polyphyletic group
a group of organisms that excludes the MCRA
17
New cards
paraphyletic group
a group of organisms consisting of their MCRA but excluding some of it’s descendants
18
New cards
Synapomorphies
Monophyletic groups (clades) can often be recognized by special features or characteristics called _______________, which are unique to (or especially characteristic of) that group. They arrive from the MCRA of that clade.
19
New cards
homologous traits
those that are inherited from a common ancestor, an example would be hair, milk and mammary glands in mammals
20
New cards
classification
the naming of taxa and their placement in a hierarchical arrangement
21
New cards
genus and family
when naming a species, the names of the what are included?
22
New cards
sister groups
two clades or species that are each other’s closest relatives (the two descendants of a single node)
23
New cards
in-group
the group of taxa under study
24
New cards
outgrip
one or more taxa (usually closely related to the in-group) that are not members of the in-group
25
New cards
cladogram
only the relative branching order is depicted, no meaning to branch lengths
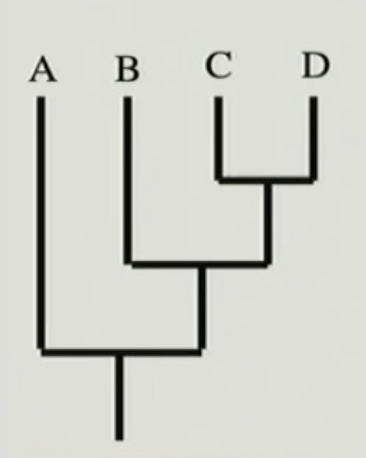
26
New cards
phylogram
branch length is proportional to the amount of character change
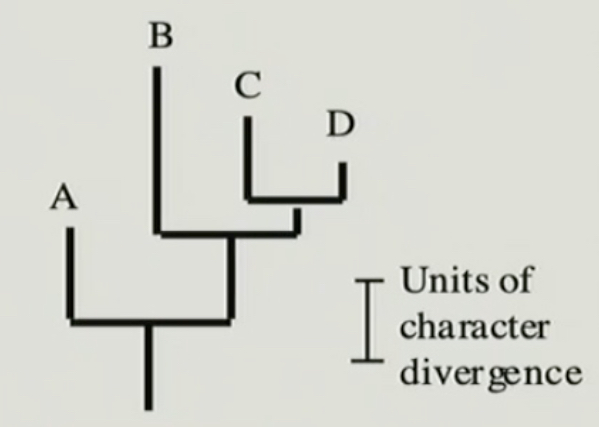
27
New cards
chronogram
branch length is proportional to time
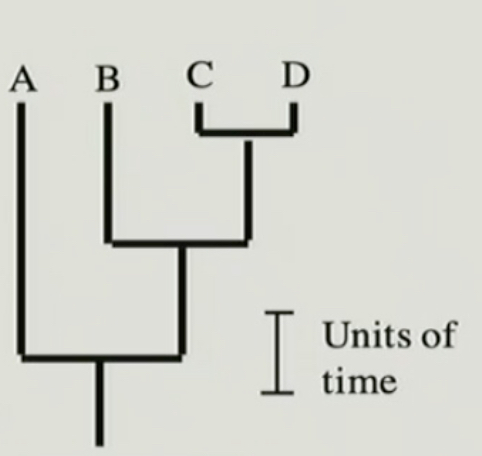
28
New cards
parsimony
if we apply this principal, then we search for a tree that requires the least amount of change in character states
29
New cards
outgroup method
in this method you use one or more outgroups to estimate the ancestral character states (the character states in the MCRA of the group)
30
New cards
unrooted trees
trees that have been removed and relationships among taxa are more ambiguous, shows splitting events but tells us nothing about the sequence
31
New cards
parsimony uninformative
invariant characters (TTTT) and one taxon different, but other three the same (ATTT)
32
New cards
parsimony informative
in the case of the four taxa, only those characters where two taxa have one state and two have a second state are this, like (ATAT)
33
New cards
phylogenetic relatedness
the --------------- ---------------- of two taxa is a function of how recently they last shared a common ancestor
34
New cards
float freely
unrooted trees can ------------------- ----------------- and the branches of the trees can rotate around internal nodes without changing the meaning
35
New cards
internal branches
unrooted trees are the same if their -------------- -------------- separate the same subsets (bipartitions ) of taxa
36
New cards
maximum likelihood
an example of a model-based approach to estimating phylogenies
37
New cards
transitions
changes from one purine to another purine (A
38
New cards
transversions
changes from one purine to a pyrimidine or vice-versa (A
39
New cards
transitions
what is more likely to occur, transitions or transversions?
40
New cards
self-incompatible
can not self fertilize
41
New cards
self-compatible
have the ability to self fertilize
42
New cards
mutualism
each organism benefits, examples are corals and symbiotic algae
43
New cards
parasitism
one organism benefits to the detriment of the other, examples are birds and lice or mammals and tapeworms
44
New cards
strict coevolution
if there has been ---------- -------------, then the phylogeny of one set of organisms should match that of the other
45
New cards
biogeography
the study of the geographical distribution of organisms
46
New cards
dispersal and geographical events
historical biogeographers are particularly interested in the roles of ------------- and --------------- ---------
47
New cards
molecular clock
the greater the genetic difference between taxa the older the MCRA also defined as if rates of DNA coveolition are roughly constant then we can estimate the divergence time between two taxa on the basis of their degree of genetic divergence
48
New cards
2 million years
two sister species are 6% divergent in their DNA. The DNA diverges 1.5% per million year. How long ago did these two species split?
49
New cards
calibrated
the relationship between genetic difference and time since divergence can be --------------- with known times from the fossil record or from geographical events
50
New cards
medicine and conservations
two uses for phylogenies are …
51
New cards
bacteria, archaea and eukarya
what are the three domains of life?
52
New cards
eukarya
what domain of the life has the smallest branch on the tree on life (there is the least of them)?
53
New cards
The Great Chain of Being
what was a common idea before 1500’s, was created by Aristotle
54
New cards
Ernest Haeckel
who put together the three kingdom tree, 1866
55
New cards
Robert Whittaker
who put together the five kingdom tree, 1969
56
New cards
microsporidium
characteristics of this organism include: unicellular parasite, infects arthropods and vertebrates, has no mitochondria, but has a nucleus and makes spores to allow for dormancy outside the host, they are fungi
57
New cards
mitochondria
there are many Eukaryotes that lack a _____________ or have a highly reduced one
58
New cards
universal homologies
characteristic found in all animals
59
New cards
last universal common ancestor
LUCA stands for what?
60
New cards
ribosomal RNA
everyone has it, contains both highly conserved and variable regions, not laterally transferred between organisms, large and growing database
61
New cards
Carl Woese
made the very first tree based on molecular data, in 1987
62
New cards
eocyte tree
a tree that has two domains, eukarya came from Archaea
63
New cards
paraphyletic
in the oocyte tree the prokaryotic bacteria are considered to be
64
New cards
prokaryotes
a group that combines bacteria and archaea, they are paraphyletic and they have a nucleoid, and they have a petidoglycan layer, they’re unicellular, have no cytoskeleton, lack a nucleus and have no membrane enclosed organelles, DNA molecules often circular and they may only have one chromosome
65
New cards
nucleoid
blob of DNA that is not surrounded by a membrane
66
New cards
peptidoglycan layer
a mesh like structure that prevents a cell from exploding, this region is often targeted by antibiotics
67
New cards
false
true or false, you can get infected by an archaea
68
New cards
antibiotics
what was discovered by Alexander Fleming in 1928?
69
New cards
antibiotic resistance
what started occurring pretty soon after the development of antibiotics?
70
New cards
antibiotic crisis
we are facing an --------------- --------, as vert fews antibiotics are being developed and the medicines that get through don’t last
71
New cards
binary fission
the primary form of cell division and reproduction in prokaryotes is known as what?
72
New cards
binary fission
asexual reproduction, gives riser to clones, rapid can divide in 20-50 minus, produces two identical daughter cells and there is a strong environmental influence
73
New cards
genetic variation
mutations and selection, plasmids and lateral gene transfer are three ways to introduce what?
74
New cards
plasmid
extra chromosomal DNA, small circular molecules, automatically replace in the host cell (via the organ of replication), are passed during bacterial multiplication
75
New cards
conjugation
one cell is connected to another cell
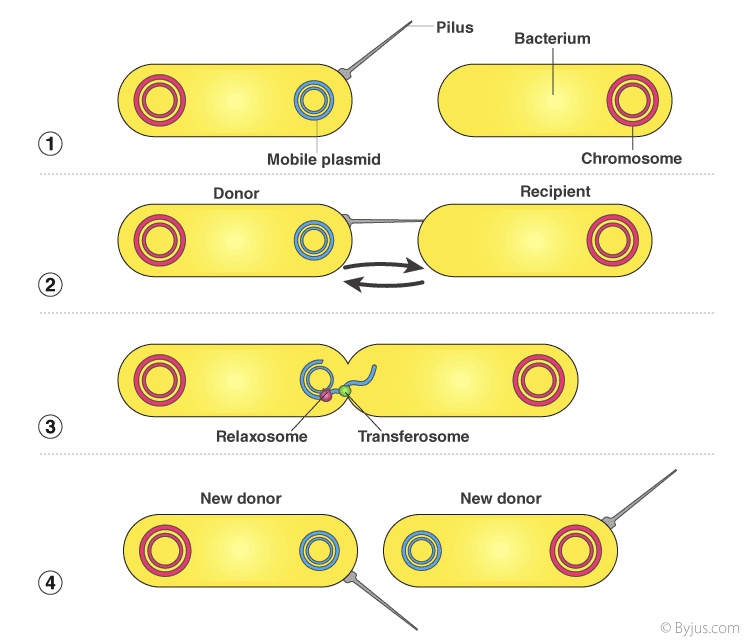
76
New cards
transformation
they are able to uptake DNA from the environment, only portions of genome transferred
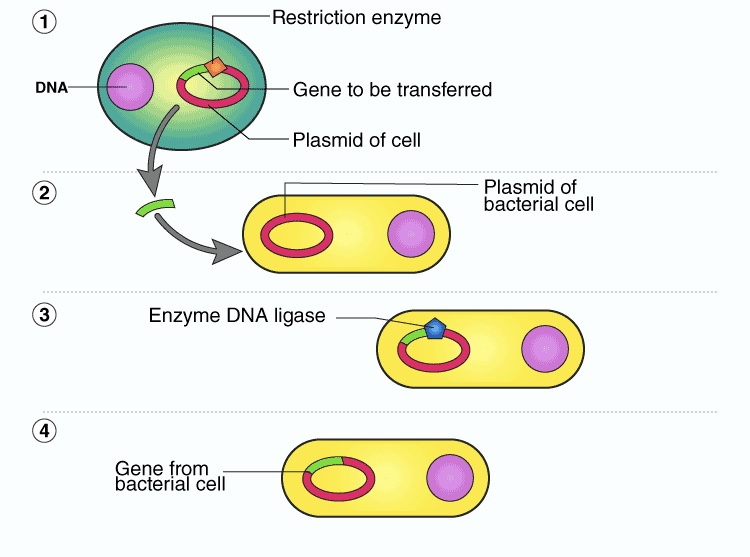
77
New cards
transduction
virus infects cell and when in the cell, it captures DNA from the cell and then injects that DNA into other cells, which causes resistance
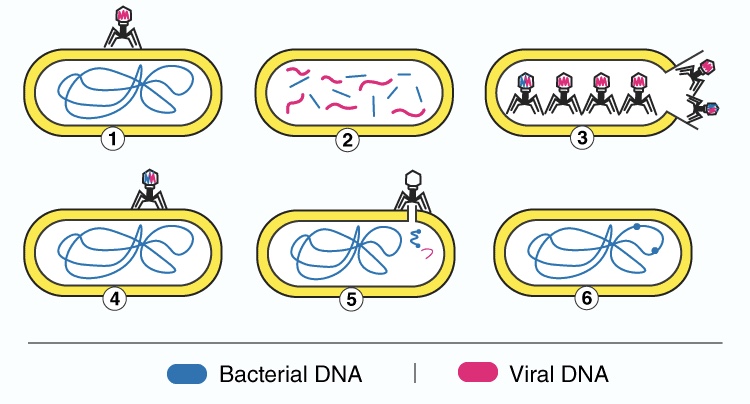
78
New cards
gene transfer
what complicates phylogenies?
79
New cards
morphology
\------------- does not predict physiology, phylogeny or ecology
80
New cards
gram positive
have a thick peptidoglycan layer
81
New cards
gram negative
have a thin peptidoglycan layer
82
New cards
ether
what is stronger an ether linkage or an ester linkage in extreme environments ?
83
New cards
anaerobes
do not and may even be killed by oxygen
84
New cards
aerotolerant anaerobes
can tolerate the presence of oxygen, even though they cannot use it
85
New cards
facultative
this type of organisms can live with or without oxygen
86
New cards
aerobes
require oxygen to live
87
New cards
microaerophiles
aerobes that can use oxygen only when it is present at levels reduced from that of air
88
New cards
D
what test tube contains microaerophiles?
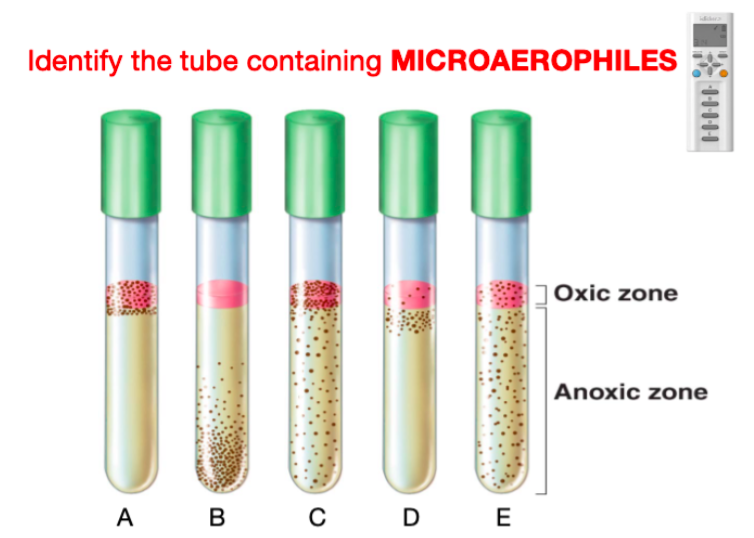
89
New cards
photo
energy source = light
90
New cards
auto
carbon source = carbon dioxide
91
New cards
chemo
energy source = inorganic substance or organic compounds
92
New cards
hetero
carbon source = organic compounds
93
New cards
microbes
what started photosynthesis, control elemental cycles, decompose, help with agriculture and are everywhere
94
New cards
extremophiles
group of organisms that can live everywhere
95
New cards
temperature
thermophile and psychrophile
96
New cards
salt
halophile
97
New cards
radiation
radiophile
98
New cards
pressure
barophile
99
New cards
desiccation
xerophile
100
New cards
pH
alkaphile and acidophile