tissues
1/133
Earn XP
Description and Tags
human anatomy and physiology lecture 3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
134 Terms
four primary tissue types
epithelial tissue
muscle tissue
connective tissue
nervous tissue
function of muscle tissue
contraction
arrangement of cells in muscle tissue
arranged in sheets, so each cell is oriented in the same way
three types of muscle tissue
skeletal muscle
cardiac muscle
smooth muscle
skeletal muscle
muscle attached to bones
result of contraction of skeletal muscle
contraction results in movement of bones
is skeletal muscle under voluntary or involuntary control?
voluntary and involuntary
endurance of skeletal muscle
low endurance
cardiac muscle
constitutes the heart
result of contraction of cardiac muscle
pumps blood
is cardiac muscle under voluntary or involuntary control?
involuntary
endurance of cardiac muscle
high endurance
smooth muscle
constitutes the walls of tracts and blood vessels
is smooth muscle under voluntary or involuntary control?
involuntary
endurance of smooth muscle
medium endurance
neuromuscular junctions
where axon terminals interact with muscle fibers
muscle fibers
cells in skeletal muscle
intercalated discs
connections between cardiomyocytes for anchoring and communication, containing desmosomes and gap junctions
cardiomyocytes
cells in cardiac muscle
pacemaker cells
cells in heart to establish heart rate
role of desmosomes
hold two cells together
gap junction
pore that allows communication between two cells
peristalsis
wave of smooth muscle contraction to move bolus of food along gastrointestinal tract
inner circular muscles
constrict and dilate the diameter of the gastrointestinal tract
outer longitudinal muscles
lengthen and shorten the gastrointestinal tract
characteristics of skeletal muscle tissue
perpendicular striations
nuclei pushed to the edges of the cells
large size
characteristics of cardiac muscle tissue
striations
central nuclei
branching
intercalated discs connecting adjacent cells
characteristics of smooth muscle tissue
spindle shape
lack of striations
single nucleus
small size
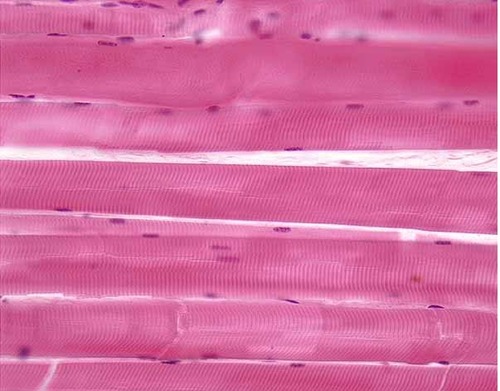
identify the type of muscle tissue
skeletal muscle
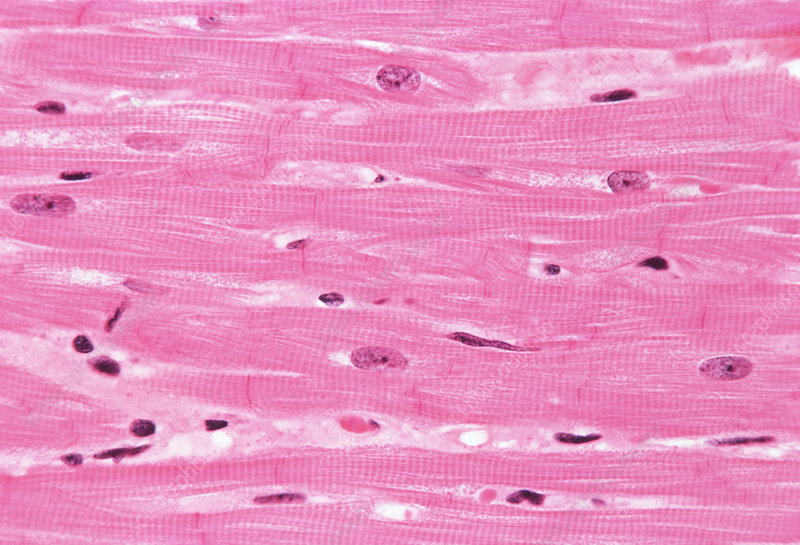
identify the type of muscle tissue
cardiac muscle
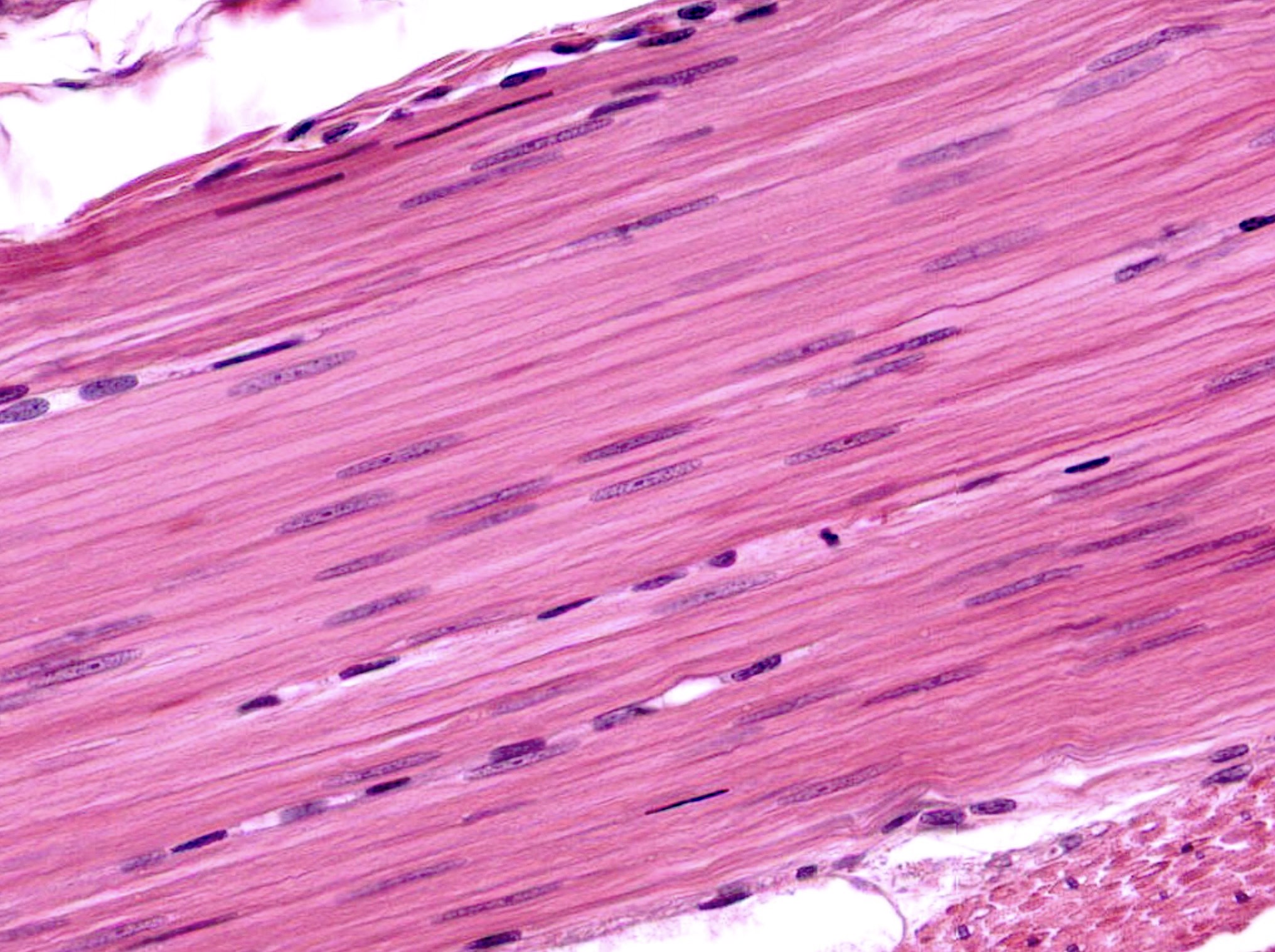
identify the type of muscle tissue
smooth muscle
four major functions of epithelial tissue
protect against abrasion and dehydration
often contain receptors that transmit sensation to the nervous system
controls the entry and exit of substances into and out of the body
epithelial cells actively secrete compounds into the surface of the epithelium
endocrine glands
secrete hormones into the bloodstream
exocrine glands
release substances onto the epithelium (out of the body)
epithelium
lines the inner surface of tracts
tract
tubular structure that is open to the outside environment
endothelium
lines the inner surface of blood vessels
hemidesmosomes
type of desmosomes connecting the deepest layer of epithelial cells to the basement membrane
avascular
no blood vessels are present
shape of squamous cells
short and flat
shape of cuboidal cells
similar length and width
shape of columnar cells
cells are taller than they are wide
simple cell layers
single layer of cells
stratified cell layers
more than one layer of cells
pseudostratified cell layers
single layer of cells of different heights
structure and functions of simple squamous epithelium
diffusion and filtration, reducing friction
structure and functions of simple cuboidal epithelium
secretion and absorption (glands), may have microvilli
structure and functions of simple columnar epithelium
secretion and absorption (along the gastrointestinal tract), may have microvilli or cilia
microvilli
brush-like border of a cell to increase surface area
structure and function of pseudostratified columnar epithelium
secreting and moving fluids (like mucus), limited capacity for protection against abrasion, infection, and chemicals, so cells must be regenerated more often, have cilia
ciliated simple columnar cells
moves the mucus spread on the upper airway upwards to the pharynx to be disposed of (swallowed or expectorated)
simple columnar goblet cells
secrete mucus in which dust particles and microorganisms present in the lumen of the respiratory tract get caught
function of stratified squamous epithelium
physical protection from abrasion, infection, and chemical attack, can be keratinized for extra protection
types of exocrine glands
unicellular and multicellular
unicellular exocrine glands
consist of a single cell
multicellular exocrine glands
have a secretory portion that secretes and a duct portion that transports
four types of connective tissue
bones and cartilage
tendons and ligaments
blood
fat
functions of bones and cartilage
support softer tissues and provide a solid framework
function of ligaments
bind two bones together
function of tendons
bind muscles to bones
functions of blood
carries and distributes many substances including hormones and nutrients
function of red blood cells
carry gases
function of white blood cells
defend against microorganisms
three types of protein fibers for the extracellular matrix
collagen fibers
elastin
reticular fibers
collagen fibers
most common fibers in the extracellular matrix, are strong and flexible
elastin
provides elasticity
reticular fibers
thinner, less common than collagen, branch and interweave to create an organ’s shape
ground substance of the extracellular matrix
largely composed of proteoglycans, occurs in various states of fluidity, can slow the movement of pathogens
three categories of connective tissue
supporting connective tissue
connective tissue proper
fluid connective tissue
supporting connective tissue
least fluid, includes bones and cartilage
connective tissue proper
loose and dense subtypes based on protein:cell ratio, regular and irregular subtypes based on arrangement of protein, most abundant
fluid connective tissue
most fluid, includes blood and lymph
features and functions of supporting connective tissue
provide support, leverage, and protection to underlying tissues and organs
features and functions of connective tissue proper
highly vascularized, provide support, cushioning, and protection, can be a storage reserve for energy, contain sensory nerves for pain, pressure, and temperature
features and functions of fluid connective tissue
involved in material transport, capable of mounting an immune reaction to defend against microbes
vascularization
presence of blood vessels
innervation
presence of nerves
connective tissue with high vascularization and innervation
loose connective tissue
dense irregular connective tissue
bone
fat
connective tissue with low vascularization and innervation
tendons and ligaments
cartilage
three types of cartilage
hyaline
elastic
fibrocartilage
bone ground substance
mineralized with calcium phosphate and with protein fibers, helps resist compression and tension
cartilage cell type
chondrocytes
bone cell types
osteocytes, osteoblasts, osteoclasts
osteocytes
maintain bone
osteoblasts
produce new bone
osteoclasts
resorb bone
chondro-
cartilage
osteo-
bone
blood cell types
red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets
fibrinogen
primary protein fiber in blood
ground substance of blood
includes the main blood proteins, albumins and globulins
plasma
contains and transports hormones, antibodies, ions, plasma proteins, and urea
platelets
prevent blood loss at injury sites by adhering to the site of injury to temporarily plug the hole
leucocytes
immunosurveillance, inflammation and defense, prevention of infection from microorganisms, production of anitbodies
white blood cells
leucocytes
erythrocytes
delivers oxygen and transports a portion of metabolic wastes
red blood cells
erythrocytes
loose connective tissue proper
more cells in its tissues compared to dense connective tissue proper
dense connective tissue proper
less cells in its tissues compared to loose connective tissue proper
irregular dense connective tissue proper
protein fibers are organized randomly to support mechanical stress from many directions