Pancreas Neoplasms
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Congenital Anomalies
-ectopic pancreatic tissue
-pancreatic divisum
-annular pancreas
-cystic fibrosis
Ectopic Pancreatic Tissue
-common pancreatic anomaly
-composed of acinar and ductal tissue
-tissues are small (0.5 - 2 cm)
-found in various places in GI tract
-susceptible to any disease that the pancreas is susceptible to esp tumor or acute pancreatits
-no vascular or structural connection to body of pancreas
Ectopic Pancreatic Tissue Locations
-stomach
-duodenum
-small and large bowel
Ectopic Pancreatic Tissue Sonographic Appearance
-polypoid tissue mass w/ central dimple
-difficult to detect sonographically
Pancreas Divisum
-most common congenital variant
-failure of dorsal and ventral ducts to fuse
-increased incidence of pancreatitis
Annular Pancreas
-ring like
-rare anomaly caused by ventral portion of pancreas not migrating normally
-pancreatic head surrounds the 2nd portion of the duodenum
Annular Pancreas Etiology
-more common in males
-may be partial or complete
-subject to same pancreatic pathologies
-associated w/ duodenal atrasia (partial or complete)
Cystic Fibrosis
-autosomal recessive exocrine gland disorder
-involves an increase in secretion of mucous by the exocrine glands
-coagulation of secretions in smaller pancreatic ducts that become hardened and obstructive
-distended areas may degenerate and undergo cystic replacement
Cystic Fibrosis Incidence
-1 in 2000
-5% are genetic carriers
-almost exclusively in caucasians
-associated w/ abdominal problems (pancreas, liver, biliar system + increases w/ age)
Cystic Fibrosis S/S
-abdominal pain
-bloating and flatulence
-failure to thrive (don't want to eat)
-glucose intolerance and diabetes mellitus
Cystic Fibrosis Sonographic Appearance
-generally hyperechoic due to microcystic changes and increased fatty and fibrotic infiltration
-inhomogenous
-cannot compare echo texture of liver to pancreas (either organ may display abnormal echo texture)
Cystic Fibrosis
Biliary/Liver Sonographic Appearance
-biliary stasis
-focal biliary cirrhosis/fibrosis is common as pt ages
-portal HTN
-cannot compare echo texture of liver to pancreas (either organ may display abnml echo texture)
Liver/Biliary Tract
GI Sonographic Appearance
-meconium ileus in neonates
-chronic obstructions (inflammatory bowel processes)
-thickened irregular folds = donut sign
-redundant GI tract and unavailable scan window thru LT lobe of liver
-non visualized GB or GB filled w/ thick echogenic bile (sludge)
True Cysts
-usually due to anomalous development of ducts
-generally asymptomatic unless large
Congenital True Cyst
-may be unilocular or multilocular
-extremely rare
-multiple cysts associated w/ polycystic renal disease
-fluid filled sac w/ epithelial lining
Acquired True Cysts
-retention cyst (secondary to dilatation of pancreatic duct)
-parasitic cyst (echinococcal)
-have an epithelial lining
True Cyst Sonographic Appearance
-round to oval
-smooth
-thin, well defined walls
-anechoic
-w/ posterior enhancement
-may be multilocular
-be sure to differentiate from fluid (surrounding GI structures)
True Cysts Treatment
-laparotomy and draining
-drained true cysts often are replaced by a fistula
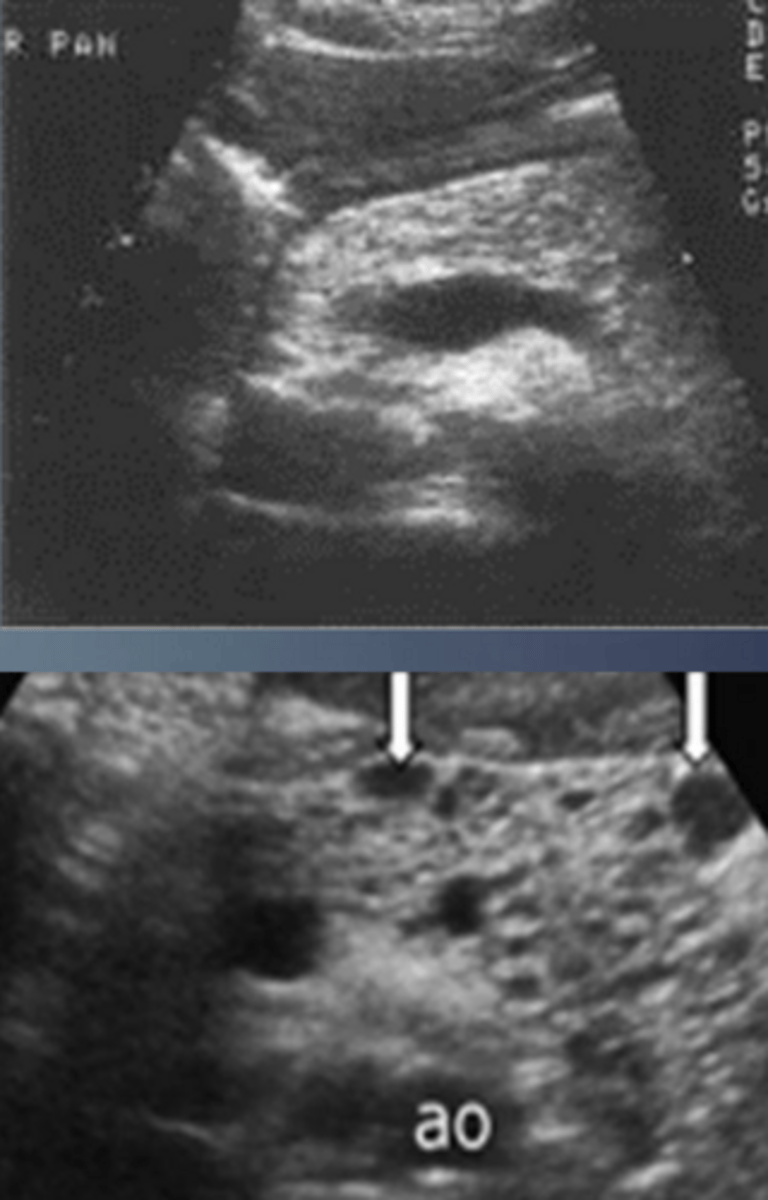
True Cyst
Islet Cell Tumor/Adenoma
-endocrine tumors
-uncommon
-small and difficult to localize
-found mostly in tail of the gland
-may represent either benign adenoma or malignant tumor
-classified as functioning and non functioning (most are functional 85% and benign; non functional are generally malignant)
Islet Cell Tumor/Adenoma Associated W/
-von hippel/lindau disease
-MEN syndrome
Common Functional Tumors
-insulinoma
-gastrinoma
Von Hippel Lindau Disease
-inherited disorder characterized by the formation of tumor and fluid filled sacs (cyst) in kidney, pancreas, and genital tract
-20-50% of pts (pancreatic syts + serous cystadenomas)
-15% of pts (neuroendocrine tumors)
MEN Syndrome
-multiple endocrine neoplasia
-inherited condition
-types 1 and 2
-associated tumors
MEN Syndrmoe Associated Tumors
-insulinoma
-gastrinoma
-medullary thyroid carcinoma
-pheochromocytoma
-parathyroid gland hyperplasia
-pituitary tumors
Insulinoma
-tumor of the insulin secreting cells (islets of langerhans-beta cell tumors)
-most common islet cell tumor
-usually benign
-associated w/ hyperinsulinism or hypoglycemia (insulin shock, dizziness, n/v, psychic disturbances)
Gastrinoma
-2nd most common tumor
-found in pancreas and duodenum
-causes hypergastric secretions
-associated w/ peptic ulcer disease (PUD)
-high malignant potential
Islet Cell Tumor (Adenoma) Sonographic Appearance
-generally homogenous and solid
-frequently hypoechoic
-larger tumors may become moderatly echogenic
-calcifications and fluid areas seen in larger lesions
-solid masses are generally functional while those w/ cystic areas of necrosis are generally non functional
-small 1-2cm tumors difficult to identify
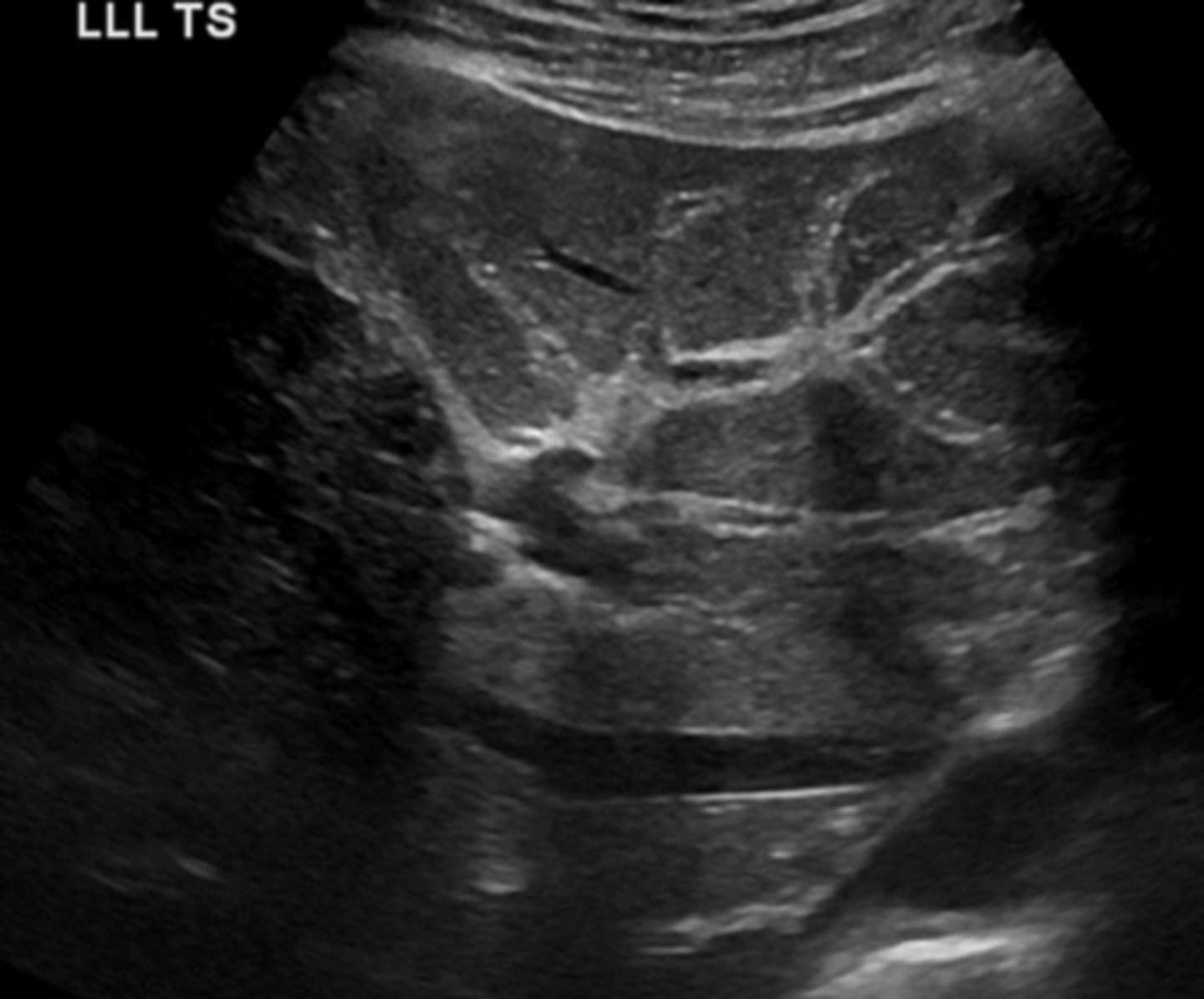
Islet Cell Tumor (Adenoma)
Microcystic/Serous Cystadenoma
-50% of pancreatic cystic neoplasms
-F>M 4:1; > 60 y/o
-may be diffuse
-typically benign
-associated w/ von hippel lindau syndrome
Microcystic/Serous Adenoma S/S
-pain
-weight loss
-palpable mass
-jaundice
Microcystic/Serous Cystadenoma Sonographic Appearance
-lobulated echogenic mass compromised of numerous small cysts
-may appear solid due to numerous small cysts found anywhere in pancreas (slightly > occurende in head)
-may be diffuse
-mass effect on pancreatic duct/CBD
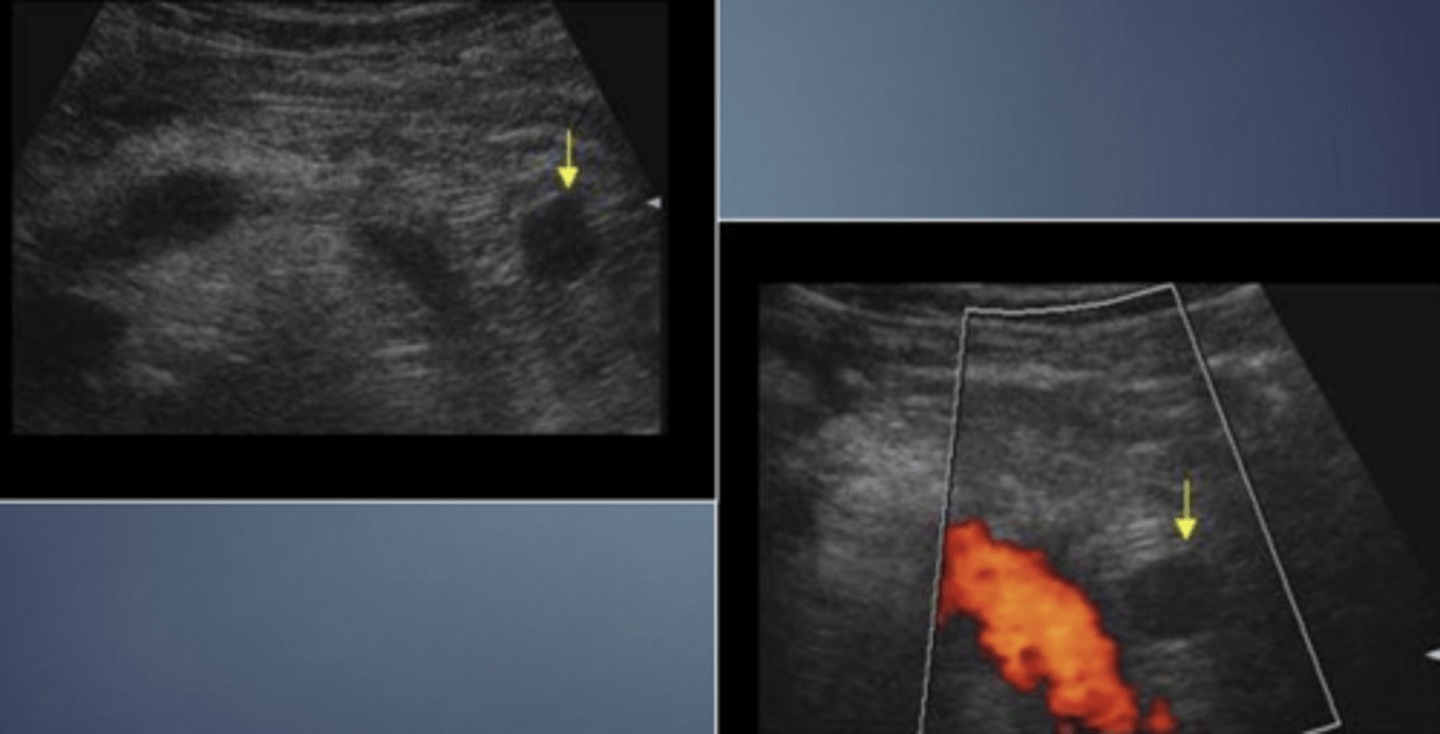
Microcystic/Serous Cystadenoma
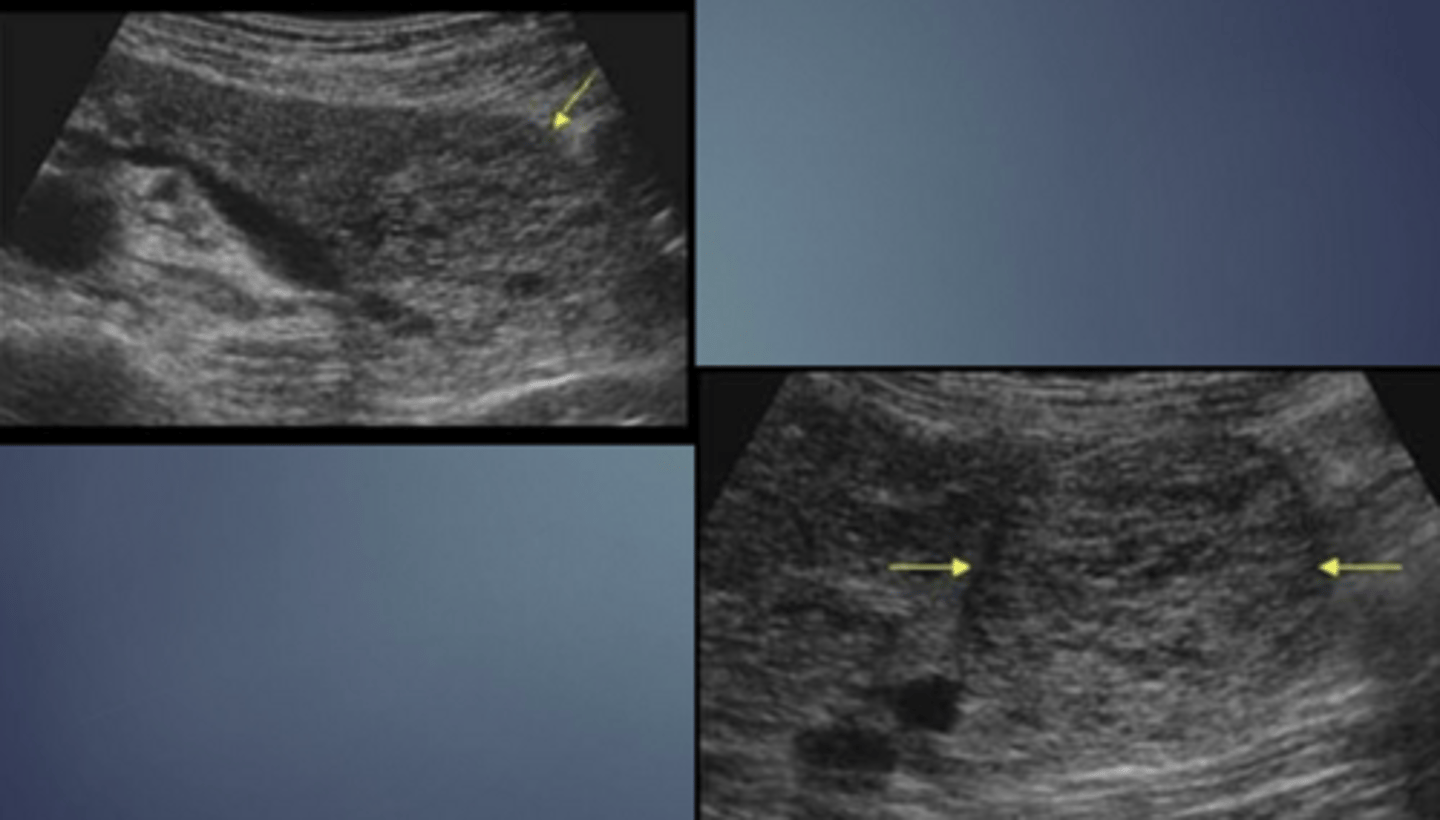
Macrocystic/Mucinous Cystadenoma
-uncommon
-slow growing, arising from the ducts
-thick walled, irregular cystic mass
-females > makes 9:1
-mean age 25 y/o
-increased in AA/east Asia
-60% in tail; 5% in head
-signification malignant potential
Macrocystic/Mucinous Cystadenoma S/S
-vague upper abdominal discomfort
-usually increased CEA and CA 19-9 serum levels therefore considered premalignant
Macrocystic/Mucinous Cystadenoma Sonographic Appearance
-large cyst w/ thick septa
-well circumscribed mass w/ thick/thin walls
-ranges from simple cysts to cysts w/ debris to cysts w/ mural nodules
-cysts w/ an increased # of papillary nodules have a > chance of malignancy
-may contain calcifications
-if mass is large enough it may cayse an obstruction of CBD. pancreatic duct or SPLV
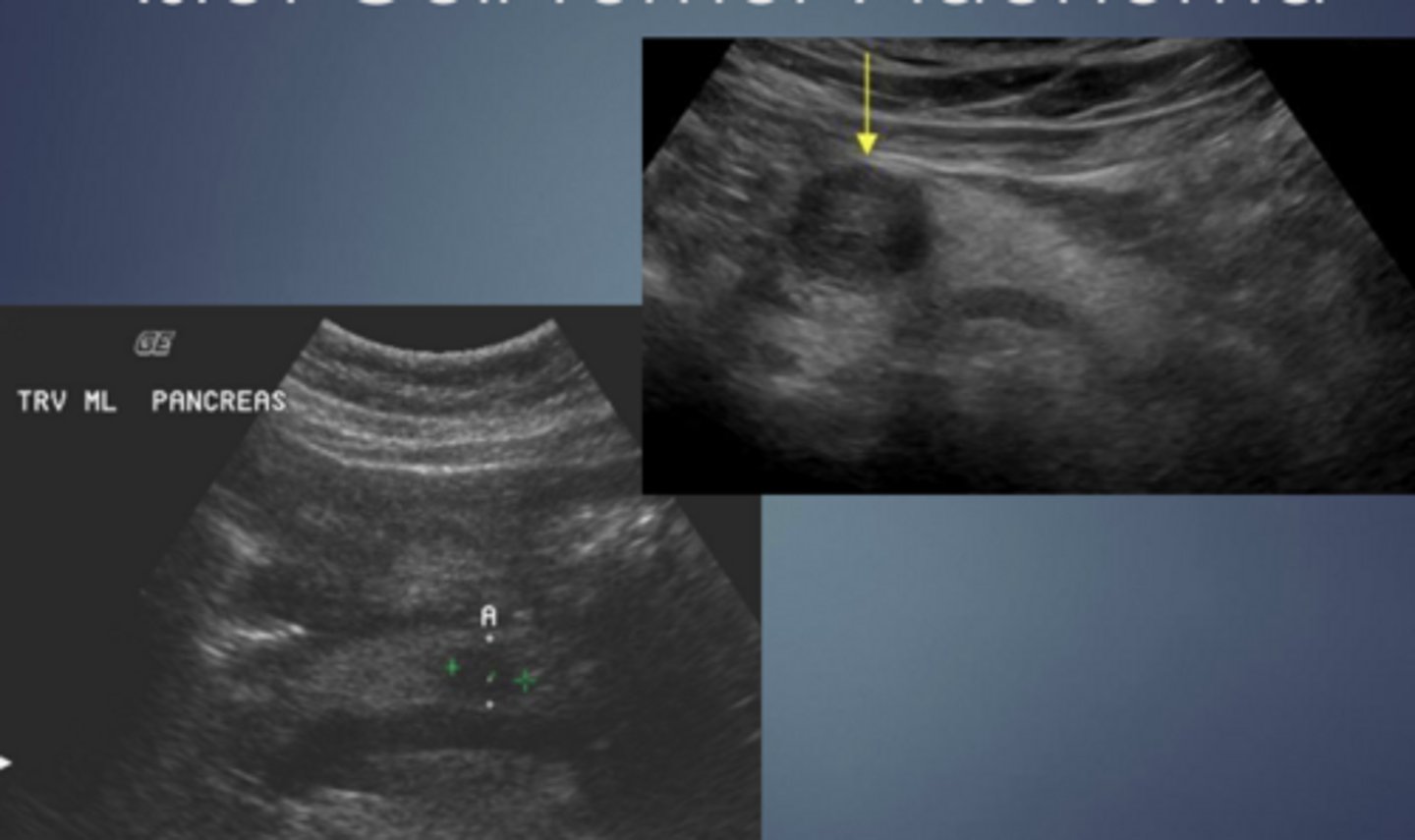
Macrocystic/Mucinous Cystadenoma
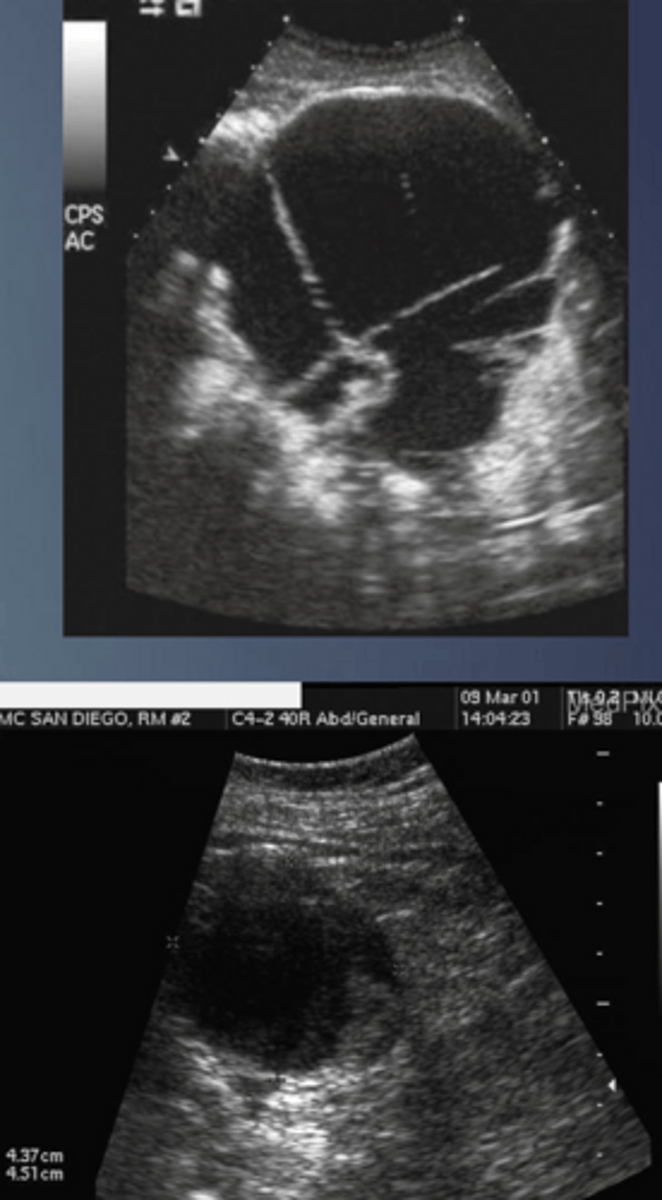
Microcystic
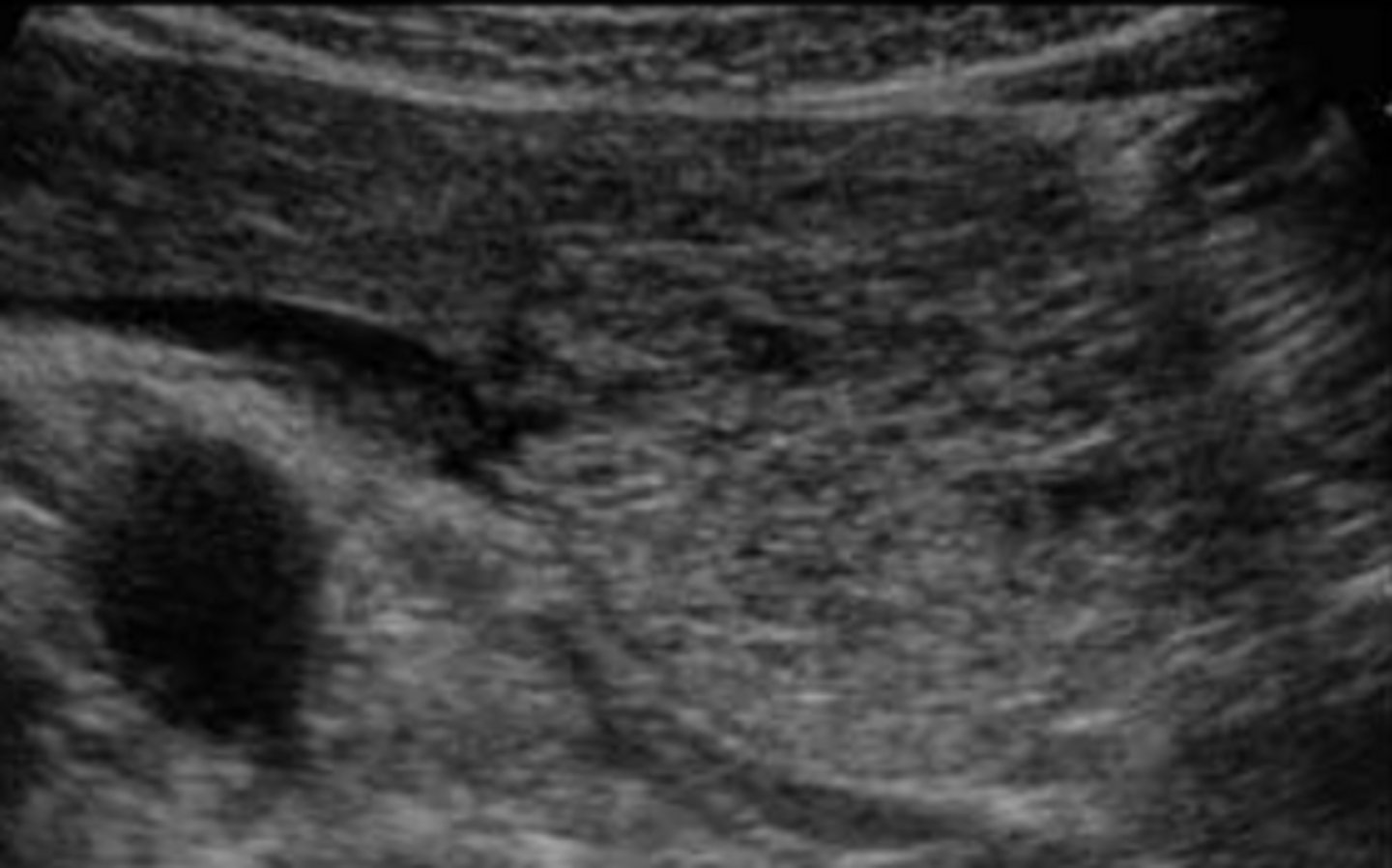
Macrocystic
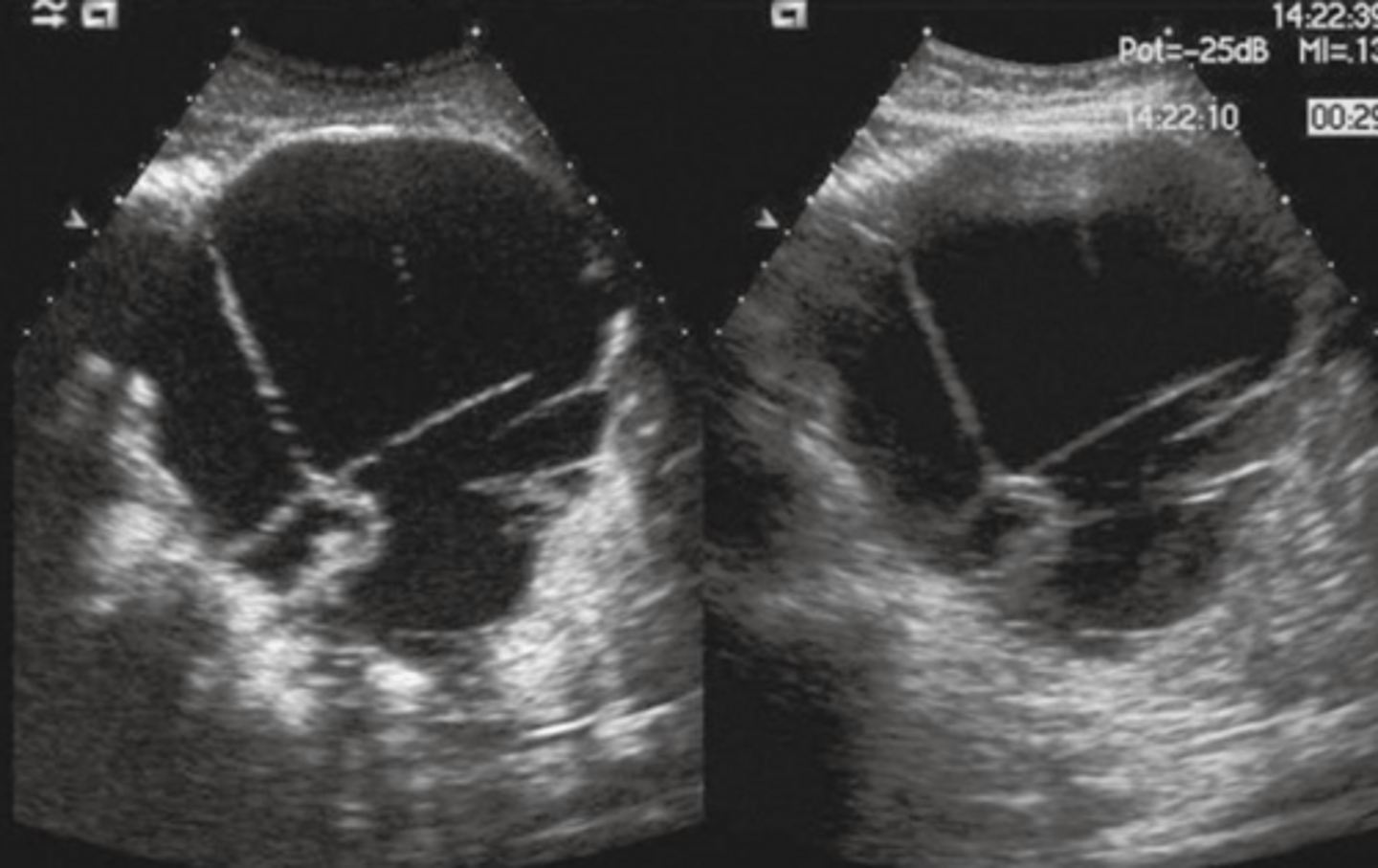
Carcinoma of Pancreas
involves exocrine portion of gland
Adenocarcinoma
-4th leading cause of death from CA in US
->99% originate from the ductal epithelium
-most lethal
-5 year survival rate of 7%
Carcinoma of Pancreas Incidence
-occurs after 5th decade
-M>F
Carcinoma of Pancreas Risk Factors
-increased risk for smokers
-high fat diet
-chronic pancreatitis
-diabetes
-cirrhosis
Carcinoma of Pancreas Occurence
-60-70% in head of pancreas (may cause obstruction of CBD)
-20-30% in body of pancreas
-5-10% in tail of pancreas
-may be diffuse w/i pancreas
Carcinoma of Pancreas S/S
-depends on location of mass (early vs late findings)
-weight loss
-anorexia
-n/v
-weakness
-malaise
-back and/or abdominal pain (steady mid epigastric aching; generally associated w/ lesions of the body of panc)
-painless jaundice (obstructive)
Painless Jaundice
-obstructive
-associated w/ lesions in head of panc
-palpable GB (courvoisier's sign)
Tail and Body Tumors
-produce late symptoms
-often silent until they have spread
-very poor prognosis due to metastasis
-may cause thrombophlebitis
-mets to lungs, liver, and stomach common
Carcinoma of Pancreas Labs
-increased bilirubin
-increased alk phos
-increased amylase
Carcinoma of Pancreas Sonographic Appearance
-80% are focal lesions
-loss of normal pancreatic parenchymal pattern
-irregular, nodular border
-localized change in echo texture
-gland enlarges at mass site
-henerally hypoechoic
-CBD, CHDs and pancreatic ducts may be dilated (courvoisier's)
-normal vascular landmarks may be obliterated or displaced (compressed IVC, spleen enlarged due to cmopression of SPLV)
-metastases to surrounding organs (liver, adrenal, GB, lymph nodes)
-ascites
Carcinoma of Pancreas
Carcinoma of Pancreas Associated Findings
-pancreatitis
-liver metastases
-lymphadenopathy
-portal venous system invovlement
-splenic vein dilatation
-SMA displacement
-ascites