chemistry - separate chemistry 2: polymers (9.17 - 9.25)
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
9.17 polymer - mass, made of
substance of high average relative molecular mass
made up of small repeating units
9.18 ethene molecules combining - type of reaction, product
ethene molecules (monomers) combine together in polymerisation reaction (addition polymerisation)
addition polymer formed called poly(ethene)
9.19 how is addition polymer poly(propene) made?
propene monomer molecules combine together
9.19 how is addition polymer poly(chloroethene) (PVC) made?
chloroethene monomer molecules combine together
9.19 how is addition polymer poly(tetrafluoroethene) (PTFE) made?
tetrafluoroethene monomer molecules combine together
9.20 deduce structure of monomer from structure of addition polymer
remove brackets & extension bond lines
draw double bond between carbon atoms
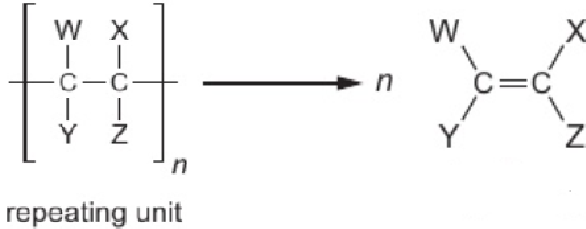
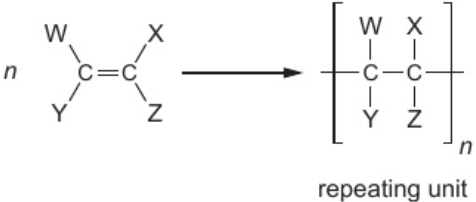
9.20 deduce structure of addition polymer from structure of monomer
add brackets & extension bond lines
draw single bond between carbon atoms
9.21 uses of poly(ethene)
flexible, cheap, good insulator
plastic bags, bottles, cling film, polytunnels
9.21 uses & properties of poly(propene)
flexible, doesn’t shatter
buckets, bowls, crates, ropes, carpets
9.21 uses & properties of poly(chloroethene) (PVC)
tough, good insulator, can be made hard/flexible
window frames, gutters, pipes, insulation for electrical wires
9.21 uses & properties of poly(tetrafluoroethene) (PTFE)
tough, slippery
non-stick coating for frying pans & kitchen utensils, burette taps, stain-proofing clothing & carpets
9.22 why are polyesters condensation polymers?
polyesters made by condensation polymerisation
monomers join together & eliminate small molecule (e.g. water)
9.22 how is polyester formed?
monomer containing 2 carboxylic acid groups reacts with monomer containing 2 alcohol groups
in presence of catalyst
water produced
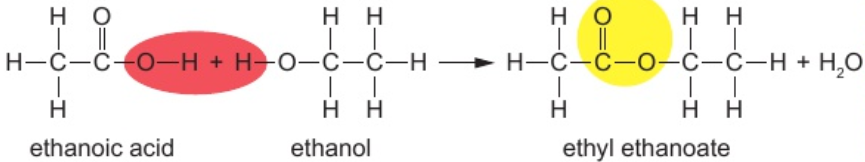
9.22 how is molecule of water formed each time ester link formed?
atoms in red oval join together to form water
leave other atoms available to bond to form ester link
9.23 problems with polymers - availability of starting materials
monomers needed to make synthetic polymers obtained from crude oil (finite, non-renewable resource)
9.23 problems with polymers - persistence in landfill sites
stay in landfill sites - non-biodegradable
9.23 problems with polymers - gases produced during disposal
disposed by combustion - produces CO2 (greenhouse gas) & toxic substances
9.23 problems with polymers - requirement to sort polymers
need to sort polymers - melted & reformed into new product
9.24 advantages of recycling polymers
monomers needed to make synthetic polymers obtained from crude oil (finite, non-renewable resource) → recycling conserves crude oil supplies
disposed by combustion - produces CO2 (greenhouse gas) & toxic substances → recycling reduces greenhouse gas emission by combustion
9.24 disadvantages of recycling polymers
many steps needed to obtain new item - difficult & expensive (to sort polymers)
9.25 DNA - what is it & what is it made from?
polymer
made from 4 diff. monomers called nucleotides
9.25 starch - what is it & what is it based on?
polymer
based on sugars
9.25 proteins - what are they & what are they based on?
polymers
based on amino acids