Economics 1.2
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
How markets work
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
1.2.1
Rational decision making
Consumers
Aim to maximise utility. Utility is the satisfaction gained from consuming a product.
Firms
Aim to maximise profit. economic theory assumes that firms are run for their owners and shareholders therefore aim to maximise profit in order to keep the shareholders happy.
Governments
Aim to maximise social welfare. Governments are voted in by the public and work for the public, so should aim to maximise their satisfaction by making decisions which increase social welfare
1.2.2
Demand
Demand
The ability and willingness to buy a particular good at a given price and at a given moment in time
Demand curve
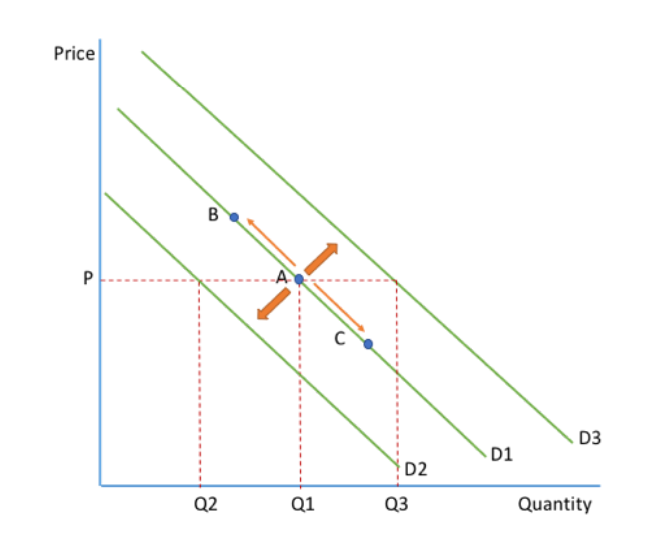
Movements
Caused by a change in price.
Contraction (is a movement from A to B) as QD falls because of an increase in price.
Extension (is a movement from A to C) as QD rises due to a decrease in price.
Shifts
Caused by a change in any of the factors which affect demand
Decrease (is a shift from D1 to D2) because fewer good demanded at every price
Increase (is a shift from D1 to D3) because more goods demanded at every price.
Conditions of demand
Factors which cause shifts in the demand curve.
Shift to the right is an increase in demand
Shift to the left is a decrease in demand
Known through PIRATES
Population
If population rises, we would expect demand for all products to increase so demand curve will shift to the right. Because more people there are in the country means more people who will want a good.
Income
For most goods, if income increases, demand increases.
A fall in income, demand decreases and shifts to the left.
For some goods, an increase in income can lead to a fall in demand, vice versa (income elasticity of demand)
Related goods
Substitutes or complements.
A substitute can replace another good. If price of the substitute falls, the quantity demanded of the original good will fall as consumers will switch to the cheaper option
A complement goes with another good. If the price of product A increases, the demand of product B will fall as fewer people will be buying product A.
Advertising
A successful advertising campaign by a firm will cause demand to increase. However if a competitor firm also carries out a successful advertising campaign, demand for the first firm will fall.
Taste
If something becomes more fashionable/in trend we expect demand to increase and if it becomes less fashionable/out of trend then demand will fall.
Expectations
If people expect a shortage of something or that price will rise in the future, demand for that product will increase. If people expect that price will fall in the future, demand will decrease.
Seasons
Some products will find their demand affected by the weather
Diminshing marginal utility
Demand curve is downward sloping, showing the inverse relationship between price and quantity.
The law of diminishing marginal utility states that the satisfaction derived from the consumption of an additional unit of a good will decrease as more of a good is consumed.
1.2.3
Price, income and cross elasticities of demand
Price Elasticity of Demand (PED)
The responsiveness of demand to a change in the price of the good. Formula:
PED = % Change of QD/% Change of Price
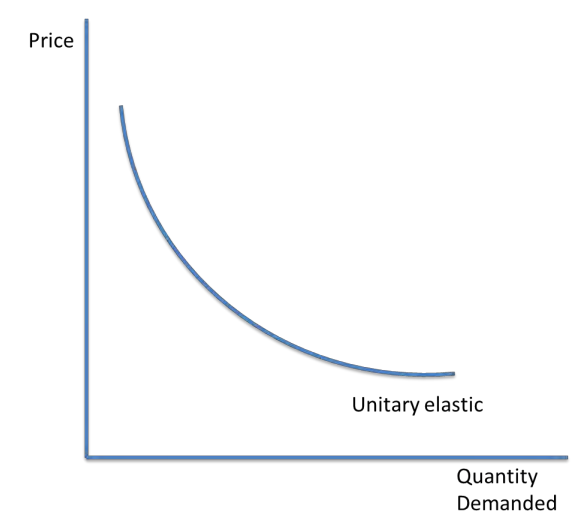
Unitary elastic PED
A unitary elastic good has a change in demand which is equal to the change in price.
PED = 1
The demand curve for a good with a PED of 1 is a curve because for a 1% decrease in the price there is a 1% increase in the quantity demanded.
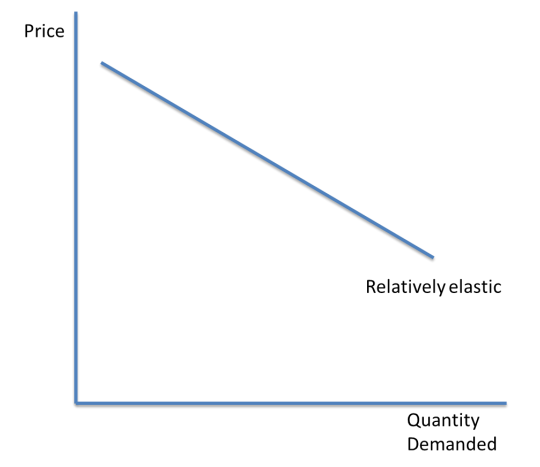
Relatively elastic PED
A price elastic good is very responsive to a change in price. The change in price leads to an even bigger change in demand.
PED > 1
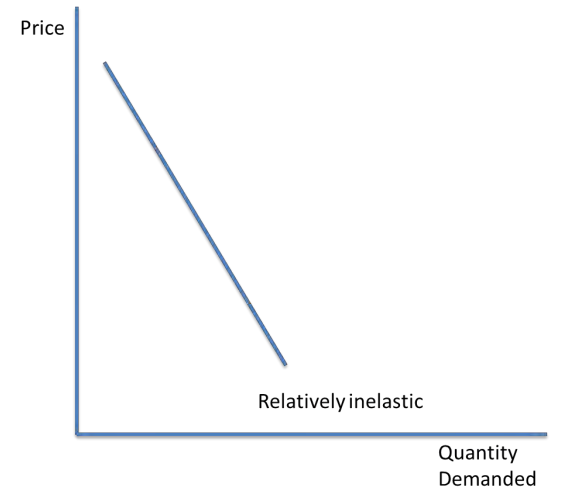
Relatively inelastic PED
A price inelastic good has a demand that is relatively unresponsive to a change in price.
PED < 1
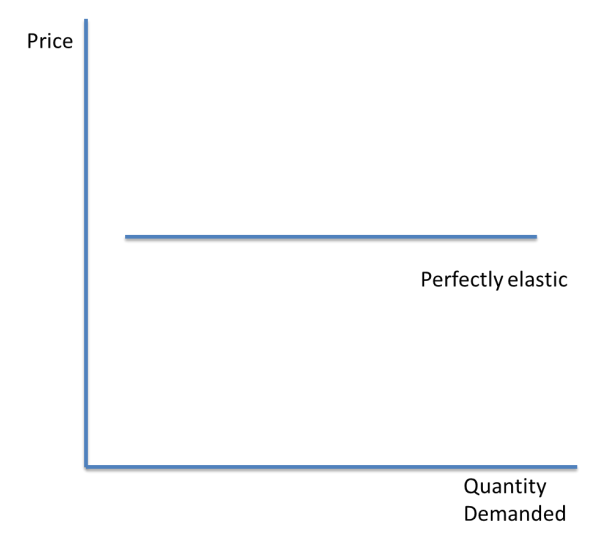
Perfectly elastic PED
A perfectly elastic good has a demand which falls to zero when price changes.
PED = infinity
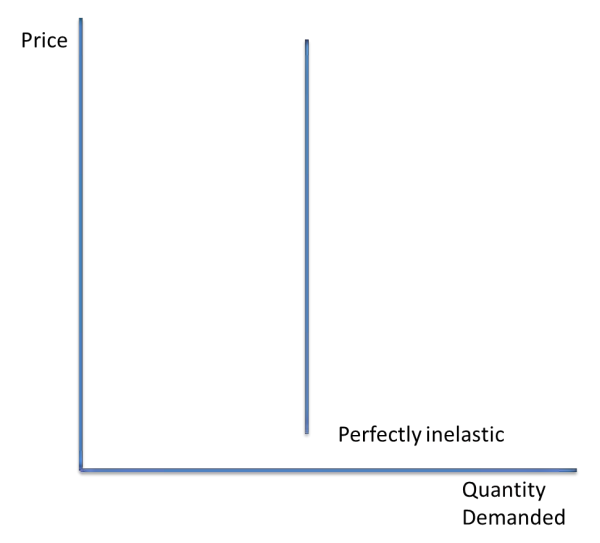
Perfectly inelastic PED
A perfectly inelastic good has a demand which does not change when price changes.
PED = 0
Factors influencing PED