BOT 3015 Chapter 3 - Cells
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
Prokaryotic cell
A type of cell lacking a membrane-enclosed nucleus and membrane-enclosed organelles; found only in the domains Bacteria and Archaea.
Eukaryotic Cell
Plants, animals, fungi, and protist are all made from this type of cell. This cell had gentic matierial covered by a membrane. Contains membrane surrounded organelles.
Prokaryotic cell structure
Cytoplasmic membrane, cell wall, cytoplasm, inclusions, nucleoid, glycocalyx, flagella, pili & fimbrae, endospores
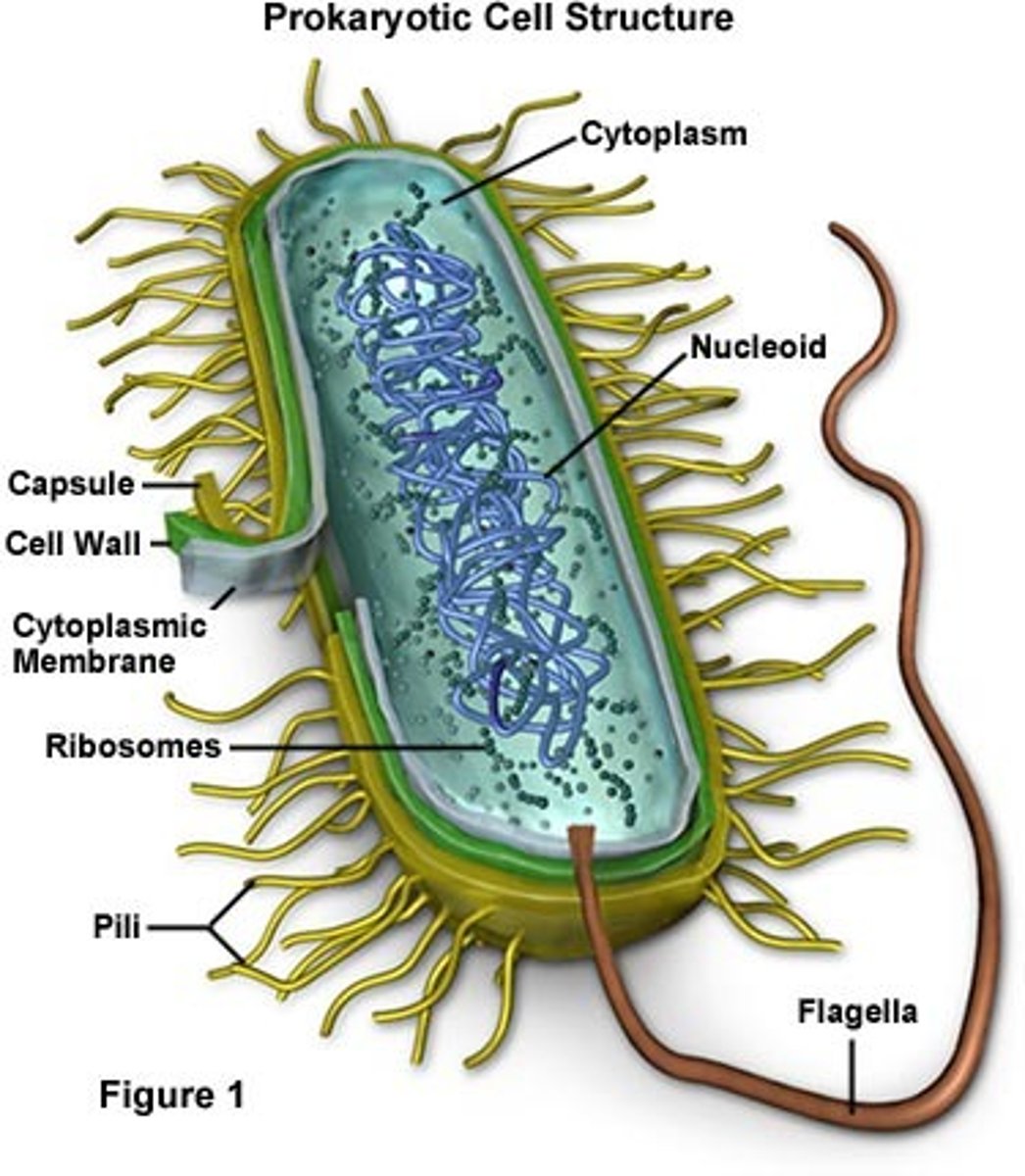
Which of the following statements concerning prokaryotes are TRUE?
(a) They have no nucleus and hence no DNA.
(b) They have no Golgi apparatus.
(c) They can form simple multicellular organisms.
(d) They include bacteria, yeast, and protozoans.
(e) They are all able to live on inorganic energy sources.
(b) They have no Golgi apparatus.
(c) They can form simple multicellular organisms.
Eukaryotic cell structure
- Nucleus-
chromatin, nucleolus, nuclear envelope, nuclear pores
- Cell membrane- phospholipid bilayer, embedded proteins,
- Cytoplasm -
Rough and Smooth ER, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, lysosomes, vesicles
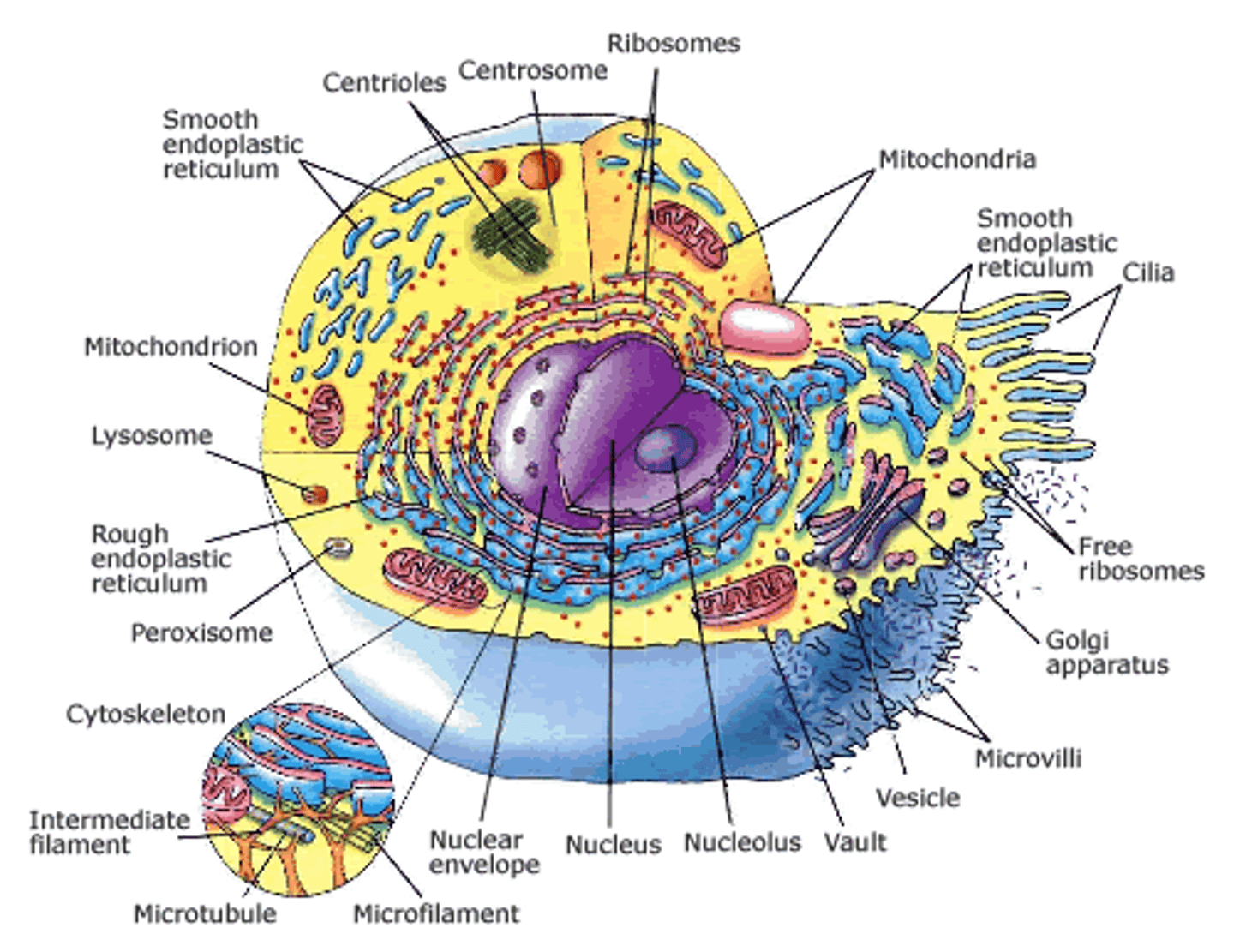
The most reliable feature distinguishing a eukaryotic cell from a prokaryotic cell is the
(a) presence of a plasma membrane.
(b) presence of a nucleus.
(c) eucaryotic cell's larger size.
(d) presence of DNA.
(b) presence of a nucleus.
Another organelle found in essentially all eukaryotic cells is the __________________, which generates the chemical energy for the cell.
Mitochondrion
If we were to strip away the plasma membrane from a eukaryotic cell and remove all of its membrane-enclosed organelles, we would be left with the 1)__________________, which contains many long, fine filaments of protein that are responsible for cell shape and structure and thereby form the cell's 2)__________________.
1) Cytosol
2) Cytoskeleton
Protoplasm
- The substance that makes up the living parts of cells
- Cell walls surrounds this
Cell wall
A rigid structure that surrounds the cell membrane and provides support to the cell
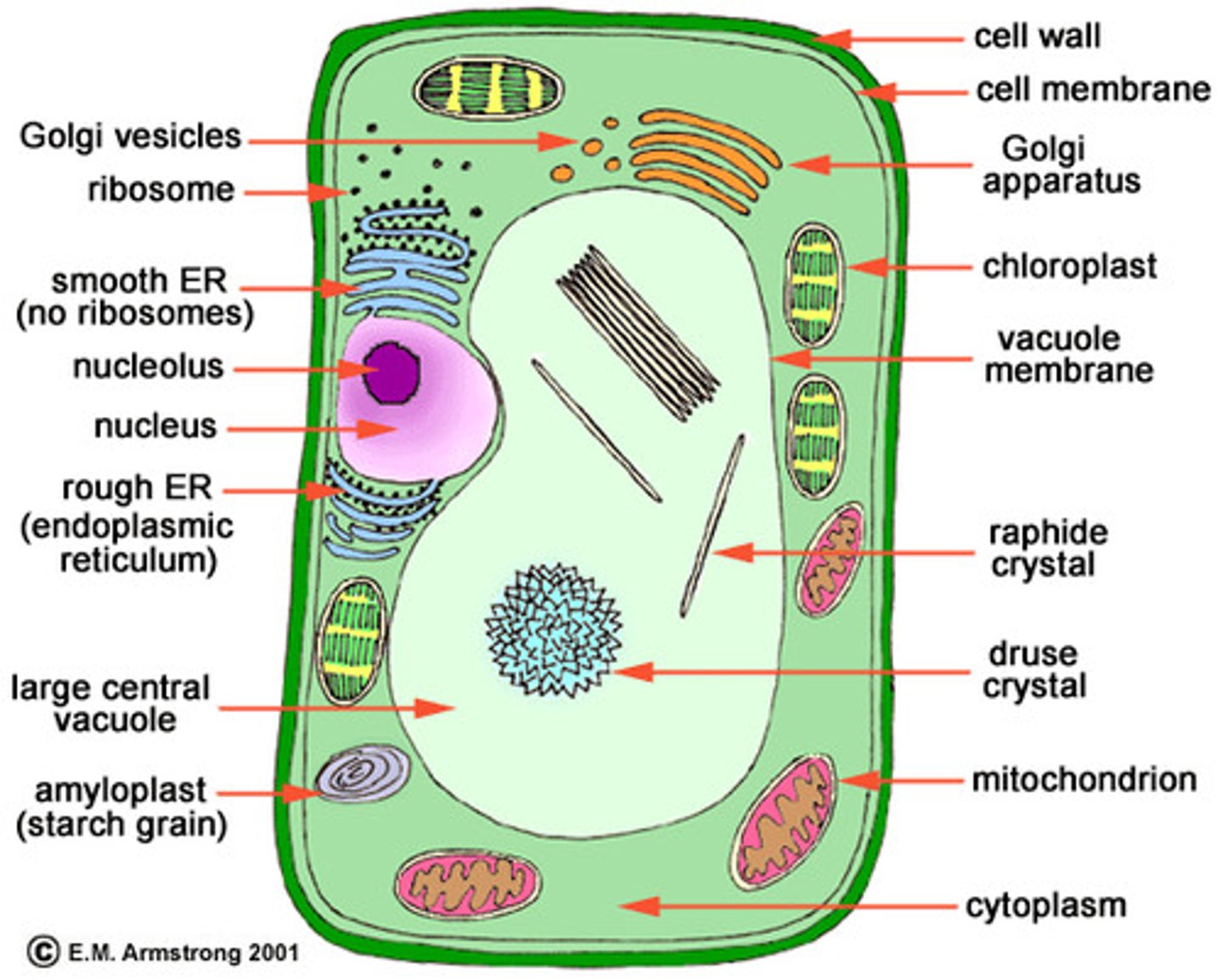
Primary cell wall
- A relatively thin and flexible layer
- Surrounds the plasma membrane of a young cell
- Laid down on either side of middle lamella
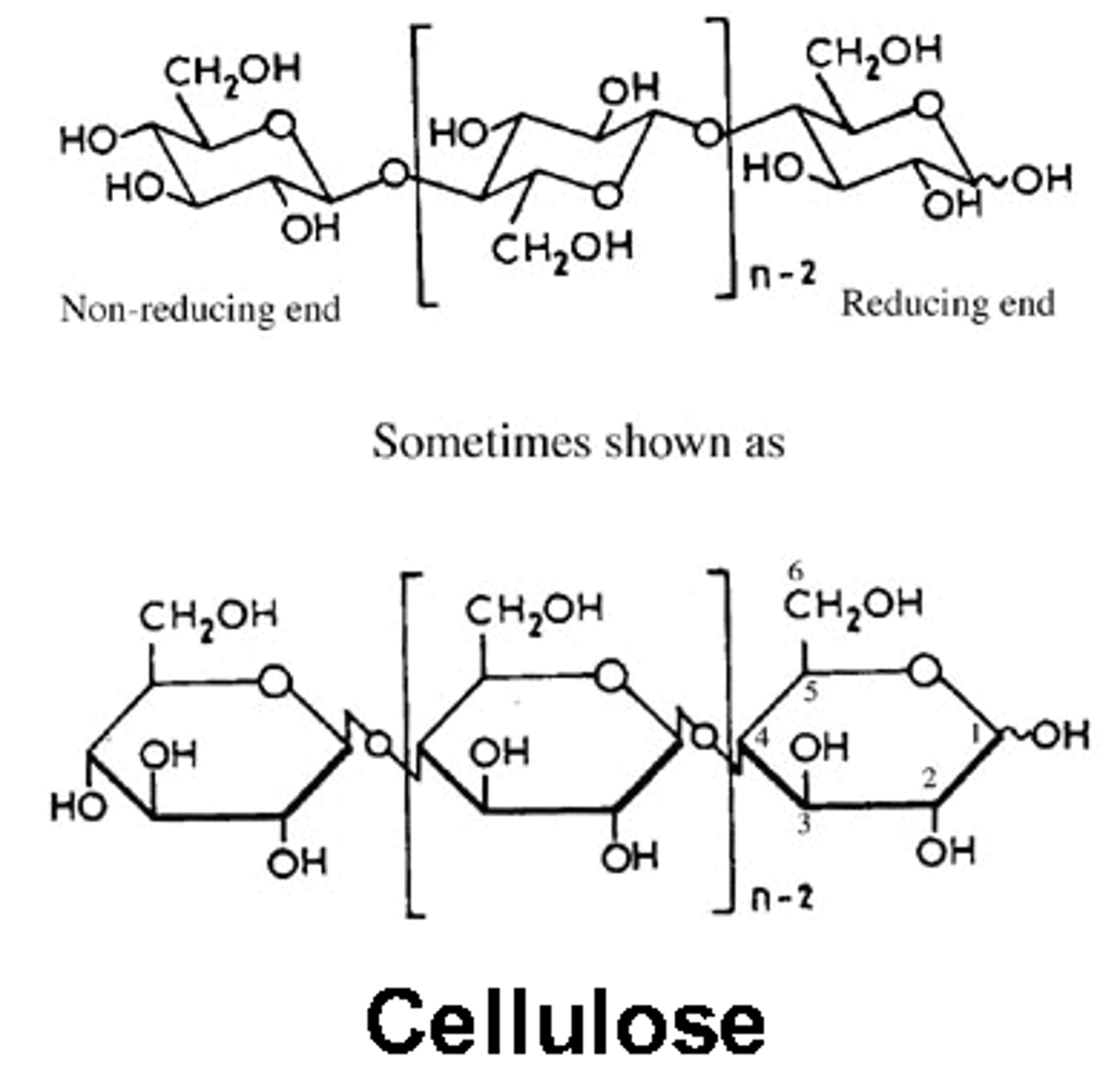
Cellulose
A substance (made of sugars) that is common in the cell walls of many organisms
The matrix of the cell wall contains
- Hemicellulose
- Pectins
- Glycoproteins
Hemicellulose
Holds cellulose fibrils together
Pectin
A soluble gelatinous polysaccharide that is present in ripe fruits and is extracted for use as a setting agent in jams and jellies.
Glycoproteins
Membrane carbohydrates that are covalently bonded to proteins.
Secondary cell wall
- A strong and durable matrix that provides protection and support.
- Produced inside primary walls
- Derived from primary wall thickening and inclusion of polymer --> lignin
- Contains more cellulose (40-80%) more than primary walls
Middle lamella
In plants, a thin layer of adhesive extracellular material, primarily pectins, found between the primary walls of adjacent young cells.
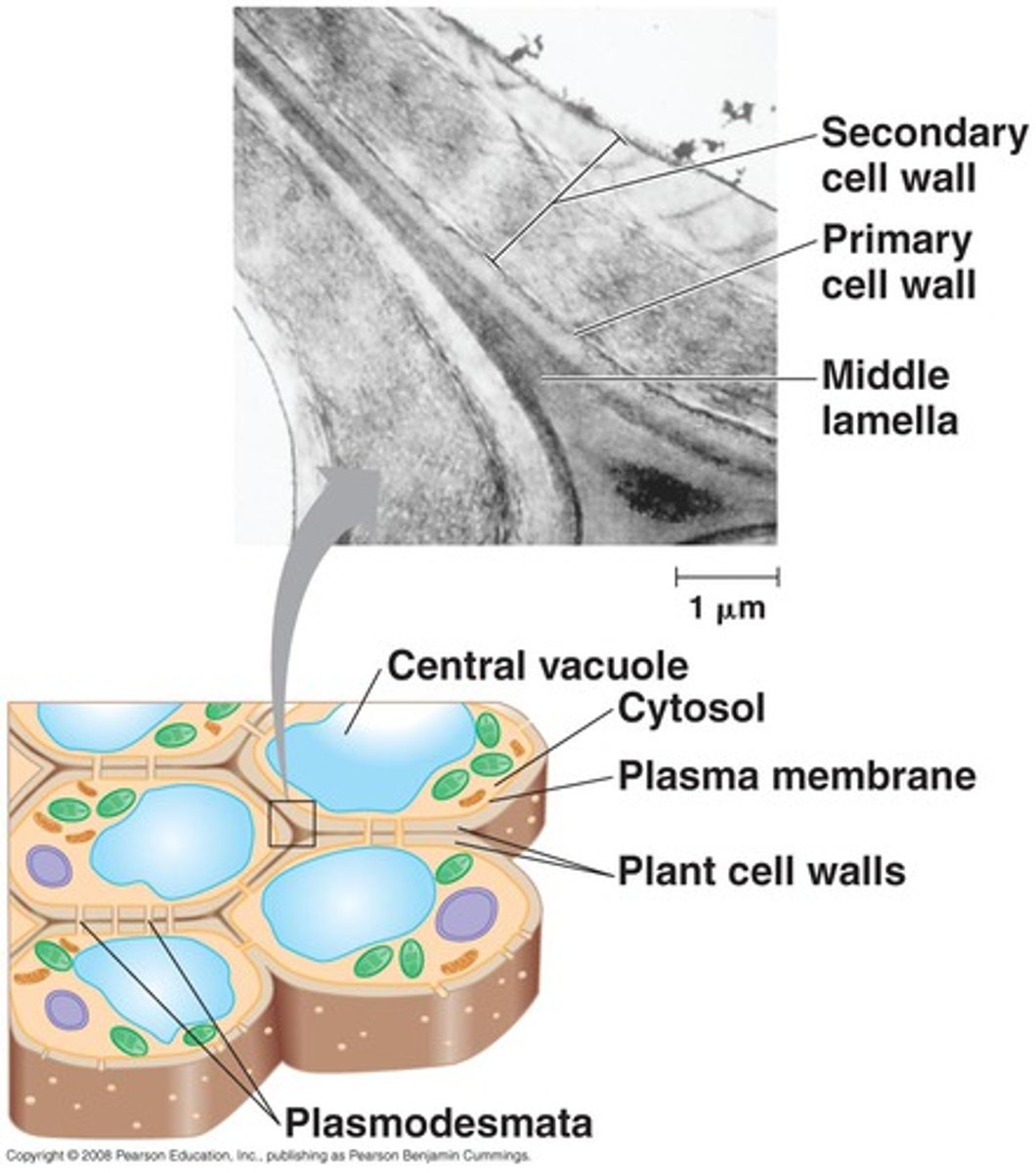
Plasmodesmata
- Minute strands of cytoplasm that extend between adjacent cells through pores in the walls
- Fluids and dissolved substances can pass through primary walls of adjacent cells
- Translocation of sugars, AA, ions
Plasma membrane
- The outer boundary of the protoplasm of a cell
- Regulates the movement of substances in/out of the cell = "semipermeable"
- Composed of 2-layer phospholipids, with interspersed proteins
- Involved in the production/assembly of cellulose --> cell wall
- Surface --> carbohydrates + lipids/proteins = covalent bonds
Fluid mosaic model
Structural model of the plasma membrane where molecules are free to move sideways within a lipid bilayer.
Nucleus
- Is control center of cell and contains DNA.
- Sends coded messages from DNA to be used in other parts of the cell.
- Bounded by 2 membranes = nuclear envelope
Ex: RNA-out & proteins-into nucleus
Nuclear envelope
- A double membrane that surrounds the nucleus in the cell
- (1/3 complex semipermeable pores: nucleus --> cytoplasm)
- Surrounds nucleus
Cytoplasm
The material or protoplasm within a living cell, excluding the nucleus.
Cytosol
The semifluid portion of the cytoplasm.
Nucleoplasm
- In the nucleus granular-appearing fluid
- Has nucleoli (made of RNA)
- Chromatin strands:
(DNA & proteins) -->
become chromosomes
Nucleoli
- Organelles in nucleus
- Composed primarily of RNA
Chromatin
- A readily staining complex of DNA and proteins found in chromosomes
- Usually not visible unless stained or is dividing
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
- The outer membrane of the nucleus is connected and continuous throughout the cytoplasm
- Facilitates cellular communication/channeling of materials (synthesis)
- 2 sections: Smooth & Rough
- Enzymes synthesized --> cellular respiration on surface of ER
- Primary site of membrane synthesis within cell
Rough ER
- Ribosomes on outer surface
- Protein synthesis, secretion and storage
Smooth ER
- Few to no ribosomes
- Lipid secretion
Ribosomes
- Electron microscope
- Size: ellipsoidal
- Composed of 2 subunits: RNA & protein
- Subunits assembled within the nucleolus
- Found in:
May occur outside Rough ER
In cytoplasm
Chloroplasts
- No bounding membranes
Dictysomes
- Golgi bodies
- Stacks of flattened discs or vesicles
- 5-8 dicytosomes/cell (max 30)
Dictysomes functions
- Modify carbs on proteins --> synthesized/packed in the ER
- Assemble polysaccharides and collect them in small vesicles
Vesicles
- Tiny, blister like bodies
- Pinched off from the margins of dicytosomes
- Vesicles migrate --> plasma membrane = fuse --> secrete: cell wall polysaccharides, floral nectars, and essential oils in herbs
Enzymes needed for the packing of proteins are produced by the 1)___________ and are further modified within the 2)___________.
1) ER
2) Dicytosomes
Plastids
- An organelle associated primarily with the storage or manufacture of carbohydrates
- They all develop from proplastides
-Chloroplasts are most common
-Bounded by double membrane
Grana
- A stacked portion of the thylakoid membrane in the chloroplast.
- Grana function in the light reactions of photosynthesis
Stroma
- The matrix of enzymes involved in photosynthesis
-Small circular DNA molecule
-Encodes for production of
certain proteins for
photosynthesis
What are the 3 types of plastids?
1) Chloroplasts
2) Chromoplasts
3) Leucoplasts
Chromoplasts
Synthesize and accumulate carotenoids (yellow, orange, red)
Leucoplasts
- Organelles that store starches (amyloplasts) or oils (elaioplasts)
- Colorless
Mitchondria
- Cell powerhouse
- Cellular respiration = molecules --> energy
- Barely seen with light microscope
- Bounded by two membranes
- The inner membrane --> cristae = increases surface area for enzymes in matrix
- Matrix includes: RNA, DNA, ribosomes, proteins
Microbodies
- Small spherical bodies distributed throughout the cytoplasm
- Bounded by single membrane
- Contains specialized enzymes
- Peroxisomes: serve in photorespiration (chloroplasts)
- Glyoxisomes: aid in conversion of fat --> carbohydrates (near mitochondria)
Lysosome
- An organelle containing digestive enzymes
- Only in animals
- Digestively similar to vacuoles
Vacuoles
- In mature cells 90% of volume (taken up by central vacuoles)
- Bounded by vascuolar membranes = tonoplasts
- Filled with cell sap (mid-high acidic)
- Helps with pressures
- Contains dissolved substances (salt, soluble proteins, pigments-anthocyanin)
Vacuole function
- Cell pressure
- pH
- Storage of cell metabolites & waste products
Cytoskeleton
- A network of fibers that holds the cell together, helps the cell to keep its shape, and aids in movement
- Network of microtubules and microfilaments
Microtubules
- Control addition of cellulose to cell wall
- Involved in movement of flagella and cilia
- Found in fibers of spindles and phragmoplasts in dividing cells
- Found in the plasma membrane
- Are thin, hollow, made of tubules (proteins)
Microfilaments
- Role in cytoplasmic streaming
- Contraction & cell movement
Differences between plant and animal cells
Plants:
-Cell walls
-Cell plate and plasmodesmata
-Plastids and (Central) vacuoles
Animals:
-Internal or external skeletons
-No cell walls
-Plasma membrane = cell membrane
-Divide by pinching in two
-No cell plate or plasmodesmata
-Centrioles present during cell division
-No plastids or vacuoles
Which are typical components of plant cell walls?
- Cellulose
- Glycoproteins
- Pectin
- Hemicellulose
As a cell becomes bigger, its 1)__________ grows much more than its 2)__________, which makes diffusion of substance into/out of the cell proceed at an inadequate rate?
1) Volume
2) Surface area
Tiny strands of cytoplasm, which extend between adjacent plant cells though minute openings in the cell wall are called _________?
Plasmodesmata
Features of secondary cell wall?
- It contains more cellulose than the primary cell wall
- Cellulose microfibrils are embedded in lignin