Neurological Disorders: Adult Onset
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lecture #2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Multiple Sclerosis
A chronic autoimmune disease that affects the central nervous system, characterized by inflammation, demyelination, and neurological symptoms such as weakness, vision problems, and coordination issues.
MS Frequency
-1,000,000 Americans (0.3%)
-2.8 million worldwide
-More common in women than men
—3:1
MS Age of Onset
-30’s-50’s
MS Causes
-Autoimmune proccess
-higher prevalence further from equator
-EBV infection increases risk
-Genetic variants in HLA (Human Leukocyte Antigen) region TRIPLES risk
What Happens to the CNS w/MS?
-loss of myelin at multiple sites; replaced with scar tissue —> SCLEROSIS
-uncF
MS: Functions Affected?
-Depends on where myelin is lost (could be sensory, motor, cognitive, affective)
-Increased chance of seizures (plaques may become seizure foci)
—2-3% also have seizure disorderW
What worsens MS symptoms and why?
higher body temperature; causes conduction of nerve impulses to slow even more or FAIL
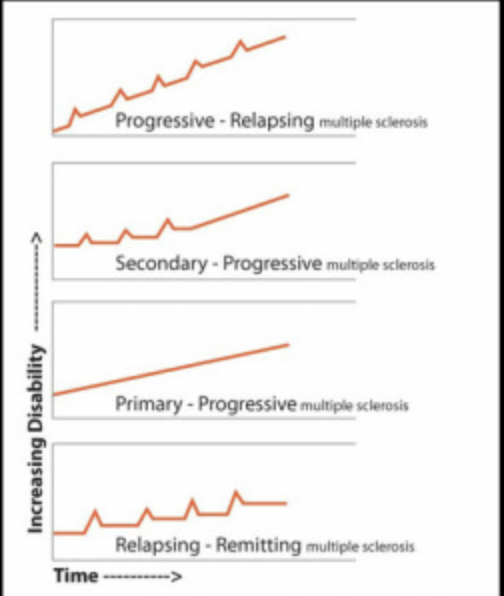
What are the subtypes of MS?
Relapsing-Remitting MS (85%—can transition to…)
Secondary Progressive MS
Primary Progressive (10%)
Progressive-Relapsing (5%)
MS and Pregnancy
-MS occurs in women of child-bearing age
-Pregnancy reduces MS progression due to natural immunosuppressants released during pregnancy
-MS progression increases after pregnancy
MS Cure/Treatment
-No cure
-Interferon/”Avonex”
—Disease modifying medication (slows progression)
—not safe for use during pregnancy or breastfeeding
ALS: Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis/”Lou Gehrig’s Disease”
Theme
ALS Incidence & Prevalence
-2/100,000
-11/100,000
30,000 in USA
8000 new cases each year
ALS Age of Onset
40s-50s
ALS Cause
90% not known, 10% genetic (familial form)
ALS Functions Affected?
-motor system ONLY
-gradual loss of motor control → leads to death by respiratory failure
-3-5 year survival after diagnosis
ALS Target?
-Upper and lower motoneurons and their axons
Lower/Spinal Motoneurons
-cell bodies in the ventral horn of spinal cord
-their axons innervate muscle fibers and provide “trophic” (nutritive) factors
-when a motoneuron dies, muscles atrophy (die)
Symptom of lowe/spinal motoneuron death?
Fasciculations
-twitches in the muscle fibers as they die
Lateral Sclerosis?
refers to the death of the lateral corticospinal tract
ALS Cure/Treatment
-no cure
-2 medications can slow the progression by MONTHS