Kinetics/ collision theory
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Kinetics
Study of factors that affect the rates of reactions and the mechanisms (steps) by which reactions take place
Reaction rate
number of particles ( atoms, ions,molecules) that react in a given time to form products.
Reaction equation:change [R]/ change in time
Collision theory
Particles must collide in order to react
Collisions must be effective ( must have sufficient energy to break existing bonds and form new ones)
must have correct orientation ( hit a specfic way)
Activation energy
The minimum energy colliding particles must have in order to react
Potential energy graph
Potential energy of reactants or products is the difference from when they are a straight line until the ground
Heat of reaction is the difference between the straight line of the products vs the reactants
The reverse reaction is from the hump up until the straight line of the products
the activation energy is from the hump up until the straight line of the reactions
the activation complex or transition state is from the hump until the ground.
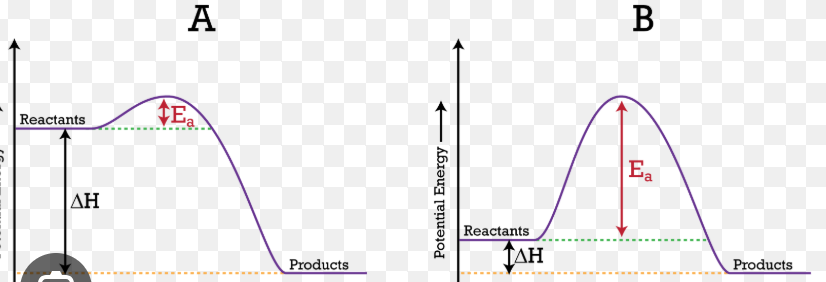
Activation complex:
Bonds break and rearrange themselves
Forward reaction
Factors that affect reaction rate
Temperature
Surface area ( particle size —> greater surface area so particles can hit easier)
Catalyst ( substance that lowers activation energy without getting used up)
Concentration ( increasing amount will increase collision with particles)
Calculating rate of reaction
Look at coefficients of the balanced equation
Multiply by the amount of moles for the substance you want ( ex oxygen) over the amount of moles you already have ex) The reaction rate of ozone is 8.76 × 10^-3 M/s over a certain interval of time. What is the rate of appearance of O2 during this interval?
Using the balanced equation you can do 8.76 × 10³ x 3/2 since in the balanced equations its 2O3 —> 3O2
Compare coefficients for each subtance
Reversible reaction
ex) A —>B
Can become B and then through collisions also go back to A
rate: change in [A]/ change in time
will reach equilibrium
Equilibrium
Rate of forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction
RATE OF PRODUCTION OF REACTANTS IS EQUAL TO THE RATE OF PRODUCTION OF PRODUCTS
RATE IS THE SAME BUT YOU CAN HAVE MORE OF REACTANTS OR PRODUCTS
Equilibrium expression:
Keq= [ products]/ [reactants]
If k > 1 products are favored ( reaction goes to completion)
if k < 1 reactants are favored ( mostly reactants in container)
if k=1 neither reactants nor products are favored ( significant amount of both reactant and products in container)
In equilibrium expressions you may only include substances ( reactants or products) that are gases or aqeuous. Liquids and solids have “ fixed” concentrations.
La Châtelier’s principle
if a “ stress’ ( change) is applied to a reaction at equilibrium the reaction “ shifts” to relieve the stress
Types of stress: change concentration of a reactant or product , change temp by adding or removing heat, change the pressure by increasing or decreasing the volume of container ( gases only)
“ shifts” one way ( forward of reverse) reaction has a temporary increase in reaction rate in one direction
How these stresses apply:
If concentration of reactants increases it shifts right
if concentration of reactants decrease it shifts left to make more of what was removed
If concentrations of products increase reaction shifts left
If heat is added to the container reaction shifts left ( shifts in the endothermic reaction)
If he is removed reaction shifts right ( in the exothermic direction).
If pressure of container is increased reaction shifts towards the side with fewer moles of gase
If pressure of container is decrease rection shifts where there are more moles.
INCREASING VOLUME= REDUCING PRESSURE
DECREASING VOLUME = INCREASING PRESSURE
Endothermic vs exothermic graphs
Endothermic reactants are low and products are high
Exothermic reactants are high and products are low.
Are reversible activation energy greater or less than forward reactions
Reversible activation energy is greater than forward activation energy because they need overcome the activation energy and reach the transition state.