A&P Cardiovascular System
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
towards
veins pump blood _ the heart
away from
arteries pump blood _ the heart
deoxygenated
veins carry mostly _ blood
oxygenated
arteries carry mostly _ blood
veins
arteries are thicker than _
low
veins have _ pressure
high
arteries have _ pressure
pericardium, myocardium, endocardium
the layers that surround the heart from superficial to deep
SA node - AV node - AV bundle - Purkinje fibers - muscle contraction
Intrinsic conduction system: the pathway of transmitting an impulse through
hypertension
high blood pressure
hypotenson
low blood pressure
Cardiac Output (CO) = HR (heart rate) x SV (stroke volume)
equation for the volume of blood pumped by the heart per minute
arteries
blood vessels with thick, muscular, elastic walls that carry oxygenated blood from the heart to body tissues
Capillaries
blood vessels with thin single-cell-layer walls that exchange oxygen, nutrients, and waste between blood and body cells
Veins
blood vessels with medium strength walls that carry deoxygenated blood to heart
Blood pressure
The force of blood against blood vessel walls (highest in arteries)
valves and skeletal muscle contractions
_ and _ _ _ help blood move through the body
Transport of vital substances (oxygen, nutrients, water)
The overall function of the cardiovascular system is
Pericardium
The covering over the heart
Myocardium
layer of pericardium composed of cardiac muscle that is very thick in the ventricle
always open and can expand
Arteries are..
collapse
Veins can...
capillaries
_ connect veins and arteries in tissues
Large arteries - Arteries - Capillaries at the tissue - venules (small veins) - veins - great veins (Vena Cava)
flow of blood through the heart
Temporal
Facial (jawline)
Carotid (neck)
brachial (inner elbow)
radial
femoral
popliteal
posterior
dorsal pedis (top of ankle)
Common arteries for pressure points
to stop hemorrhages
why would you want to stop blood flow?
acivity, emotions, and posture
what affects pulse rate?
Tachycardia
abnormally fast heart rate (over 100 bpm)
bradycardia
Abnormally slow heart rate (under 60 bpm)
1. autonomic nervous system = sets the pace of your heart
2. Intrinsic conduction system = sets the rhythm
2 systems that regulate heart activity
Systole
BP when the heart contracts
Diastole
BP when the heart is in a relaxed state
cardiac cycle
one complete cycle of both diastole and systole pressure is called _ _
120/80
Normal BP
90 & 140
systolic BP is between
60 & 90
diastolic BP is between
aorta / aortic arch with arteries
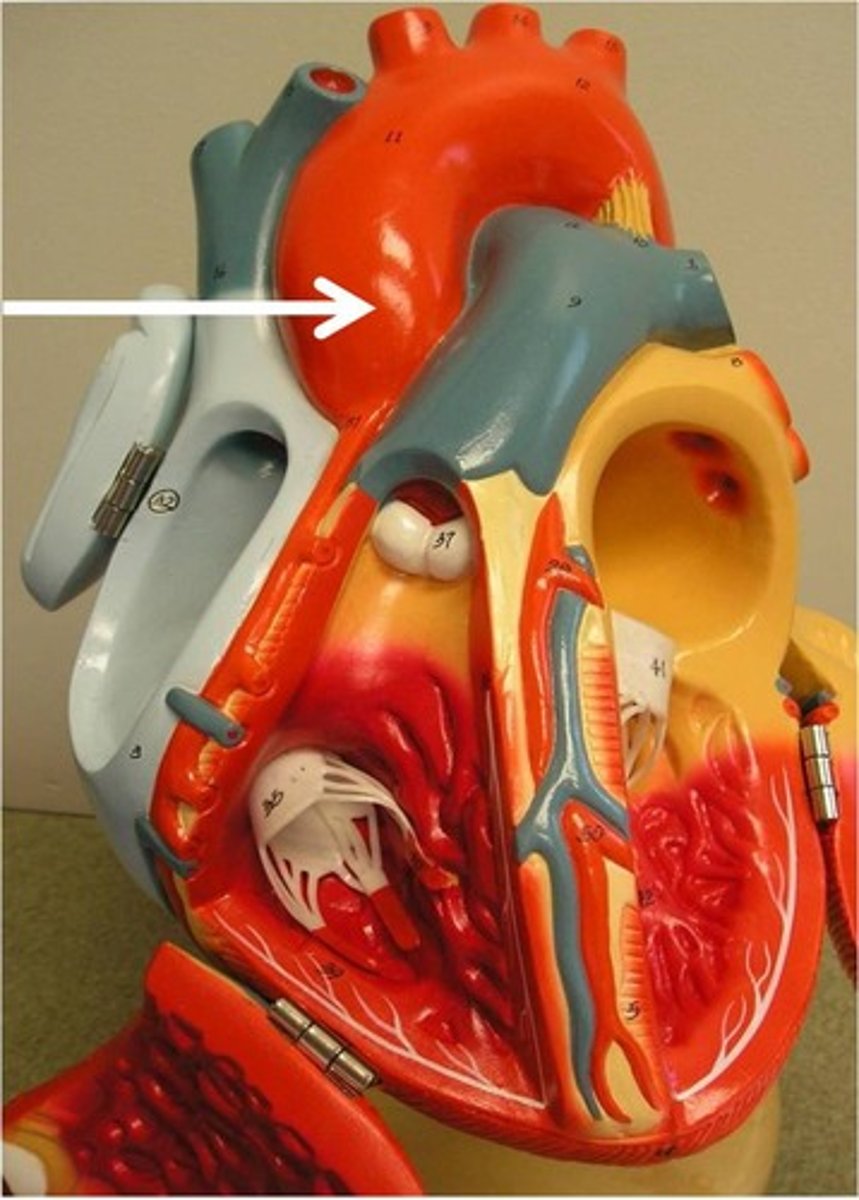
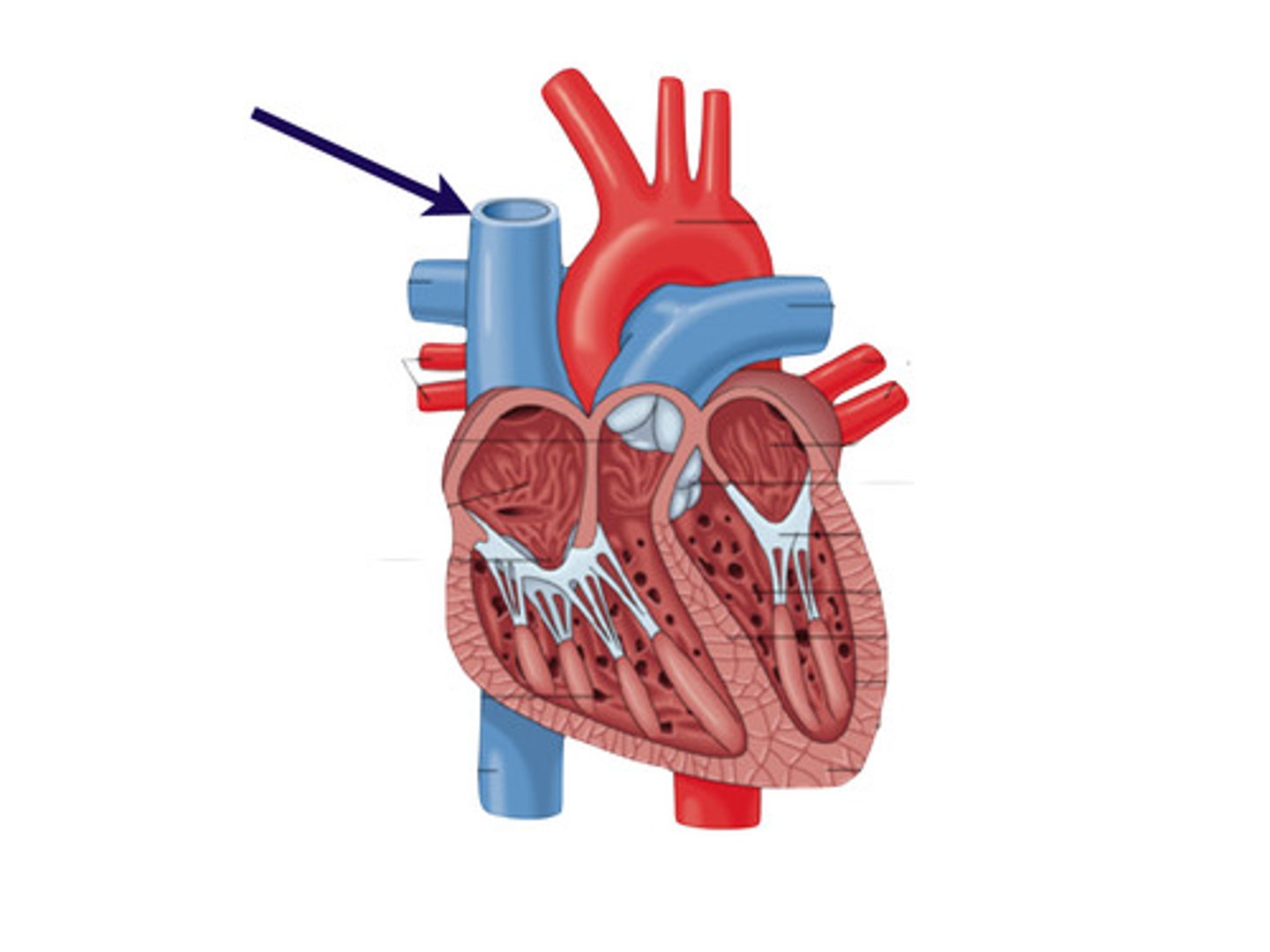
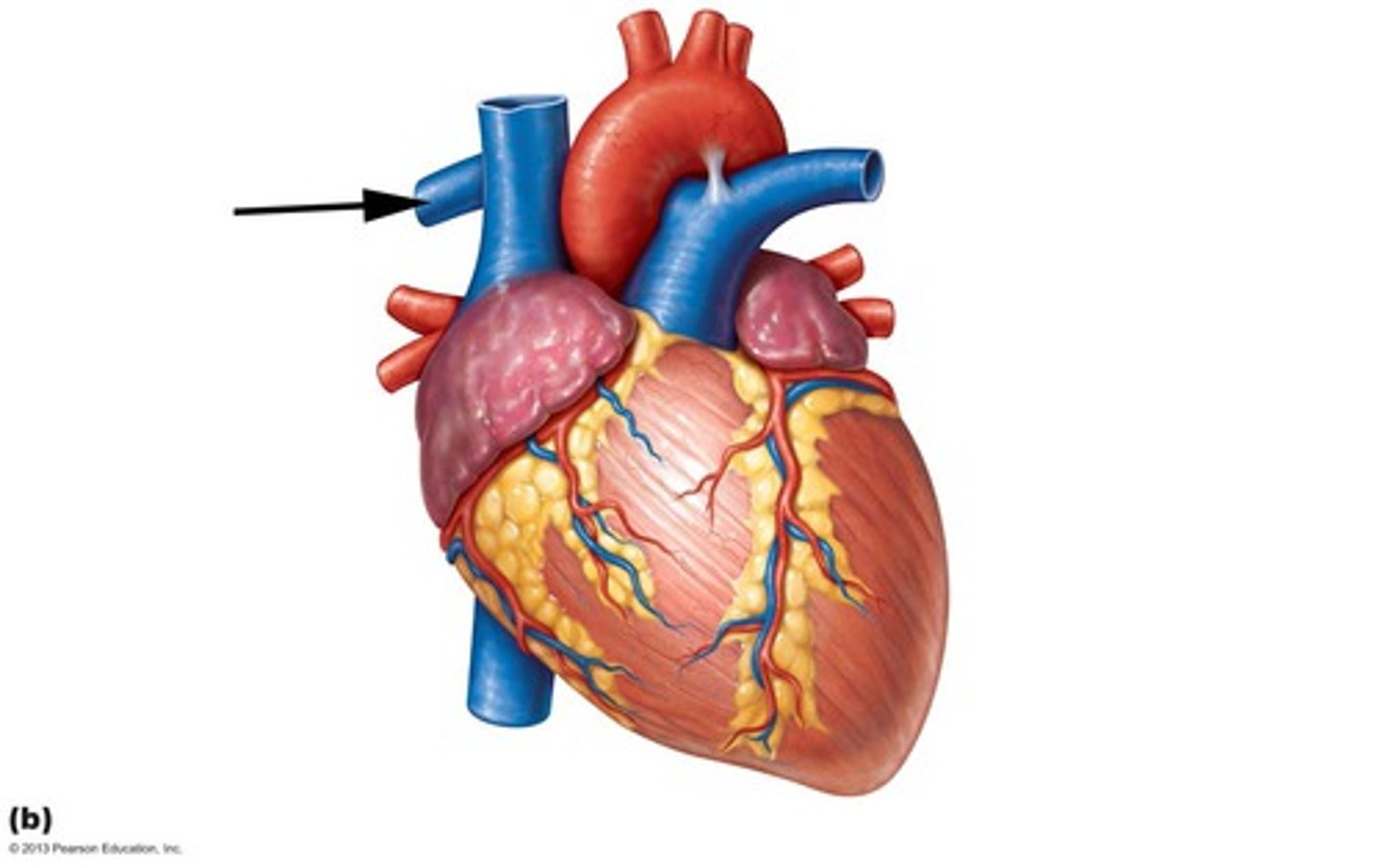
superior vena cava
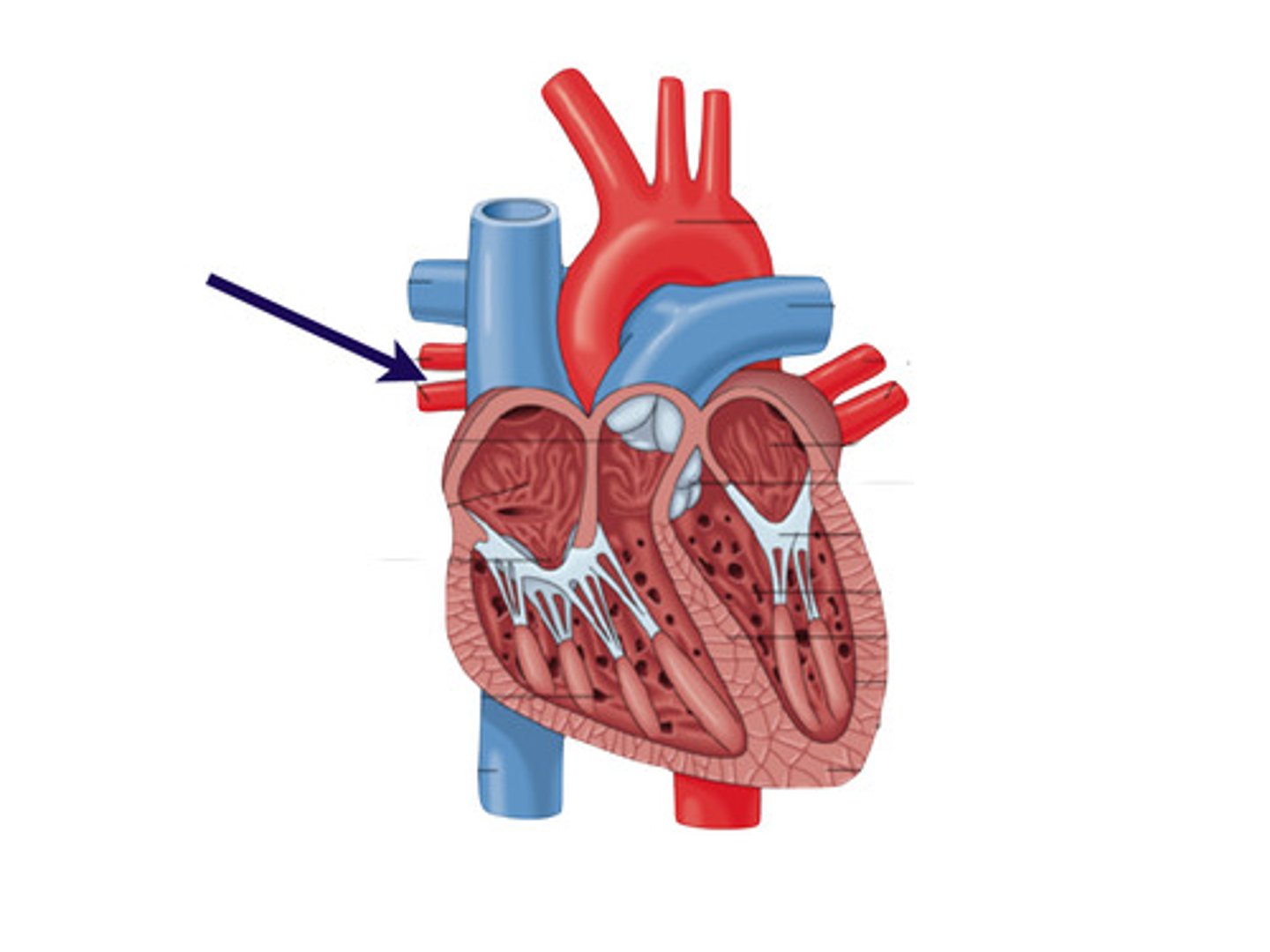
right pulmonary artery
right pulmonary veins
right atrium (exterior)
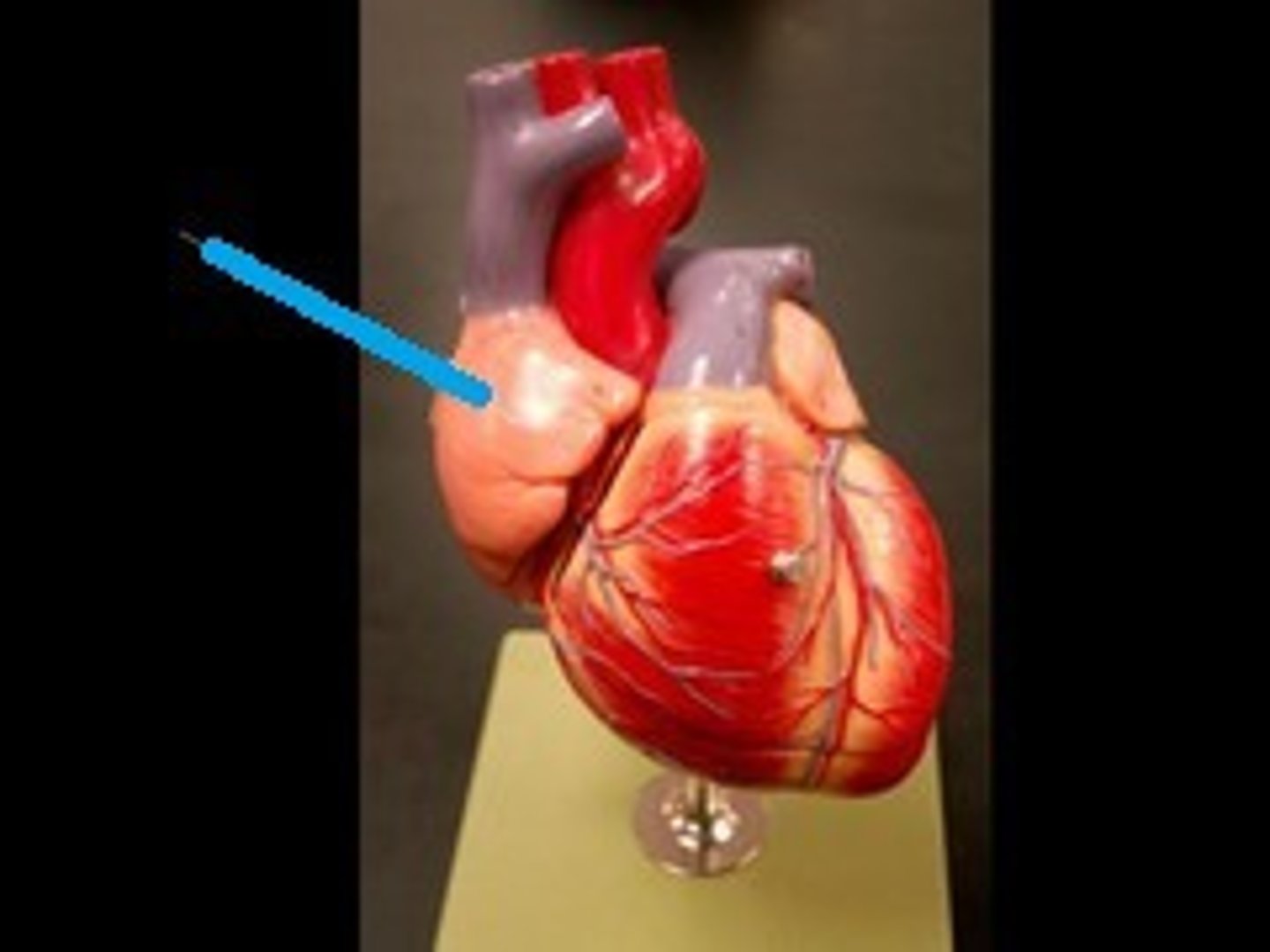
right ventricle (exterior)
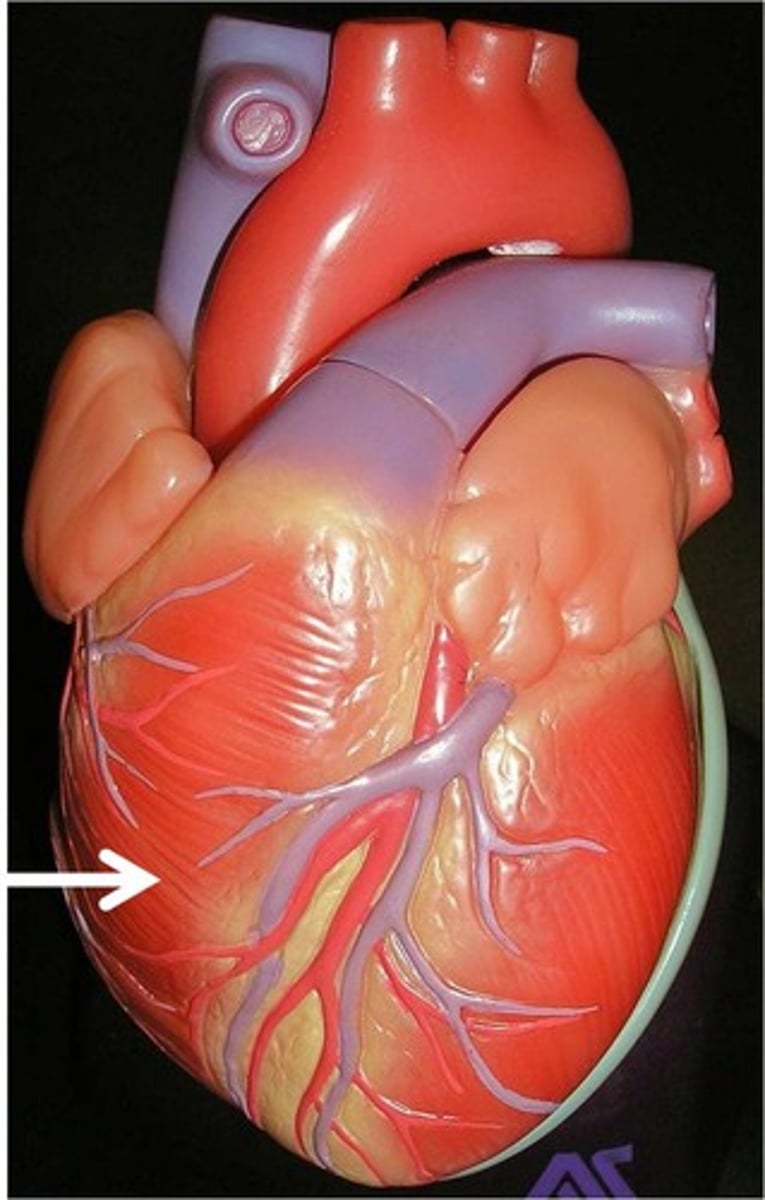
inferior vena cava
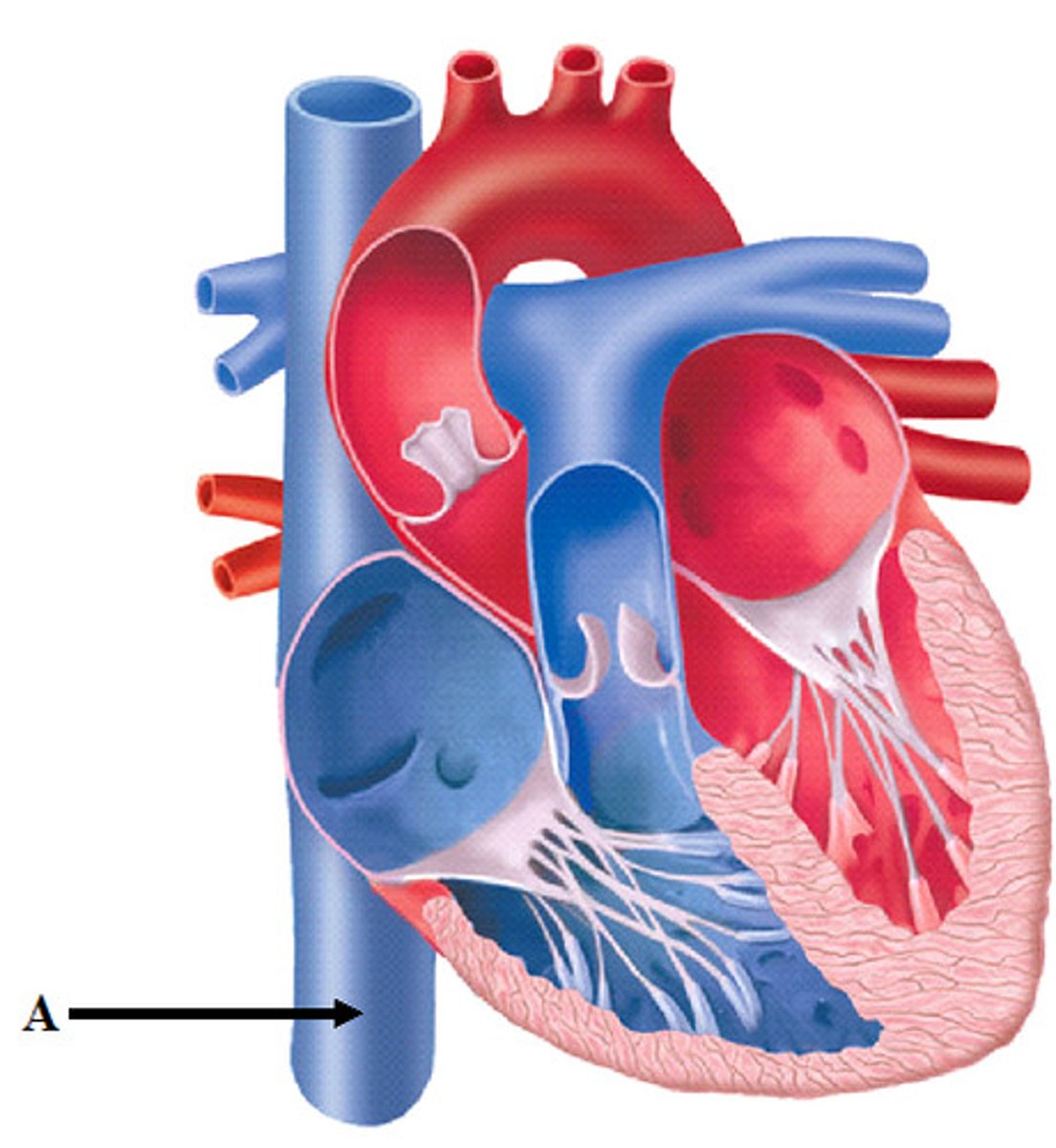
apex of heart
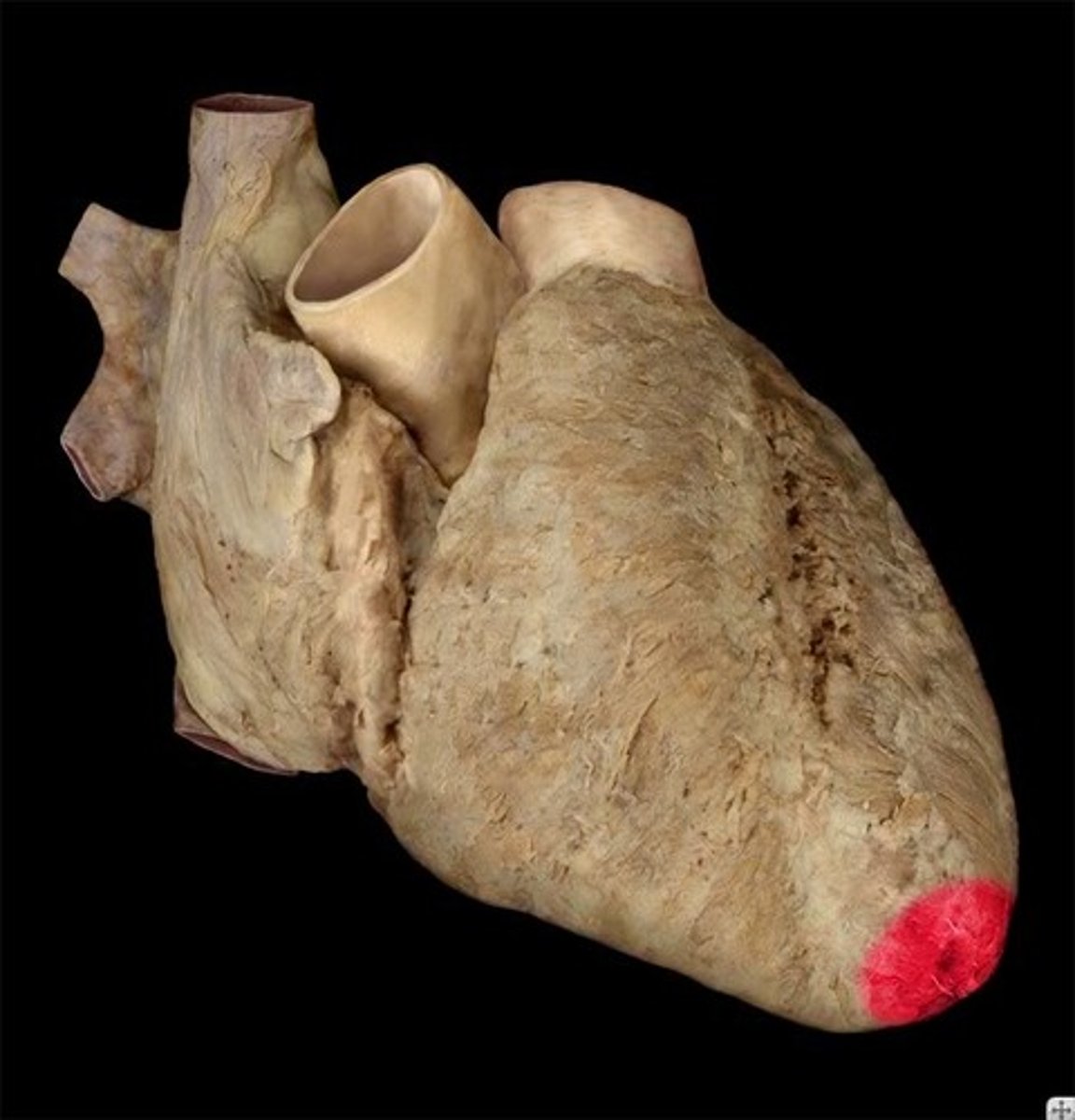
left ventricle (exterior)
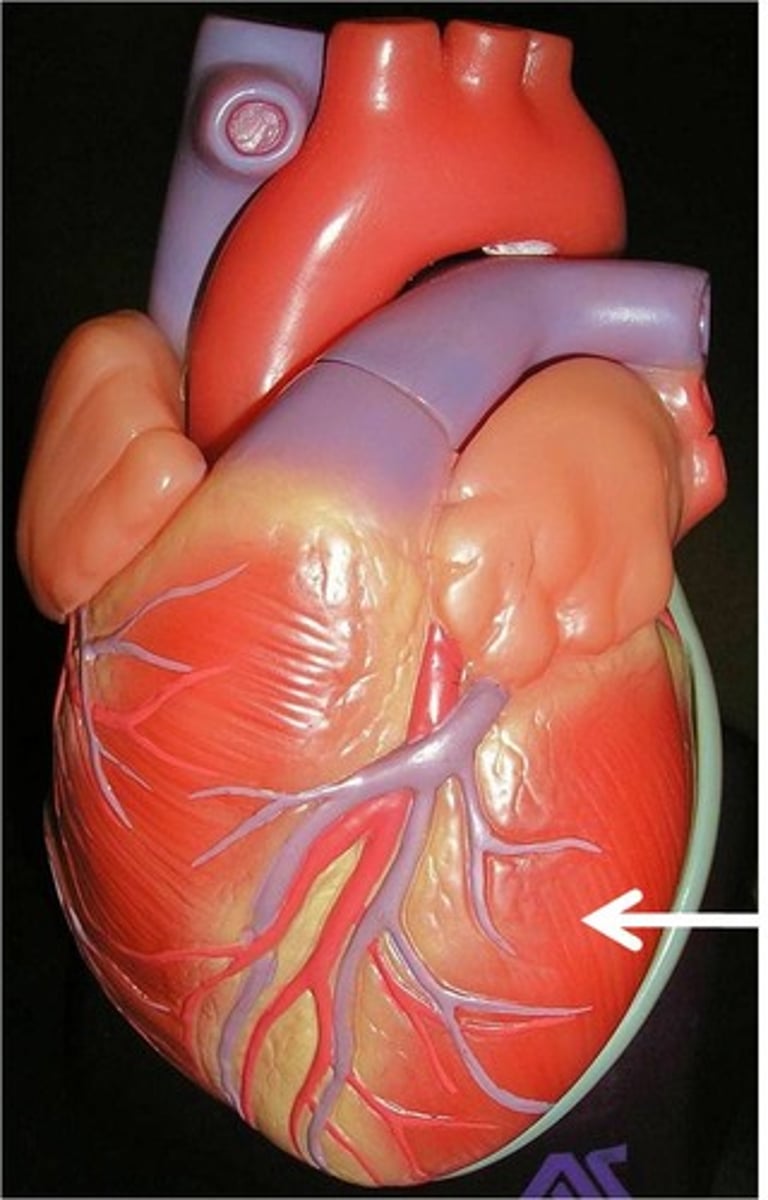
left atrium (exterior)
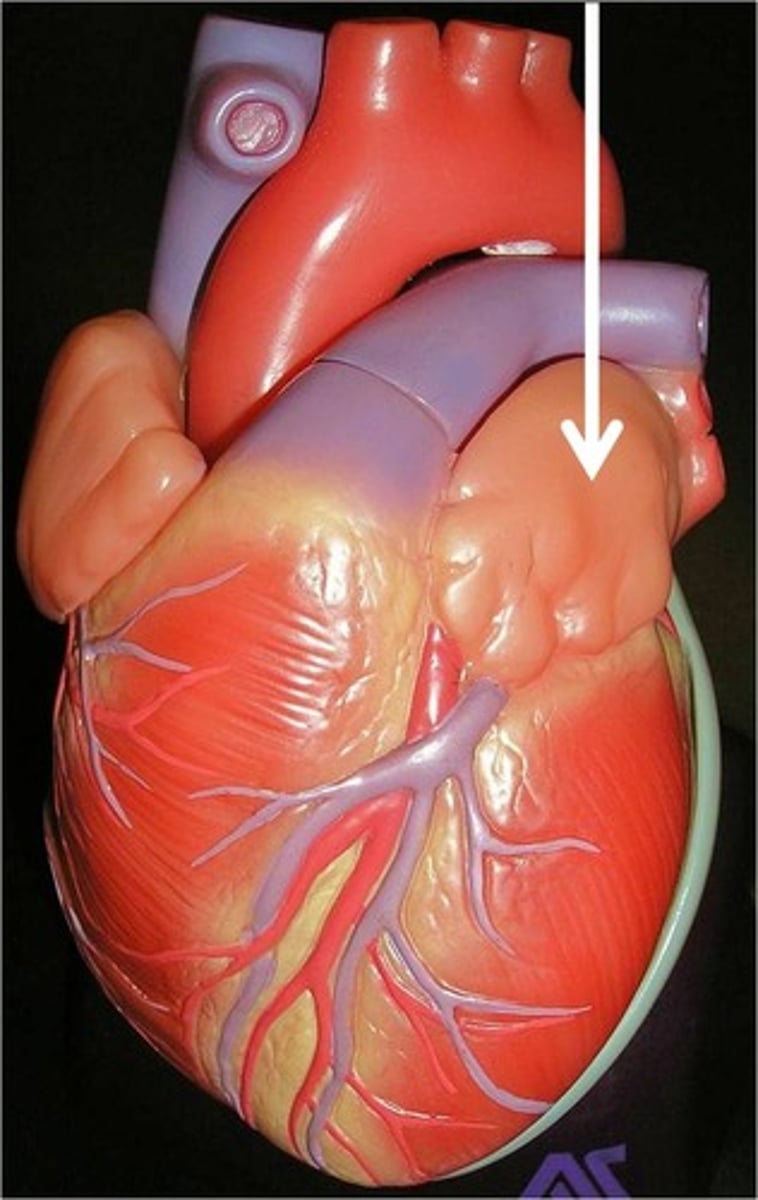
left pulmonary veins
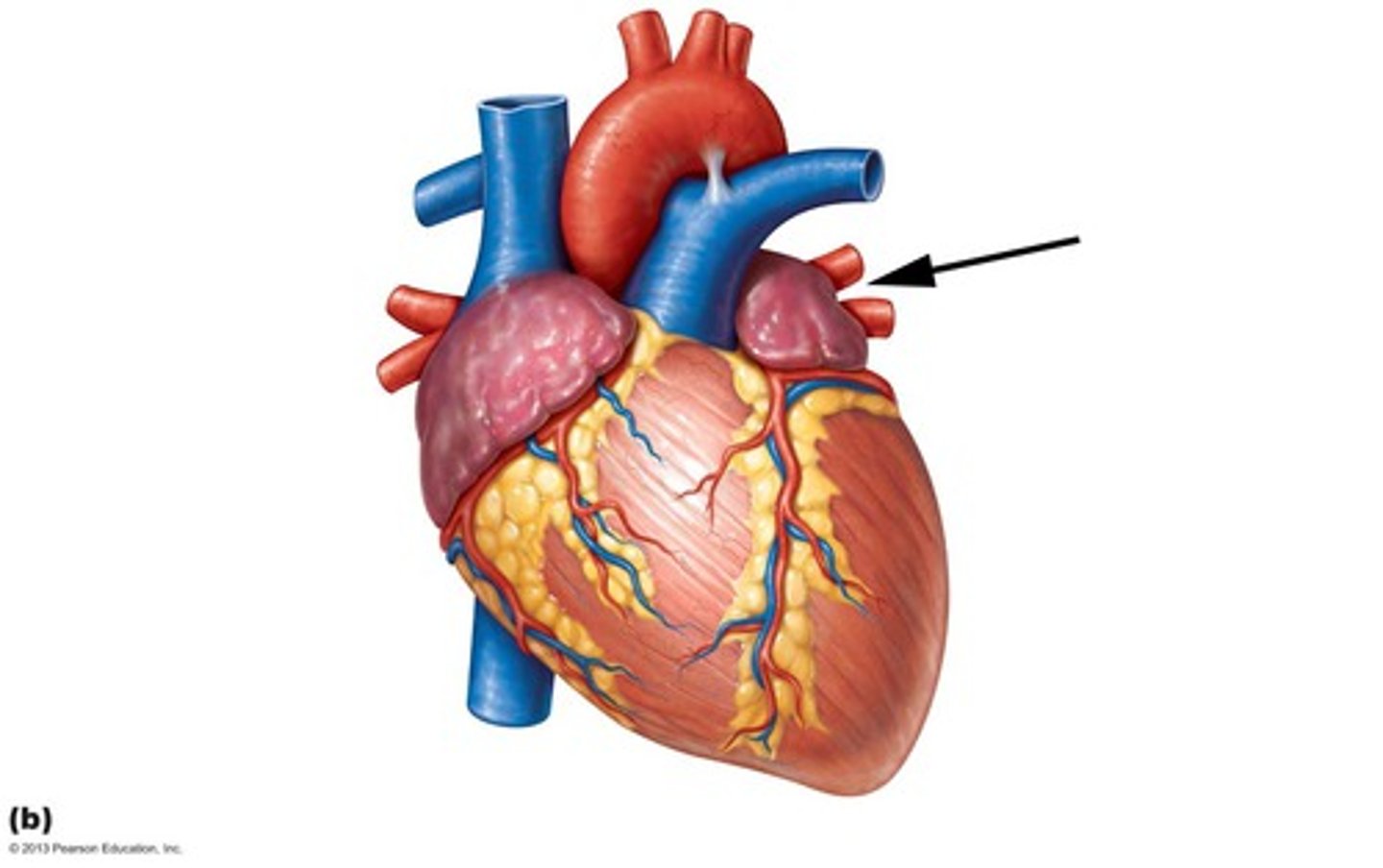
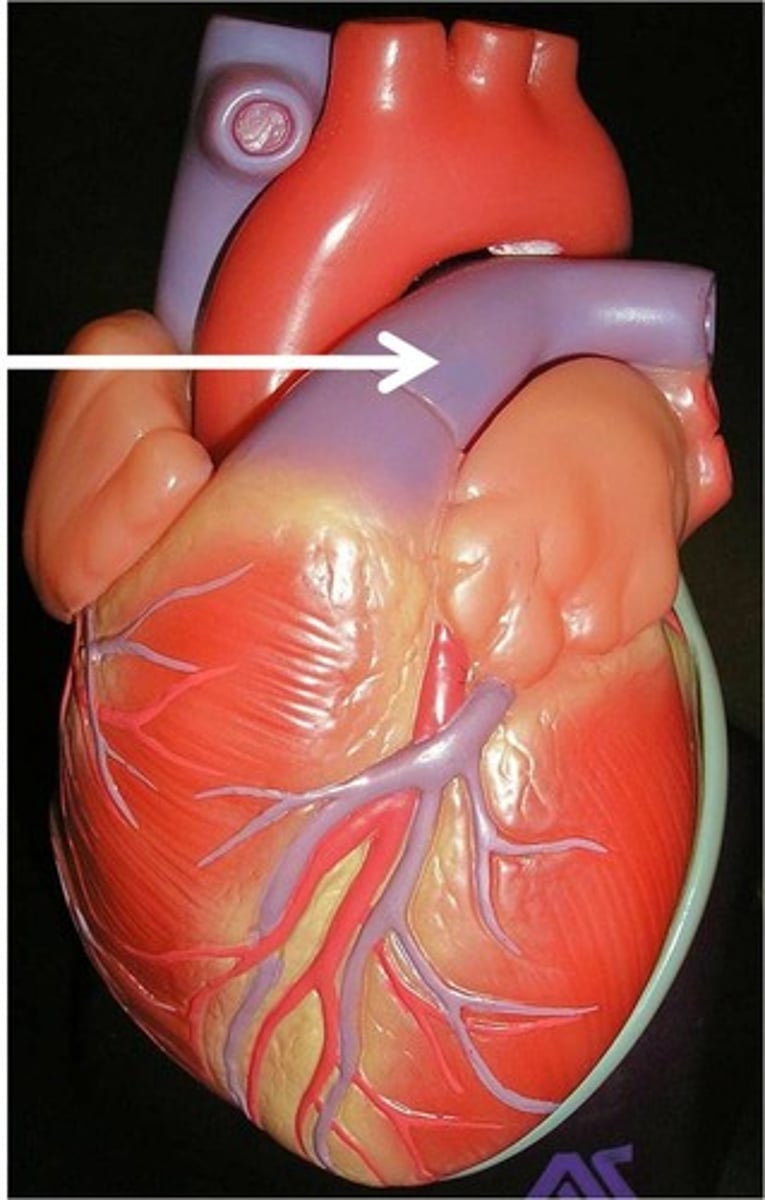
left pulmonary artery with pulmonary trunk
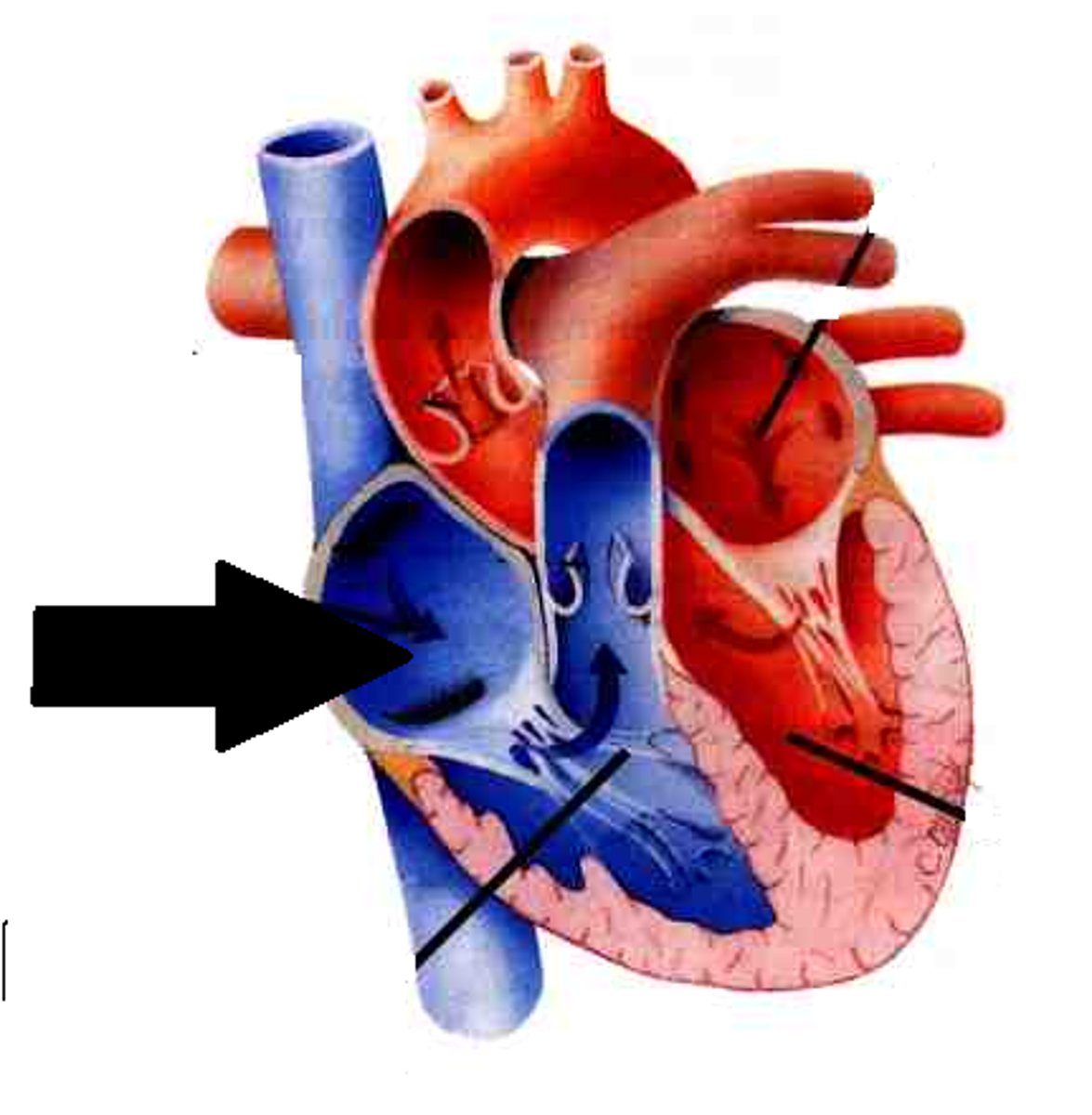
right atrium (interior)
pulmonary semilunar valve
right atrioventricular valve (tricuspid)
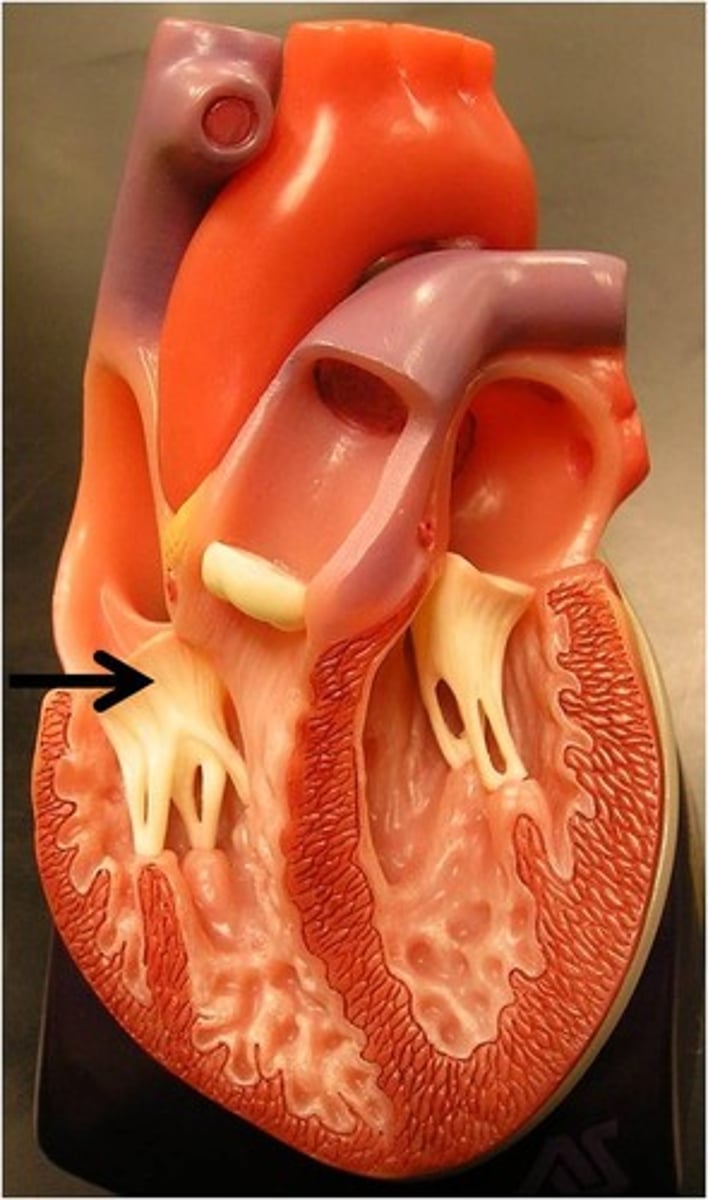
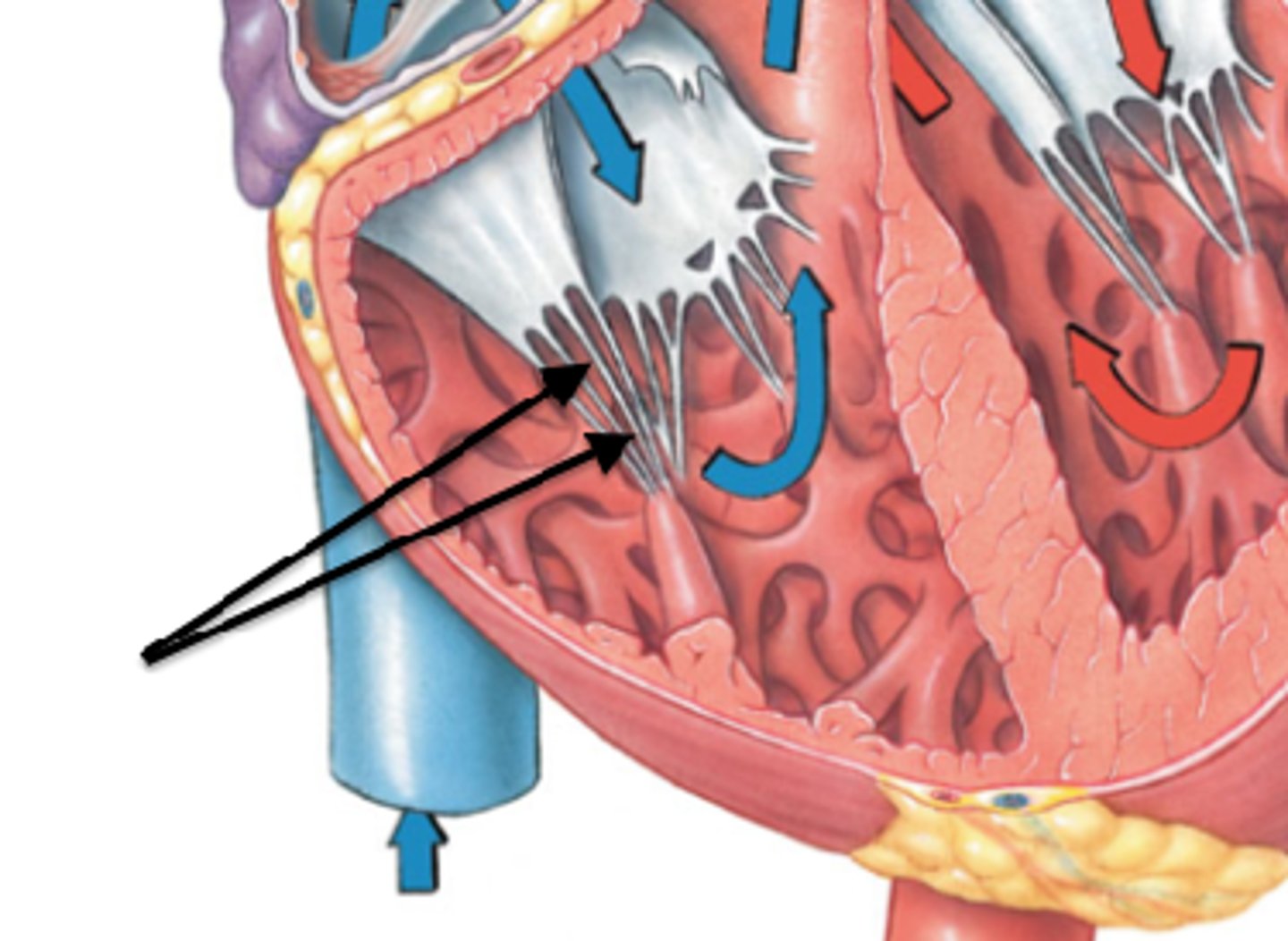
chordae tendineae
intraventricular septum
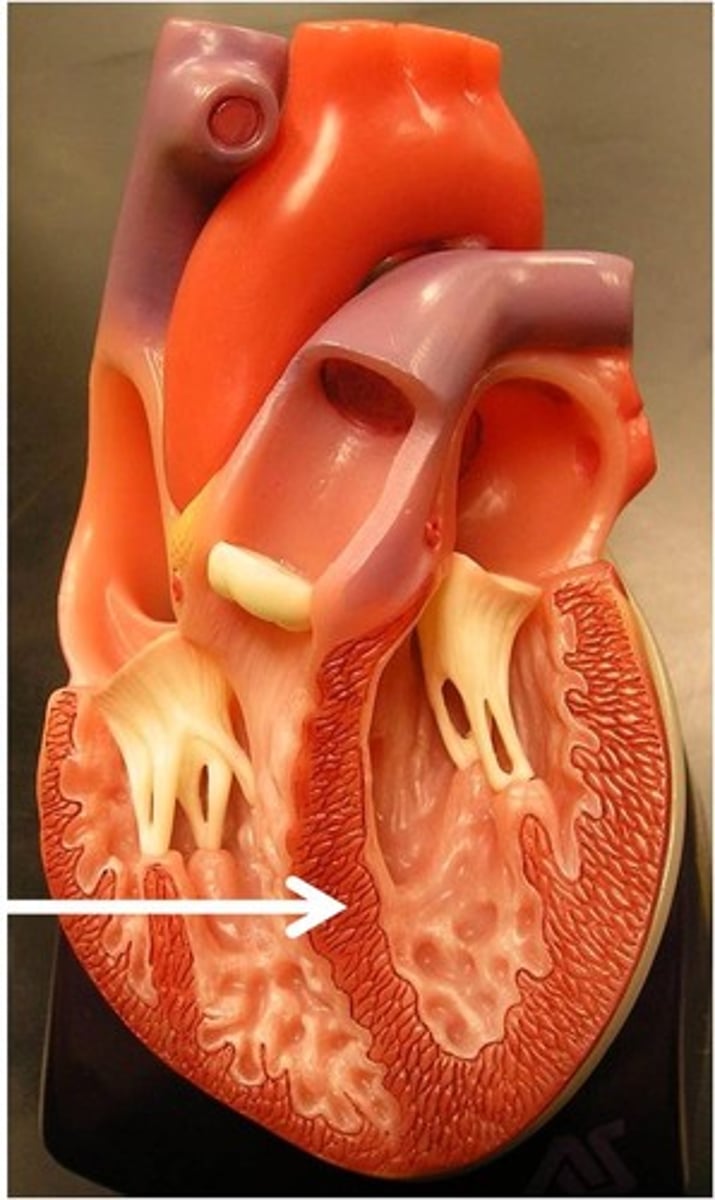
epicardium
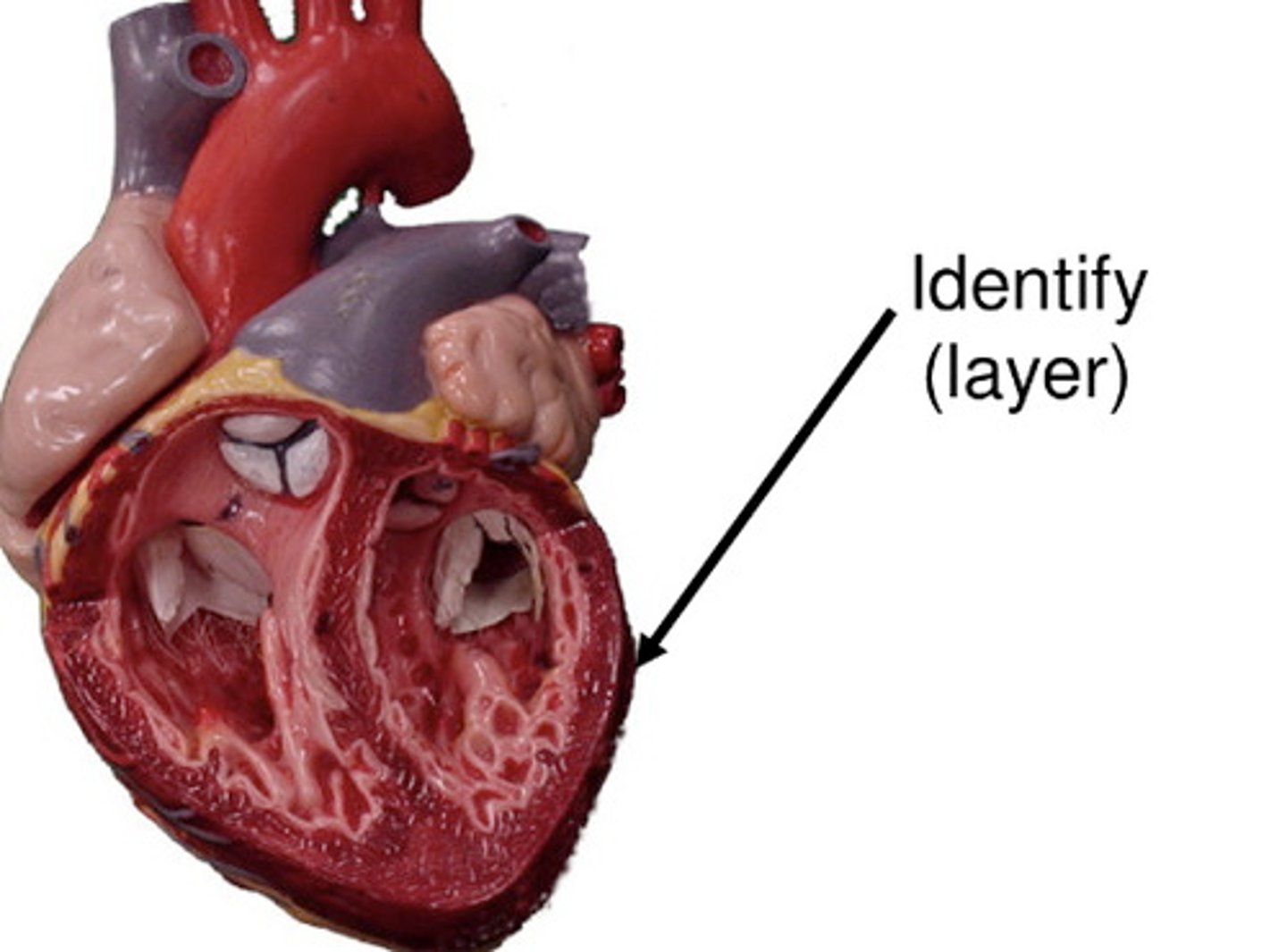
myocardium
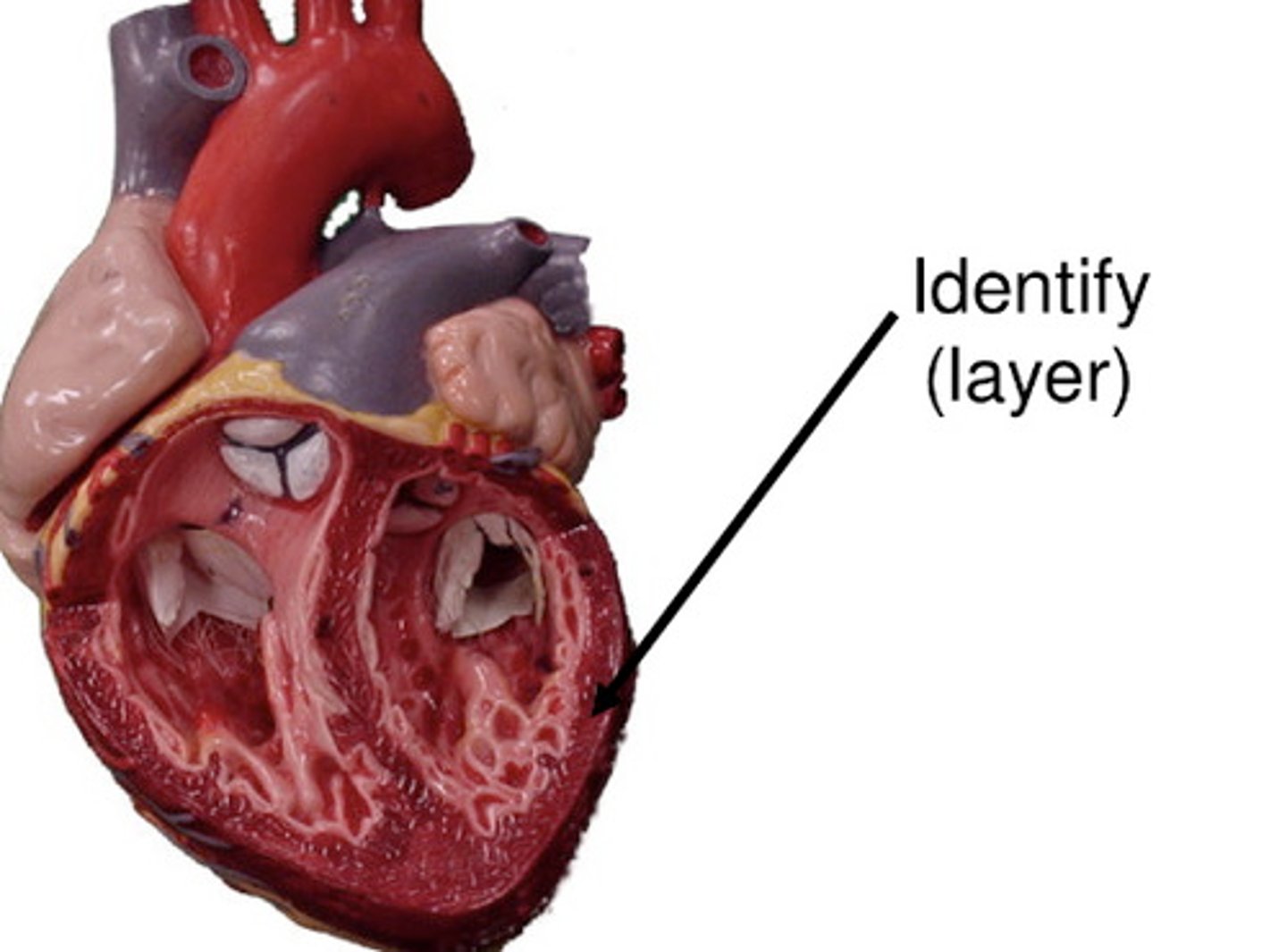
endocardium
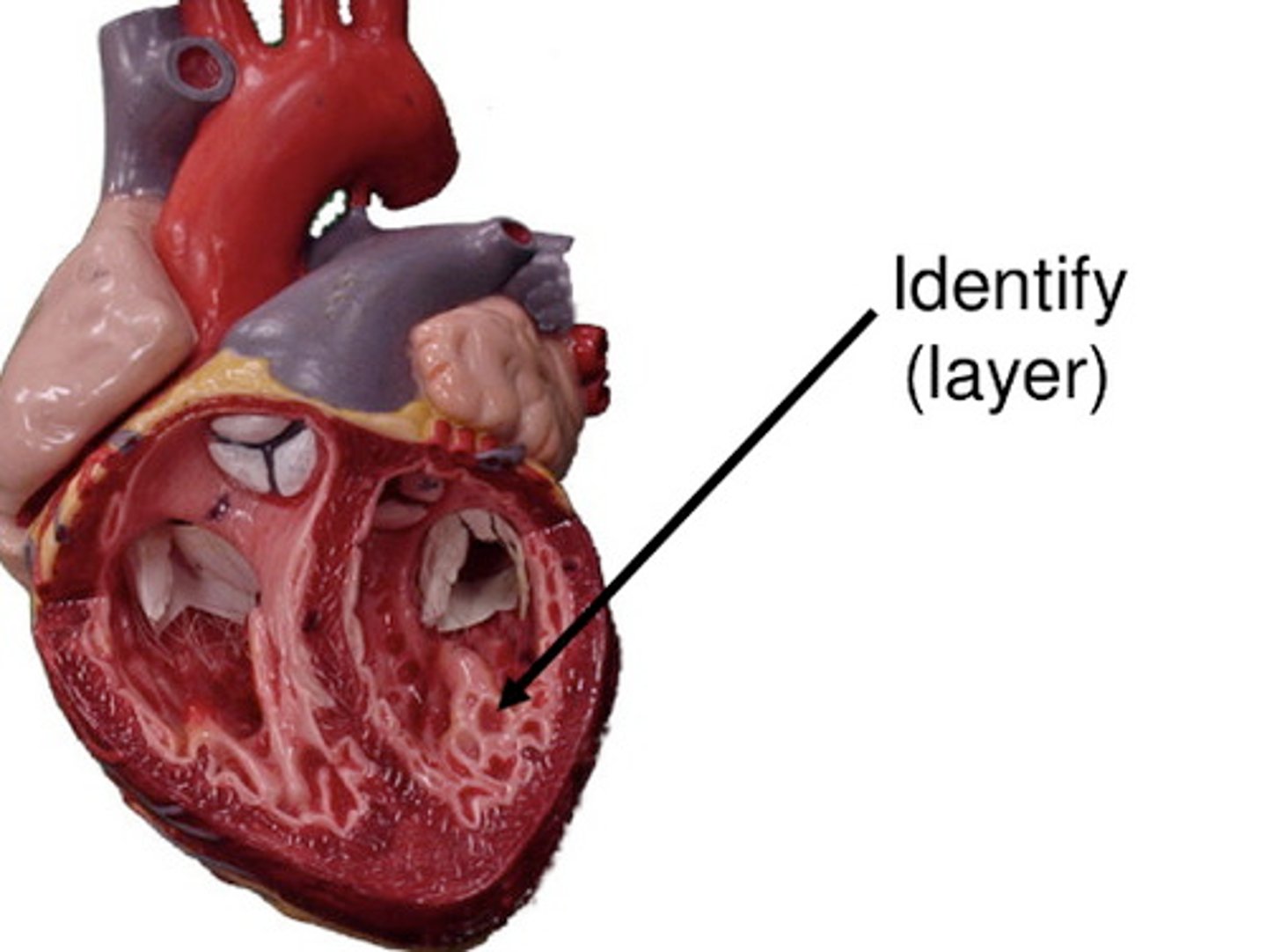
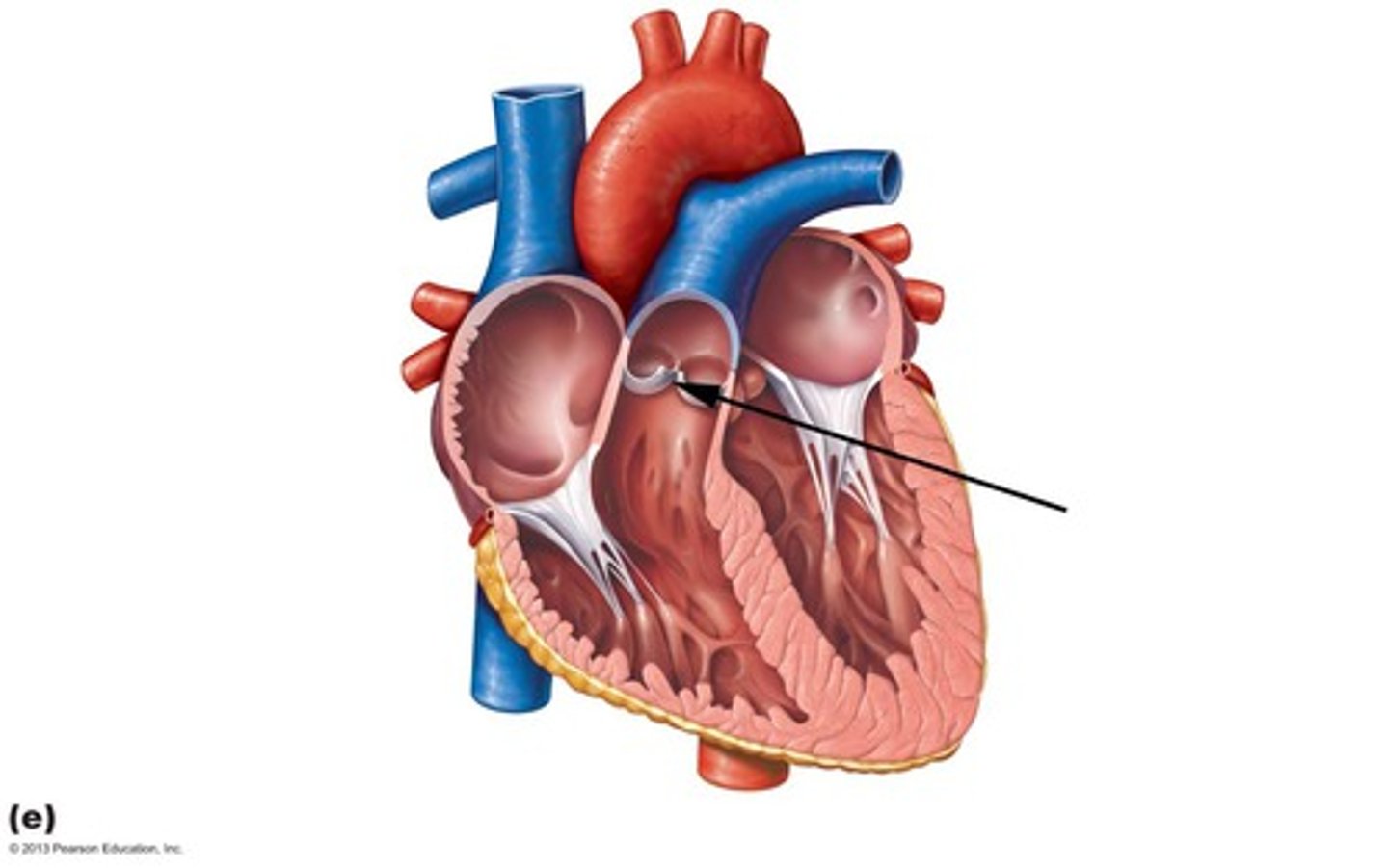
aortic semilunar valve
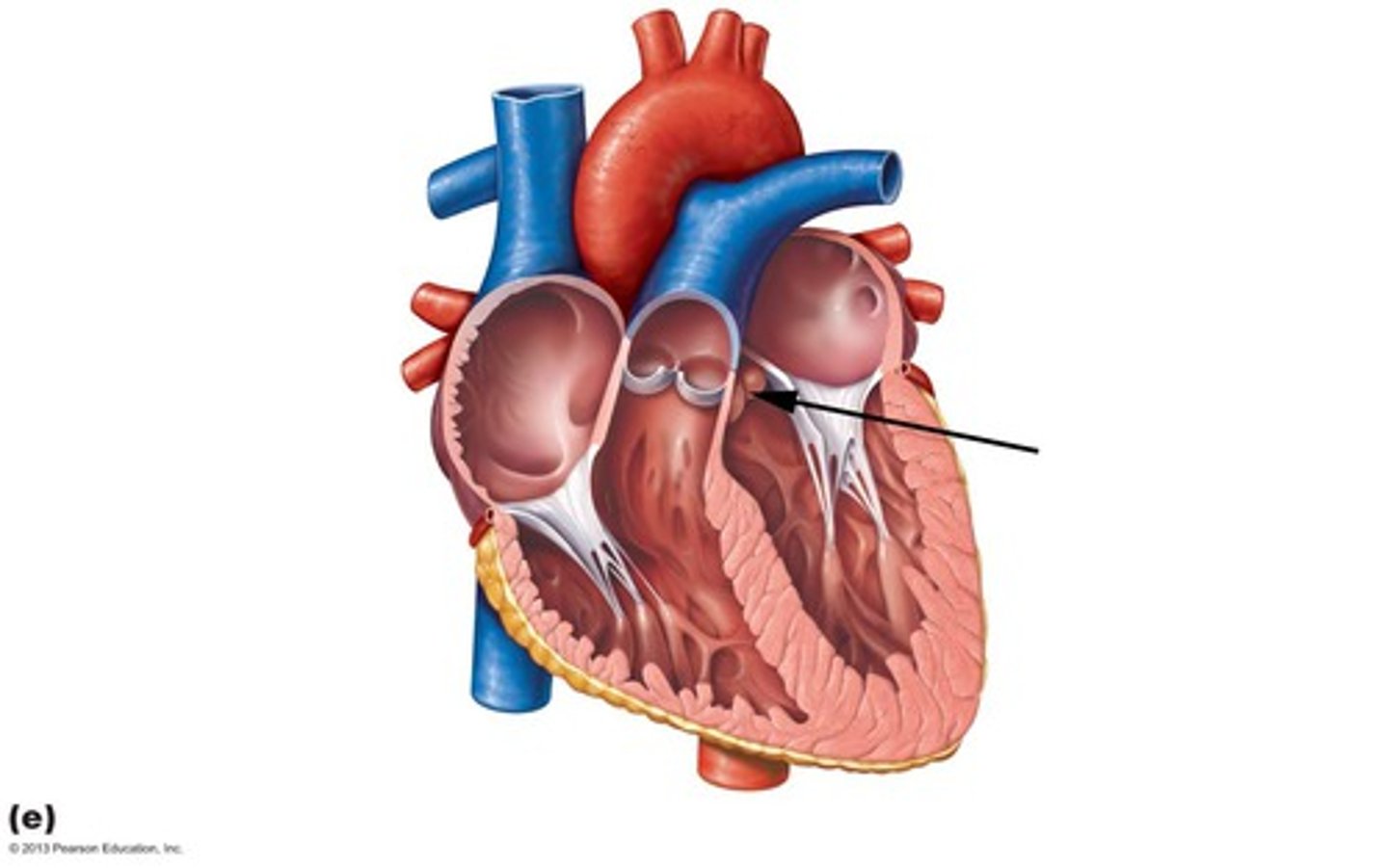
left atrioventricular valve (bicuspid)
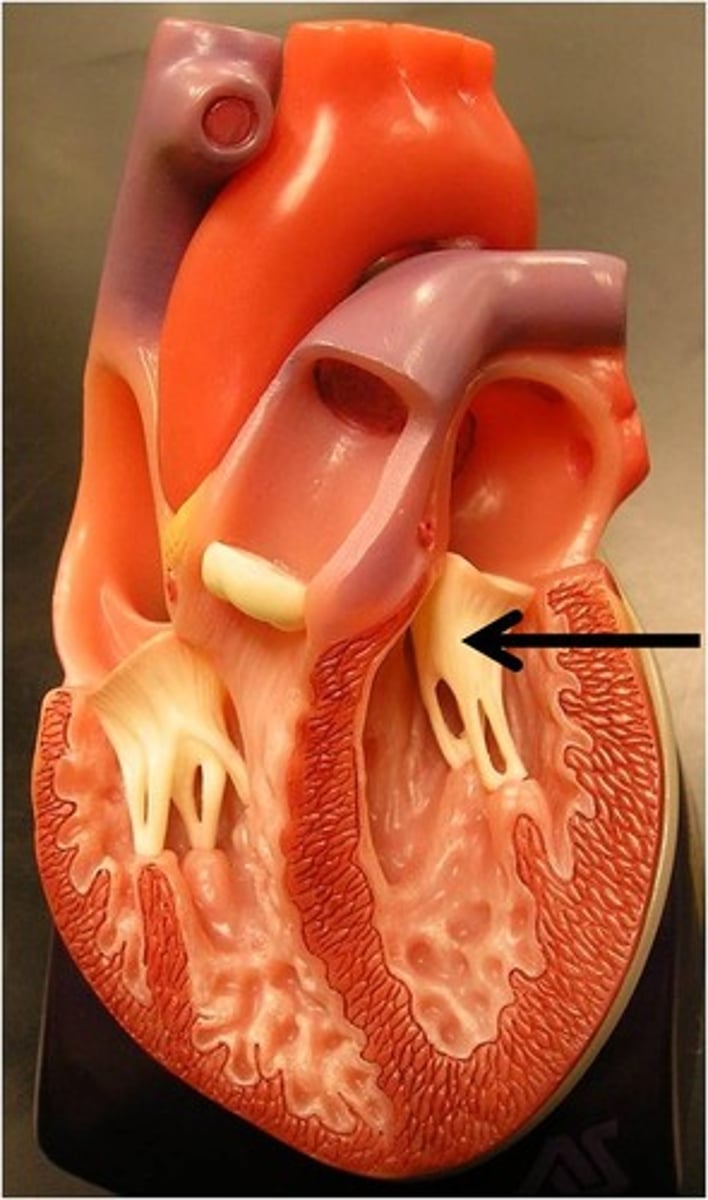
left atrium (interior)
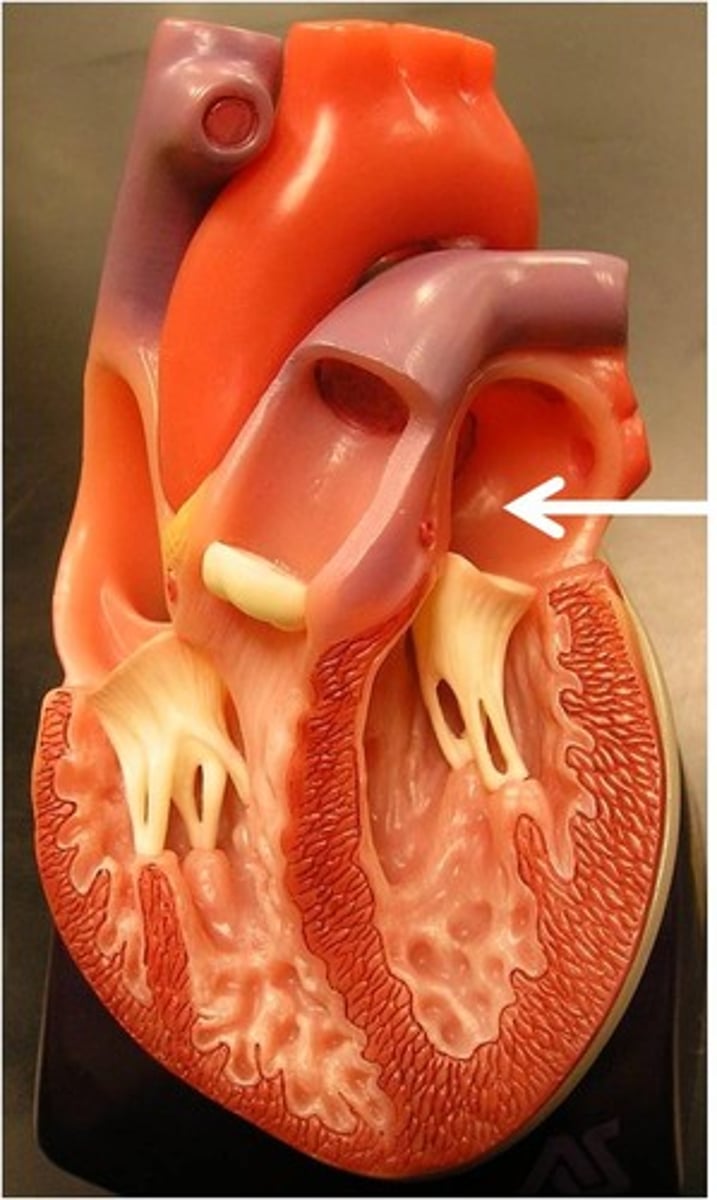
Sinoatrial (SA) node
"pacemaker" starts heartbeat at the right atrium
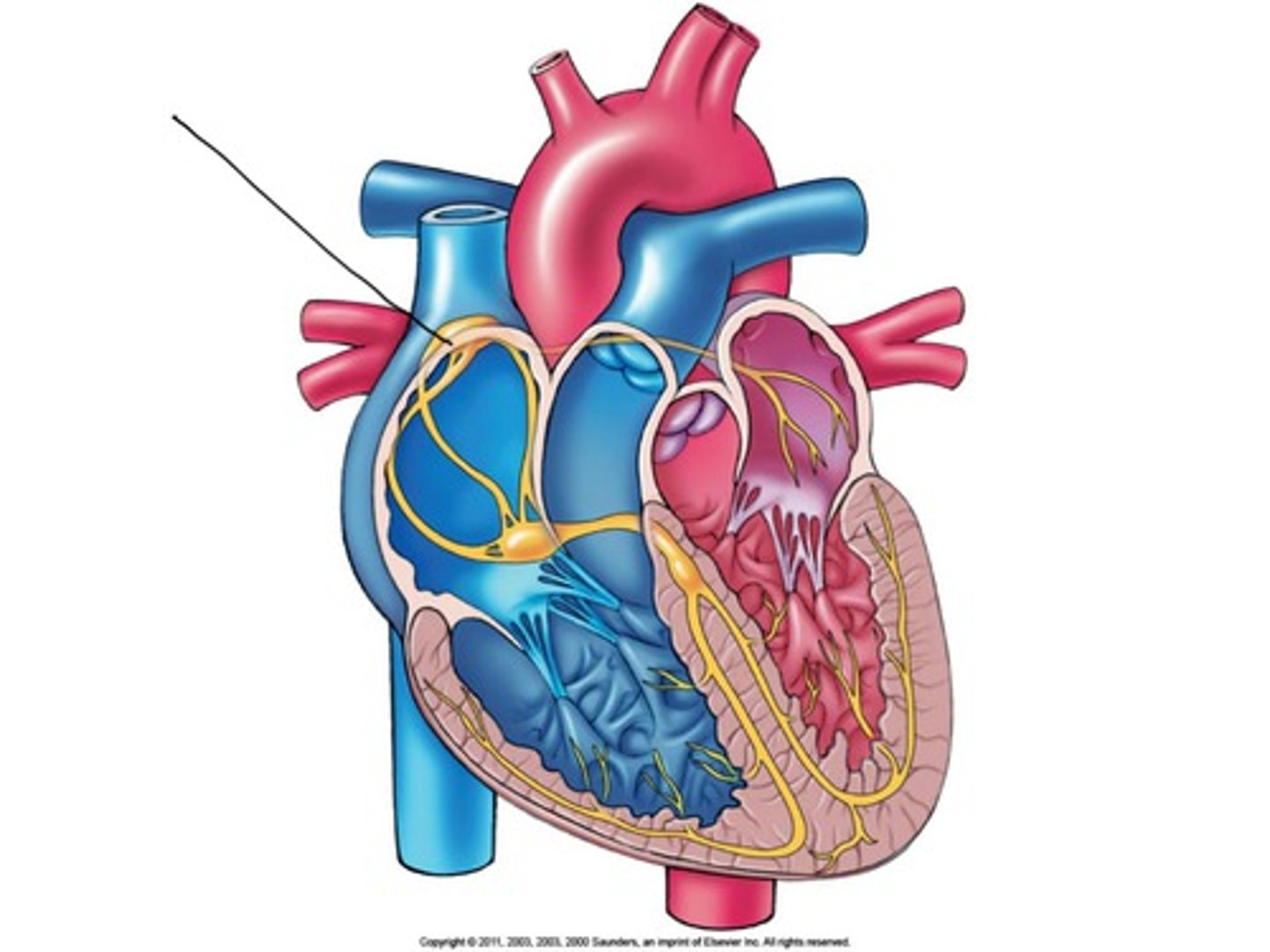
Atrioventricular (AV) node
allows cuspids to open
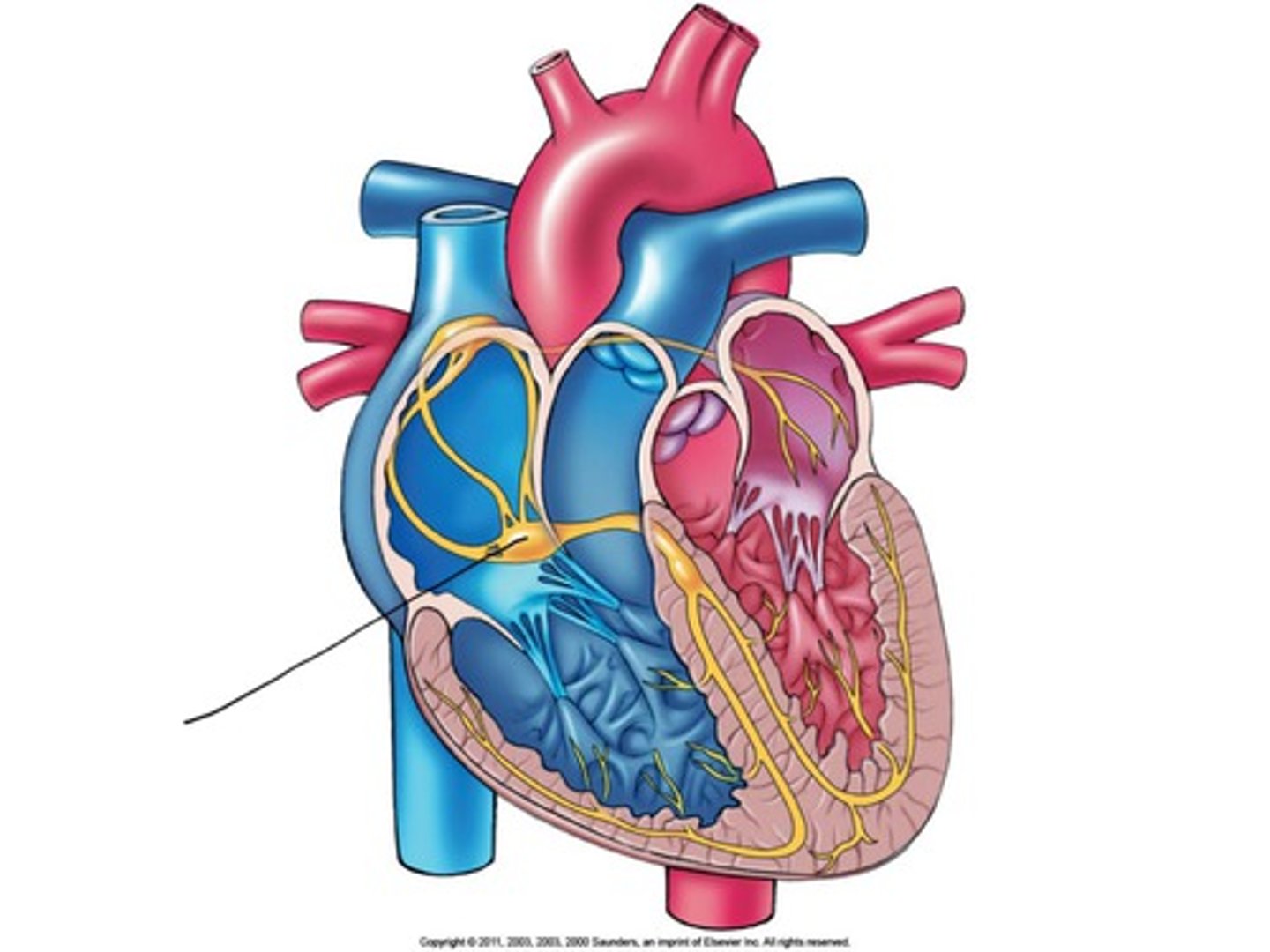
AV bundle
nerves that run down the introventricular septum
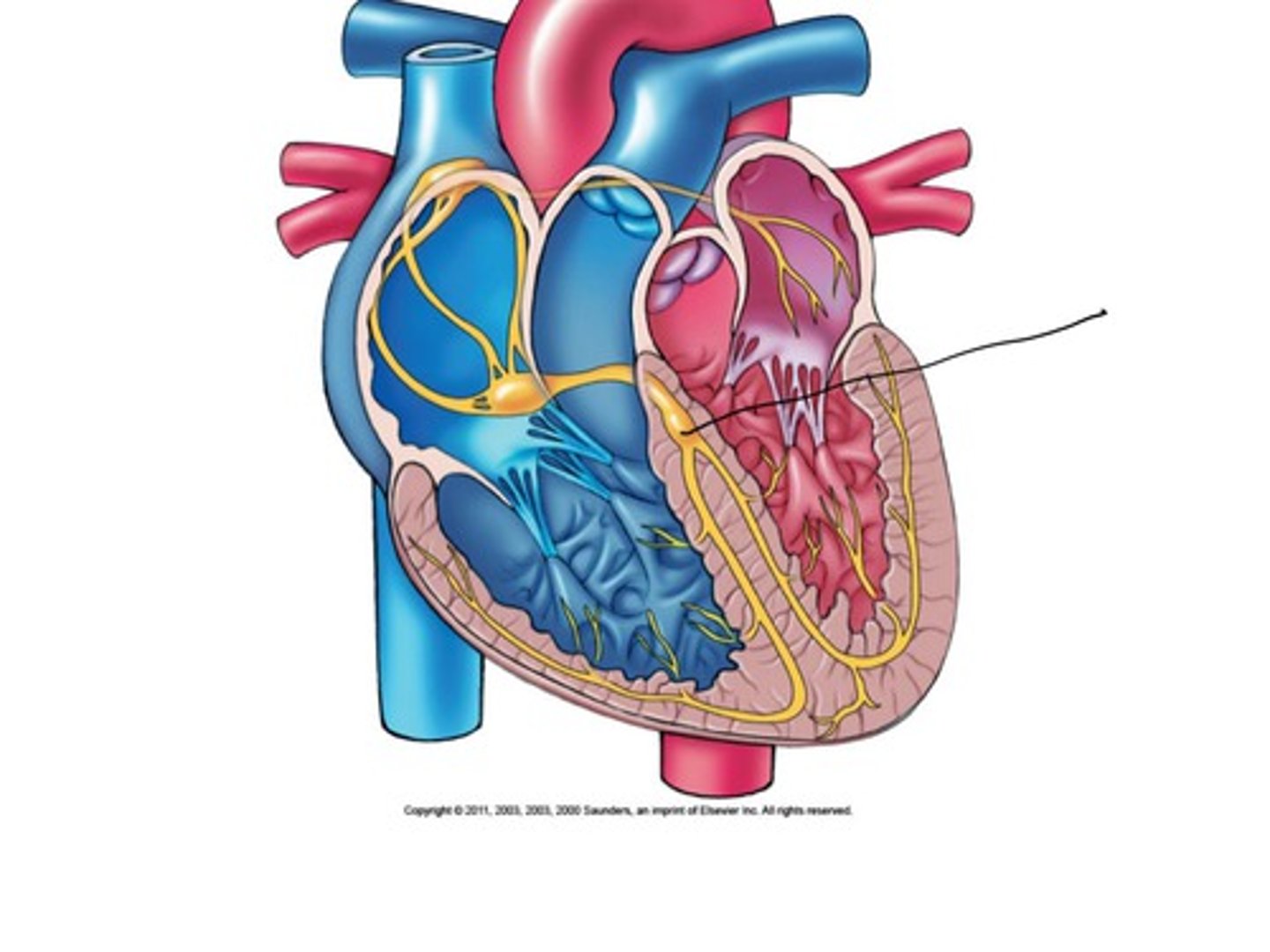
Purkinje fibers
branches into ventricles
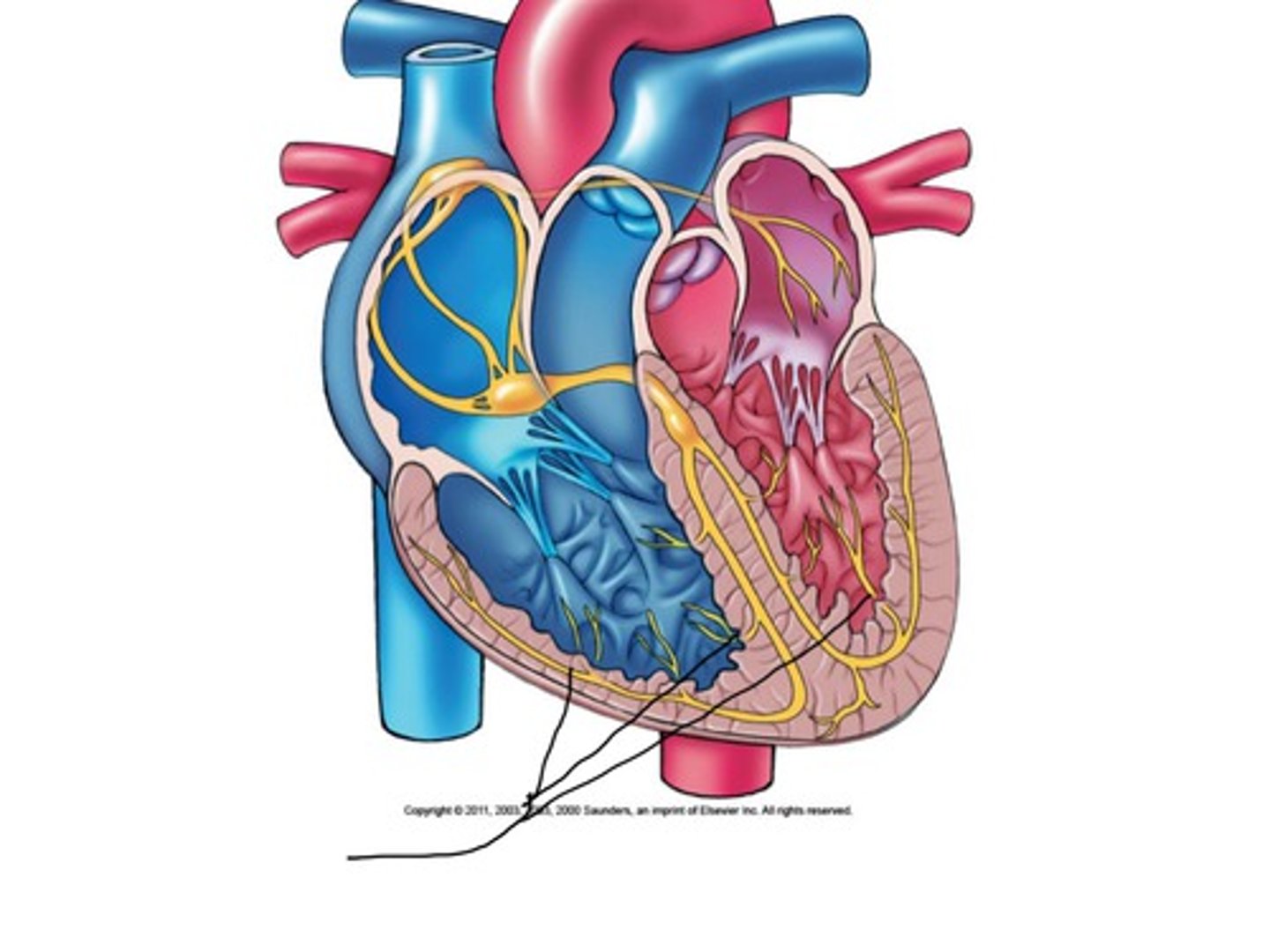
deoxygenated blood from vena cava enters the right atrium
blood through heart - step 1
blood goes from right artium, through tricuspid, into right ventricle
blood through heart - step 2
right ventricle pumps deoxygenated blood out the pulmonary artery
blood through heart - step 3
pulmonary artery carries blood to the lungs, where it releases CO2 and becomes oxygenated
blood through heart - step 4
oxygenated blood returns to the left atrium through pulmonary veins
blood through heart - step 5
Blood moves from left atrium, through bicuspid, into left ventricle
blood through heart - step 6
left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood through aorta
blood through heart - step 7
aorta branches out and delivers oxygenated blood to all parts of the body
blood through heart - step 8