The Retina
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
From Study Guide
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
What are the two types of photoreceptor cells and their functions?
Rods see in dim light/night, and cones see color and detail in bright light.
What is a retinal detachment and how is it treated?
t’s when the retina peels away from the back of the eye. Treated with laser surgery or freezing (cryotherapy) to reattach it.
What is papilledema?
Swelling of the optic disc caused by increased pressure in the skull.
What area of the retina gives the clearest vision?
The fovea in the macula.
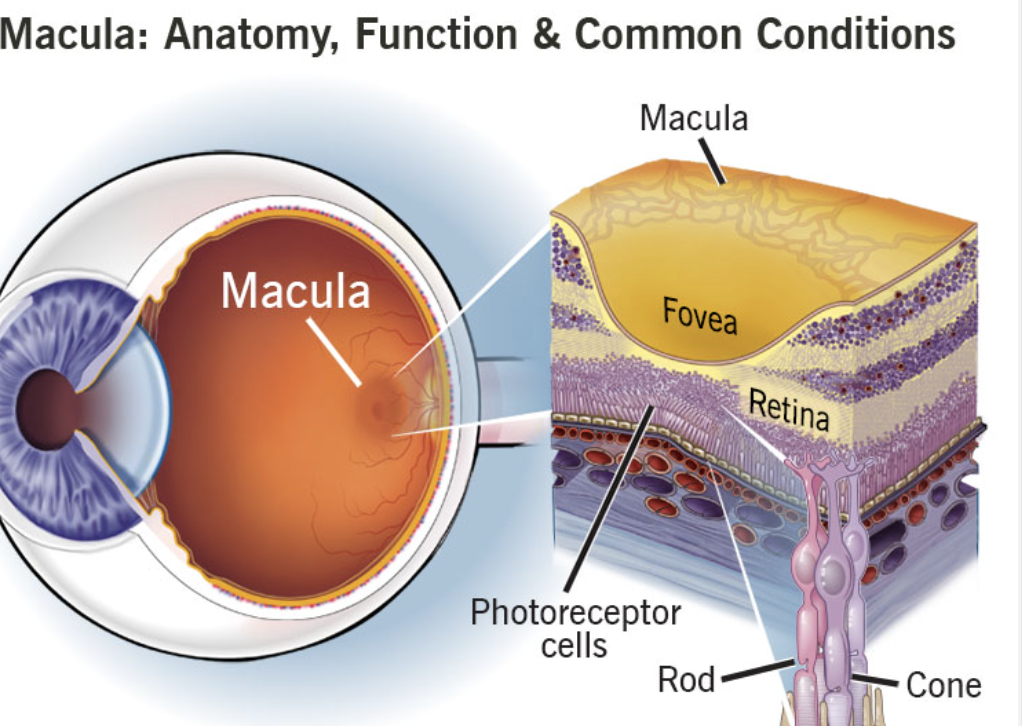
What is the first layer of the retina with a single layer of pigmented cells?
The retinal pigment epithelium (RPE).
Which layer contains ganglion cells that form the optic nerve?
The nerve fiber layer (NFL) — sends signals for visual acuity.
What does the optic nerve do?
Carries visual messages from the retina to the brain.
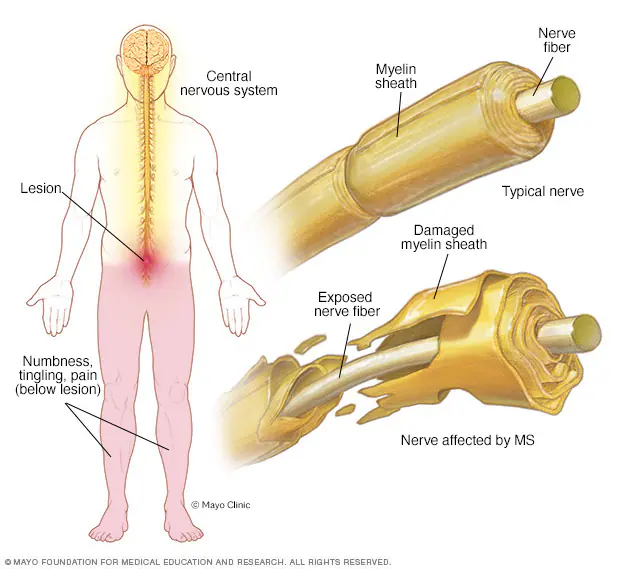
What’s the inflammation of the optic nerve called?
Optic neuritis.
What’s another name for the retina?
Nervous tunic.
What is the most anterior part of the retina?
The ora serrata — scalloped edge marking the retina’s front end.
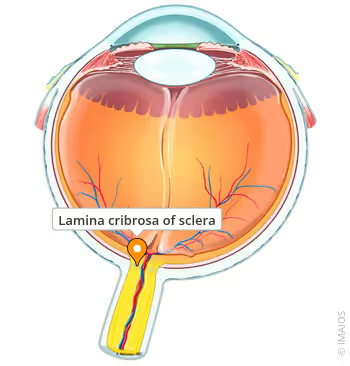
What is the lamina cribrosa?
A sieve-like part of the sclera where the optic nerve exits.
What disease is linked with optic neuritis?
Multiple sclerosis (MS).
What is papilledema associated with?
Increased intracranial pressure.
Why is the retina important?
It turns light into signals so the brain can see images.
What area of the retina helps with night and dim light vision?
The peripheral retina (full of rods).
What diseases can be seen on fundus photography?
Diabetes, hypertension, glaucoma, macular degeneration, and optic nerve swelling.