BIOL 1105: Lesson 08: Energy from Organic Molecules I
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
How do autotrophs obtain energy?
Produce their own ATP and organic molecules through photosynthesis
How do heterotrophs gain energy?
They live on organic molecules produced by autotrophs
How do cells extract energy?
Through oxidizing organic molecules
All organisms use ________ ____________ to extract energy from chemical bonds of organic molecules.
cellular respiration
Cellular Respiration involves a series of _________ _________ reactions.
enzyme catalyzed
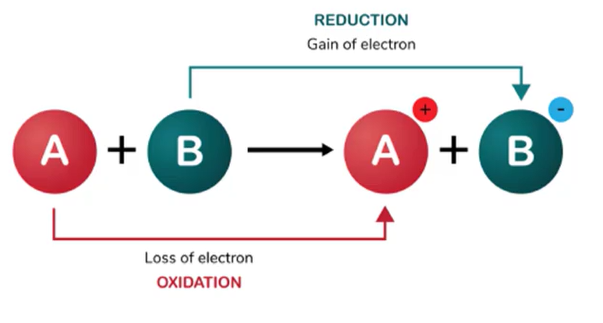
Oxidation involves the gain of electrons (true or false)?
False; oxidation = loss of electrons
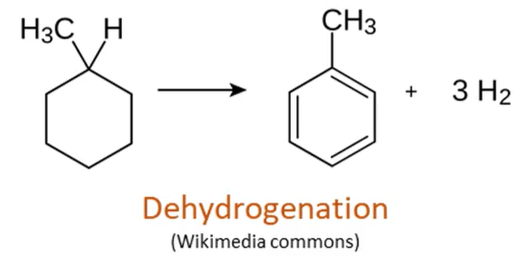
Dehydrogenation
loss of protons
Harvested electron undergo a series of __________ reactions.
redox
Electrons _________ (lose/gain) energy with each transfer.
lose energy
What do redox reactions transfer?
electrons and associated energy
What happens to released energy from a reaction?
It can be lost as heat or converted to ATP
Electrons posses energy when they are….
harvested from organic molecules
When are energy-depleted electrons transferred to the final electron acceptor protein?
After multiple redox reactions
Cofactor
small chemicals that assist enzymes
(True or False) Electron carriers cannot be reversed once oxidized or reduced.
False; they can be easily reversible
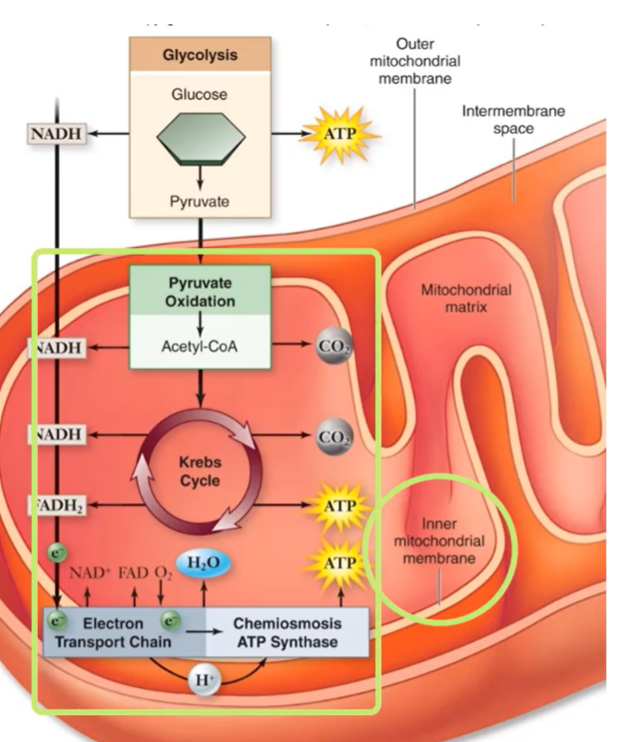
What are the Four Stages of Glucose Oxidation?
(1) Glycolysis, (2) Pyruvate oxidation, (3) Krebs Cycle, (4) Electron transport chain and chemiosmosis
Glycolysis converts ______ Glucose(s) into ______ pyruvate(s)
(1) One, (2) Two
What are the two phases of glycolysis?
(1) Energy input, (2) Energy production (ATP)
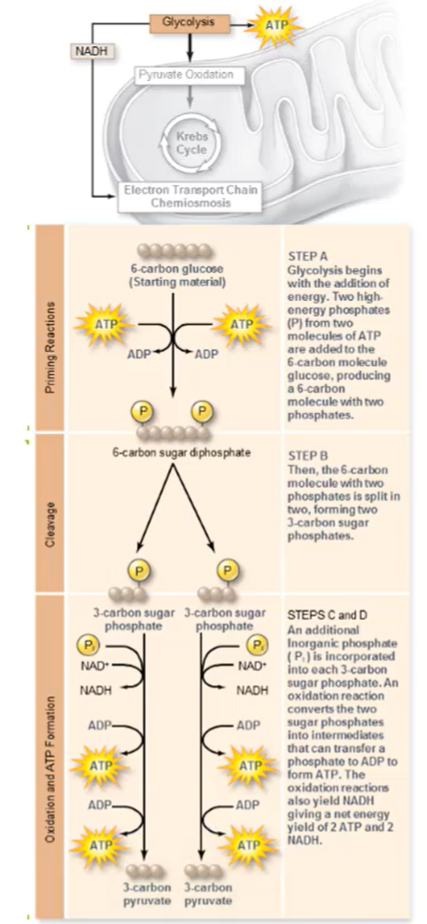
What is Glucose first converted into?
Two G3P Molecules
What does the generation of G3P require?
Energy input
Glucose involves the ________ of 2 ______ molecules
(1) Hydrolysis, (2) ATP
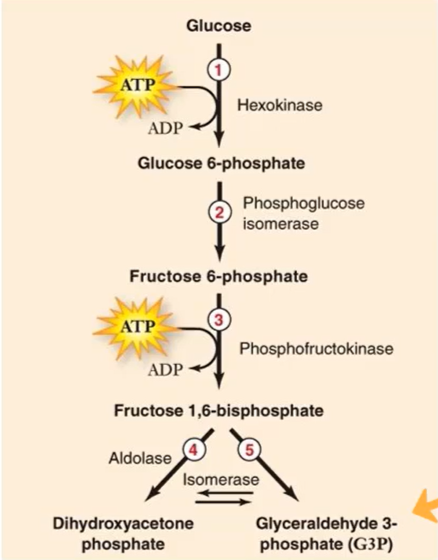
What is each G3P molecule converted into?
Pyruvate
NAD+ => NADH
G3P is oxidized
After Pi is added to G3P, each Pi (4 total) will be….
transferred to ADP
What are the products of glycolysis?
2 ATP (net) + 2 NADH
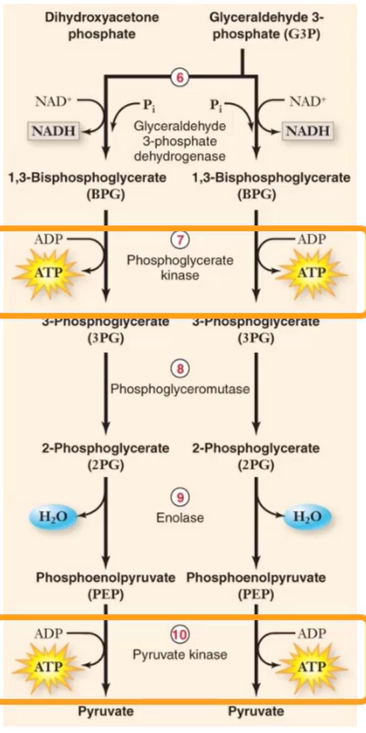
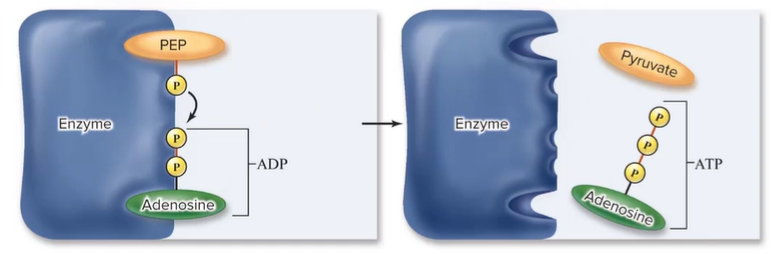
How does ATP synthesis occur during glycolysis?
Substrate-level phosphorylation
ATP Synthesis in glycolysis is _________ ___________.
enzyme catalyzed
Oxidative phosphorylation
allows eukaryotes to synthesize much more ATP in the presence of oxygen
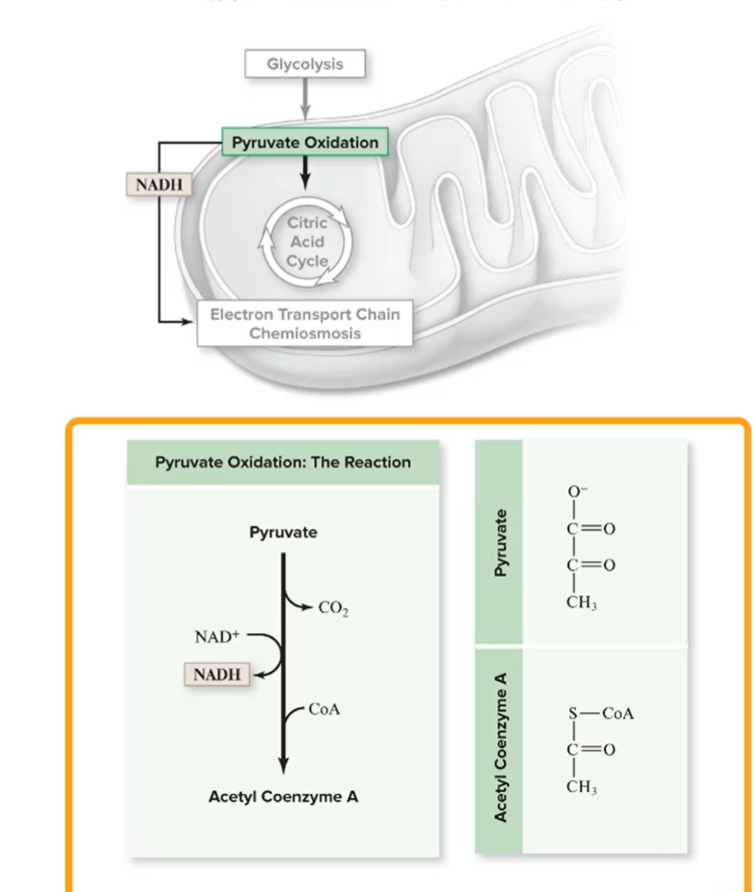
Where does pyruvate oxidation occur during aerobic respiration?
the mitochondrial matrix in eukaryotes
Plasma membrane of prokaryotes
catalyzed by pyruvate dehydrogenase
What is a coenzyme?
small organic molecule that functions as a cofactor
Each pyruvate molecule is used to generate…
1 CO2
1 NADH
1 acetyl-CoA => then fed into krebs cycle
In the Krebs cycle, oxidation of the acetyl group is generated by ___________ _______________.
pyruvate oxidation
Where does the Krebs cycle occur?
In the matrix of the mitochondria
What are the three parts of the nine steps in Krebs cycle?
Acetyl-CoA + oxaloacetate -> citrate
Citrate rearrangement and decarboxylation (2 CO2 released)
Regenerations of oxaloacetate
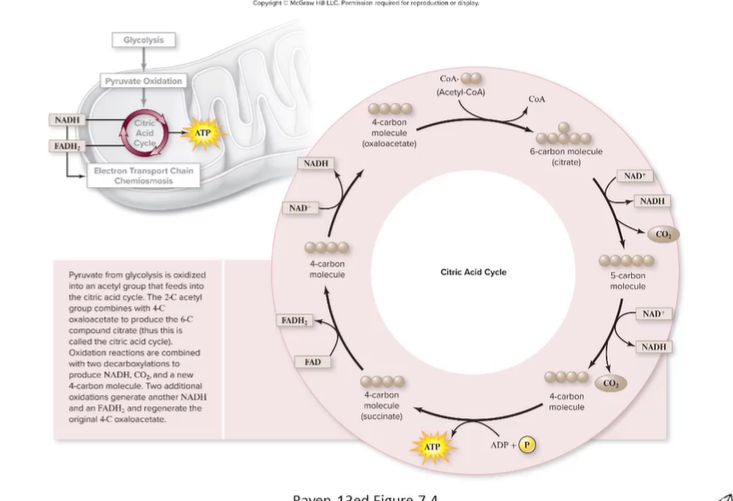
What is decarboxylation?
process by which a carbon atom in the form of CO2 breaks off from a larger organic molecule. Catalyzed by pyruvate dehydrogenase ( a multienzyme complex)
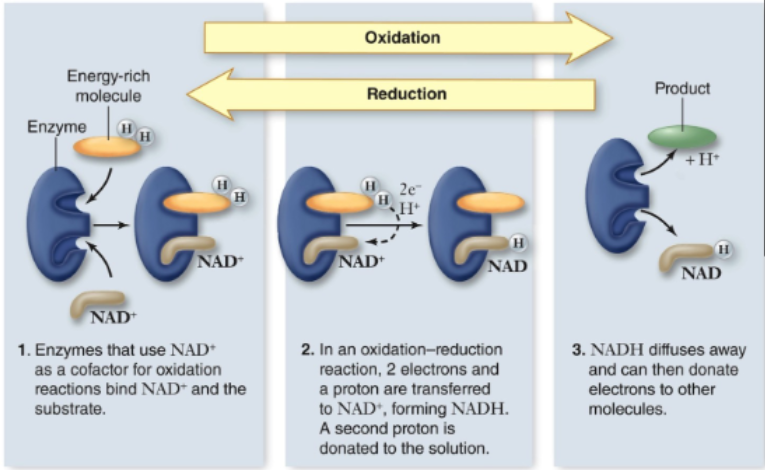
NAD+ Accepts _________ to Form________.
(1) Electrons, (2) NADH
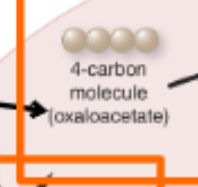
The Krebs cyclic pathway starts and ends with ______________.
oxaloacetate
Per Glucose, what does the Krebs Cycle produce?
2 ATP
6 NADH
2 FADH2