CHAPTER 3: THE E-MARKETING PLAN (copy)
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
The e-marketing plan is
a blueprint for e-marketing strategy formulation and implementation.
The plan serves as a road map to guide the firm, allocate resources, and make decisions.
Napkin plan
Entrepreneurs jot down ideas on a napkin.
Large companies create a just-do-it, activity-based, bottom-up plan.
The Venture Capital E-Marketing Plan
A more comprehensive plan for entrepreneurs seeking start-up capital
SOURCES OF FUNDING
• Bank loans
• Private funds
• Angel investors
• Venture capitalists (VCs)
E-MARKETING PLAN
7 steps
1. Situation analysis
2. E-Marketing strategic planning
3. Objectives
4. E-Marketing strategy
5. Implementation plan
6. Budget
7. Evaluation plan
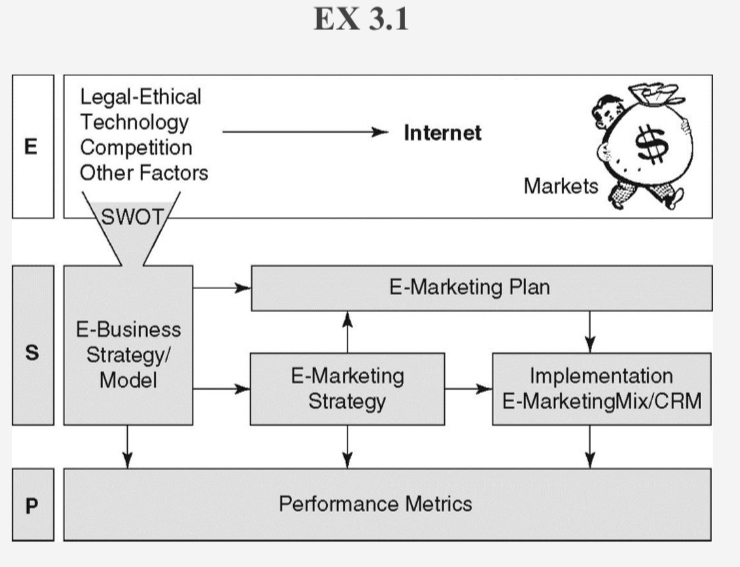
E-MARKETING PLAN
STEP 1: SITUATION ANALYSIS
• Review the firm’s environmental and SWOT analyses.
• Review the existing marketing plan and any other information that can be obtained about the company and its brands.
• Review the firm’s e-business objectives, strategies, and performance metrics.
E-MARKETING PLAN
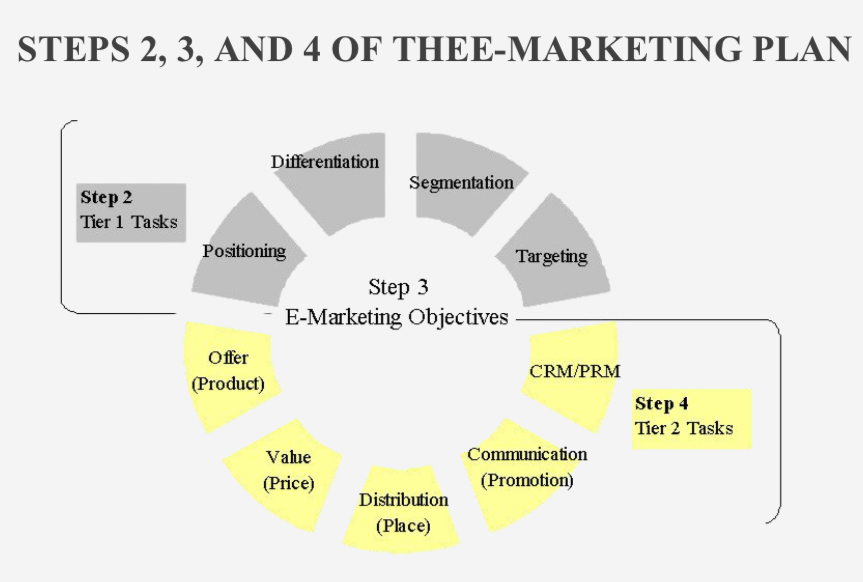
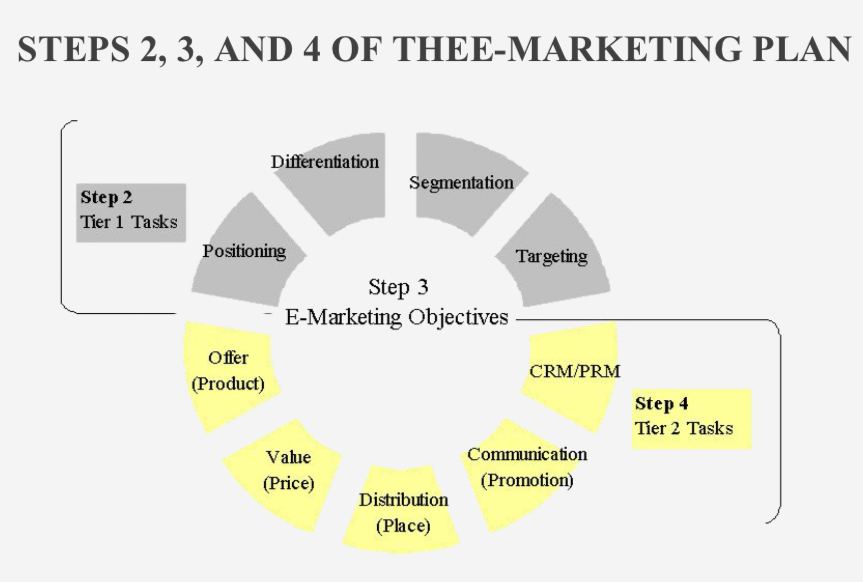
STEP 2: E-MARKETING STRATEGIC PLANNING
Determine the fit between the organization and its changing market opportunities.
Perform marketing opportunity analysis, demand and supply analyses, and segment analysis.
Tier 1 Strategies
Segmentation
Targeting
Differentiation
Positioning
Tier 1 Strategies include
Segmentation: by conducting Market Opportunity Analysis (MOA), including demand & supply analysis
Targeting: by conducting Market Opportunity Analysis (MOA), including demand & supply analysis
Differentiation
Positioning
E-MARKETING PLAN
STEP 3: OBJECTIVES
include the following aspects:
• Task (what is to be accomplished)
• Measurable quantity (how much)
• Time frame (by when)
Most e-marketing plans aim to accomplish the following objectives:
• Increase market share
• Increase the number of comments on a blog
• Increase sales revenue
• Reduce costs
• Achieve branding goals
• Increase database size
• Achieve customer relationship management goals
• Improve supply chain management
E-MARKETING PLAN
STEP 4: E-MARKETING STRATEGIES
Identify revenue streams, suggested by e-business models
Tier 2 Strategies
Design the offer, value, distribution, communication, and market/partner relationship management strategies.
Modify objectives in step 3 as warranted
Tier 2 Strategies Include
strategies related to the 4 P’s and relationship management to achieve plan objectives.
• Product strategies
• Pricing strategies: Dynamic pricing, Online bidding
• Place: Distribution strategies: Direct marketing, Agent e-business models
• Promotion: Marketing communication strategies
• Relationship management strategies: Some firms use CRM (customer relationship management) or PRM (partner relationship management) software to integrate customer communication and purchase behavior
Dynamic pricing
This strategy applies different price levels for different customers or situations.
For example, a first-time buyer or someone who hasn't purchased for many months may receive lower prices than a heavy user, or prices may drop during low demand periods.
Online bidding
This approach presents a way to optimize inventory management.
For instance, a few Seattle hotels allow guests to bid for hotel rooms on slow days, instructing its reservation agents to accept various minimum bid levels depending on occupancy rates for any given day.
E-MARKETING PLAN
STEP 5: IMPLEMENTATION PLAN
Tactics are used to achieve plan objectives:
• Marketing mix (4 Ps) tactics
• Relationship management tactic
• Marketing organization tactics: Staff, Department structure
• Information-gathering tactics: Web site log analysis, Business intelligence and secondary research
E-MARKETING PLAN
STEP 6: BUDGET
The plan must identify the expected returns from marketing investments, including:
• Cost/benefit analysis
• ROI calculation
• Internal rate of return (IRR) calculation
• Return on marketing investment (ROMI)
E-Marketing costs
• Technology
• Site design
• Salaries
• Other site development expenses: - such as registering multiple domain names and hiring consultants to write content ; perform other development and design activities.
• Marketing communication
• Miscellaneous: Other typical project costs might fall here —expenses such as travel, telephone, stationery printing to add the new URL…
E-MARKETING PLAN
STEP 7: EVALUATION PLAN
Marketing plan success depends on continuous evaluation.
• E-marketers must have tracking systems in place to measure results.
• Various metrics relate to specific plan goals.
• E-marketers must show how intangible goals will lead to higher revenue.
• Accurate and timely metrics can help justify expenditures.
In general, today’s firms are
ROI driven
E-marketers must show how … goals will lead to higher revenue.
intangible
The demand analysis portion includes
market segmentation analyses
to describe and evaluate the potential profitability, sustainability, accessibility, and size of various potential segments.
The purpose of a supply analysis is to
assist in forecasting segment profitability as well as to find competitive advantages to exploit in the online market.