Astronomy 1101 Final Exam
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
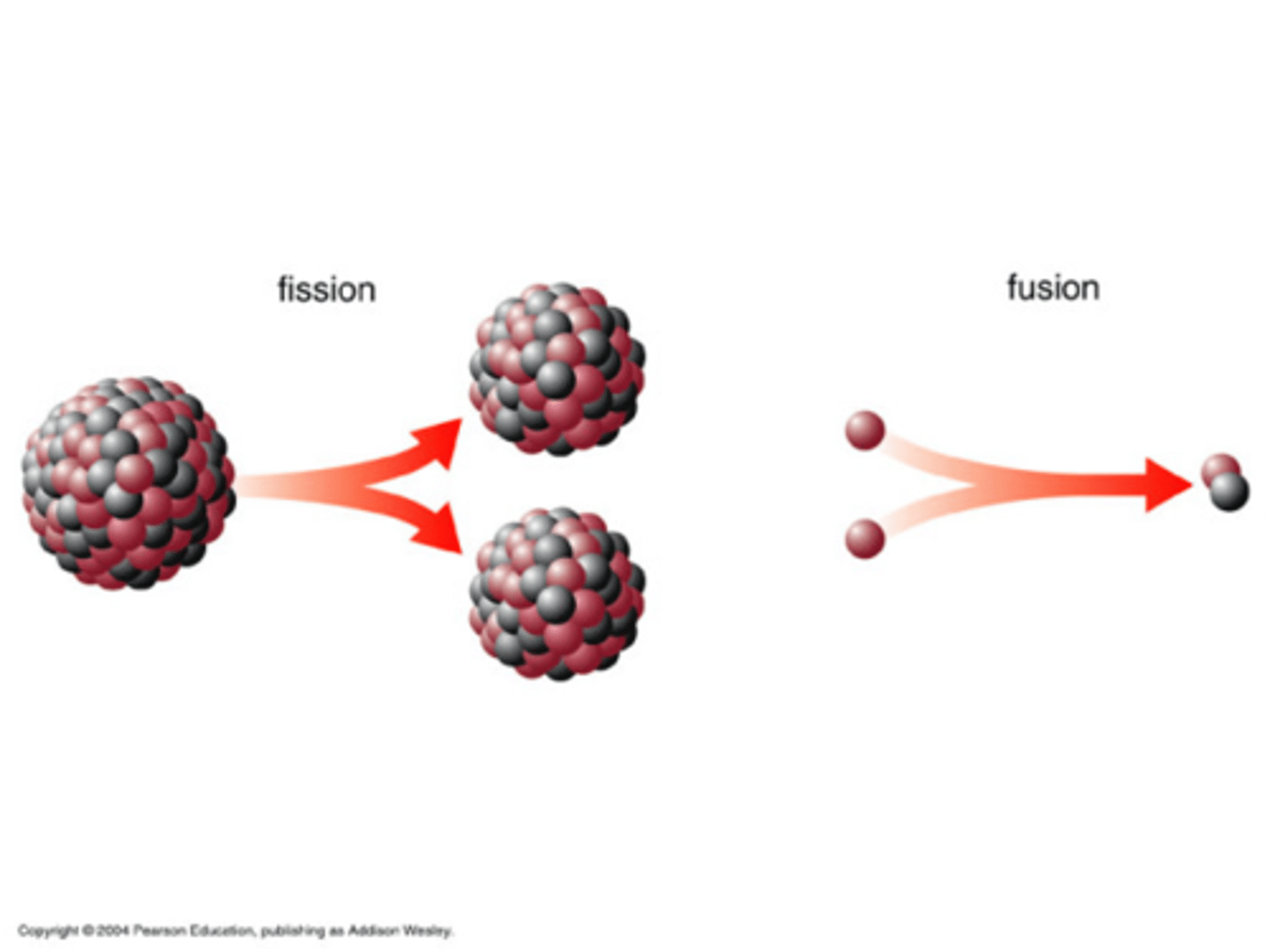
How does the Sun's method of producing energy differ from the method used in human made nuclear power plants?
Sun: nuclear fusion - hydrogen protons fuse together to make helium
Pow. Pla.: nuclear fission - heavy protons like uranium-235 or plutonium-239 split apart when struck by a neutron
If a newly discovered comet has a highly elongated orbit, moves retrograde, is steeply tilted relative to the ecliptic, and takes about 2,000 years to orbit the Sun, where did it most likely originate?
The Oort Cloud
Why?
- Oort cloud = elongated orbit; Kuiper Belt = short-period orbit
- highly elongated and steeply tilted are common characteristics of comets coming from Oort cloud
-Oort cloud = retrograde movement; Kuiper Belt = prograde and close to ecliptic

Which of the following can occur when the Sun's activity increases?
- more sunspots
- more solar flares
- more coronal mass ejections (CMEs)
- stronger auroras on Earth (more intense and visible further from poles)
- interference with GPS and radio signals
- potential disruptions to power grids

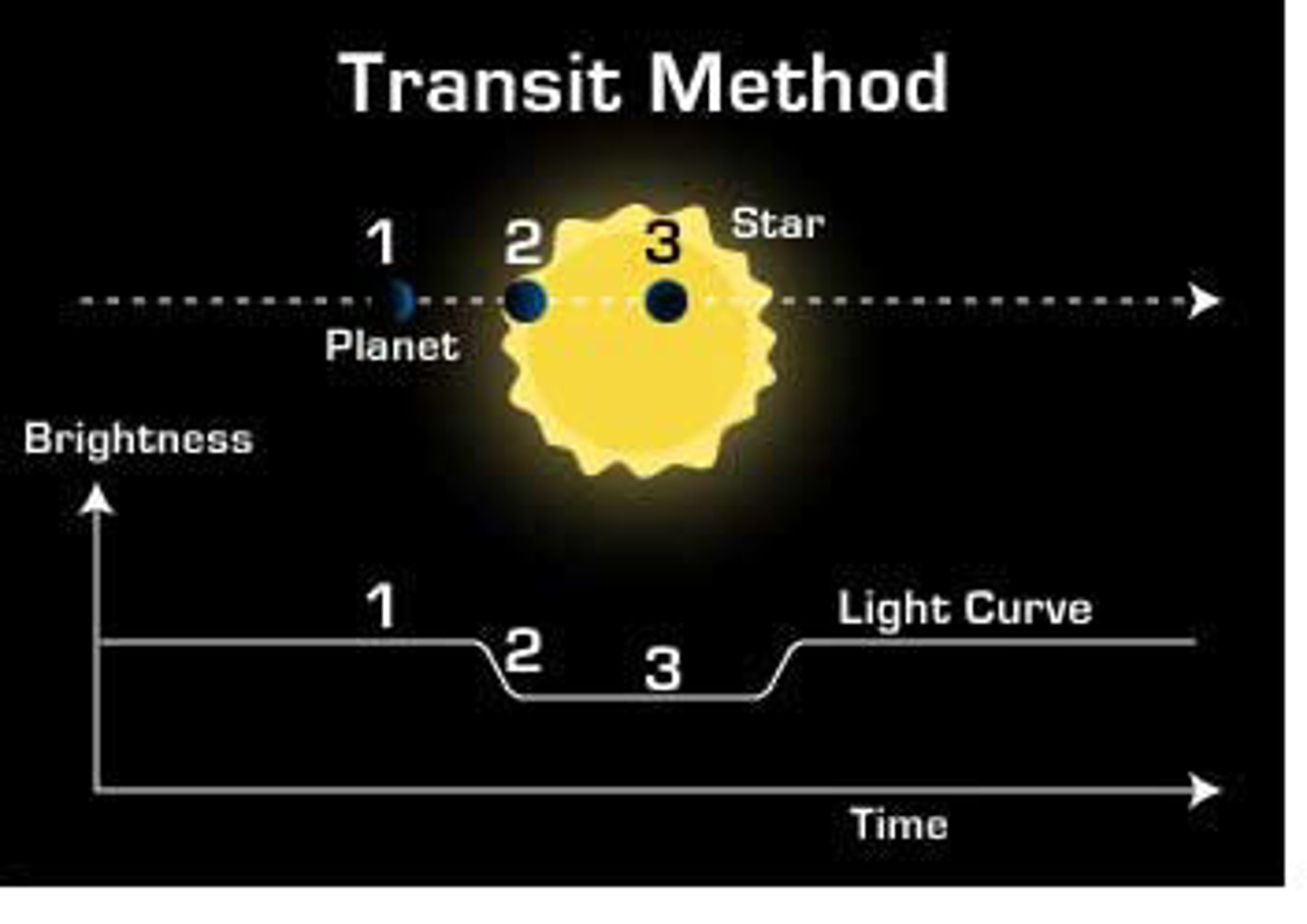
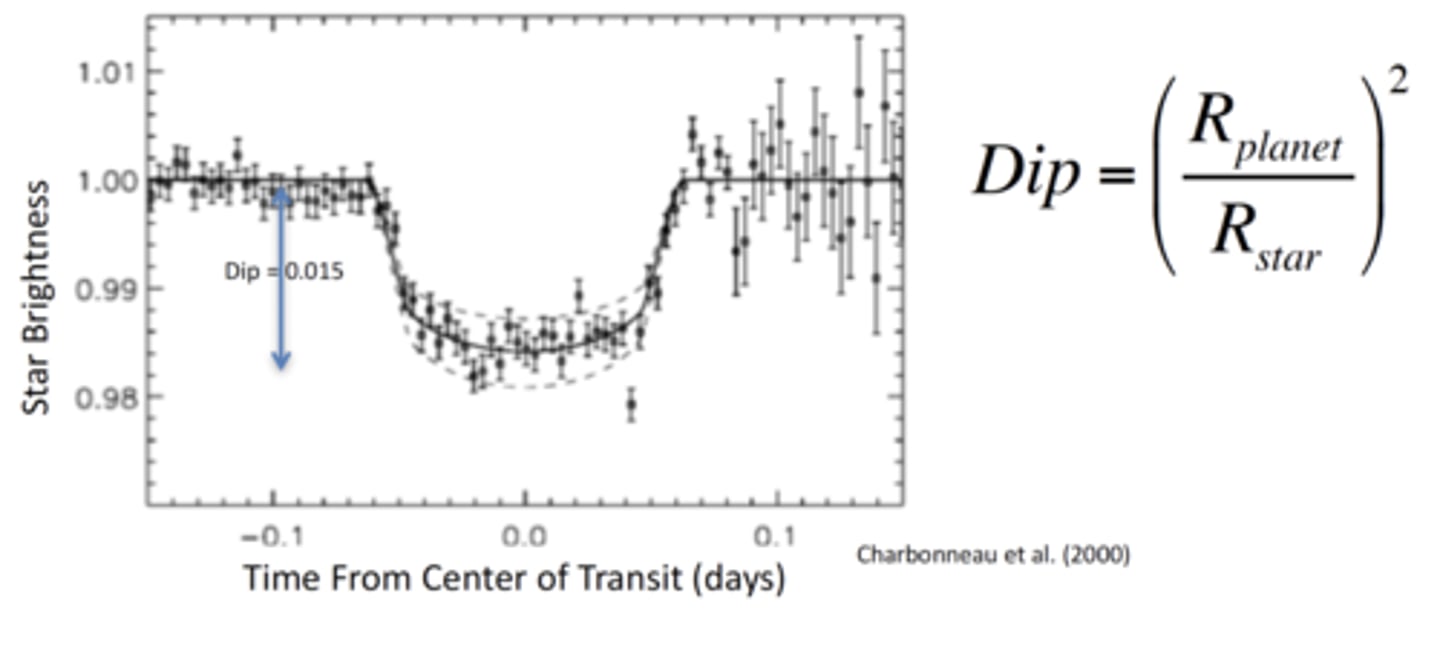
The transit method for detecting exoplanets is most effective for:
Large planets in close orbits around their stars.
Why?
- Large planets block more of the star’s light, making the dip easier to detect.
- Planets close to the star transit more frequently, giving astronomers more chances to observe repeated dips in brightness.
Which stars are the most common in the Universe?
Red dwarves.
Why?
- They make up about 70–80% of all stars.
- They are small, cool, and faint, which is why none are visible to the naked eye from Earth.
- They burn their fuel very slowly and can live trillions of years.
If we were searching for other civilizations in the Milky Way, where would be a promising region to look?
Galactic Habitable Zone
Why?
- Not too close to the galactic center, where radiation, supernovae, and stellar crowding are dangerous
- Not too far out, where there are fewer heavy elements needed to form rocky planets
This region has
- Lots of sun-like stars
- Stable environments
- The right chemical ingredients for Earth-like planets
When a planet is discovered using the Doppler method, the change in the star's velocity tells us information about:
the planet's minimum mass and sometimes info about the orbital period and distance
Why?
- a planet's gravity makes its star "wobble"
- the size of that wobble depends on how big the planet is
The depth of the dip in a star's brightness during a planetary transit depends most directly on:
The size (radius) of the planet relative to the size of the star
Why?
- A larger planet blocks more of the star’s light, producing a deeper dip. A smaller planet blocks less light, producing a shallower dip.
Why do astronomers put telescopes in space?
1. To avoid Earth’s atmosphere (makes stars "twinkle"
2. To observe wavelengths blocked by the atmosphere (absorbs light like UV, X-ray, Gamma, much of infrared)
3. To get uninterrupted observation time (no weather, day/night, clouds)
4. To see fainter and more distant objects (can see very faint light from far away better)

What causes one star to appear blue and another to appear red?
A star appears blue or red because stars of different surface temperatures emit different colors of light.
blue = hotter
red = cooler

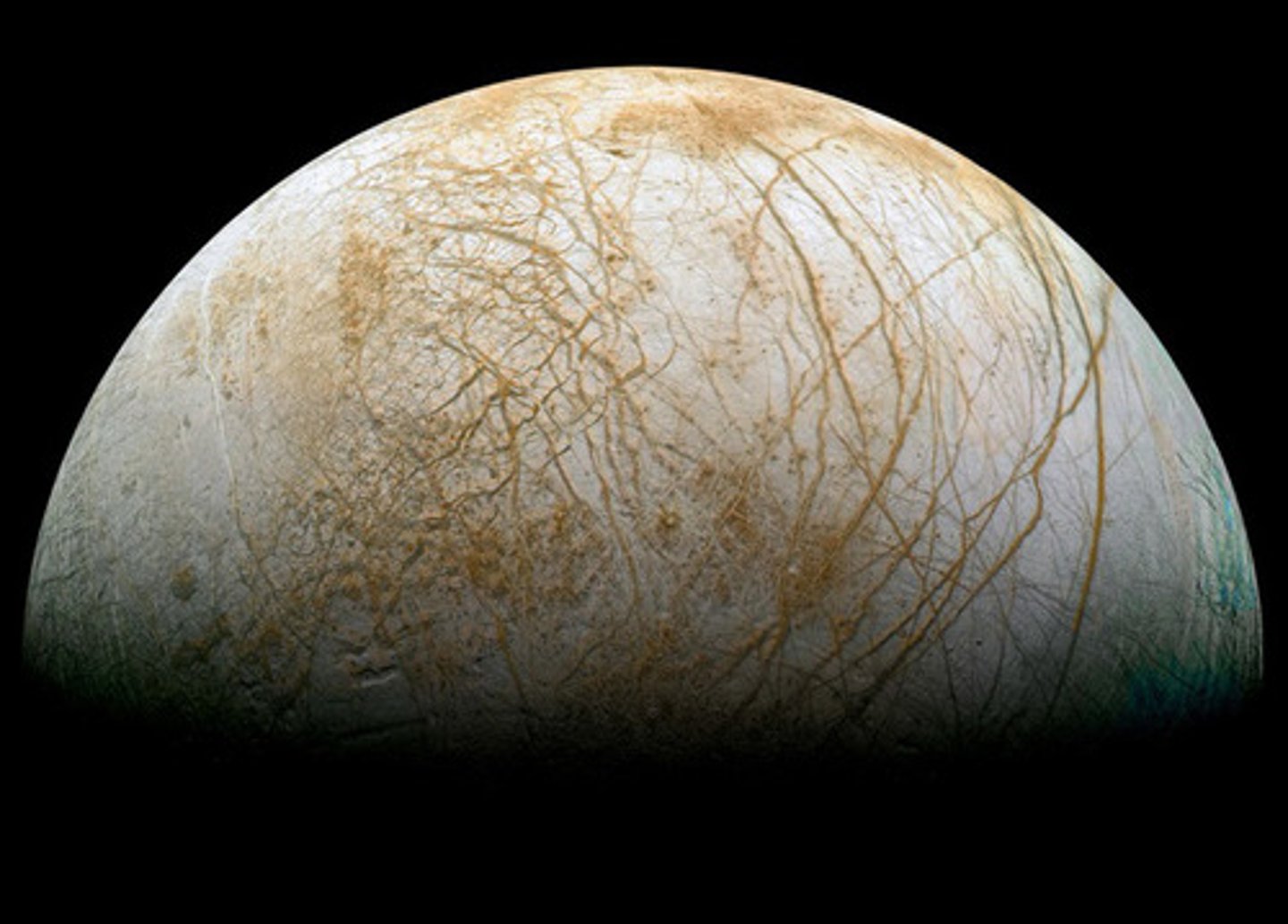
Why do scientists consider Europa a promising place to search for life?
Contains liquid ocean, energy sources, and chemical ingredients necessary for life

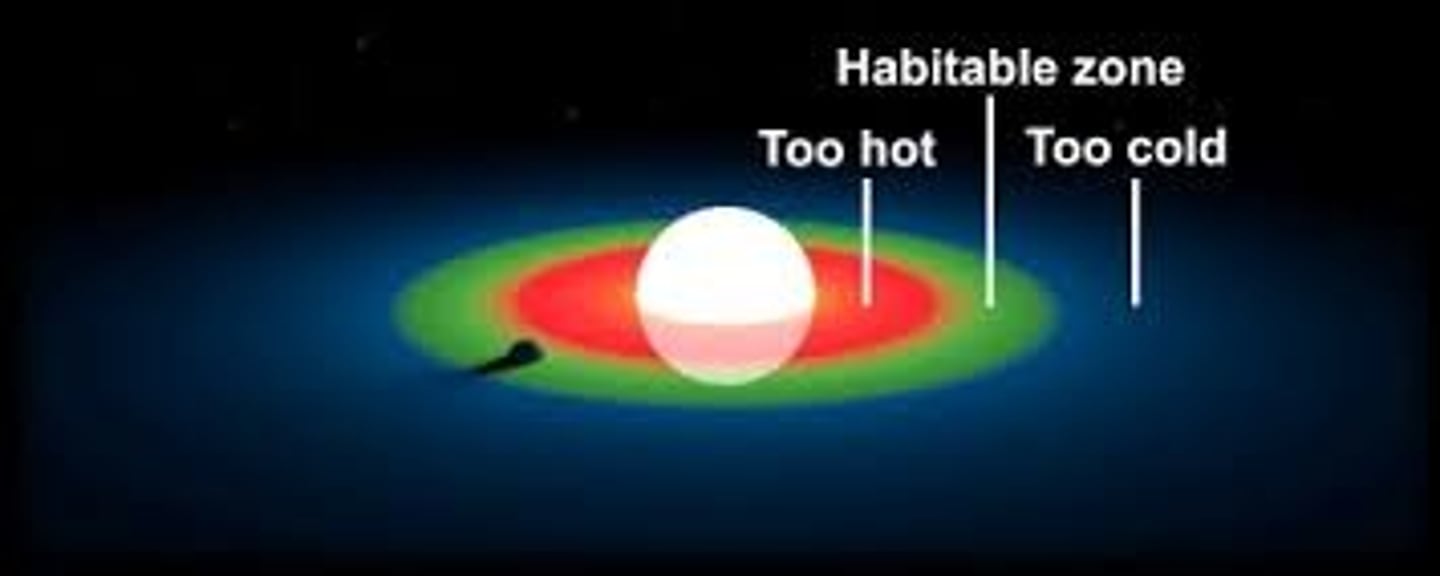
When astronomers refer to a star's "habitable zone," what do they mean?
A star’s habitable zone is the region around the star where conditions are just right for liquid water to exist on a planet’s surface.
It’s the “Goldilocks zone”; not too hot and not too cold.
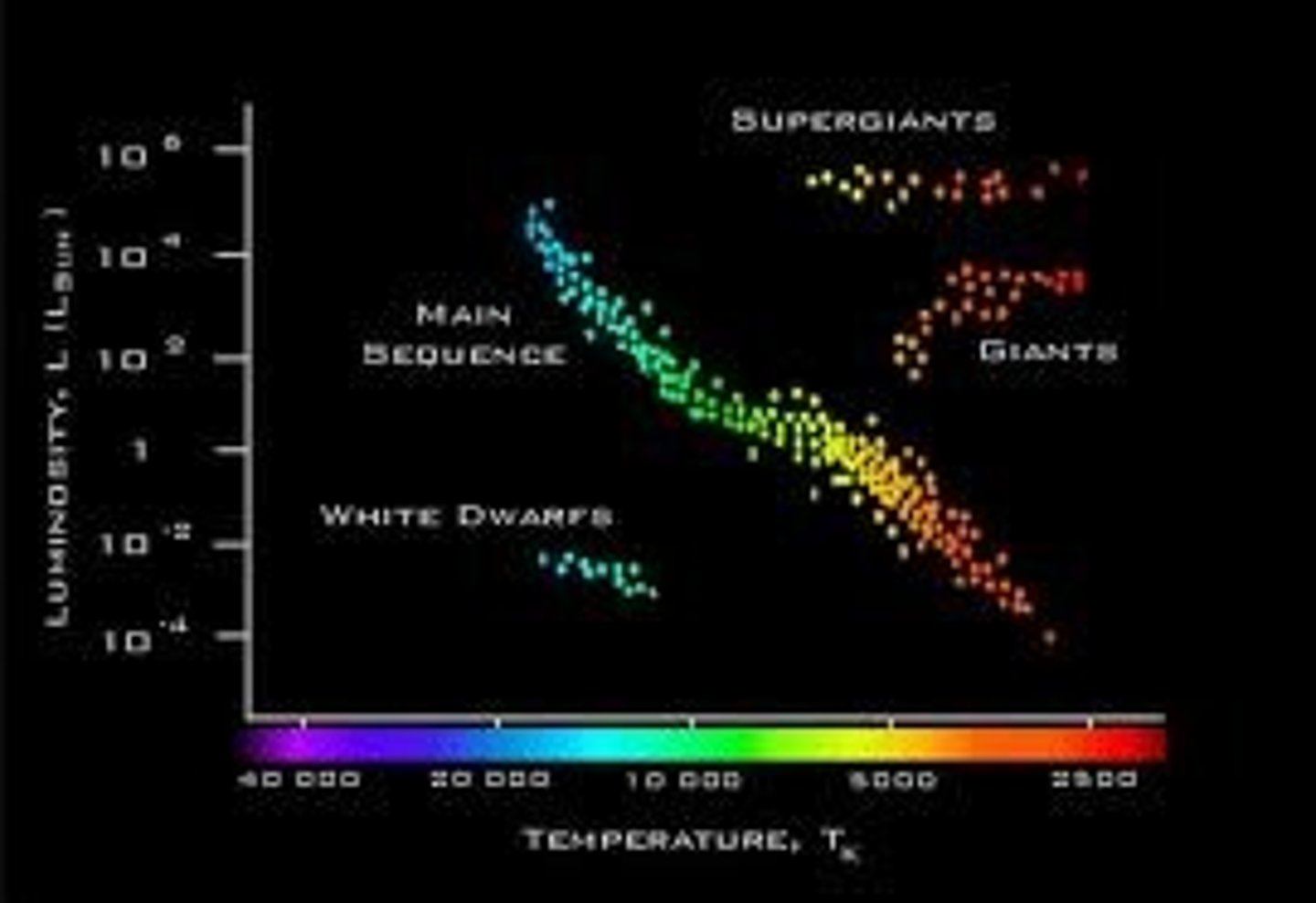
On a Hertzsprung-Russell (HR) diagram, where would we find stars that are cool and dim?
Lower right corner.
If you are using the Doppler method to search for planets around another star, what do you need to do?
Measure the periodic shifts in the star's spectral lines caused by its motion toward and away from us.
Why is it so challenging to directly photograph planets around other stars?
It’s challenging because exoplanets are very faint, very close to very bright stars, and often lost in the glare, making direct imaging technically demanding.
True or False?
Since no other discovered planetary system looks exactly like ours, we can conclude that our Solar System is highly unusual.
False.
Why?
We don’t yet have enough unbiased data to say our Solar System is unusual.
What would be the main factors determining whether water could exist in a liquid state on the surface of a planet?
Surface temperature, atmospheric pressure, atmospheric composition, distance from the star (habitable zone)
Why might planets that orbit very close to their stars not experience a normal day-night cycle?
Tidal locking (the planet always shows the same face to the star, much like the moon always shows the same face to Earth)
Result = one side is in permanent daytime, and the other is in permanent nighttime.
What does the term "SPONCH" refer to?
The core chemical components of life.
S - sulfer
P - phosphorus
O - oxygen
N - nitrogen
C - carbon
H - hydrogen
What is the main way in which the Drake equation is useful?
The Drake equation is valuable because it structures our thinking about the probability of extraterrestrial civilizations, even though its numerical predictions are uncertain. ("calculating" habitability)

Which term in the Drake equation is the most uncertain?
L = the average lifetime of a communicative civilization -- L could be hundreds, thousands, or millions of years, but we simply don’t know.
Which Drake-equation term has become much better constrained thanks to exoplanet discoveries?
fₚ — the fraction of stars that have planets
Why?
Observations from missions like Kepler and ground-based surveys have shown that most stars have planets, including Earth-sized planets in their habitable zones.
In the Drake equation, we expect the term f₍intelligence₎ to be small if what is true?
Intelligent life rarely evolves from life in general
Why?
- Even if life arises on many planets, most life might remain microbial or simple for billions of years.
- Complex, intelligent life could require very rare conditions or a long evolutionary process.
The Sun's habitable zone location:
Inner edge: just inside Earth's orbit (~0.95 AU)
Outer edge: just outside Earth's orbit (~1.4 AU)
Which of the following is not a characteristic of life as we know it on Earth? (IDK why this is a question on the study guide y'all)
Something not universal to ALL life is the ability to move
Characteristics of life include:
- Growth and development
- Reproduction
- Metabolism (energy use)
- Response to stimuli
- Homeostasis
- Cellular organization
- Evolution/adaptation over generations
Which of the following is NOT considered a possible explanation for why we have no evidence of a galactic civilization (familiarize yourself with the Fermi Paradox)
NOT = “Civilizations don’t exist because physics forbids life entirely” (Wrong bc Earth exists)
Actual plausible reasons include:
- civilizations are extremely rare
- they choose not to communicate
- we are too far away to detect them
Which of the following is NOT an example of extremophiles?
NOT = A typical human gut bacterium → lives in moderate, “normal” conditions
Examples of extremophiles include:
- thermophiles
- psychrophiles
- halophiles
- acidophiles
- barophiles
Which of the following places is NOT generally considered a potential home for life in our solar system?
NOT = the sun, too hot...
Examples of potential homes for life:
- Europa
- Enceladus
- Mars
- Titan
If we were to discover simple life on moons such as Europa or Enceladus, what would this most likely suggest about life in the galaxy?
Life may be more common in our galaxy than we thought.
Why?
Life on multiple moons would hint that life is likely to emerge wherever conditions are favorable, making it potentially widespread in the galaxy.
Which of the following is essential for all known forms of life?
Liquid water, carbon-based molecules, energy source, cells
If we develop spacecraft that can take humans to nearby solar systems at a few percent of the speed of light, how long would it be before we could conceivably populate all habitable planets in the Milky Way?
Even at a few percent of light speed, populating all habitable planets in the Milky Way would take millions of years.
What central issue does the Fermi paradox address?
The paradox highlights the apparent contradiction between the high probability of extraterrestrial civilizations and the lack of observable evidence for them.
As the Sun ages and becomes a red giant, what happens to the habitable zone?
The habitable zone shifts outward as the Sun becomes a red giant, making formerly cold regions potentially habitable and currently habitable planets too hot.
Humanity is currently where on the Kardashev Scale?
Type 0 Civilization
The Great Filter proposes that:
The Great Filter is the idea that some step in the development of life or civilizations is extremely hard to pass, making advanced civilizations very rare.