Bio
1/53
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Properties of water
adhesion, cohesion, high specific heat capacity, high specific heat vaporization, hydrogen bonding and density
Adhesion purpose
water molecules form H-bonds with other polar molecules, capillary action, makes polar substances souble
Cohesion
Water molecules form H-bonds with each other, high surface tension
High specific heat capacity
Large quantities of water are able to be absorbed by water without a significant change in its temperature, allowing organisms to maintain body temperature
High specific heat vaporization
Liquid water can absorb large amounts of energy to become a gas, allows an organism to rid heat by sweating.
Hydrogen bonding and density
H-bonds keep molecules spread out to reduce its density in solid form, allows ice to float
Weak acids
Don’t fully dissociate, are reversible, and allows the blood to remain at 7.35-7.45 pH
Properties of carbon
Can form four bonds
Can bind in chains, rings or branched structures
molecules with C-H bonds are hydrocarbons
Can form double or triple bonds
Functional groups
Branched groups of a hydrocarbon consisting of atoms other than hydrogen or carbon, they can make a molecule polar, ionic, soluble, or insoluble or acidic or basic
Buffers
Chemical that compensates for changes in pH by absorbing or releasing hydrogen
Monosaccharide
Simplest form of a sugar, categorized by number of carbons, have polar functional groups hydrophilic and water-soluble. Exist in linear form but fold when in water
Disaccharide
two monosaccharides in a DEHYDRATION reaction, becomes a glycosidic bond
Polysaccharide
100s of 1000s of monosaccharides linked. Provides energy storage and structural support
Polysaccharide characteristics
Highly polar, hydrophobic, too big to dissolve in water.
Types of polysaccharides
Starch (amylose): glucose storage in PLANTS
Glycogen: glucose storage in ANIMALS
Cellulose: fibres of plant cell wall
Chitin: insect exoskeleton
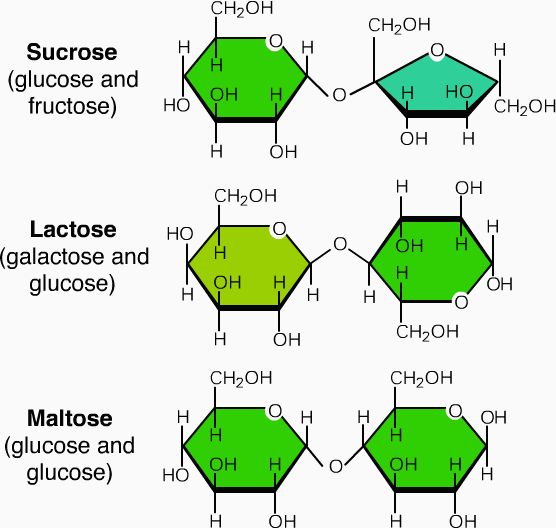
Dehydration/ glycosidic bonds
Isomer
Molecules with the same chemical composition, but different arrangement of atoms
Macromolecules
Lots of subunits binding together and forming a chain
Polymerization
Chemical bonding of subunits
Monomer
Each individual subunit
polymer
String of chemically joined subunits
Lipids
CHO, non-polar, insoluble in water, form cell membranes, store energy, and act as hormones
Fatty acids
Carboxyl group attached to a long hydrocarbon chain, as length increases, solubility decreases
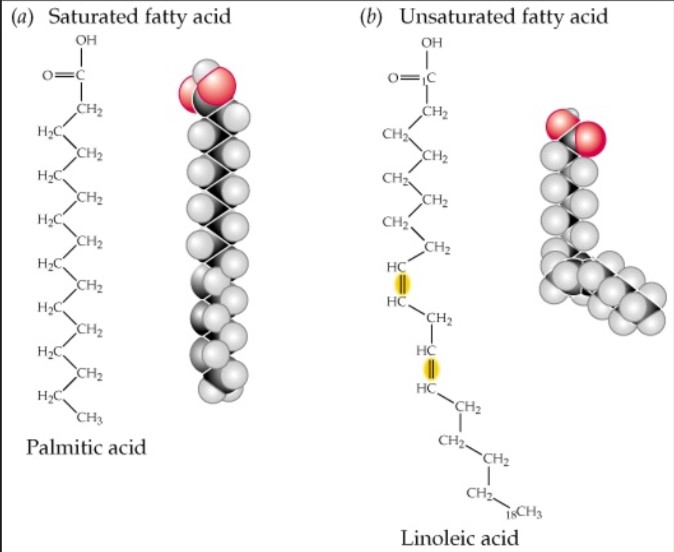
Fats
1-3 fatty acids bonded to a glycerol through dehydration synthesis. Stores 2X the amount of energy of carbohydrates
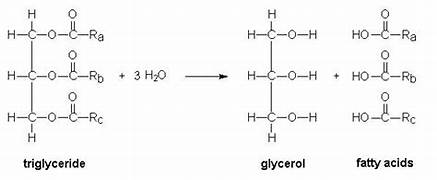
Phospholipids
2 fatty acid chains and a Phosphate group attached to a glycerine. Contains polar head and non-polar tail. makes up Bilayer of cell membrane
Steroids
Four fused carbon rings, has side groups to give unique properties, Ex. Cholesterol
Waxes
Long fatty acid chains connected to Alcohol or carbon ring group, nonpolar, hydrophobic, soft solid at room temp
Saturated Fats
Single bonds in fatty acid chains, usually animal fats, are more compact, causes build up of fat in blood vessels (bad)
Unsaturated Fats
At least one double bond, usually found in plant produce, liquids at room temp, important to diet (good)
Trans Fats
An unsaturated fat chemically forced to accept more hydrogen, causing it to behave like a saturated fat. Solid at room temp, used for frying.
Protein
One or more polypeptides. Polymer made of amino acid, long chain folded into 3D structure, most diverse and vital worker of the cell
Amino acid
Monomer of protein, join together in different combinations. The central carbon is attached to an amino group, carbonyl functional group, and an “R” group.
“R” group
A hydrogen atom or carbon chains and rings. Gives amino acid its functional properties
Peptides
Chains of amino acid. Amino acid monomers form covalent bonds by dehydration synthesis, the amino joins with the acid group. A nitrogen terminal end, and a carbon terminal end.
Polypeptide
50 or more amino acids
4 levels of protein structure
primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary
Primary protein structure
Unique sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain, linear, almost limitless combinations.
Secondary protein structure
Primary structure of coils and bands, b-pleated or a-helix
Tertiary protein structure
“R” groups interact to create a 3D structure. Makes the protein functional
Quaternary protein structure
Two or more polypeptides come together. Polypeptides are bonded with the same intermolecular forces as a tertiary structure
Prosthetic groups
Non-protein components embedded in the structure to carry out a function. (Hemoglobin in blood cells)
Nucleic Acids definition
Instructions for the production of proteins
DNA – deoxyribonucleic acid (stores genetic info)
RNA – ribonucleic acid (single stranded nucleotide involved in protein synthesis)
Nucleotide
Monomer unit of nucleic acid, contains nitrogenous base, 5-carbon sugar and 1-3 phosphate groups
Nucleic acid creation
The polymer chain that is created by the dehydration reaction between phosphate group and hydroxyl
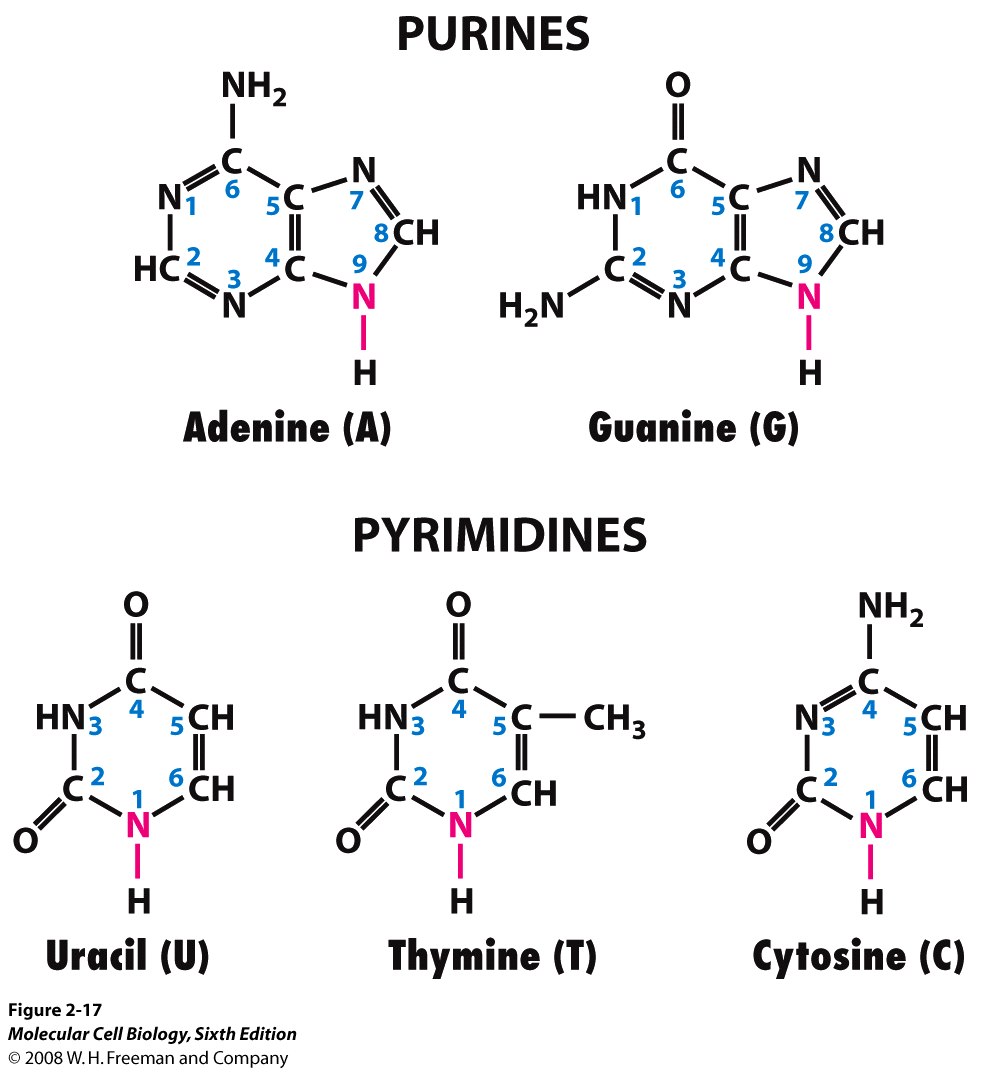
Nitrogenous bases
Pyrimidines
Uracil (U) → only in RNA
Thymine (T) → only in DNA
Cytosine (C)
Purines
Adenine (A)
Guanine (G)
A-T: 2 H-bonds
G-C: 3 H-bonds
DNA
Double-stranded molecule, deoxyribose, phosphate, 4 bases. Two nucleotides that run antiparallel
RNA
Single stranded molecule, ribose, phosphate and 4 bases. can take on thort, linear forms
Phosphodiester bonds
The link that creates the backbone of a nucleic acid chain. on C-3 and P-4
Enzymes
Biological catalysts that increase activation rate. About 4000 in a typical cell. They have an activation site specific to the shape of the substrate and tightly close after it bonds with the substrate
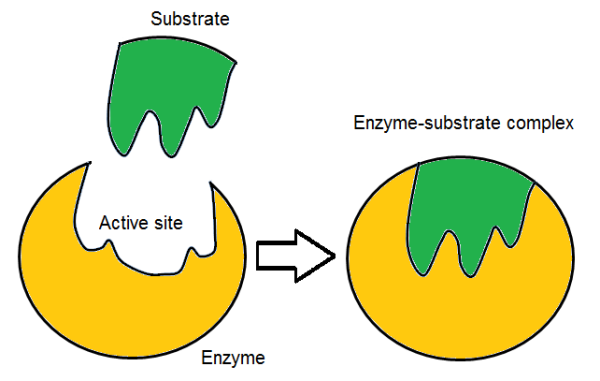
Enzyme example
Lactase – catalyzes the breakdown of lactose
Chymosin - Hydrolysis of casein protein in milk to produce cheese curds
Other enzymes – break starch into glucose and improve stain removal
Enzyme cofactors
Many enzymes require cofactors to help them function. A non-protein component of and ion or organic molecule.
1) Enzyme and substrate concentration
The reaction rate depends on the amount of enzyme available
as substrate increases → collision increases → higher rate of reaction. However, max amount of enzymes limits combinations with substrate.
2) Enzyme inhibitors
Competitive: inhibitor competes with the substrate for the activation site (reversible, inhibitor binds weakly)
Non-competitive: inhibitor binds to another location on the enzyme, deactivating it (irreversible, inhibitors permanently deactivate it)
3) allosteric regulation
Natural regulator of enzyme activity (reversible)
binds to enzymes to stimulate activity, causing it to