Diode Info
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
What is this symbol for
Varactor
What is the potential uses for a varactor
A variable capacitor
What is the normal operating bias for a varicap
Reverse bias
What is a varicap’s normal operation
As a variable capacitor
What happens to the depletion region when a varicap diode is in reverse bias
It expands
What does the depletion region in a varicap act as
capacitor dielectric
How do the P and N regions act in a varicap diode
As capacitor plates
Are the P and N religions conductive in varicap diodes
Yes
How does increasing the reverse bias voltage in a varicap diode increase the capacitance
As this widens the depletion region and the Separation between the P and N increases, this increases the plate separation
What happens when reverse voltage in a varicap diode decreases
The depletion region narrows so the capacitance increases
What is the equation for dialectic constant
Material permittivity/permittivity of free space
Why is a varicap diode highly doped
To increase the capacitance
What is the capacitance of a varactor controlled by
reverse bias voltage, diode size, doping method, alignment of charges
Do varactors have a high or low capacitance
low
What are the applications of varactor diodes
tuning circuits, high, very high and ultra high frequency signals
What is the drawbacks of varicap
If an AC signal is used there will be harmonic distortion
How can harmonic distortion be avoided in varacaps
by having 2 connected next to each other
What is the normal biasing operation for a light emitting diode
Forward bias
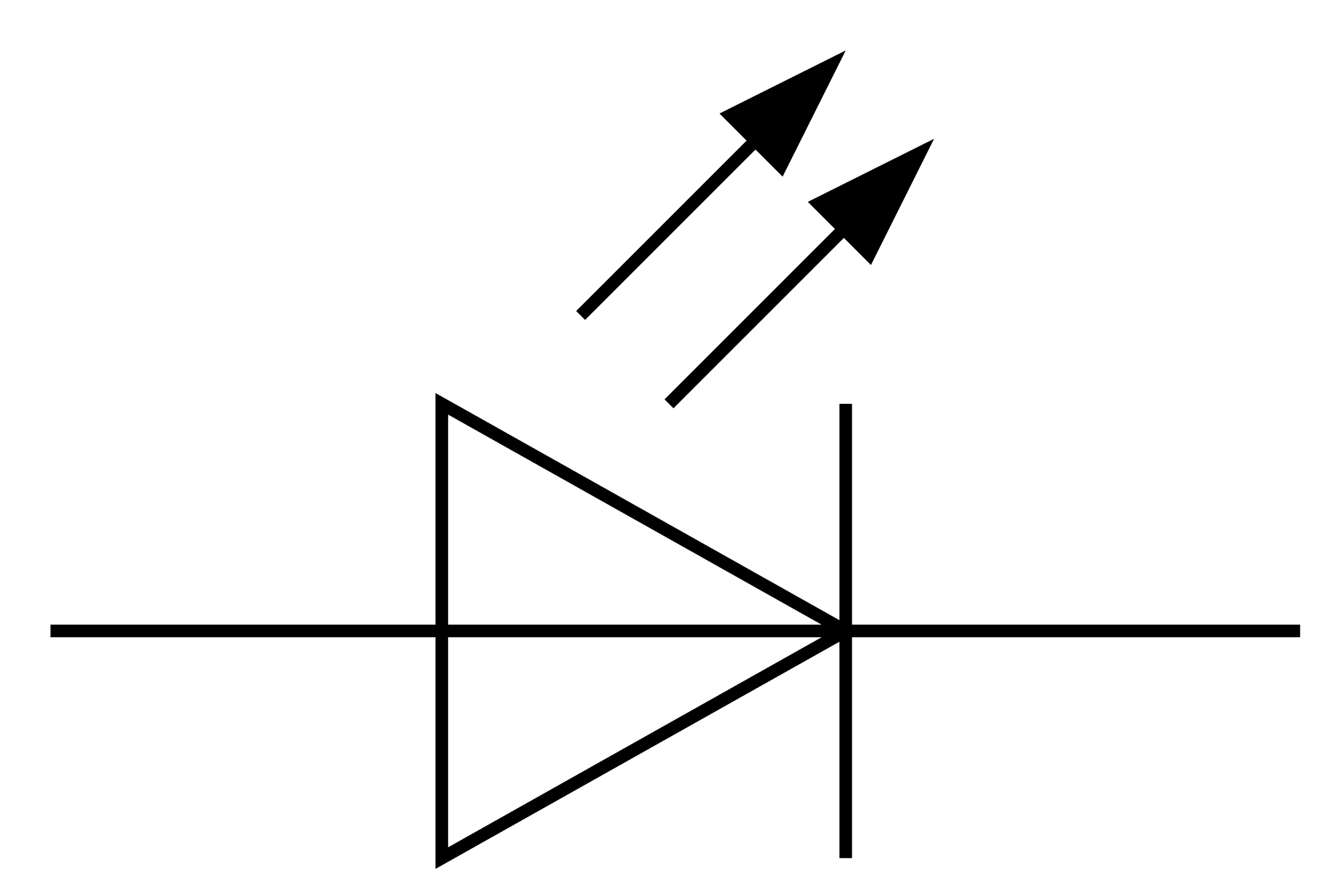
What is this symbol for
LED
What is the forward voltage drop of an LED
1.2 to 3.2
when do LED's experiance reverse breakdown
between 3 and 10 volts which is quicker than normal diodes
What intially happens to the electrons when an LED is in forward bias
Electrons cross the PN junction from the n type material and recombine with the holes in the P-type material
What happens in a forward bias LED when the elections recombine with the holes
The electrons release energy in the form of photons
Why in a forward bias LED do the electrons release photons when they recombine with the holes
As there is a difference in energy that corresponds to the energy of monochromatic visible light
What is the power output translated into light directly proportial to in LED 's
The forward current
What is light output dependent on (LEDs)?
Temperature
What happens in an LED when the temperature increases
The current decreases and so does the light output
What is a reverse bias LED's behaviour the same as
A normal diode
What is this symbol for
Photodiode
What is the normal biasing operation of a photodiode
Reverse bias
How do photodiodes allow light in
Through a very small window which lets the light hit the PN junction
What happens in a photodiode when the light hits the PN junction
It starts conducting as it creates charge carriers in the depletion region by increasing their energy and making them jump to the conduction band
What increases the reverse current in a photo diode
light intensity
What happens to a photo diode in reverse bias when there is no light
No current flow, practically there may be a small amount
What happens to an LED in reverse bias when there is light
A current will flow
What is the small amount of revese current called in a reverse-bias LED with no light incident
Dark current
What is the all the current though a photodiode
Reverse current
What are the two factors that impact reverse current in a photodiode
Reverse voltage and light intensity
What are the applications of photodiodes
Automatic lights
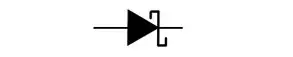
What is this symbol for
Schottky Diode
What is the structure of a Schottky diode
An N-type region bound to a metal
Examples of metals used in a Schottky diode
Gold/Silver/Platinum
What does the structure of a Schottky diode mean for the depletion region, and why
No depletion region as there is only 1 type of charge carrier
What is the charge carrier in a Schottky diode
Electrons
What is the typical voltage drop of a Schottky diode
0.3
What are the uses of a Schottky diode
High current ratings used for fast switching and high frequency applications
Why is there no reverse leakage current in Schottky diodes
As there is no minority charge carriers
What happens to a Schottky diode in reverse bias
No current, it has a higher reverse leakage current
What happens in terms of conductance for a Schottky diode in forward bias
It conducts immediately
What happens in a Schottky diode in forward bias
A number of electrons are injected into the metal region and will lose some energy and join the free electrons in the metal
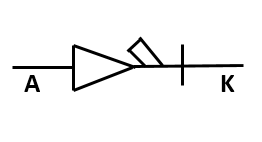
What is the symbol for
Pin diode
What is the structure of a pin diode
It has P and N regions, however they have an intrinsic semiconductor region between them
What is an intrinsic semiconductor
A semiconductor that hasn’t been doped
What does a PIN diode act as in reverse bias
A constant capacitor - meaning the plate separation is the same
In reverse bias what does the intrinsic region of a PIN capacitor act as
Dielectric
In reverse bias what does the P and N regions of a PIN capacitor act as
Capacitor plates
How does a PIN diode act in forward bias
As a current controlled variable resistor
What happens to the intrinsic region of a PIN diode in forward bias
Charge carriers flood it and enable it to conduct
What happens to the forward resistance of the intrinsic region as current increases
It decreases
What are the applications of PIN diodes
Attenuator applications - volume control, DC controlled microwave switches
What is an attenuator
An electronic device or circuit that reduces the amplitude of a signal without distorting its waveform

What is this symbol for
Tunnel diode
What are doping levels in a tunnel diode and what does this increase
High, increasing both majority and minority charge carriers
What happens to a tunnel diode in reverse bias
There is a high reverse current due to the amount of minority charges and there is no breakdown
What are tunnel diodes made of
Geranium or gallium arsenide
What effect does the heavy doping have on the depletion region of a tunnel diode
The depletion region is very narrow
What special characteristics do tunnel diodes have
Negative resistance
What is negative resistance
When voltage increases, current decreases
What are the potential applications of a tunnel diode
Oscillator circuits and microwave amplifier applications
What does having a high amount of doping in a tunnel diode allow the electrons to do
They can tunnel though the PN juction in any biasing
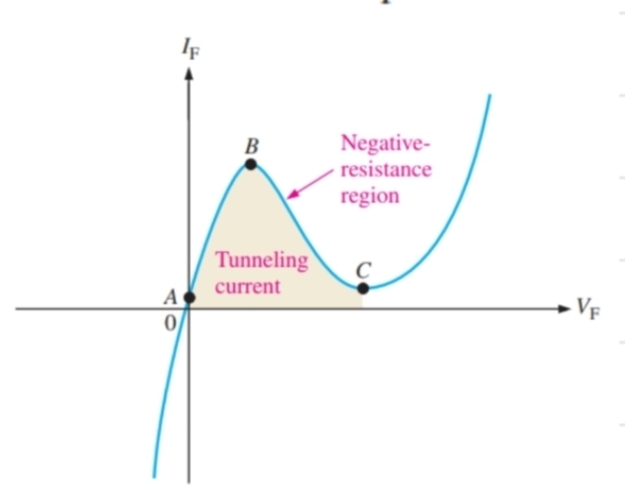
What happens to a tunnel diode in forward bias between A and B
The diode will start conducting after a very small amount of voltage and the current increases
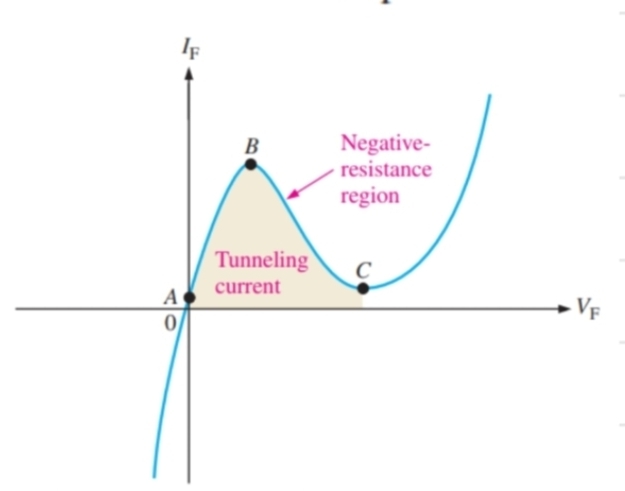
What happens to a tunnel diode in forward bias between B and C
It shows negative resistance, and a potential barrier will start to form again
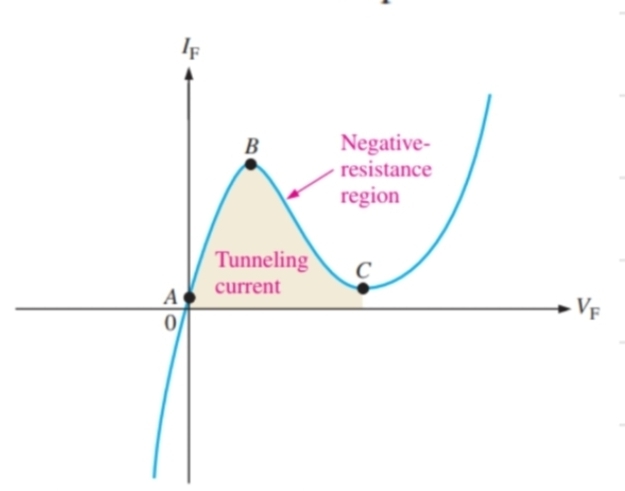
What happens to a tunnel diode in forward bias after point C
It begins to act as a normal diode again
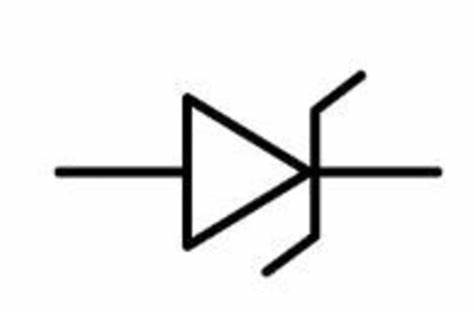
What is this the symbol for
Zener Diode
What does a Zener diode behave like in forward bias
A standard diode
How does a Zener diode act in reverse bias before the breakdown point
Like a standard diode, all the voltage is dropped over it
What happens to the Zener diode at the breakdown point
Instead of breaking down it sustains that voltage and maintains that output
What is Zener voltage
The voltage at which the diode begins to conducts a significant amount of current and maintains a constant voltage
What is the ideal approximation for a Zener diode in forward bias
It will conduct as soon as it has a positive voltage
What is the ideal approximation for a Zener diode in reverse bias
It will have a constant Zener voltage drop
What is Vz (diodes)
Zener voltage
What is the practical approximation for a Zener diode in reverse bias
There is a small increase in Zener voltage as the input voltage increases
Why does the Zener voltage increase as the input voltage increases
Due to the impedance (dynamic resistance)
What is Zz
Zener impedance
What is the equation for Zener impedance
Change in Zener voltage/change in current
What is Izk
The minimum amount of current needed to keep the diode in the Zener region
What is Izm
The maximum about of Zener current that can be sustained before the diode damages
What is the equation for Izm
Pd/Vz
What is PD (diodes)
The max power the diode can take
To use a Zener diode to regulate, what do you want the Zener voltage to be
Slightly below the bottom of the ripple