Biology 20 AP: Unit F - Muscles
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Muscle cells
highly specialized to convert chemical energy (ATP) into kinetic energy
3 main types of muscles
Smooth
Cardiac
Skeletal
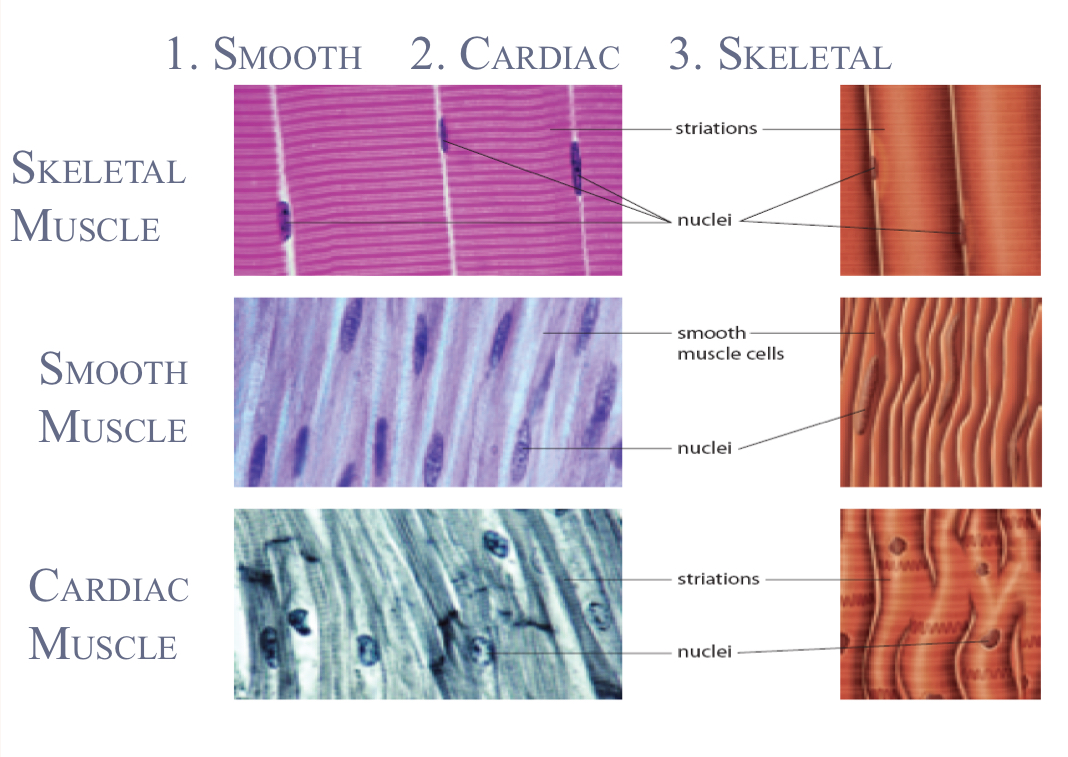
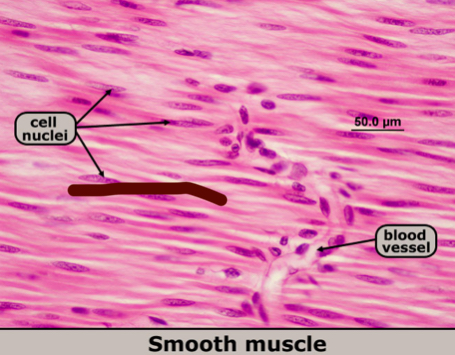
Smooth muscle cells
non-striated (no lines)
single nucleus
contract involuntarily
walls of internal organs
sustain prolonged contraction without fatigue
locations: walls of blood vessels, digestive tract, internal organs, iris
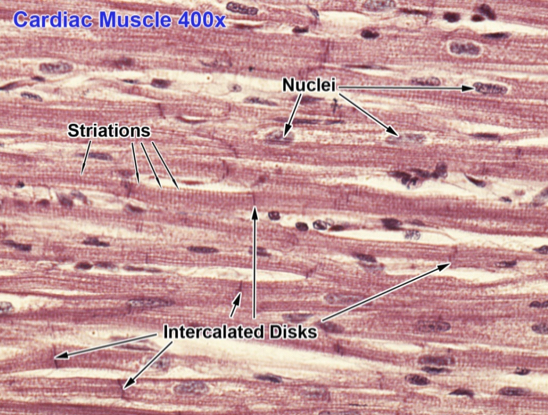
Cardiac muscle cells
striated, tubular, & branched
single nucleus
contract involuntarily
walls of heart (only)
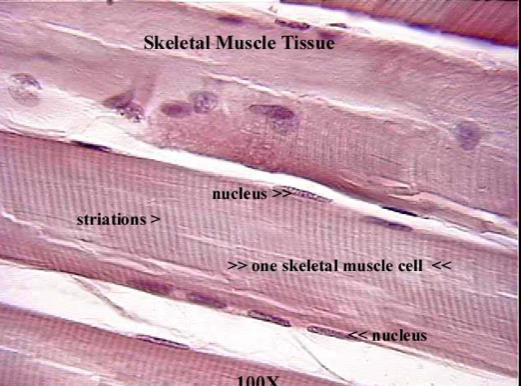
Skeletal muscle cells
striated & tubular
many nuclei
contract voluntarily
attached to bones of skeleton and eyelids
Skeletal muscle function
support: contraction of muscles opposes force of gravity
movement: allows for movement of bones (arms & legs) as well as eyes and face
maintain body temp: ATP breakdown releases heat then spreads throughout body
protection: pads bones and cushions organs
stabilize joints: tendons help hold bones to joints
Cooperation of skeletal muscles
when muscles contract, they shorten (PULL, not push)
contraction = work
relaxation = no work
muscles are found in pairs (one action always has an opposing action)
Hierarchy of muscle structure
muscles: largest unit; attached to bone by tendons
muscle fibres: organized into larger bundles; up to 20cm long
myofibrils: thousands of cylindrical subunits
myofilaments: protein structured responsible for muscle contraction
actin
myosin
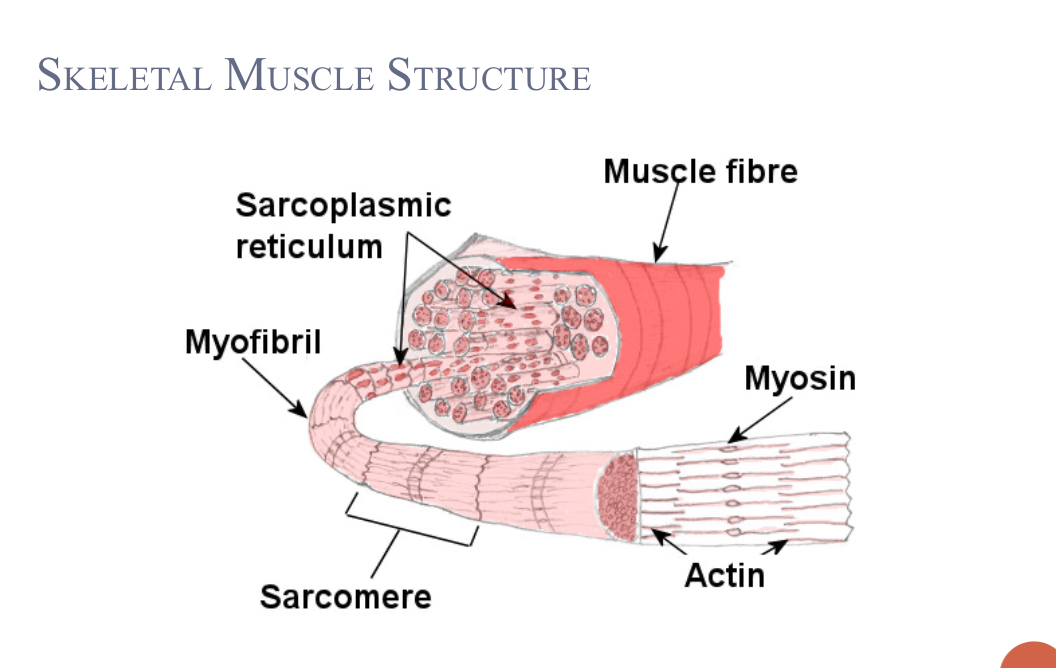
Parts of skeletal muscle fibre
myogoblin
sarcolemma
sarcoplasm
sarcoplasmic reticulum
Myoglobin
oxygen-binding pigment (like hemoglobin)
stores oxygen for muscle contractions
Sarcolemma
membrane surrounding muscle fibre
regulates entry and exit of materials
Sarcoplasm
cytoplasm of muscle fibre
site of metallic processes
contains myoglobin and glycogen
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
smooth ER in muscle fibre
stores calcium ions for muscle contractions
intersection: Z lines
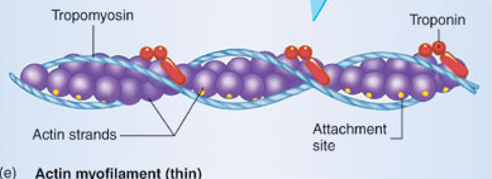
Actin
thin myofilament(s)
composed of globular actin proteins and ion receptor proteins called troponin and tropomyosin
strand of pearls
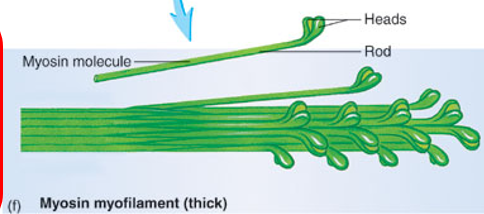
Myosin
thick myofilament(s)
composed of myosin proteins → two polypeptide chains wrapped around each other
ends have globular heads
look like golf clubs
Sarcomere
contractile unit of muscle cell
contains actin and myosin
Sliding filament model
sliding of actin past myosin during muscle contraction
Major steps of sliding filament model
Presence of calcium ions allow myosin head to attach to actin
Myosin head flexes; pulling on the actin filament
Myosin head releases and unflexes via ATP
Myosin reattaches to actin further down fibre
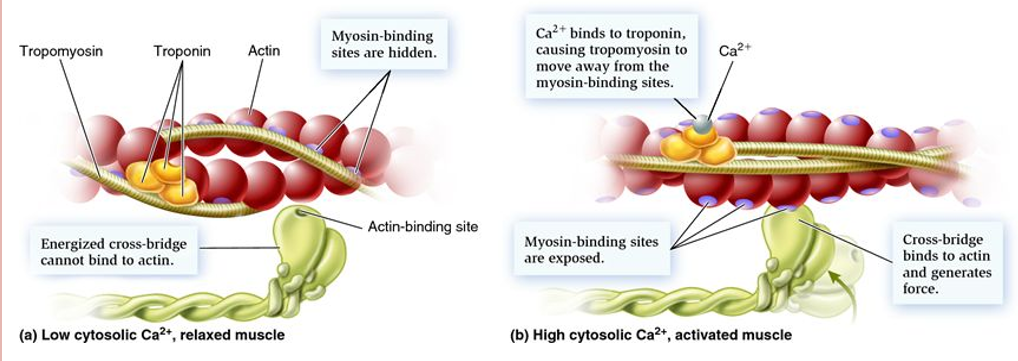
Role of calcium (specific details of step 1 of sliding filament model)
muscle relaxed: tropomyosin blocks myosin binding sites along the actin molecule
muscle contracted: Ca2+ bind to troponin on actin causing tropomyosin to reposition and expose myosin binding sites
Energy for muscle contraction
ATP produced before exercise gets used up very quickly → muscle cells must acquire new ATP
3 mechanisms to make ATP
What are the 3 mechanisms to make ATP?
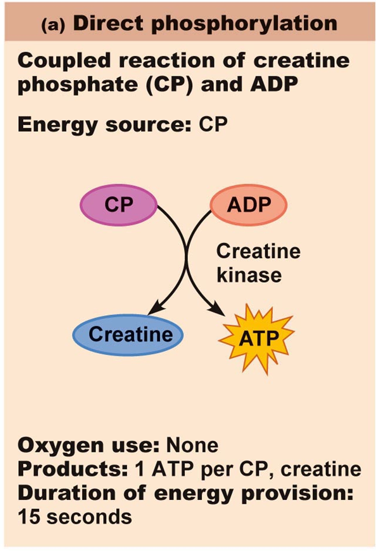
Breakdown of creatine phosphate (no oxygen)
Aerobic cellular respiration
Fermentation (no oxygen)

Ways to use energy
ATP
Creatine phosphate
Glucose
Glycogen (animal carb storage in muscles & liver) → glucose
Lipids → fatty acids → glucose (skip if starving)
Protein → glucose
Creatin phosphate breakdown
4-6s
creatine phosphate: high energy molecule that is built up during rest → CANNOT directly generate muscle contraction
regenerates ATP by contributing a phosphate in the midst of sliding filaments
Aerobic cellular respiration
long term
provides majority of energy for muscles (up to 95%)
oxygen present → glucose (from glycogen) or fatty acids (from fat) converted to ATP
myoglobin: pigment that has higher affinity for oxygen than hemoglobin
→ provides oxygen to mitochondria at beginning of cellular respiration
Fermentation for lactic acid
up to a minute
accumulation of lactate in muscle fibre makes sarcoplasm more acidic → enzymes stop functioning
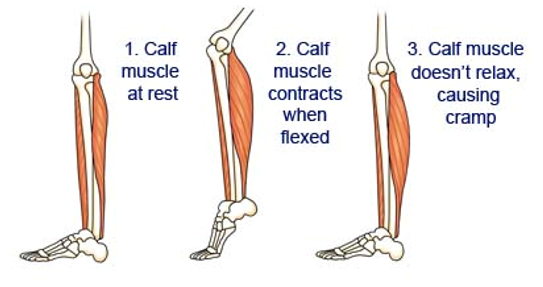
fermentation longer than 2-3 minutes → cramping, fatigue (lack of ATP therefore muscles cannot relax)
Brain vs. muscles
muscles lack oxygen → fermentation provides some ATP
brain cells lack oxygen for some amount of time → brain damage
muscles can use glucose OR fatty acids to make ATP
brain can ONLY use glucose
Effect of athletic training
increases muscle mitochondria
allows fatty acids to be used my muscles and saving blood glucose for brain
Rigor mortis
animals die → no more ATP → no release of myosin from actin myofilament (lasts ~36 hours)
Tendons
connect muscle to bones
Ligaments
connect bones to bones (within joints)
Sprain
stretching/tearing of ligaments
Atrophy
reduction of size, tone, and power of muscle; often caused by disuse
Hypertrophy
exercise induced increase in muscle mass
Myograms
force of a muscle contraction in a skeletal muscle with time
simple muscle twitch: three periods (latent, contraction, and relaxation)
muscle not allowed to relax completely between stimuli: contraction gradually increases in intensity until it reaches a maximum (tetanus) which is sustained until the muscle fatigues
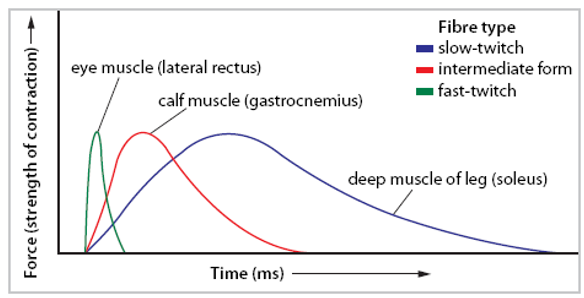
Slow-twitch
type 1 of muscle fibres
dark
contain myoglobin and have many surrounding capillaries
contract slowly but resist fatigue
produce most ATP aerobically (tire only when fuel supply is gone)
glycogen and fat allow the abundant mitochondria to maintain steady, prolonged ATP production
best for endurance
Fast-twitch
type 2
light
little or no myoglobin and fewer blood vessels
adapted for rapid generation of power but fatigue quickly
rich in glycogen; large number of sarcomeres
depend on anaerobic energy production, putting them at risk of lactate accumulation
best for short-term
Intermediate fibres
fast twitch but high oxidative capacity (fatigues slowly)
increased by endurance training and genetics
Force & response times
skeletal muscles have different proportions of fast-twitch and slow-twitch fibres
force and response times of their contractions differ
Latent period of sliding filament theory
time it takes for the stimulus to reach the sarcoplasmic reticulum
Ca2+ diffuses into the spaces between actin and myosin, reposition tropomyosin
Contraction period of sliding filament theory
myosin heads attach to the actin molecules in a series of ratchet-like movements and pull the Z lines together
Relaxation period of sliding filament theory
ATP used to detach myosin heads from the actin
Ca2+ ions are pumped back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum
tropomyosin returns to block the binding of myosin heads to the actin
Z lines move apart and the myofilaments slide into resting positions