GI physiology and pathophysiology
1/211
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
212 Terms
Beginning of the GI tract
The oral cavity
ending of GI tract
Anus
Mouth contents
Reservoir for chewing and mixing of food with saliva • Taste buds (chemoreceptors) • Salty, sour, bitter, and sweet • Olfactory nerve • Teeth • 32 permanent teeth
Salivary Glands
Moistens and lubricates food, contains enzymes and begins digestion of carbohydrates and some lipids. • Three pairs • Submandibular • Sublingual • Parotid • Saliva • Water with mucus, sodium, bicarbonate, chloride, potassium, and salivary α-amylase (carbohydrate digestion)
Esophagus
an 18- to 25-cm long muscular tube with cervical, thoracic, and abdominal parts.
• Wall comprises striated muscle in the upper part, smooth muscle in the lower part, and a mixture of the two in the middle.
• The myenteric plexus is well developed in the smooth muscle but is also present in the striated muscle part of the esophagus.
Early Esophagus development and pregnancy
•Develops from foregut and by week 10 is lined by ciliated epithelial cells.
• The development of various elements of the esophageal wall requires the coordination of a variety of genes and mediators.
• peristalsis appears in the first trimester, and gastroesophageal reflux can be documented in the second trimester.
Esophogus Swallowing
Esophagus • Upper 1/3 striated (motor neuron innervation) • Middle 1/3 mixed striated and smooth • Lower 1/3 smooth (Vagus nerve)
Dysphagia
Difficulty swallowing
Oral phase of swallowing
Voluntary • Food bolus to back of mouth
Pharyngeal phase of swallowing
Food bolus stimulates this phase by contact • Involuntary
Esophogeal phase of swallowing
Involuntary peristalsis is triggered • LES opens (relaxes) via X innervation
Peristalsis
Series of involuntary wave-like muscle contractions which move food along the digestive tract
Local controls of digestion
Myentertic plexus (Auerbach) • Submucosal Plexus (Meissner)
Autonomic controls of digestion
Parasympathetic (Vagus Nerve X) Secretion
Sympathetic
• Parasympathetic (Vagus Nerve X) Secretion
Motility • Intestinal reflexes (relaxation of cardiac sphincter)
Sympathetic
Vasoconstriction • Inhibits motility
Stomach boundaries
• Cardiac orifice • Pyloric sphincter • Pylorus
Stomach functional areas
• Fundus • Body • Antrum
Muscle layers
• Longitudinal • Circular • Oblique
Factors affecting Gastric emptying rate
Volume
Osmotic pressure
Chemical composition
Volume effect on Gastric emptying rate
causes an increase in gastric pressures which stimulates peristalsis and increases emptying
Osmotic pressure effect on Gastric emptying rate
gradients change with fats, non-isotonic solutions, and solids which delay gastric emptying
Chemical composition effect on Gastric emptying rate
• Low blood glucose stimulates vagus nerve
• High glucose slows peristalsis and thus emptying
Hormones produced in the stomach
Gastrin
Histamine
Stomatostatin
Ghrelin
Gastrin fxn
Stimulates secretion of HCL, pepsinogen and histamine
Produced when Protiens
Histamine
Stimulates acid secretion
Produced with Gastrin
Somatostatin
nhibits acid, pepsinogen, histamine and gastrin release
Produced when Acid in stomach
Ghrelin
Stimulates GH to increase appetite
Produced when Fasting
Neurotransmitters in the stomach
Vagus nerve X & local nerves
Acetylcholine functions in the stomach
Stimulates release of pepsinogen and HCL
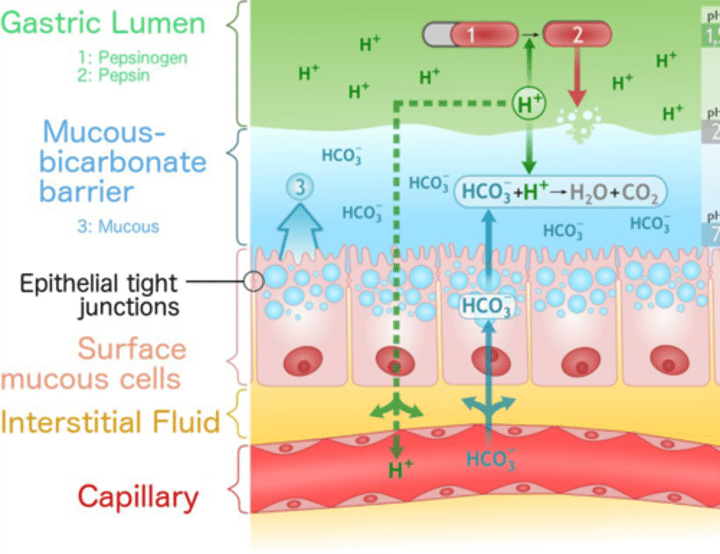
Mucosa layer
for protection, acts as barrier against autodigestion
parietal cells
secrete HCl and intrinsic factor
Chief cells
secrete pepsinogen
Enterochromaffin cells
secrete histamine and serotonin
D cells
Secrete somatostatin (inhibits gastric acid secretion)
Three phases of Gastric secretion
Cephalic Phase
Gastric Phase
Intestinal Phase
Cephalic Phase
the earliest phase of digestion, in which the brain thinks about and prepares the digestive organs for the consumption of food
Hyperglycemia stimulates endocrine pancreas to secrete insulin which in turn stimulates gastric secretions
Gastric Phase
phase of gastric secretion that begins when food enters the stomach
Intestinal Phase
Stage in which the duodenum responds to arriving chyme and moderates gastric activity through hormones and nervous reflexes
Secreting & Cholecystokinin stimulate pancreatic enzyme release into duodenum
Segmentation
localized contractions that are rhythmic
Ileogastric reflex
blocks gastric motility when ileal distension
Intestinointestinal reflex
blocks intestinal motility when a part is over distended
Gastroileal reflex
Triggers relaxation of ileocecal valve
Allows materials to pass from small intestine into large intestine
Motilin
A gastric hormone in the small intestine that activates duodenal/ jejunal receptors to initiate peristalsis
Secretin
A hormone secreted by the small intestine (duodenum) in response to chyme and Stimulates the pancreas to release alkaline fluid and the liver to secrete bile. Inhibits motility and gastrin.
Cholecystokinin
secreted in response to Chyme and fat. An intestinal hormone that stimulates the gallbladder to release bile release of alkaline fluid. Inhibits gastrin
Gastric inhibitory peptide
hormone secreted by the small intestine in the presence of fats and glucose; it also inhibits acid production and peristalsis in order to slow down the rate at which food enters the small intestine, also stimulates insulin
Pancreatic poly peptide
It is stimulated in response to Protein, fat, and glucose. Decreases pancreatic HCO3 & enzyme secretion
Serotonin
It is stimulated in response to intestinal distention, vagus, Stimulates SI secretion
Enzymes secreted by Salivary gland
Amylase
Enzymes secreted by Stomach
Pepsin, HCL, gastric lipase
Enzymes secreted by the pancreas
Amylase, Trypsin, Chymotrypsin, Carboxypeptidase
Small intestine
Enterokinase, Maltase, Sucrase, Lactase & Peptidases
Amylase
Enzyme in saliva that breaks the chemical bonds in starches
Pepsin
An enzyme present in gastric juice that begins the hydrolysis of proteins
HCl in stomach
activates pepsinogen to pepsin
Gastric lipase
Enzymes produced in the stomach that cleaves fatty acids from glycerol molecules.
Trypsin
an enzyme from the pancreas that digests proteins in the small intestine
Chymotrypsin
One of the main pancreatic proteases; it is activated (from chymotrypsinogen) by trypsin.
Carboxypeptidase,
pancreatic enzyme necessary for protein digestion
Enterokinase
A duodenal enzyme that activates trypsinogen (from the pancreas) to trypsin.
Maltase
A digestive enzyme that breaks maltose into glucose.
Sucrase
breaks down sucrose into glucose and fructose
Lactase
enzyme that breaks down lactose
Peptidases
Enzymes that break down proteins into amino acids
Intestinal Microbiome
-The environment of the stomach is relatively sterile because of HCL
-Bile acid secretion, motility, and antibody production keeps bacterial numbers in the duodenum low
-There is a low concentration of aerobes in the jejunum
-Anaerobic bacteria are distal to the ileocecal valve
hepatic portal system
the veins that carry blood from the digestive organs to the liver
dysphagia
difficulty swallowing
• Types of obstructions
• Mechanical
• Functional
Achalasia
Rare form of Dysphagia
• "failure to relax"
• Denervation of smooth muscle in the esophagus and lower esophageal sphincter relaxation
• Risk for esophageal cancer
Anorexia
• A lack of desire to eat despite physiologic stimuli that would normally produce hunger
Vomiting
• The forceful emptying of the stomach and intestinal contents through the mouth
• Projectile (spontaneous vomiting) without nausea/retching
Nausea
A subjective experience that is associated with a number of conditions
Retching
Nonproductive vomiting
Abdominal pain
• Acute or chronic
• Parietal pain arises from parietal peritoneum localized
• Visceral pain from another stimulus; distention, inflammation
• Referred pain
Manifestations of Gastric dysfunction
Anorexia, vomiting, nauseam retching, abdominal pain
RUQ pain
Hepatitis, cholecystitis, cholangitis, biliary, pancreatitis, pneumonia, subdiaphragmatic abscess
Epigastric pain
MI, Pericarditis, PUD, Gastritis, GERD, Pancreatitis, Ruptured Aortic aneurysm
LUQ pain
Splenic abscess, Splenic infarct, Gastritis, Gastric Ulcer, Pneumonia, Subdiaphragmatic abscess
LLQ pain
Diverticulitis, Salpingitis, Ectopic pregnancy, Inguinal hernia, Urolithiasis, IBD
RLQ pain
Appendicitis, Salpingitis, Ectopic pregnancy, inguinal hernia, urolithiasis, IBD, Mesenteric adenitis
Periumbilical pain
Early appendicitis, Gastroenteritis, Bowel obstruction, Ruptured AAA
Constapation
• Infrequent bowel movements associated with straining
•Chronic likely functional
• New changes to bowel habits should be concerning
Medications that can lead to constipation
Opioids Anticholinergics CCB's Diuretics Iron supplements
Risk factors for constipation
• Female, older, sedentary, low caloric, or low fiber intake at risk
Causes of constipation
SCI Parkinson's Multiple sclerosis Hypothyroidism Obstructive GI lesions
Diarrhea
• Abrupt onset of increased frequency and/or fluidity of bowel movements
Causes of acute diarrhea
• Infectious agents-most are viral, lasting
Osmotic diarrhea
Non-absorbable substance draws water into the GI tract
Secretory diarrhea
excessive mucosal secretion of fluid and electrolytes produces large-volume diarrhea
Motility diarrhea
excessive motility decreases transit time, mucosal surface contact, and opportunities for fluid absorption
Upper GI bleeding locations
Esophogus, Stomach, Duodenum
Lower GI bleeding locations
Jejunum, ileum, colon, or rectum
Causes of GI Bleeding
Gastroesophageal reflux, Peptic ulcers, Colon cancer
Which symptom accompanies hemorrhage into the stomach?
A. Hematemesis
B. Occult blood
C. Coffee-ground vomitus
D. Melena
C. Coffee-ground vomitus
gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
backflow of contents of the stomach into the esophagus, often resulting from abnormal function of the lower esophageal sphincter, causing burning pain in the esophagus AKA heart burn
GERD Risk Factors/Causes
• Factors that relax LES
• Peppermint, chocolate, high levels of estrogen, Chocolate, alcohol
• Increased abdominal pressure
• Pregnancy, obesity, ascites
• H. Pylori
• Stress
• Delayed gastric emptying
• Hiatal hernia
Barrets esophagus
• Replacement of normal squamous epithelium with columnar epithelium
• Precancerous lesion
• Diagnosed in 5% to 15% of patients with chronic reflux
Hiatal Hernia
Stomach herniates through the diaphragm
Mallory-Weiss Syndrome
tear of distal esophagus from retching in alcoholic or bulimic
Tears may be only in mucosa or perforate the wall
THE GASTRIC MUCOSAL BARRIER
Protects underlying tissue Prostaglandins inhibit HCO3 secretion which breaks down mucous barrier