Unit 1 Nutrition Test
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Canada’s Food Guide
½ fruits and veggies (leafy greens, berries, carrots)
¼ whole grains (quinoa, steel cut oats)
¼ plant based/animal proteins (eggs, lean beef, nuts/seeds, fish)

Mandatory Parts of a Food Label (6)
Common name of food
Net quantity of food
Ingredient list/allergy information
Best before and packaging dates
Country of origin
Nutrition facts
Common Content/Health Claims
Nutrient content (good parts of the story)
“Reduced in fat / source of calcium”
Health claims (effects on health)
“Healthy for you” “Disease reduction”
Salmonella
Found in raw chicken and eggs
E.Coli
Found in ground beef
Campylobacter
Found in chicken, raw shellfish, unpasteurized dairy, untreated water, pets
Vitamin A
Fat Soluble
Retinol (animal) + Beta-carotene (plants)
Carrots, sweet potatoes, peppers, leafy greens
Vision, health of skin, nails, bones
Def: Night blindness, hair loss
Vitamin D
Fat soluble
Body can produce its own (sun)
Put into fortified dairy products to absorb calcium
Fatty fish, egg yolks
Bone and teeth health
Def: Rickets (bow legs)
Vitamin E
Fat soluble
Vegetable oils, nuts, eggs
Antioxidant (protects body tissue from damage)
Anti ageing
Rare to be deficient
Vitamin K
Fat soluble
Dark leafy veggies (kale, spinach)
Clots blood
Deficiency is uncommon
Vitamin C/ascorbic acid
Water soluble
Citrus fruits (red/green peppers, broccoli, tomatoes)
Prevents cell damage
Absorbs iron in plant form
Gum and teeth health
Prevents bruising
Def: Scurvy (swollen gums)
B1 Thiamine
Water soluble
Whole grains, cereals, legumes (lentils, peanuts, soybeans)
Helps use carbs and protein for energy
Def: Wet beriberi (heart); dry beriberi (nerves); Wernicke-Korsakoff Syndrome (confusion, memory loss)
Vitamin B2 Riboflavin
Water soluble
Enriched breads/cereals, milk, leafy veggies, eggs, meat
Helps to use fat, protein, and carbs into energy
Def: Ariboflavinosis (cracks on mouth, swollen tongue)
Vitamin B3 Niacin
Water soluble
Meat, fish, nuts, eggs, peanut butter, legumes
Helps body use fat, protein, and carbs to make energy
Def: Pellagra (dermatitis, diarrhea, dementia, death)
Vitamin B9 Folate/folic acid
Water soluble
Green leafy veggies, nuts, legumes, enriched grain products
Builds red blood cells and genetic material, prevents birth defects
Def: Spina Bifida (spinal cord sticks out)
Monosaccharides (simple carb)
1 sugar
Fructose, glucose, galactose
Disaccharides (simple carb)
2 sugars
Maltose (glucose x2)
Lactose (galactose + glucose)
Sucrose (fructose + glucose)
Starches (complex carb)
Polysaccharides made of glucose
Main fuel for brain and muscles
Beans, quinoa, brown rice, oats
Fibre (complex carb)
SOLUBLE FIBRE dissolves in water to slow digestion of foods to make you feel full for longer (psyllium, flax seeds)
INSOLUBLE FIBRE helps food move through system and prevents constipation (spinach, beans)
Classes of Lipids
Triglycerides (made of fatty acids and glycerol)
Phospholipids
Sterols (like cholesterol)
Triglycerides
Glycerol + 3 fatty acids
Hydrogenation
Chemical process of adding hydrogen to unsaturated fatty acids
Makes liquid to a soft or solid state to increase its stability
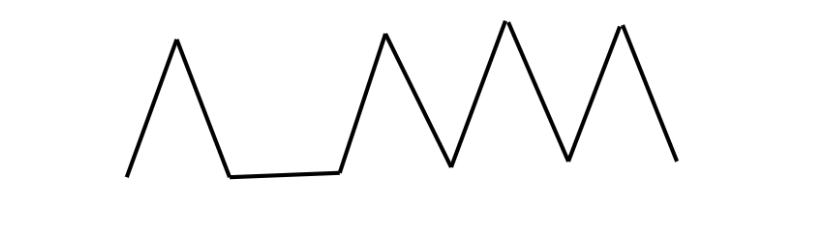
Monounsaturated Fat
Slightly liquid at room temperature
1 hydrogen is missing (1 double bond)
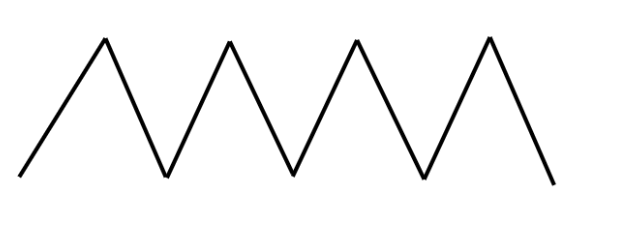
Saturated Fat
Usually animal sources
Solid @ room temperature
Holds no double bonds (no missing hydrogen)
Coconut oil
Polyunsaturated fat
Liquid at room temperature
2 or more hydrogen missing (2+ double bonds)
Sunflower oil, olive oil
Trans-fatty acids
Formed during the process of hydrogenation
Used in baking (chips, cookies)
Artificial trans fats were banned in 2018
Worst for raising cholesterol
Omega 3 fatty acids
Polyunsaturated fat that is good for the heart
Fish (tuna, salmon), flaxseeds
Low Density Lipoproteins (LDL)
Bad cholesterol
Builds up along the blood vessel walls as plaque (heart attack)
High Density Lipoproteins (HDL)
Good cholesterol
Transports cholesterol away from blood vessel tissues to liver
Incomplete protein
Lacking in 1 or more amino acids
Most plant sources
Complete protein
Supply all 9 essential amino acids
Meat, fish, eggs, dairy, soy, quinoa, chia
9 Essential Amino Acids
Histidine, Isoleucine, Leucine, Lysine, Methionine, Phenylalanine, Threonine, Tryptophan, Valine
Functions of Proteins
Growth/maintenance/repair of muscles, transports nutrients, antibodies
Function of Carbohydrates
Quickest energy source, makes mucus protective coating for organs
Function of Fats
Stored energy, protects internal organs, carries fat soluble vitamins
Daily Recommendations for Carbs
Complex carbs: 45-60% of total calories
Refined sugars: No more than 10%
Dietary fibre: 25g daily
Daily Recommendations for Fats
20-35% of total calories
Saturated fats should be no more than 10%
Cholesterol = 300mg daily
Daily Recommendations for Protein
No more than 10-35% of total calories
Weight in kg x 0.8g of protein