The Skeletal System
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
the skeletal system includes —-,——, and ——
bones, cartiladge, joints
how many bones are in a persons hand?
27

how many bones are there in a person foot?
26

what are the main functions of bones?
a. support and framework for the body
b. provide protection for internal organs
c. serve as a storage place for mineral salts-calcium and phosphorous
d. play an important role in the formation of blood cells
e. helps to make movement possible through articulation

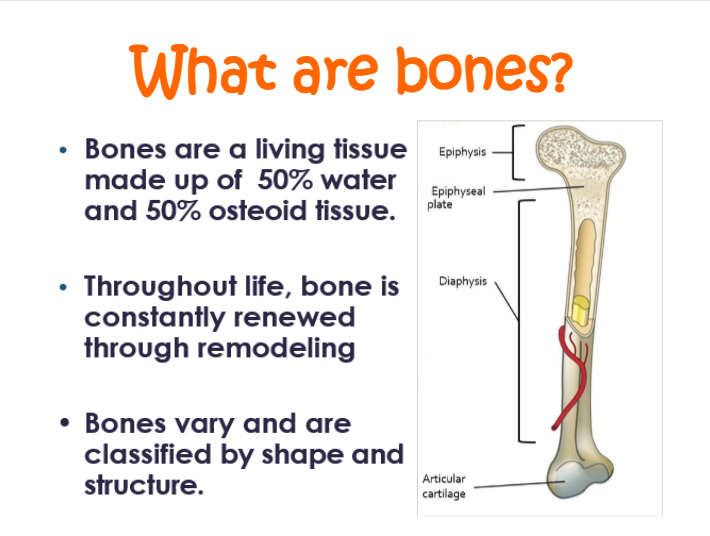
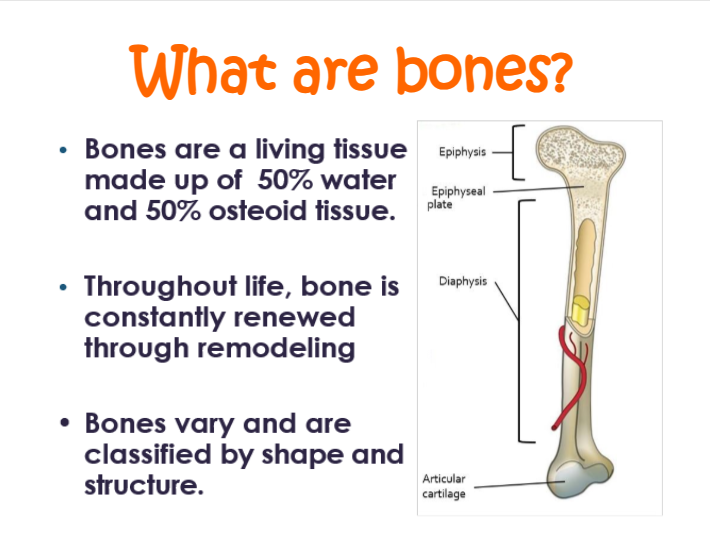
bones are a living tissue made up of —% water and —% osteoid tissue
50, 50
when is bones constantly renewed through remodeling?
throughout life
bones vary and are classified by — and —-
shape, structure
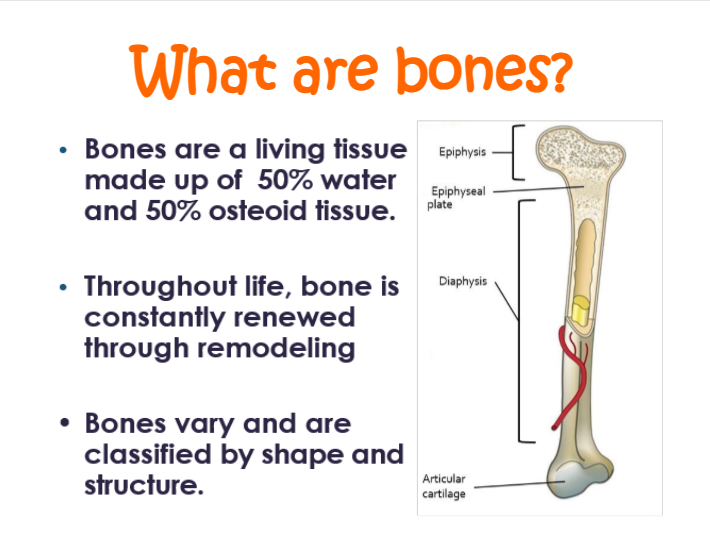
what is the functions of the 35% osteoid
a. provides the flexibility and tensile strength required to keep bones from constantly breaking
b. lack of collagen causes “brittle bone disease”

what is the function of the 65% mineral salts and calcium?
a. provides bone strength and hardhness
b. lack of hydroxapitie causes rickets

how are bones classified?
shape and internal structure

what are the different classifications based on shape?
a. flat bones (ex: scapula)
b. irregular bones (ex: vertabae)
c. long bones (ex: femur)
d. short bones (ex: wrist)
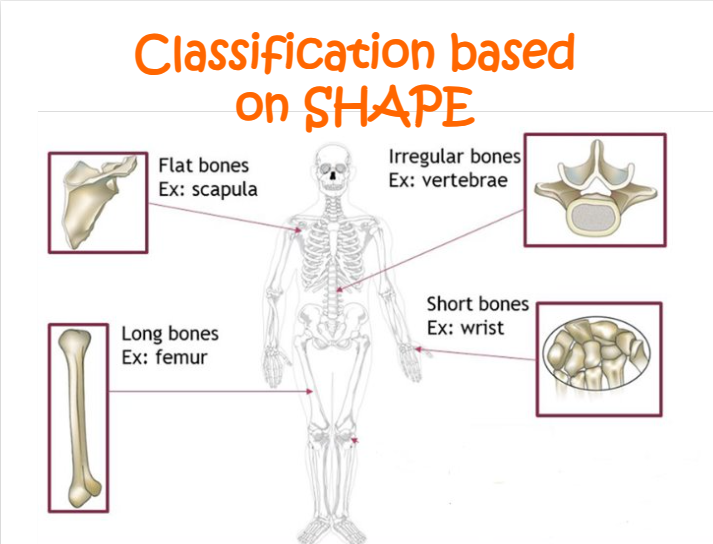
what are the flat bones?
sternum, ribs, skull

what are the long bones?
tibia, fibula, femur, radius, ulna, humerus

what are the short bones?
carpals, tarsals

what are the irregular bones?
vertebrae, pelvic

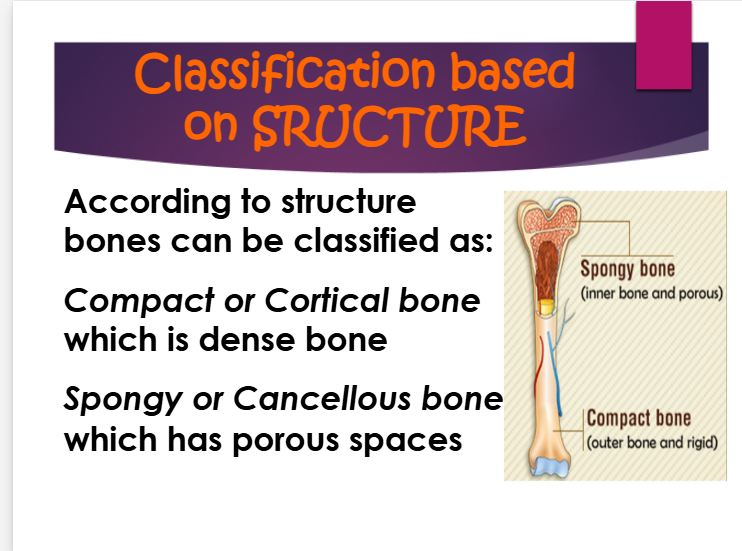
according to structure, bones can be classified as
compact, cortical = dense bone
spongy, cancellous = porous space
structure of the medullary cavity:
a. center of shaft
b. filled with yellow bone marrow containing fat cells, blood vessels. and some cells that form white blood cells
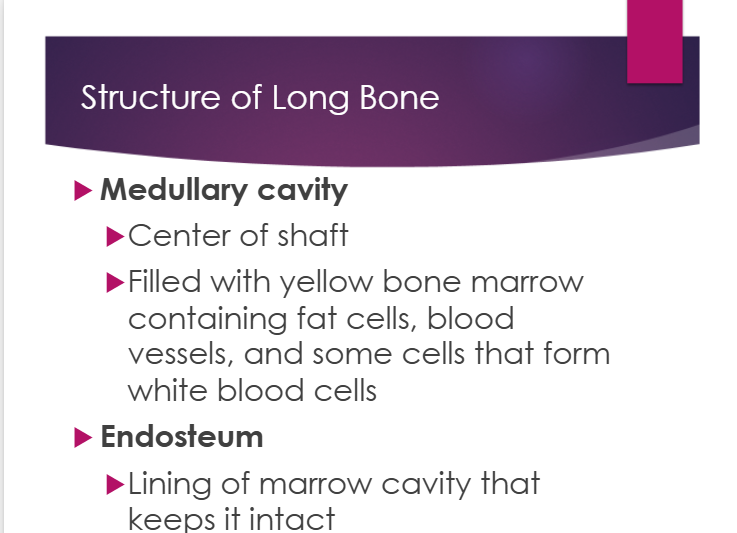
structure of endosteum:
a. lining of marrow cavity that keeps it intact
structure of spongy/cancellous bone:
a. found at ends of long bones; form center of all other bones
structure of haversian canals:
a. channels that carry blood vessels that nourish osteocytes
structure of osteocytes:
a. mature bone cells
structure of red marrow:
a. contained in the ends of long bones
b. manufactures blood cells
structure of periosteum:
a. hard outer covering on the outside of the bone
b. necessary for bone growth, repair, and nutrition
structure of articular cartilage:
a. covers the epiphysis and acts as a shock absober
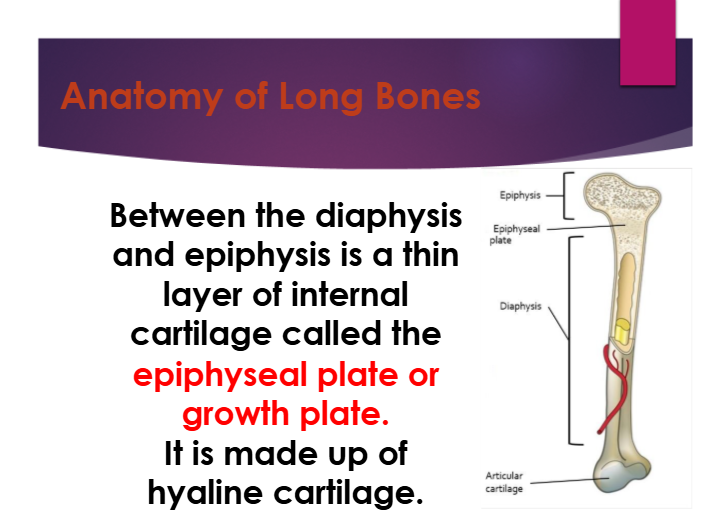
between the diaphysis and epiphysis is a thin layer of internal cartilage called ——-.
epiphyseal/growth plate
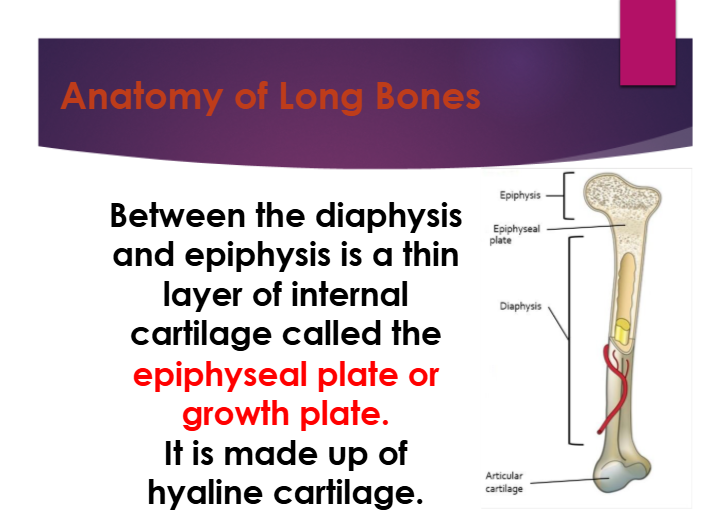
what is the epiphyseal/growth plate made up of?
hyaline cartilage
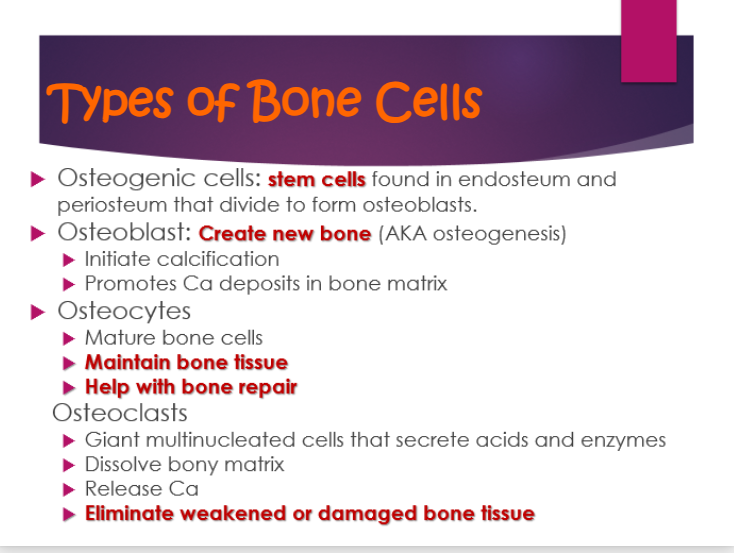
what is osteogenic cells?
stem cells found in endosteum and periosteum that divide to form osteoblasts
what is osteoblast
create new bone (osteogenesis)
a. intiate calcification
b. promotes Ca in bone matrix
what is osteocytes
a. mature bone cells
b. maintain blood tissue
c. help with bone repair
what is osteoclasts?
a. giant multinucleated cells that secrete acids and enzymes
b. dissolve bony matrix
c. release ca
d. eliminate weakend or damaged bone tissu
bones grow in length from the —- plate
epiphyseal

length of bone shaft continues to grow until all the epiphyseal cartilage is ——
ossified

bone growth in circumfrence, or girth
a. osteoblasts deposit new bone to outer surface of diaphysis
b. osteoclasts dissolve the bone material from central part of diaphysis forming the medullary cavity where bone marrow is located

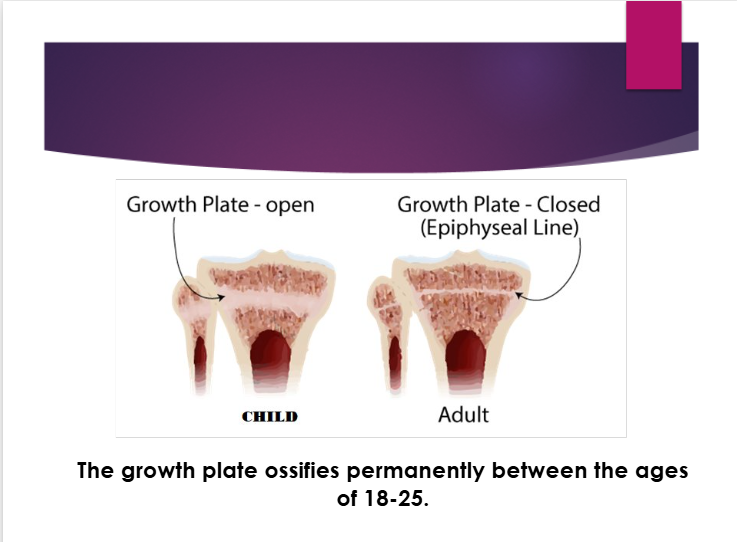
the growth plate ossifies permanently between ages — - —--
18-25
an embryos skeleton is made up of
cartilage
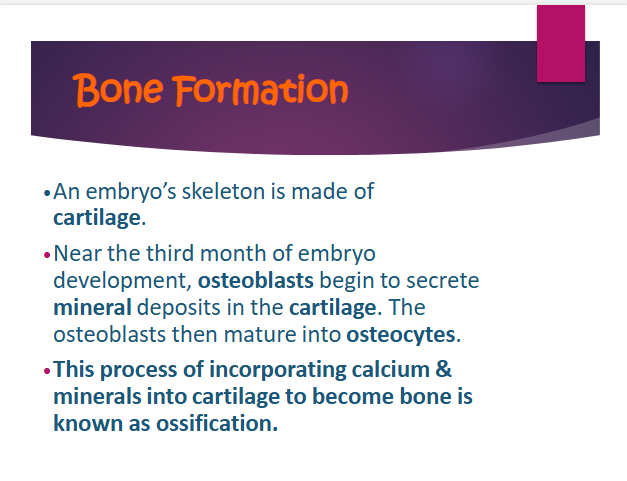
near the third month of embryo development, —- begin to secrete — deposits in the —-
ostebolasts, mineral, cartilage
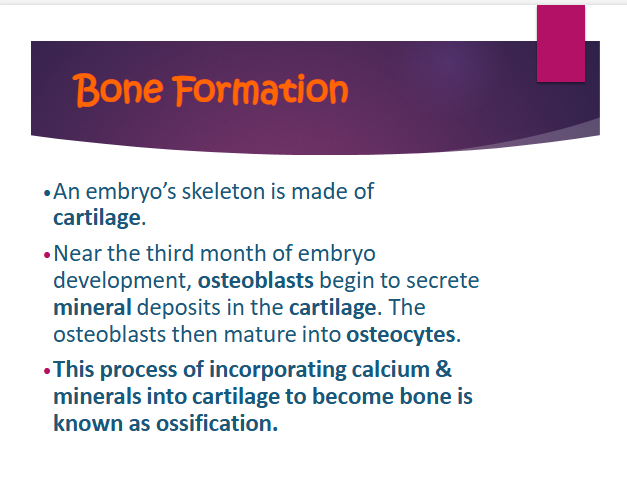
the osteoblasts mature and turn into
ostebocytes
ossification
the process of incorporating calcium & minerals into cartilage to become bone
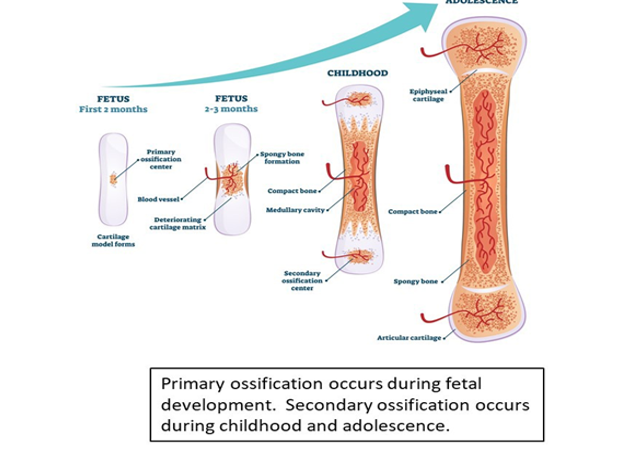
primary ossification occurs during when?
fetal development
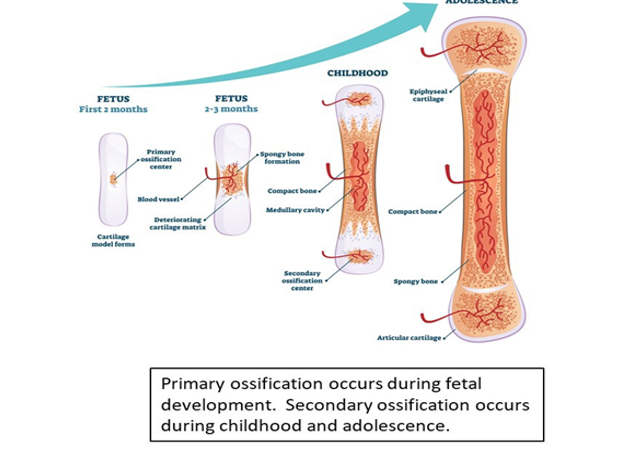
secondary ossification occurs during when
childhood and adolescence
bone is constantly renewed through
remodeling
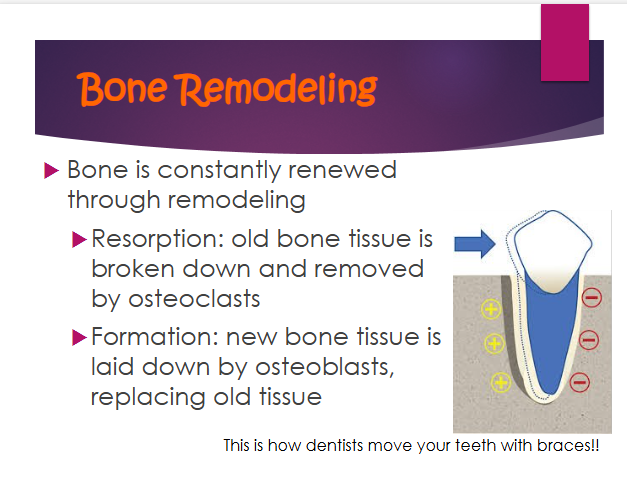
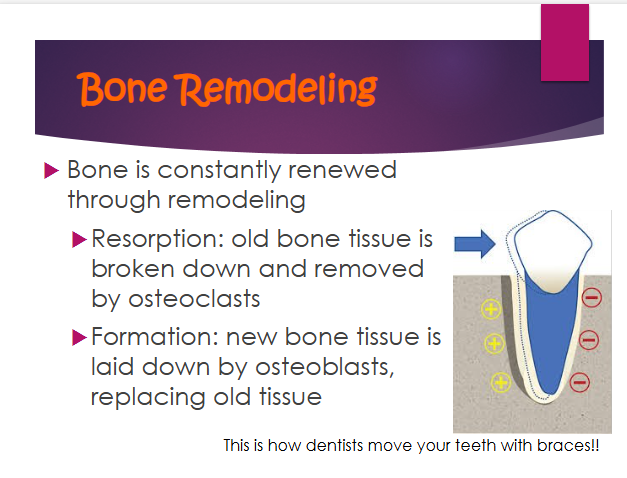
resorption
old bone tissue is broken down and removed by osteoclasts
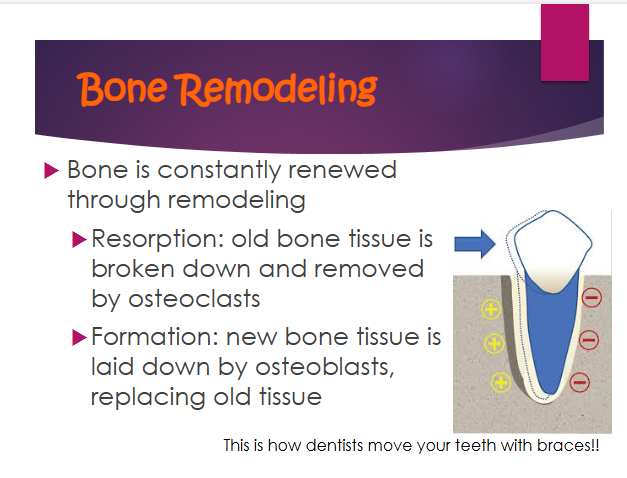
formation
new bone tissue is laid down by osteoblasts, replacing old tissue
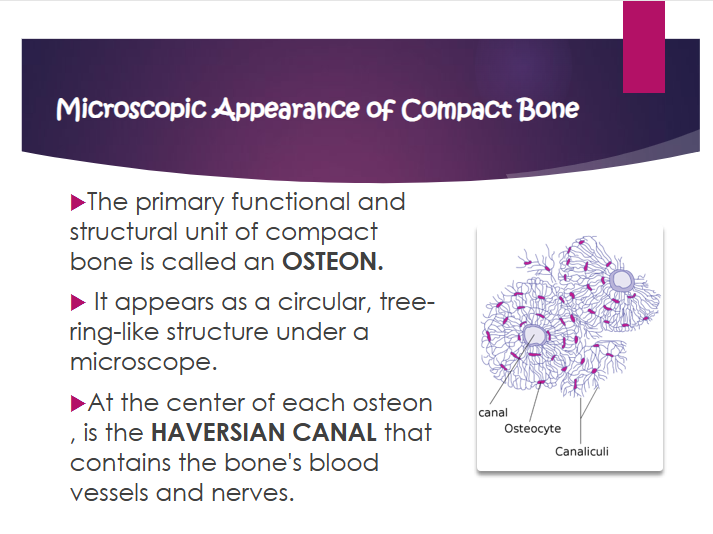
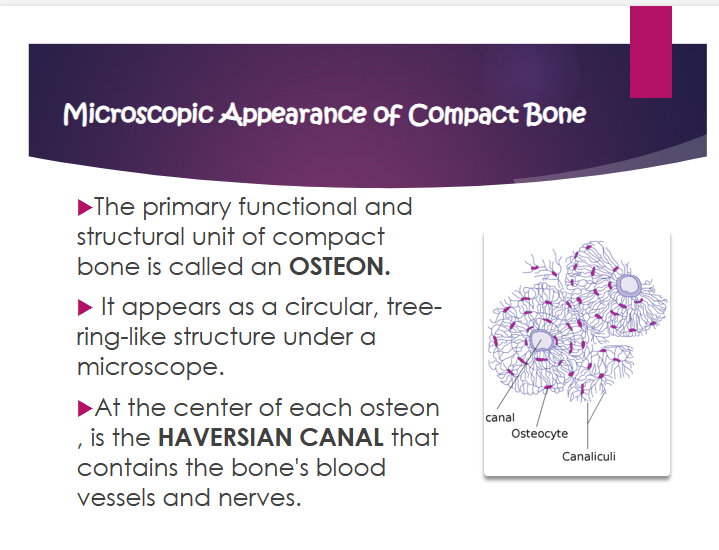
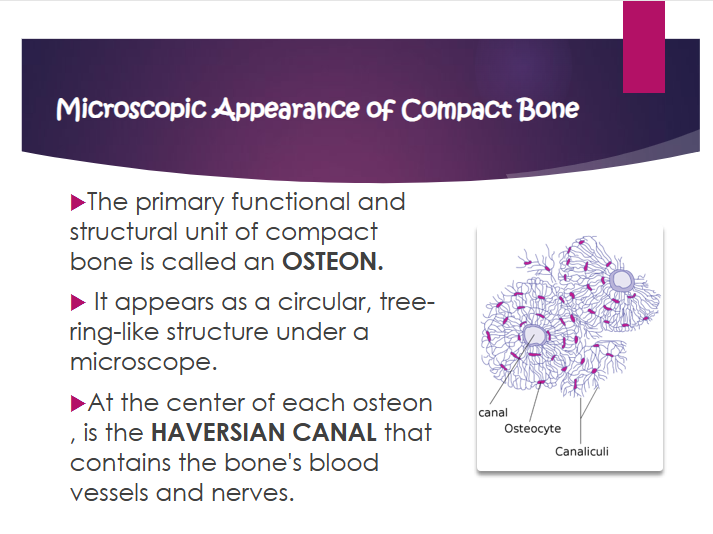
osteon
primary functional and structural unit of compact bone
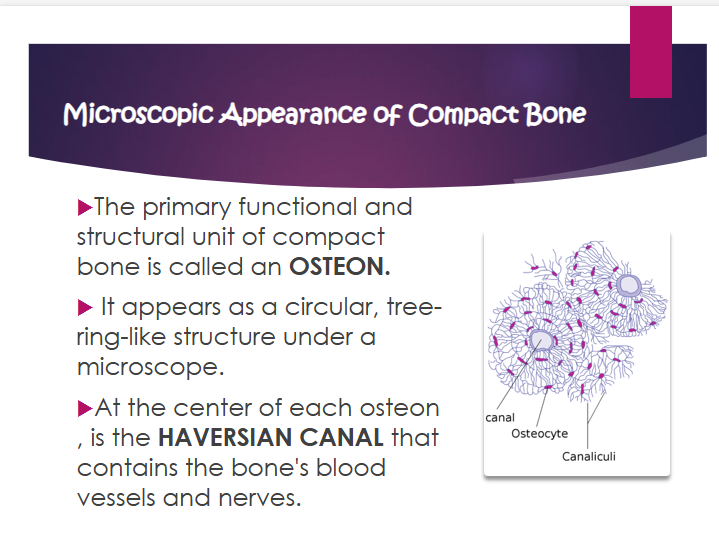
what does osteon look like
circular, tree-ring-like structure under a microscope
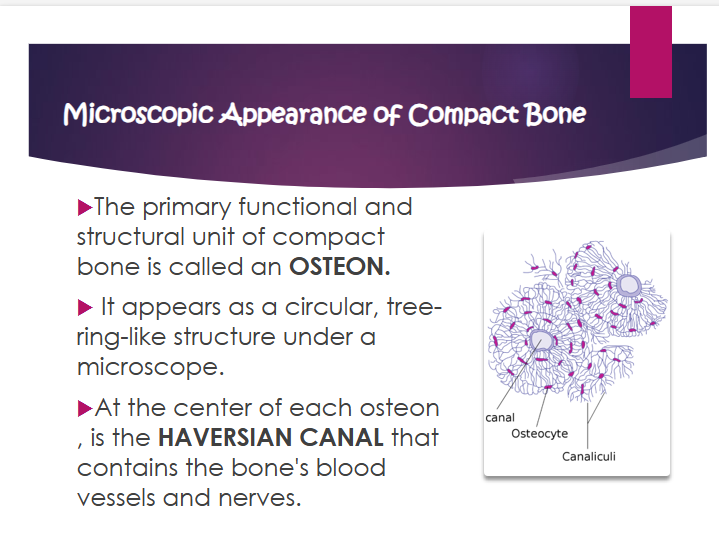
what is the haversian canal?
contains the bone’s blood vessels and nerves
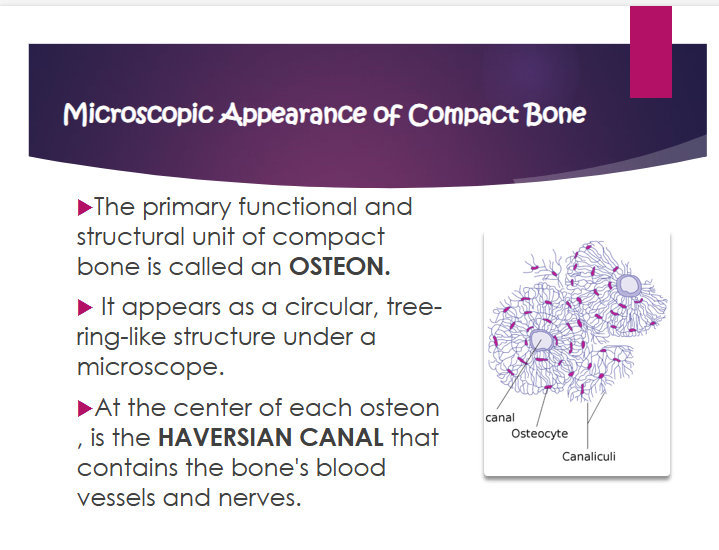
where is the haversian canal?
at the center of each osteon
lamellae
the concentric rings of calcified matrix that surround the central haversian canal

lacunae
small hollow spaces situated between the lamellae. these spaces contain bone cells or osteocytes

osteocyte
a mature bone cell that was once an osteoblast. osteocytes resident in the lacunae and maintain the bone matrix

canaliculi
tiny channels that radiate outward from the lacunae and connect to other lacunae and the central canal

the haversian centrals are connected by perforating —— ——
volkmann’s canals
what way is the volkmann’s canals
perpendicular