Art History Works
1/552
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
553 Terms
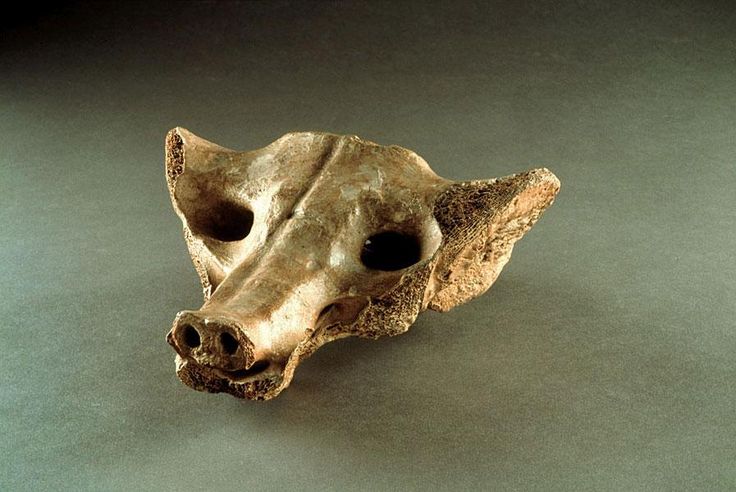
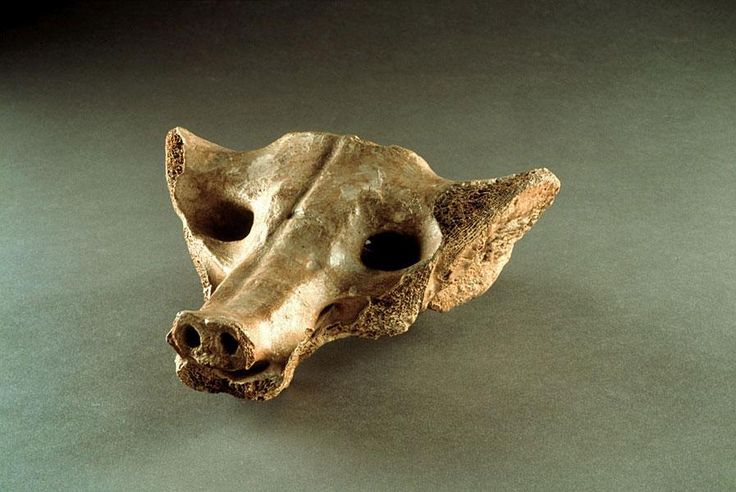
Camelid Sacrum in the shape of a canine
Bone sculpted from camel-like animal
Made to be a dog or a wolf
Sacrum is the base of the spine and sometimes symbolized the soul
In mesoamerica, the sacrum is a ‘second skull’
Produced ~14,000-7,000 BCE
Created by the Olmec Community


What is this work?
Camelid Sacrum in the shape of a canine
Anthropomorphic Stele
Was likely a grave marker
Found near ancient trade routes
Found in Arabia
Made of sandstone
4000-3000 B.C.E.


What work is this?
Anthropomorphic Stele
Jade Cong from Laingzhu
Abstract pattern; design may relate to a face with spirits/dieties
Some spirits have masks and maybe a headdress
Found within graves of the rich, some showing signs of burning
3300-2200 B.C.E.
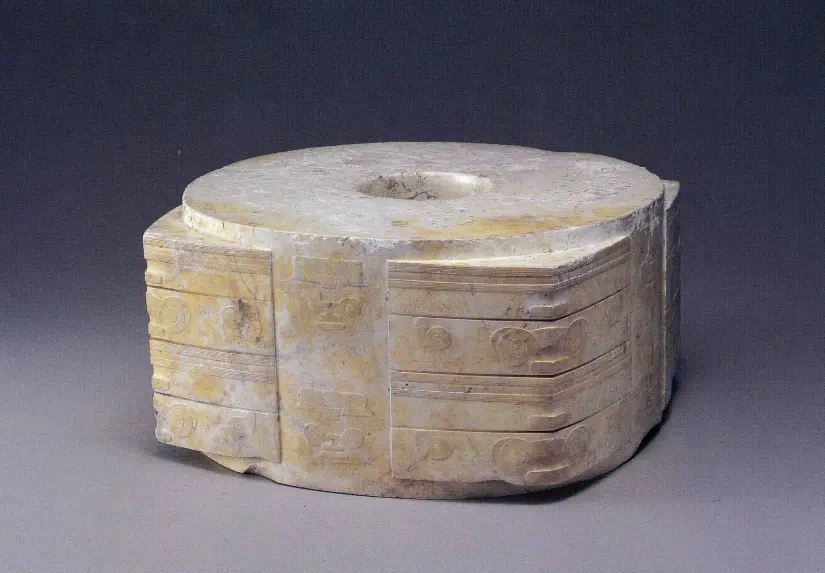
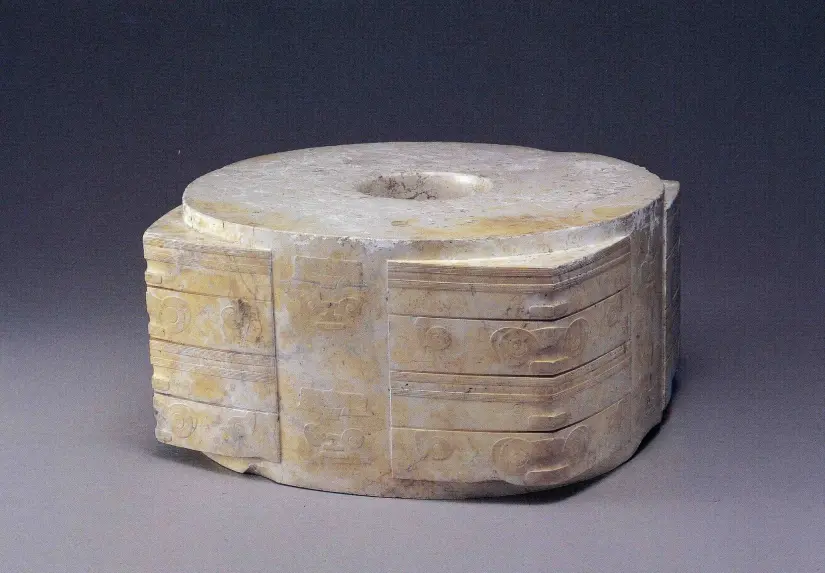


What work is this?
Jade Cong from Laingzhu
The Ambum Stone from Papau New Guinea
Masked human with likely anteater head
May be related to tool making
Perhaps had a ritual purpose and sacred
~1500 B.C.E.
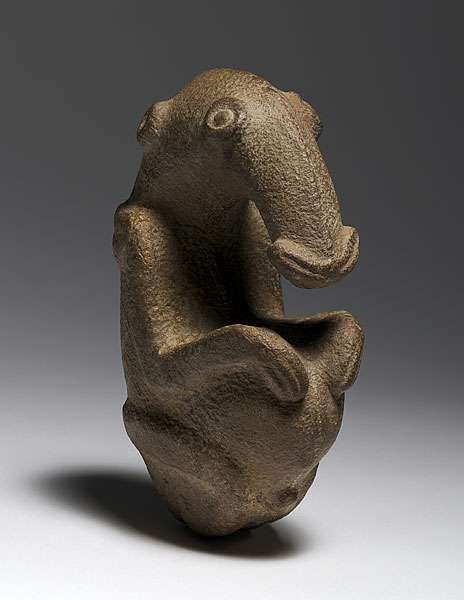


What work is this?
The Ambum Stone from Papau New Guinea
Tlatilco Female Figures
Exaggerated physical features and bare of anything but jewelry
Highly detailed female figures w/ hair and body ornaments
May have had shamanistic elements
Variations with physical deformities that may have also bee symbolic
1200-900 B.C.E.


What work is this?
Tlatilco Female Figures
Terracotta Fragment
Originates from the Lapita culture of Solomon Islands
Use of designs may have inspiration from tattoo designs
Likely used comb like tool to make these designs
1000 B.C.E.
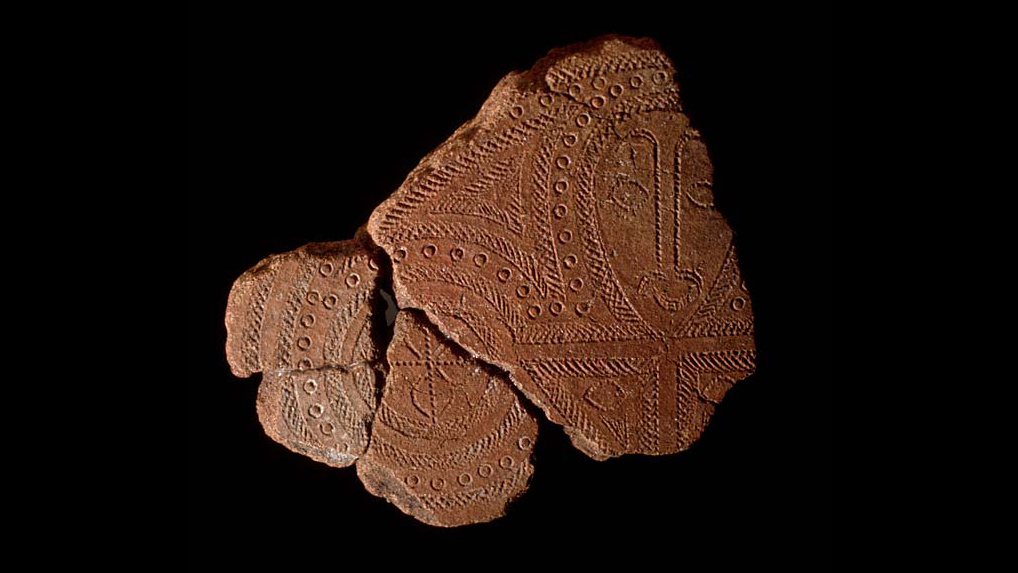
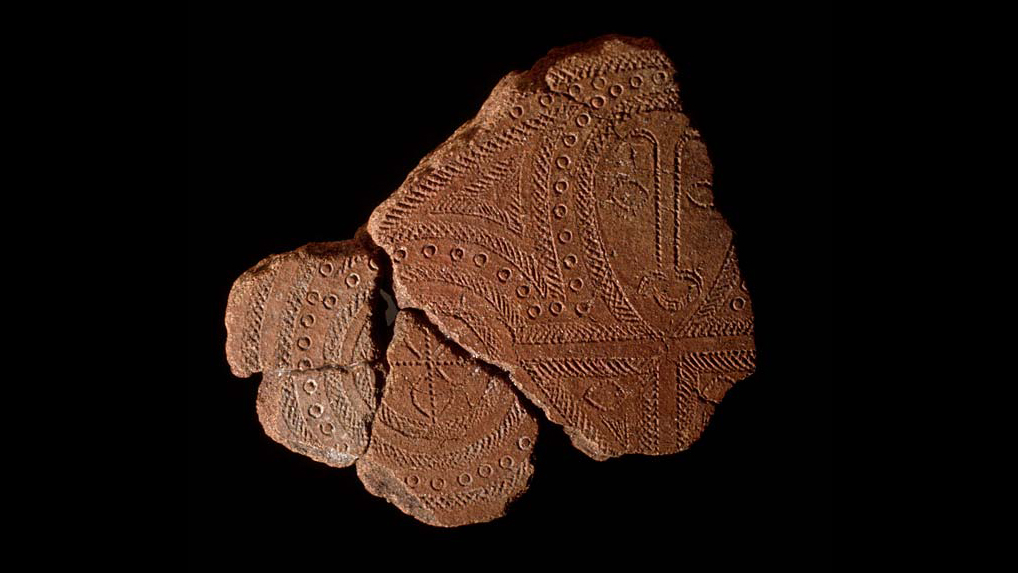


What work is this?
Terracotta Fragment of the Lapita Culture
Apollo 11 Stones / Animal facing Left
Likely meant to be transported around
Not quite sure exactly what the animal is
Made in charcoal
Found in Namibia
25,500 - 25,300 B.C.E.


What work is this?
Animal Facing Left —> Namibia
Lascaux Caves
Paintings featuring cows, bulls, horses, deer
Overlapping figures and done over many generations
Composite view
Some handprints might have been signatures
15,000 - 13,000 B.C.E.


What work is this?
Lascaux Caves
Running Horned Woman
The area was initially grasslands but now desert
It was made by various groups
May have been ceremonial or shown her on the way to a ceremony
6,000 - 4,000 B.C.E.
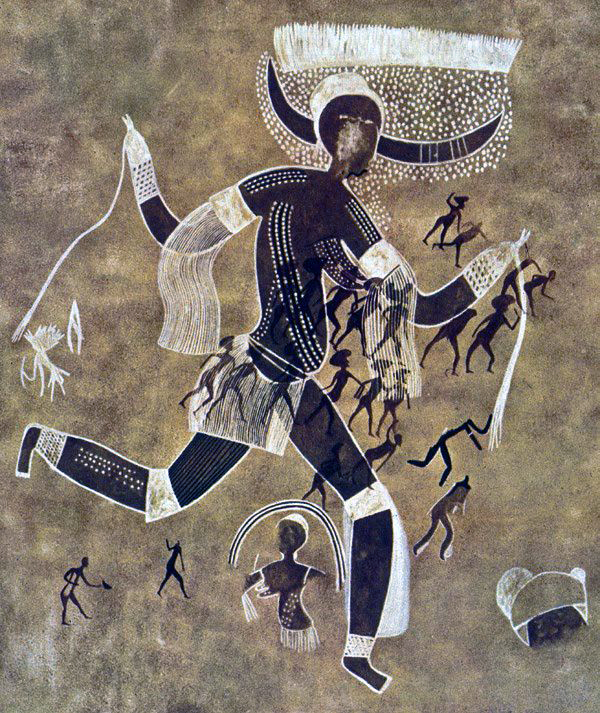
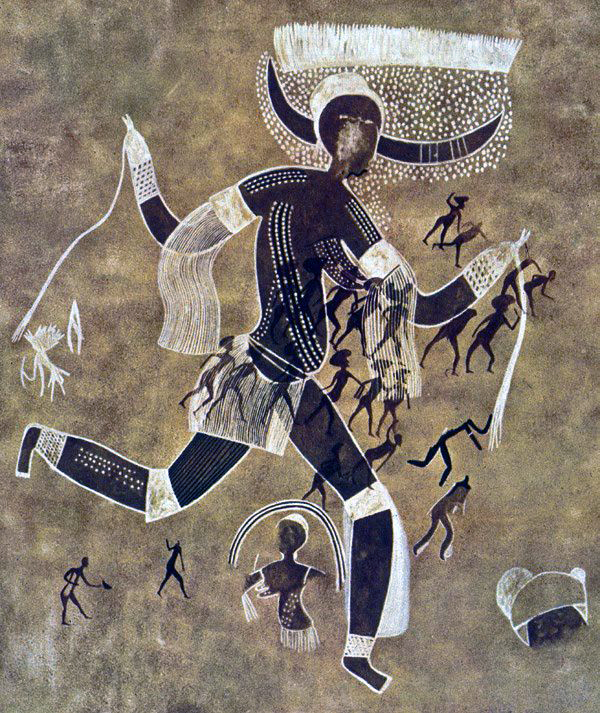


What work is this?
Horned Running Woman
Beaker with Ibex Moteifs
Has aquatic birds and running dogs along with Ibex
Likely made on a pottery wheel
The middle of horns likely is sign of clan family ownership
Found near a burial site in Susa Iran
4,200 - 3,500 B.C.E.
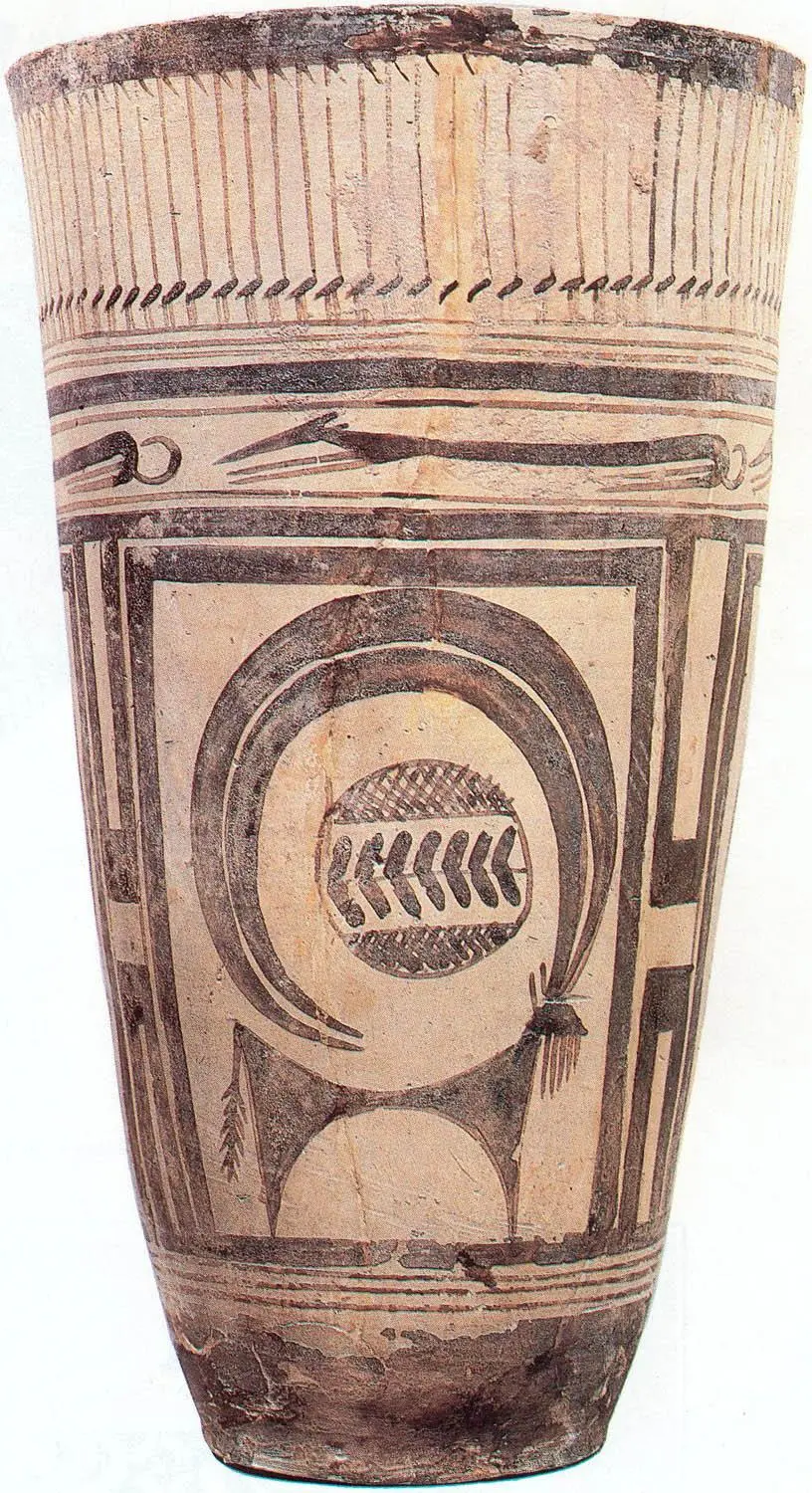
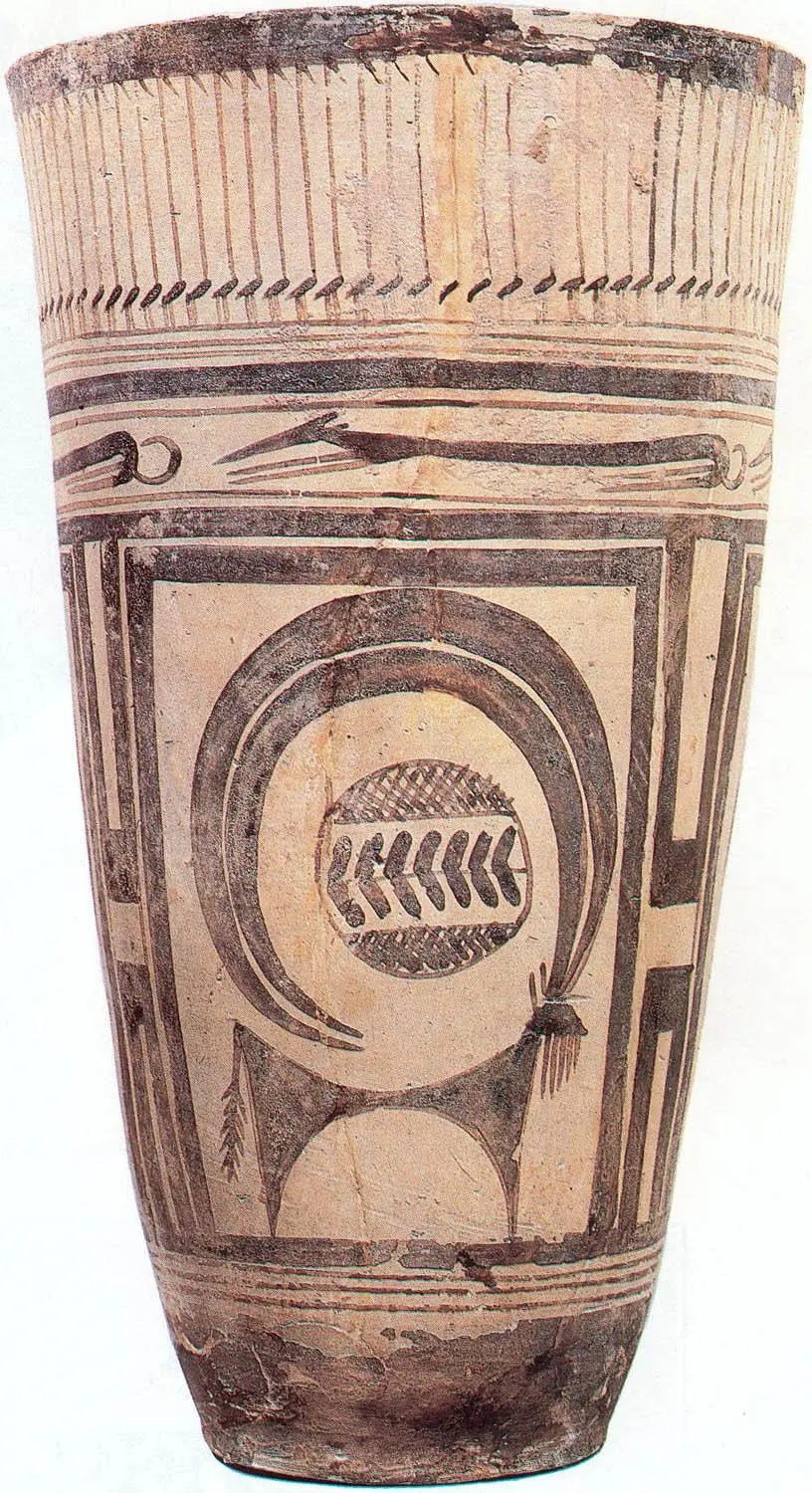


What work is this?
Beaker with Ibex motifs
Stonehenge
Post-and-Lintel building; a system to keep everything attached
Megolithic stones imported from 150+ miles away
Smaller stones gathered around
Large stones all surround a horseshoe
Either for summer solstice, a burial site with elite males, site for healing the sick
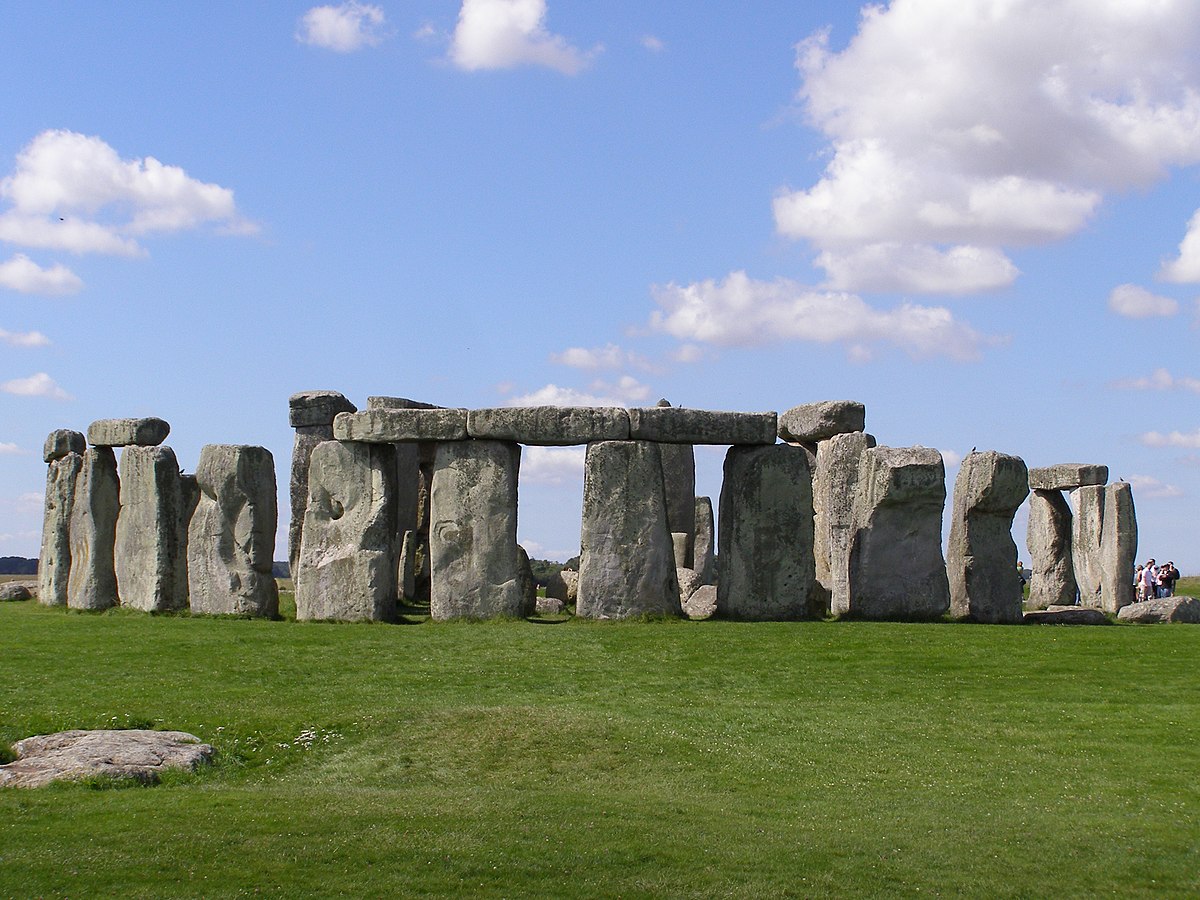
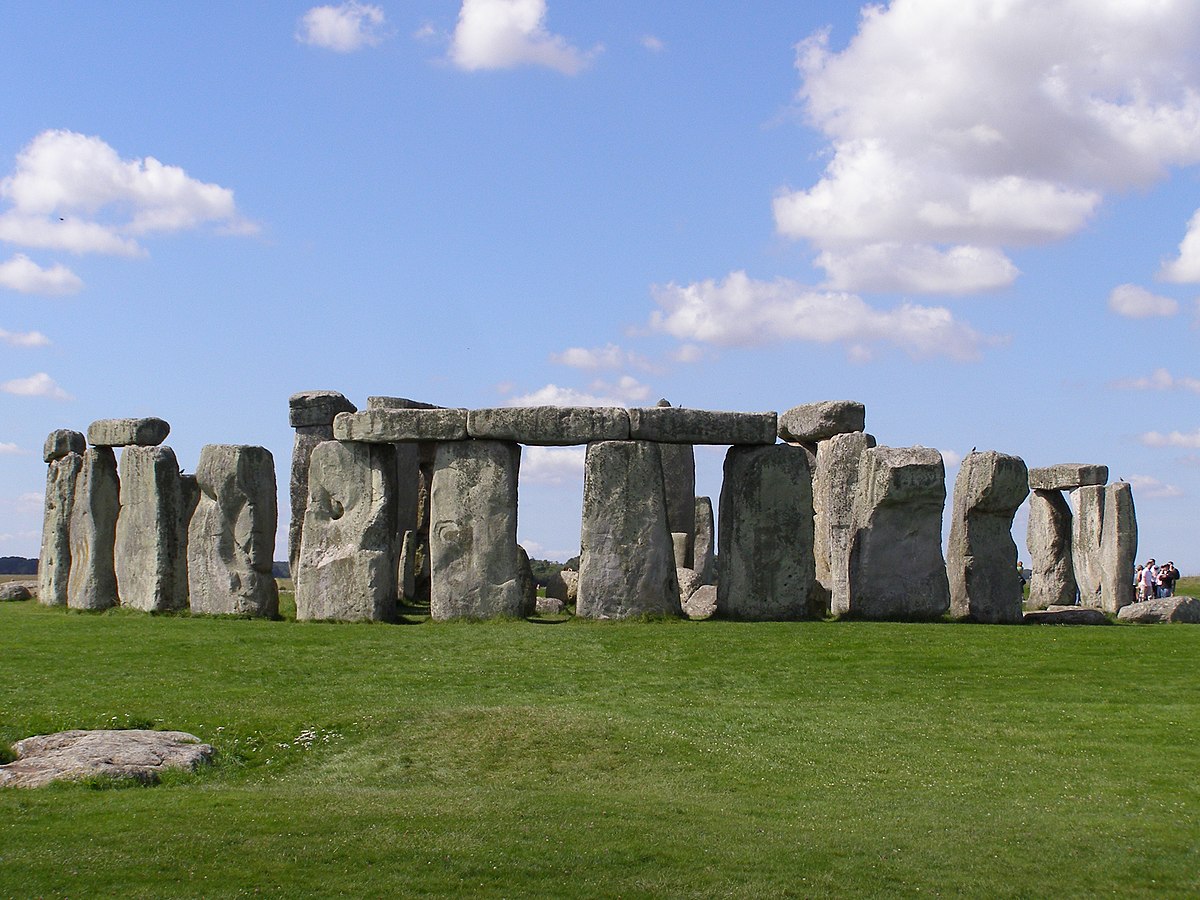


What work is this?
Stonehenge
White temple and its ziggurat
Elevated for closeness to gods and tapers to shed rainwater
Bent Axis plan —> people have to see the whole thing as they approach
Main temple was likely for royalty and clergy
The corners were oriented to a compass
Made from mudbrick and whitewashed to hide the mud
Diety was Anu and worshiped by the SUMERIANS
3,500 - 3,000 B.C.E.
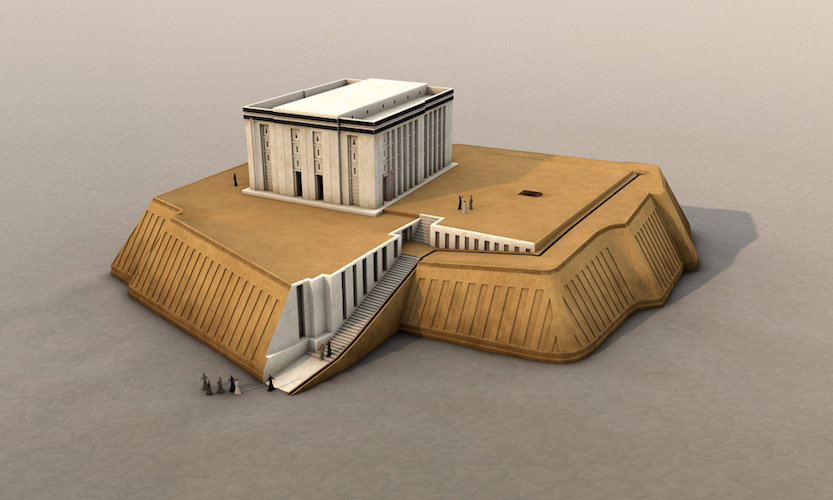
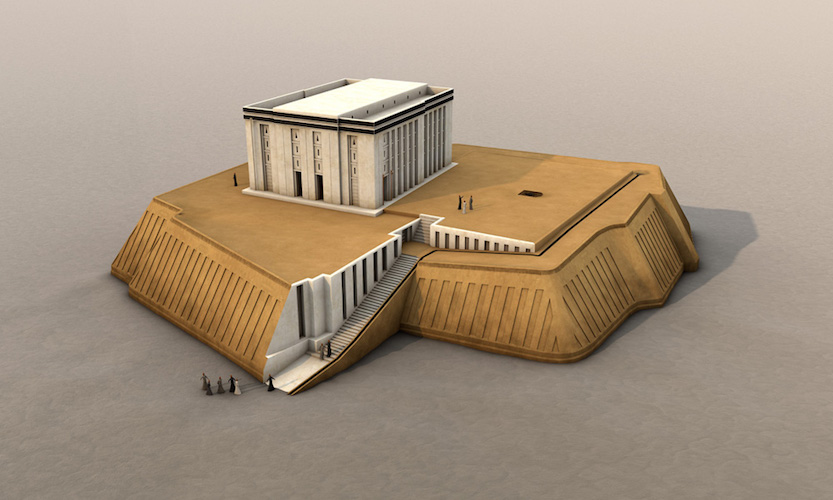
What work is this?
White temple and its ziggurat (SUMERIAN)
Statues of votive figures
Different height for heiarchy of scale
Eyes wide and hands praying for worship to the gods
Represent morals praying to the gods w/ inscriptions saying that it prays
Most have been buried under the temple floor
Made of gypsum, shell, and black limestone
2,700 B.C.E. (SUMERIAN)
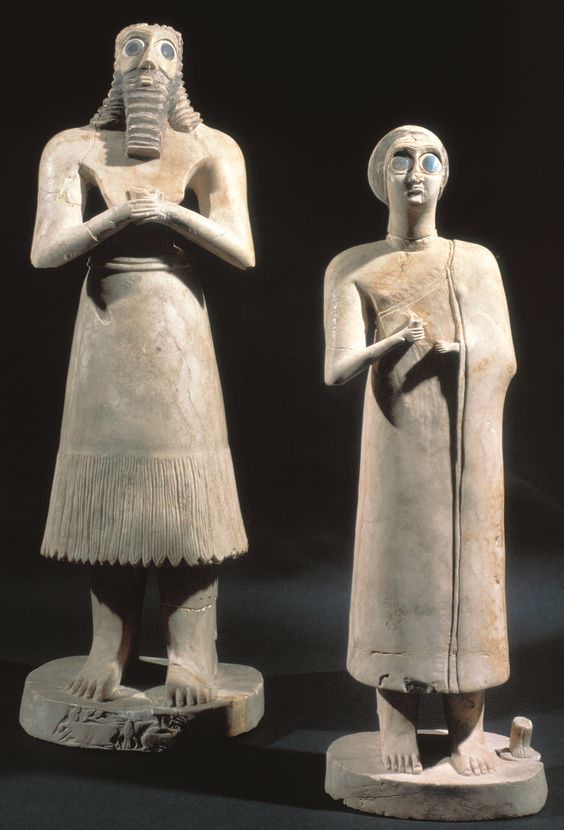
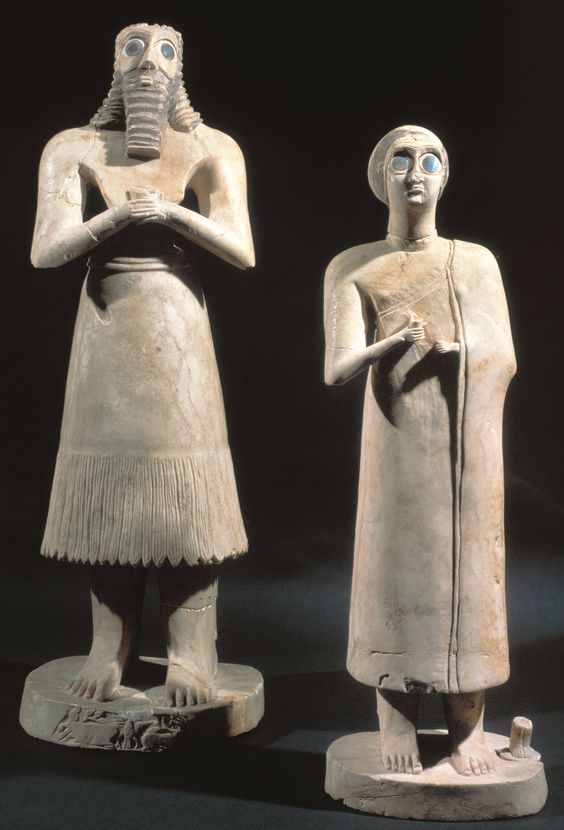


What work is this?
Statue of votive figures (SUMERIAN)
Standard of Ur
Organized in registers read from top to bottom
There are two sides, one with peace and one with war
War side: Sumerian king inspects captives taken to him while chariots run over dead
Peace side: There are musicians, banquets, likely victory celebration
Fond in a tomb but NOT a standard —> may have been a soundbox for an instrument
2,600 - 2,400 B.C.E. (Sumerian)


What work is this?
Standard of Ur (Sumerian)
Code of Hammurabi
Earliest representation of written down laws for a community
Sun god (Samash) hands the laws to Hammurabi
Lowkey a display of wealth
Made of Basalt
1792-1750 B.C.E. (Babylonian)


What work is this?
Code of Hammurabi (Babylonian)
Lamassu
Have five legs but from most angles, look like they only have 4
Guarded the chambers for a king
Display power
Ward of seen and unseen enemies
Megolithic pieces of stone
Combination of man and bull
720- 705 B.C.E. (Assyrian)


What work is this?
Lamassu
Audience Hall of Darius and Xerxes
Column bottoms are a lotus while the top is a bull
Meant to make the viewer feel as small as possible
Intended for when people come and visit the king
A hypostyle hall —> shows egyptian influence
Relief sculptures with people bringing gifts
Built to be a display of wealth and power of the empire
520-465 B.C.E. (Persian)
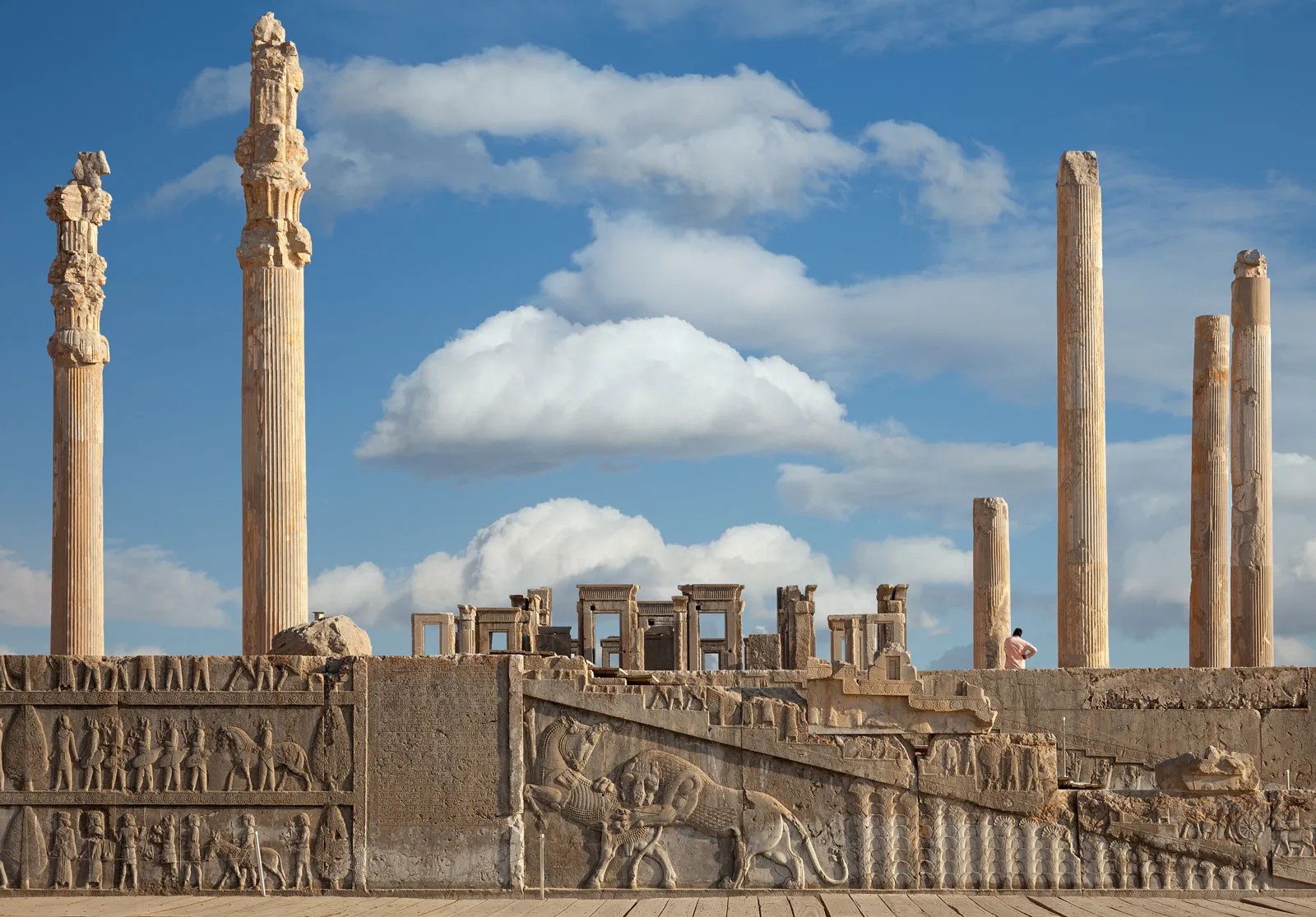
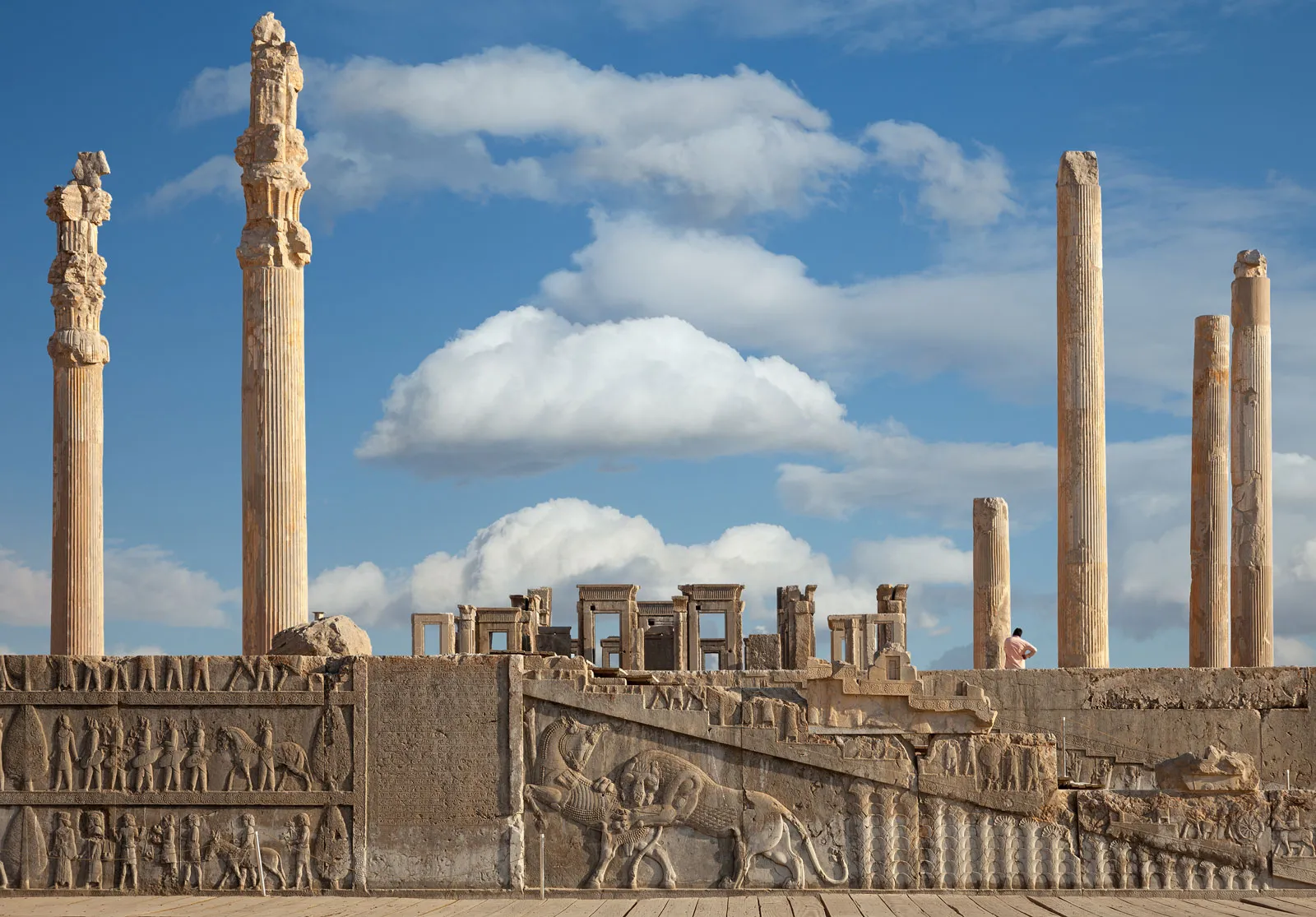


What work is this?
Audience hall of Darius and Xerxes (Persian)
Narmer Pallette
Was a makeup palette where everything could be ground up
Shows reunification of upper and lower egypt
Bird is lower egypt, horus is upper egypt
Upper egypt is actually southern
Happened over a long period so this is more symbolic
3,000 -2,920 B.C.E.


What work is this?
Narmer Palette
Seated Scribe
Not a pharoah because not as idealized
Not a portrait, but instead representation of a scribe
Held papyrus in his lap but its now gone
Painted limestone
2,620 - 2,500 B.C.E.


What work is this?
Seated Scribe
Great Pyramids
Giant monuments for the pharaoh’s burial
Hold Menkaura, Khufu, and Khafre
May be influenced by a relic called the benben
Limestone
Points of the pyramid were facing the parts of a compass
Sphinx may have been portrait of Khafre and cats were seen as sacred
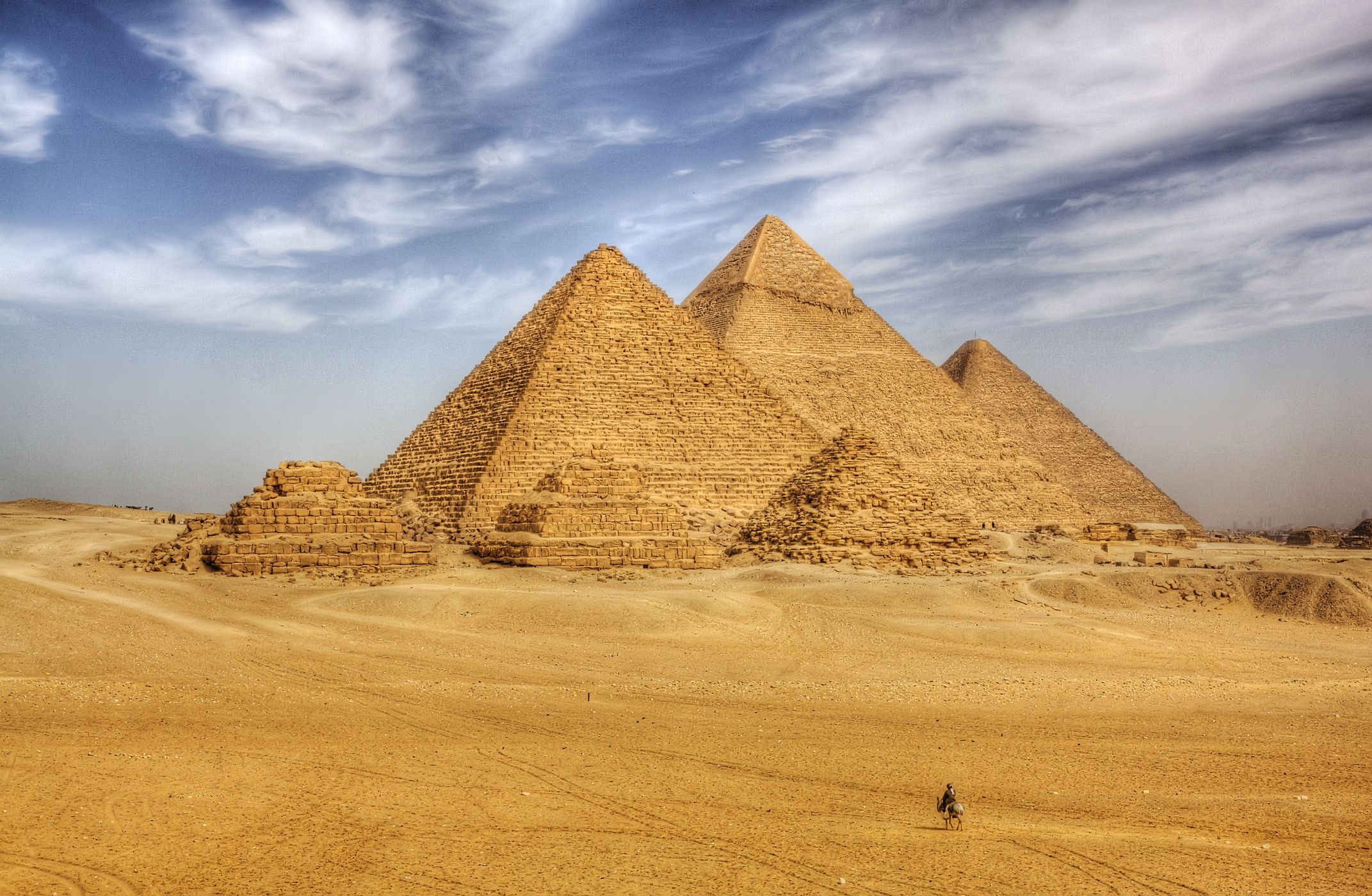


What work is this?
The great pyramids of giza
King Menkaura and Queen
Made from Greywacke (strong material)
Legs are still attached to stone behind them
Wife may either be a goddess or the Queen presenting him to the gods
Interesting hierarchy of scale where they are not too different in height
2,490 - 2,472 B.C.E.


What work is this?
King Menkaura and queen
Temple of Amun-Re
Built along the nile with easier access for festivities
Some symbolism with the back of the building being farther way (gets more quiet)
Thick columns allow little light
Painted
Sunken relief
Temple for the worship of Amun-Re
The higher priests could go into the darker potions of the temple


What work is this?
The temple of Amun-Re
Mortuary temple of Hatshepsut
Did not use the same pyramids because of grave robbing
The terraces were used as gardens
She built the temple for her (alleged) father, Amun (god)
Only a few rituals were conducted here
She was actually buried behind the mountian, through the valley of the kings
Temple aligned with winter solstice
1473-1458 B.C.E.


What is this work?
Mortuary temple of Hatshepsut (maybe by Senenmut)
Queen Hatshepsut with Offering Jars
Holds multiple male attributes but slight indication of breasts
one of 200 statues in complex
She is offering specifically to sun god —> pharoahs only knelt to gods
1473-1458 B.C.E.
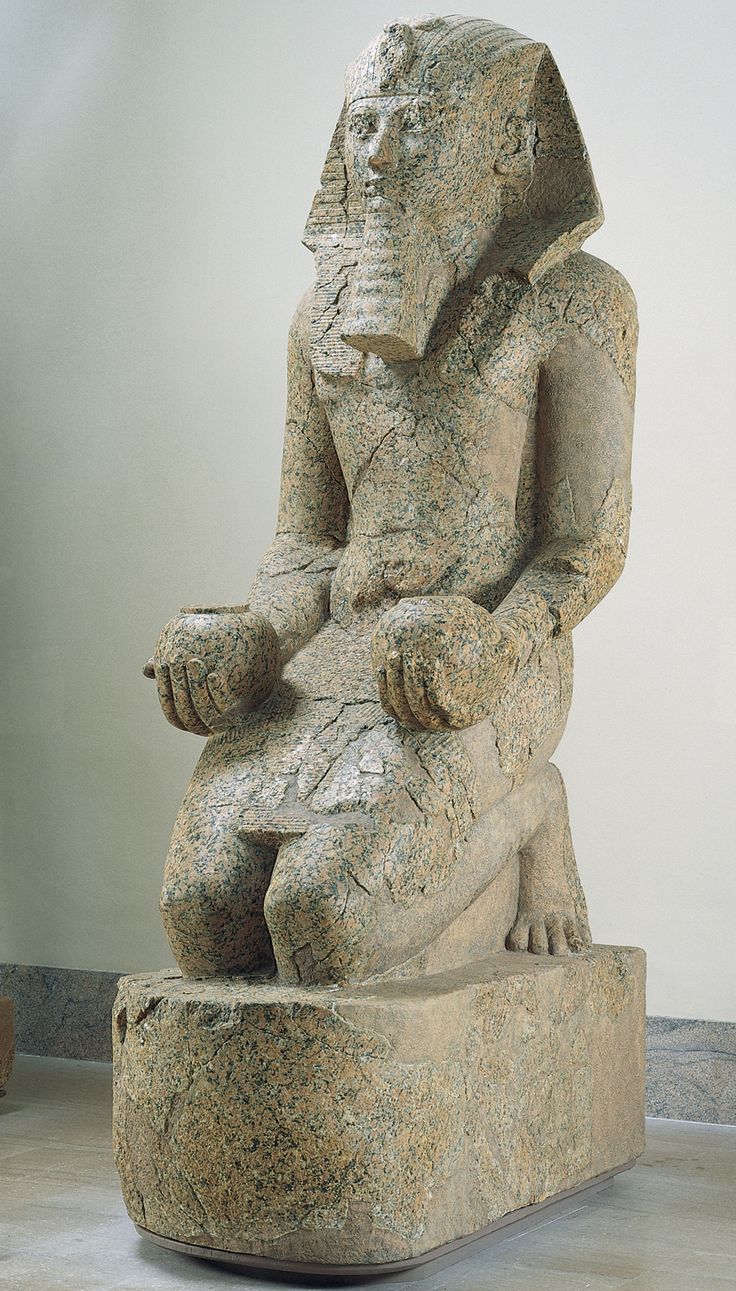
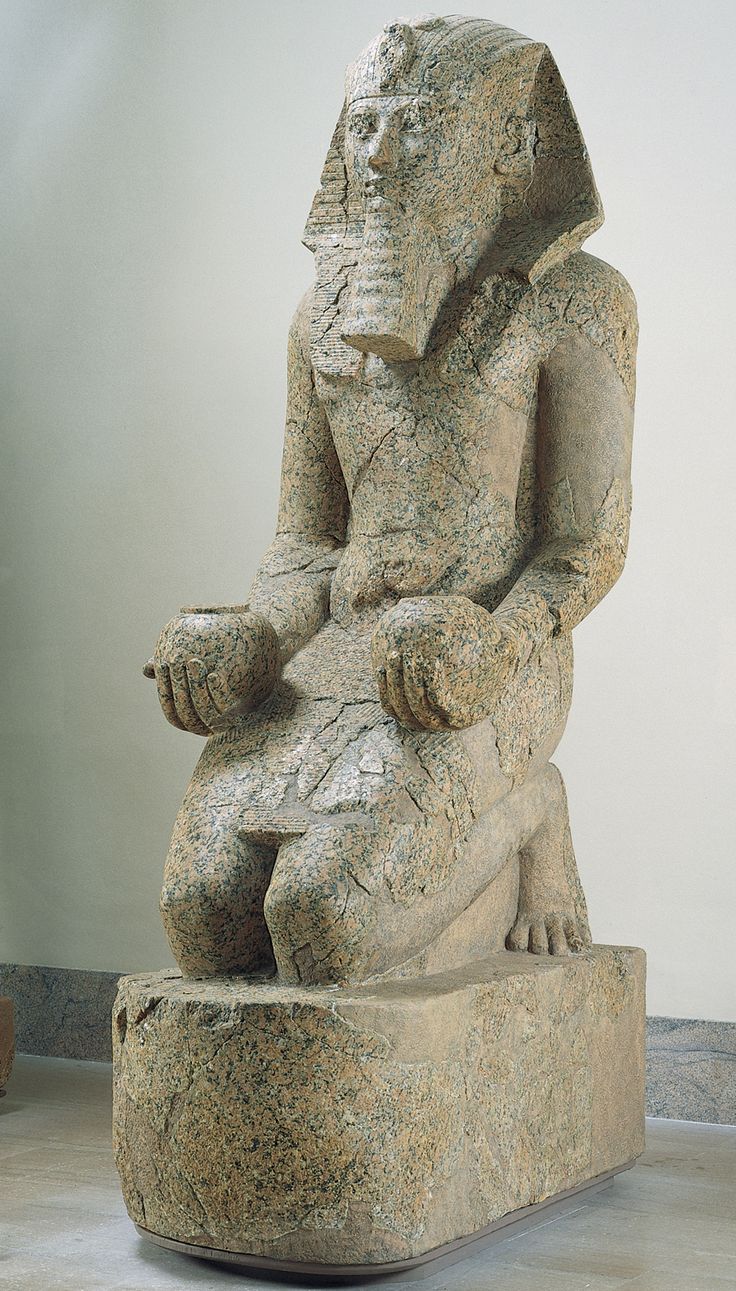


What work is this?
Queen Hatshepsut with Offering Jars
Akhenaton, Nefertiti and Three Daughters
Akhenton holds daughter on left, Nefertiti on right
Tried to create a shift within egyptian art
Altered the way their bodies were shone
Akhenaton created new capital named after him and just worshiped sun disk
Sun rays = life in egypt and are pointing at queen and king


What work is this?
Akhenaton, Nefertiti, and Three Daughters
Innermost coffin of King Tutankhamun
He wasn’t really important, but when his tomb was discovered, it was a big deal
Buried with a bunch of stuff
Holding symbols of Osiris
1323 B.C.E.
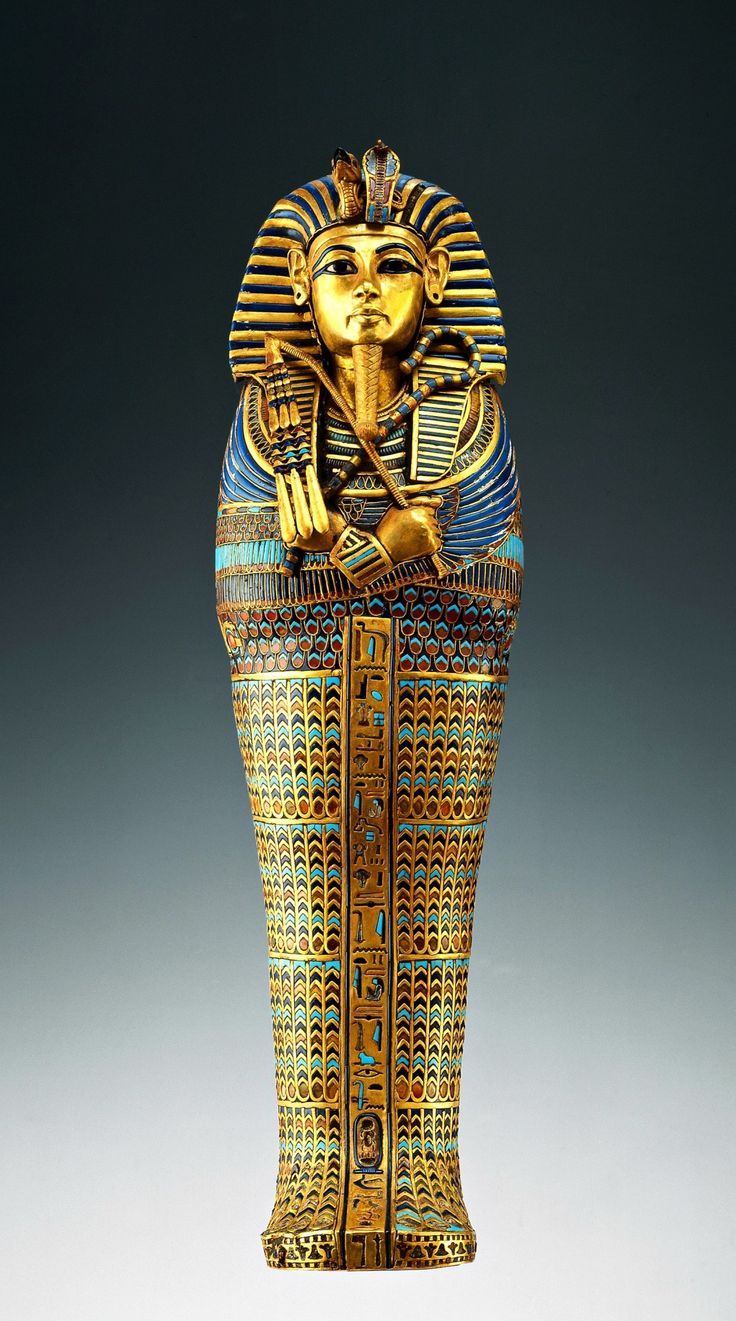
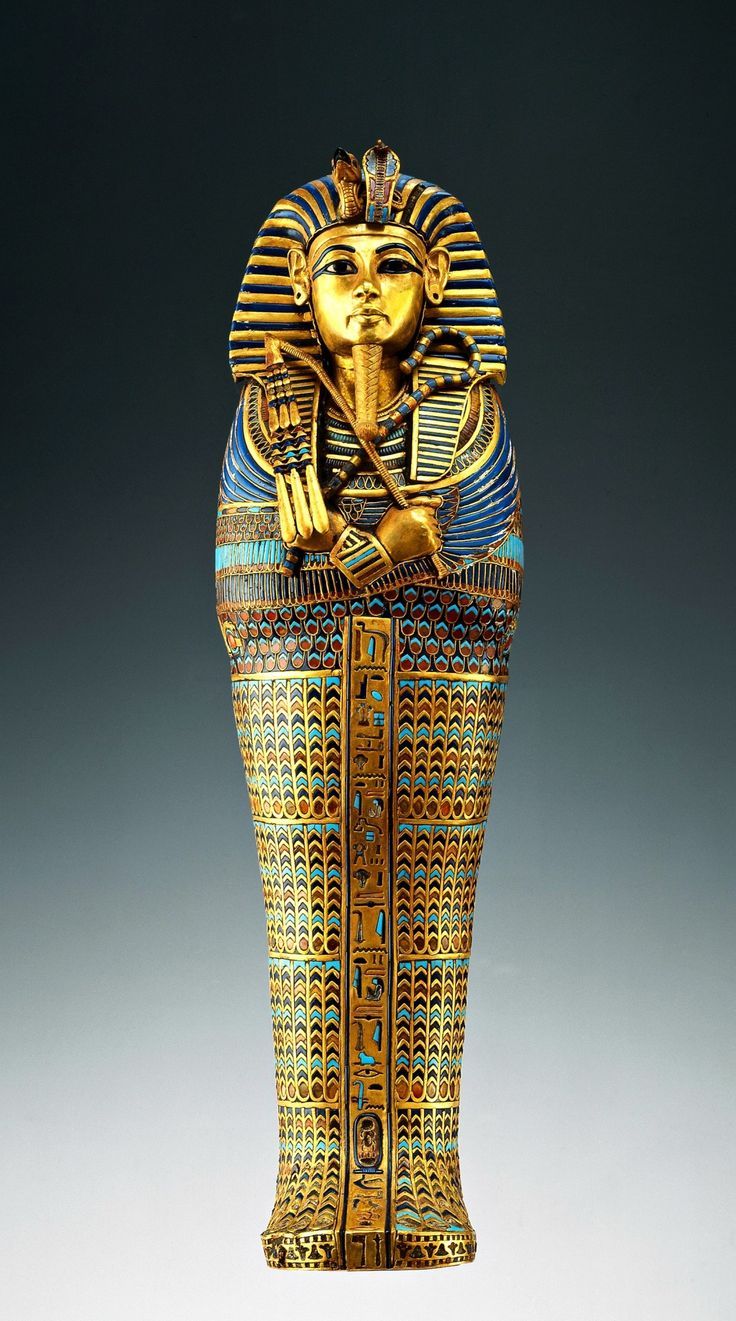


What work is this?
The innermost coffin of King Tutunkhamun
The Last Judgement of Hu-Nefer
Continous narrative on various registers
Part of the book of dead telling egyptians how to get to the afterlife
Aubis leads the deceased to weight soul against a feather
Ammit will eat heart if weighs more
Thoth writes down all the events
Osiris will do a day of judgement
Painted on papyrus scroll
1275 B.C.E.
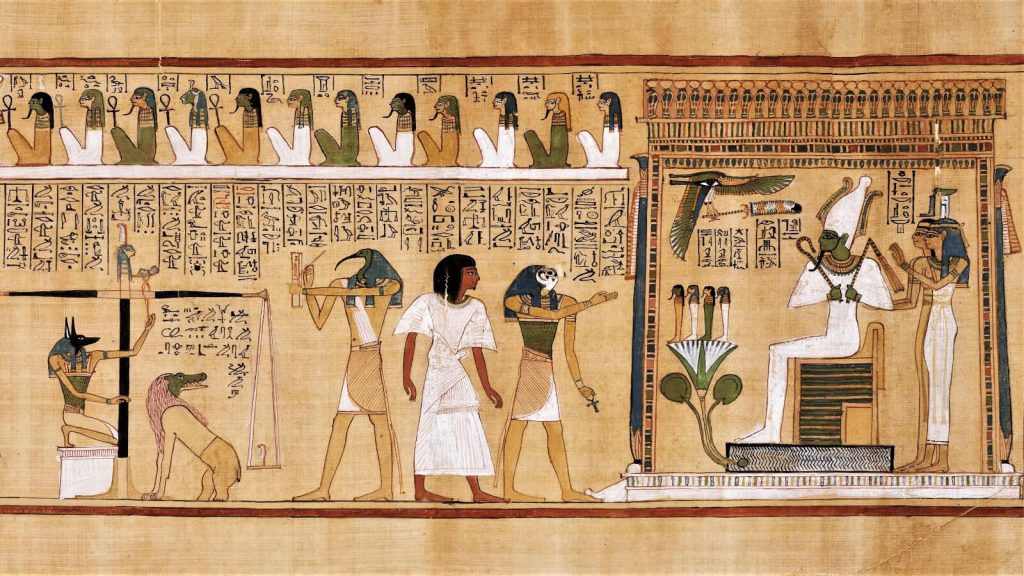
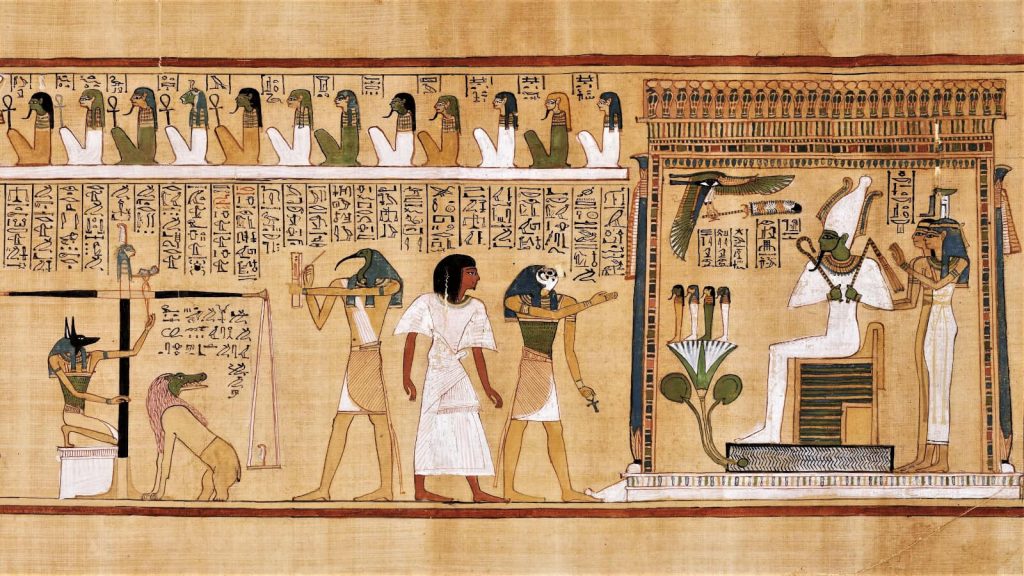
What work is this?
The judgement of hu-nefer
Anavysos Kouros
Archaic greek sculpture
Smile was meant to show alive rather than joy
Similar to egyptian statues, but able to stand on its own without support
It was a grave marker for an aristocratic son
Not accurate, but generalized depiction of deceased
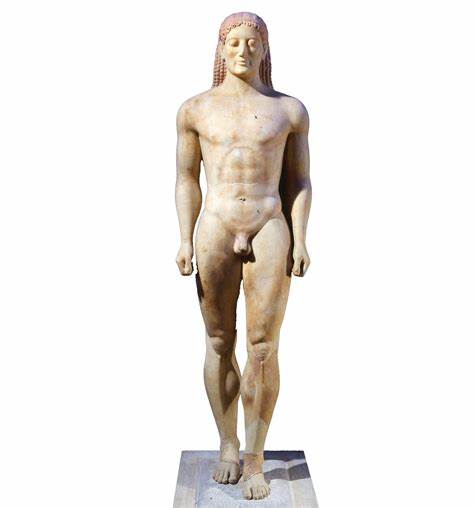
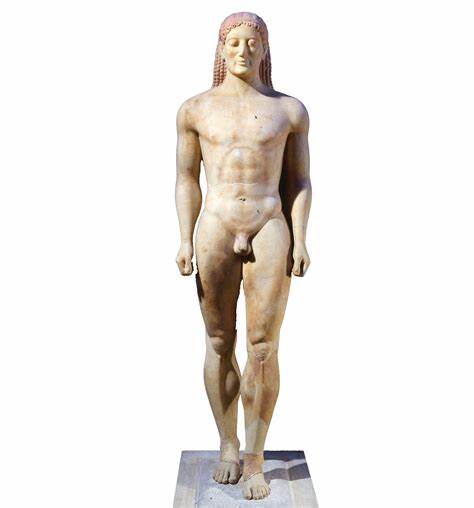


What work is this?
Anavysos Kouros (Archaic)
Peplos Kore
Found on the acropolis and thought to be worshipping girl
Later disproven and now thought to be Artemis
May have held bow and arrows
Paint still remains on her
530 B.C.E. (Archaic)
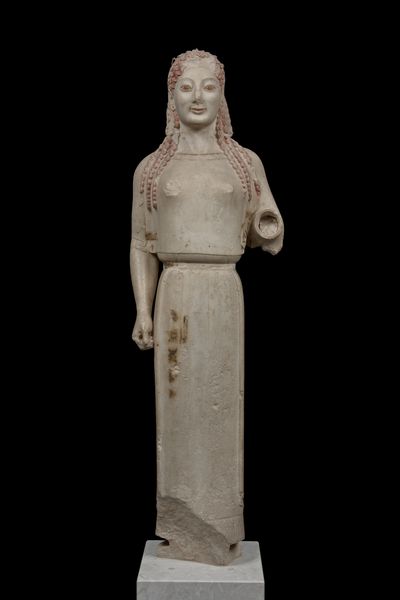
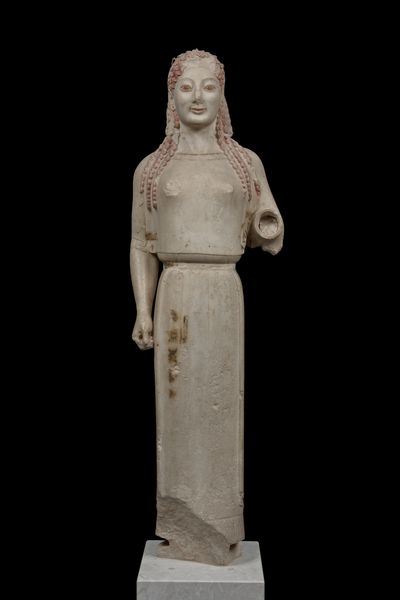


What work is this
Peplos Kore (Archaic)
Doryphoros (Spear Bearer)
First case of controposto and the author wrote this whole book about it
Idealized form of a male athlete
Once held a spear
Made by Polykleitos
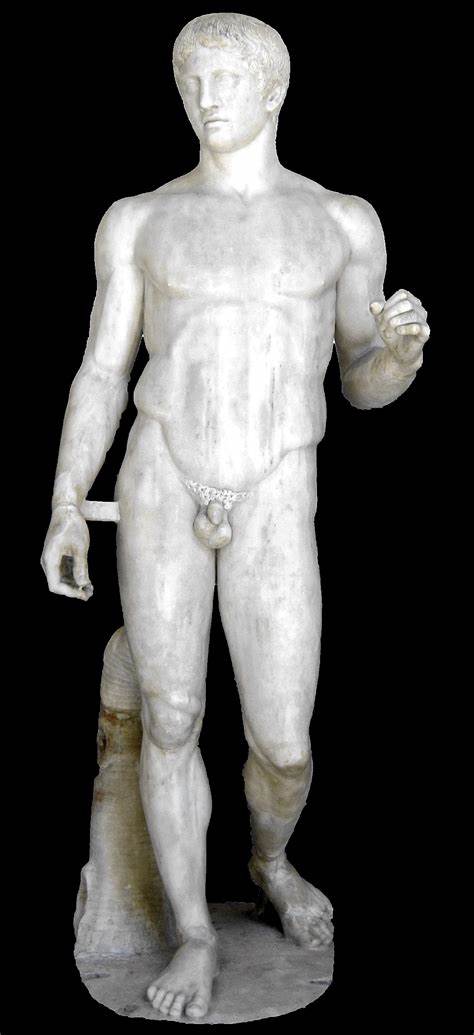
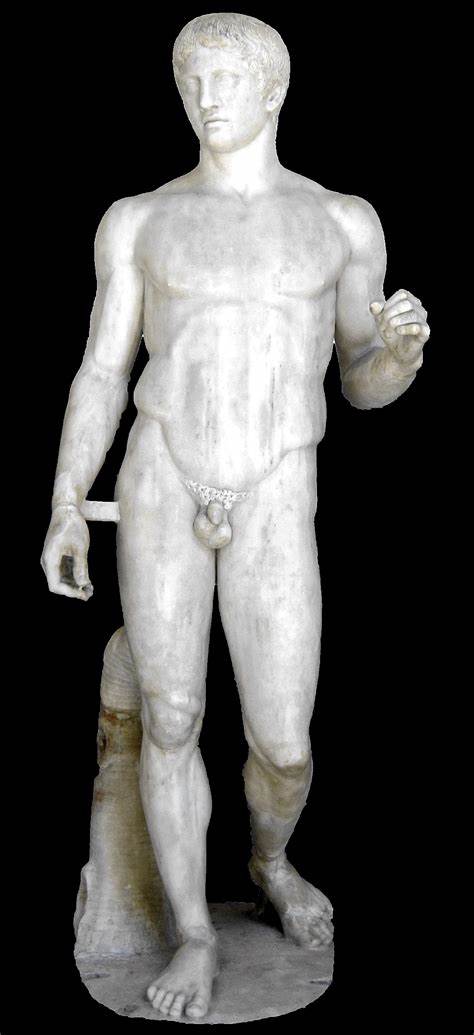


What work is this?
Doryphoros (Spear Bearer) by Polykleitos
Helios, Horses, and Dionysus
Part of the Parthenon pediment
Elements of contrapposto
All show parts of the life of Athena
Made in Phidias’s workshop
438 - 432 B.C.E.


What work is this?
Helios, Horses, and Dionysus (Located on Pantheon) by Phidias
Plaque of the Ergastines
The higher up, the more 3D, so people could actually see it
Part of the Parthenon showing the Panathenaic procession
First depiction ofa human event on a temple
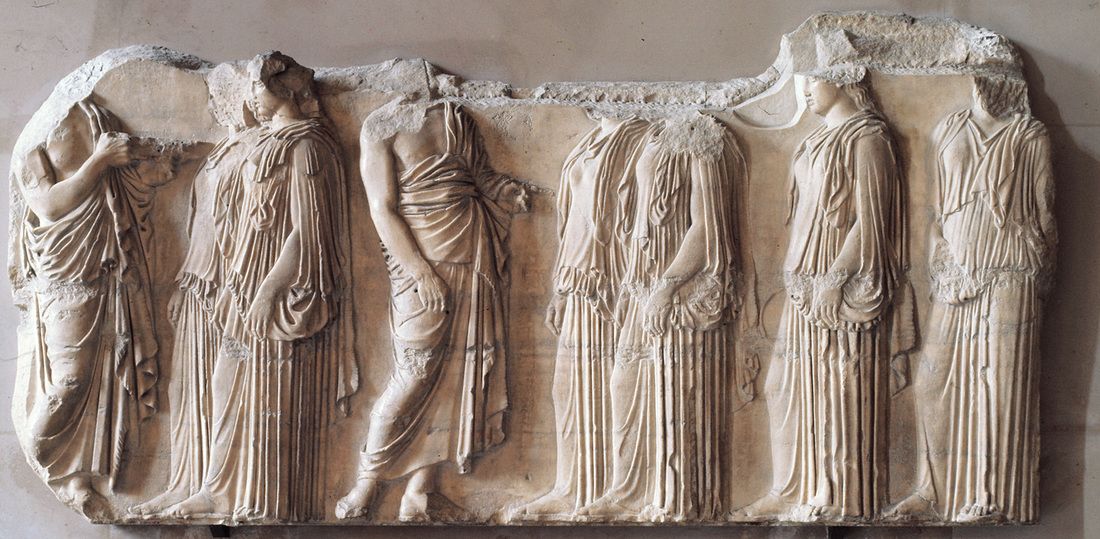
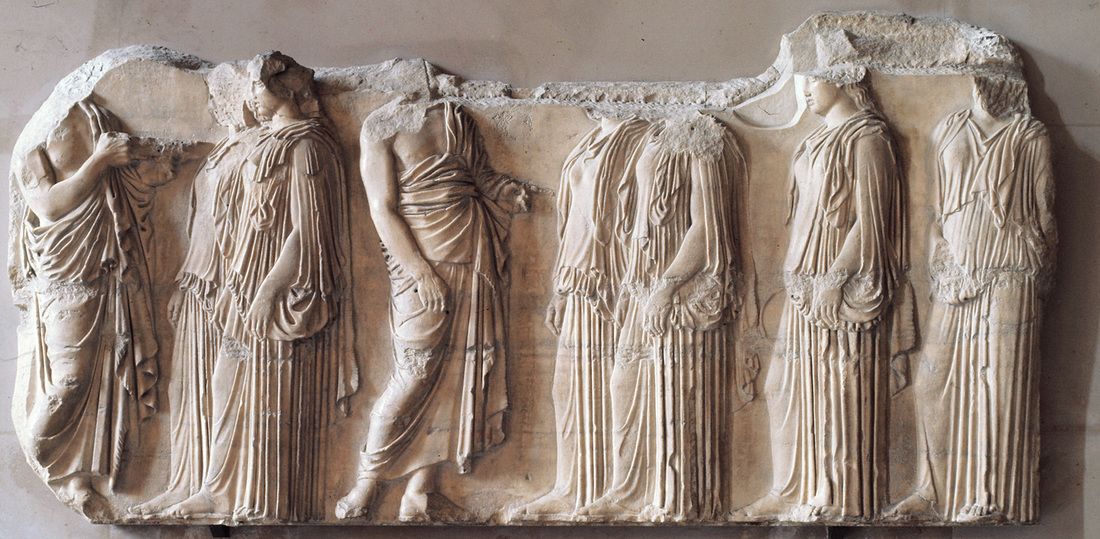


What work is this?
Plaque of the Ergastines (Parthenon)
Victory Adjusting her Sandal
Wet drapery reveals her body
Part of Temple Athena Nike
410 B.C.E.
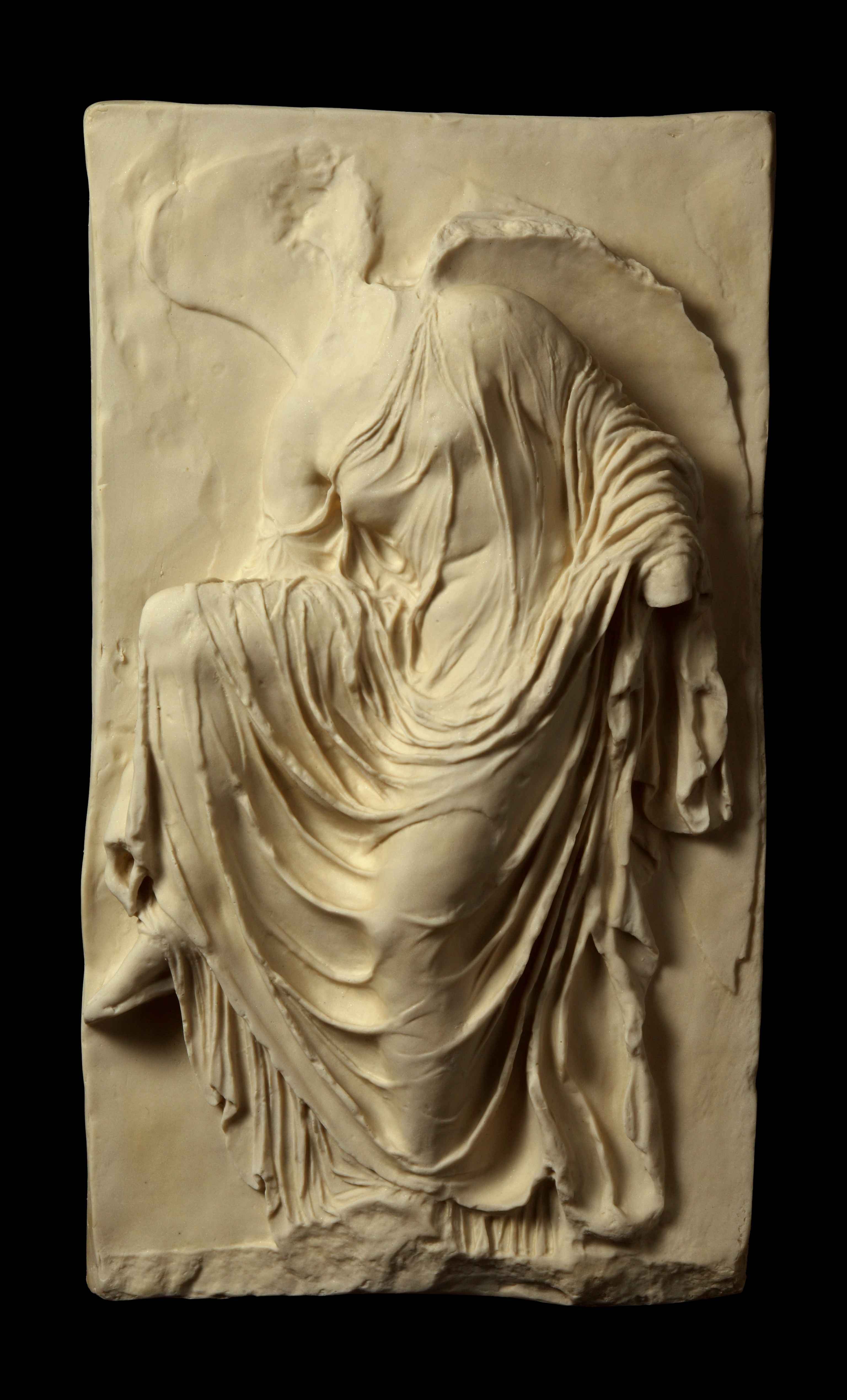
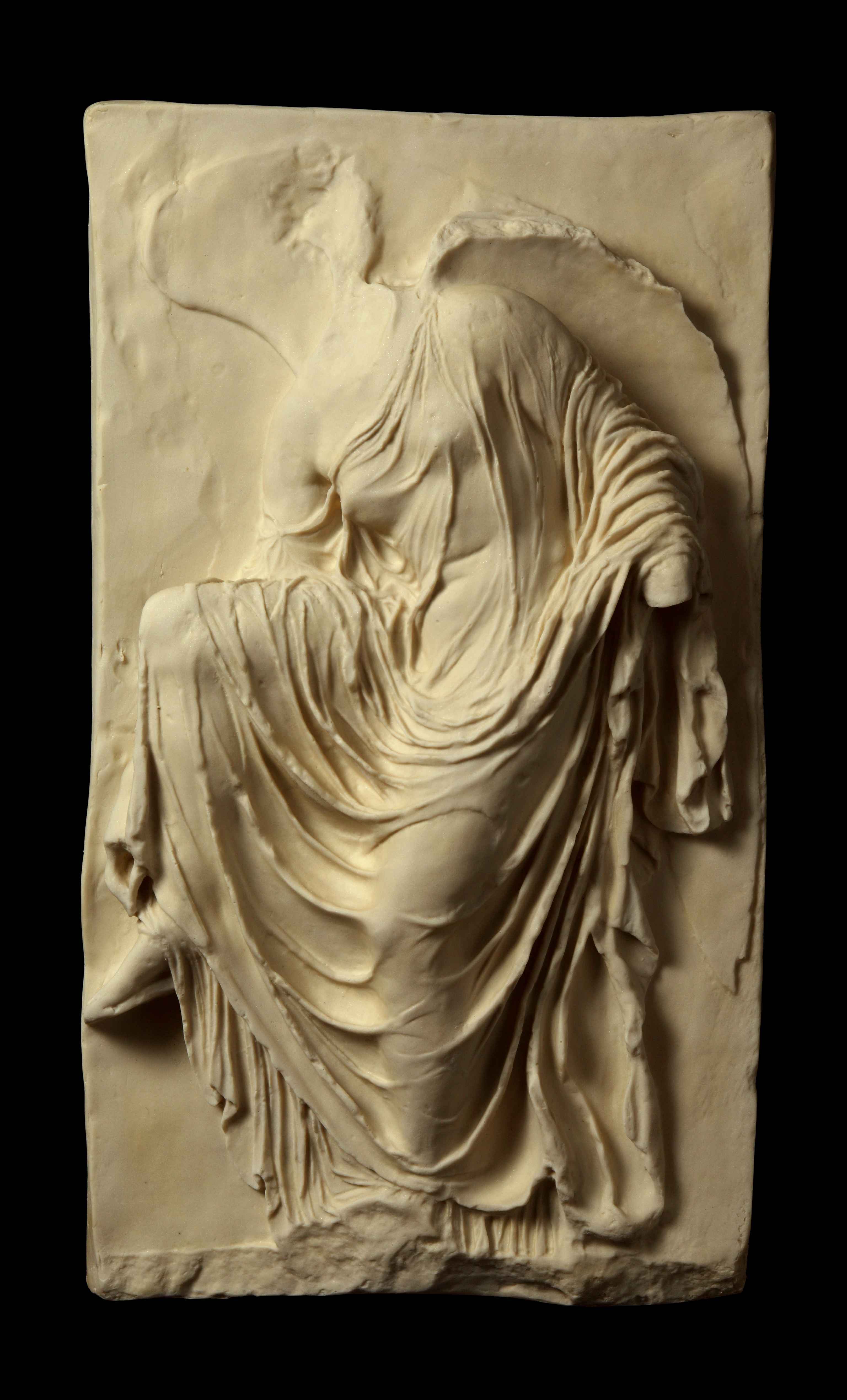


What is this work?
Nike Adjusting her sandal (Temple athena nike)
Grave stele of Hegeso
Severe hierarchy of scale between servant and the woman
The jewelry was likely painted in (May have been a dowry)
Took place within private women’s quarters
Served as a grave marker
Attributed to Kallimachos
410 B.C.E.


What is this work?
Grave stele of Hegeso
Winged victory of Samothrace
Meant to sit in a fountain and look like a figurehead of a boat
Likely commemorated naval victory
Dramatic contrapposto and use of wet fabric
190 B.C.E.
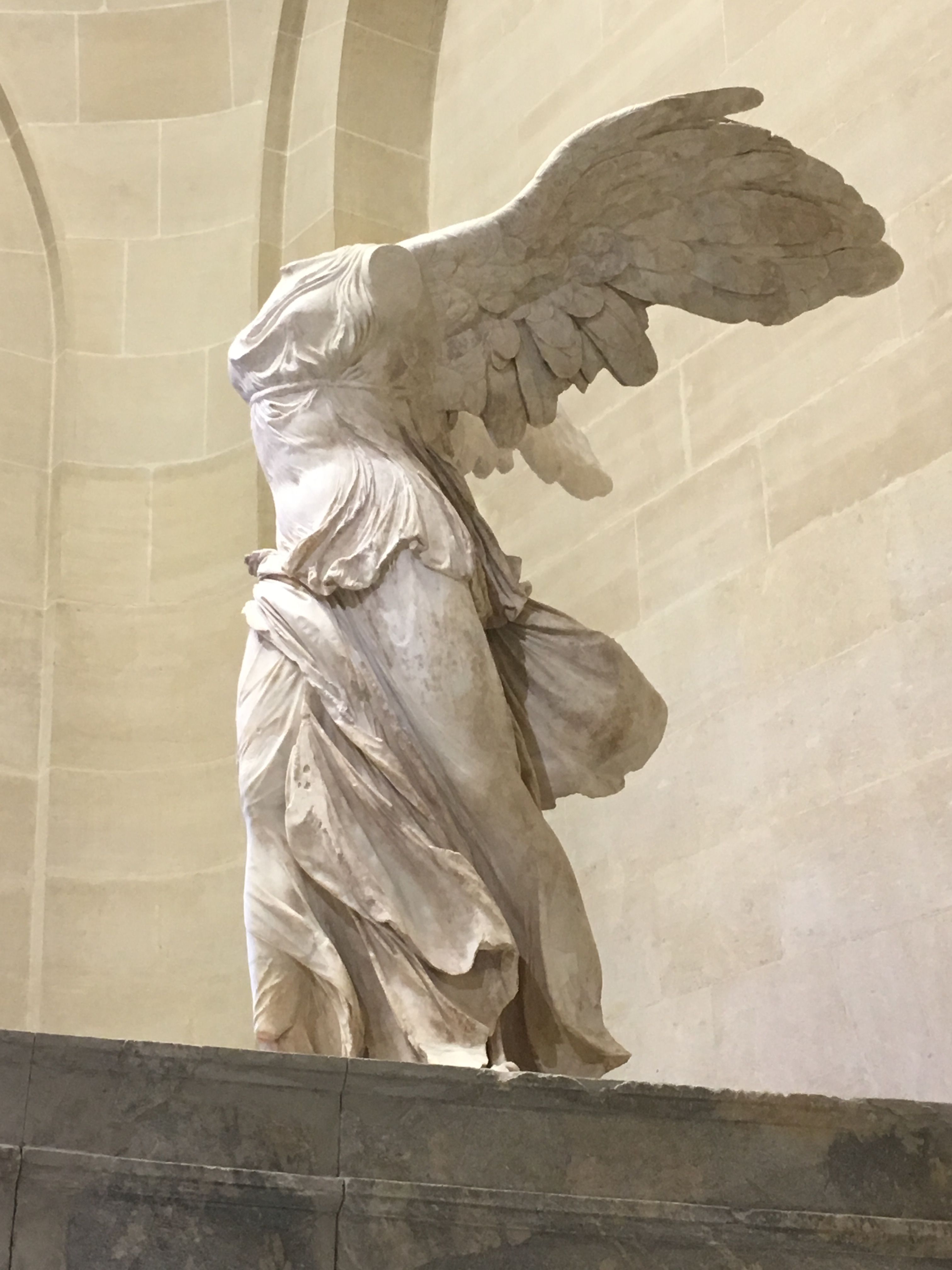
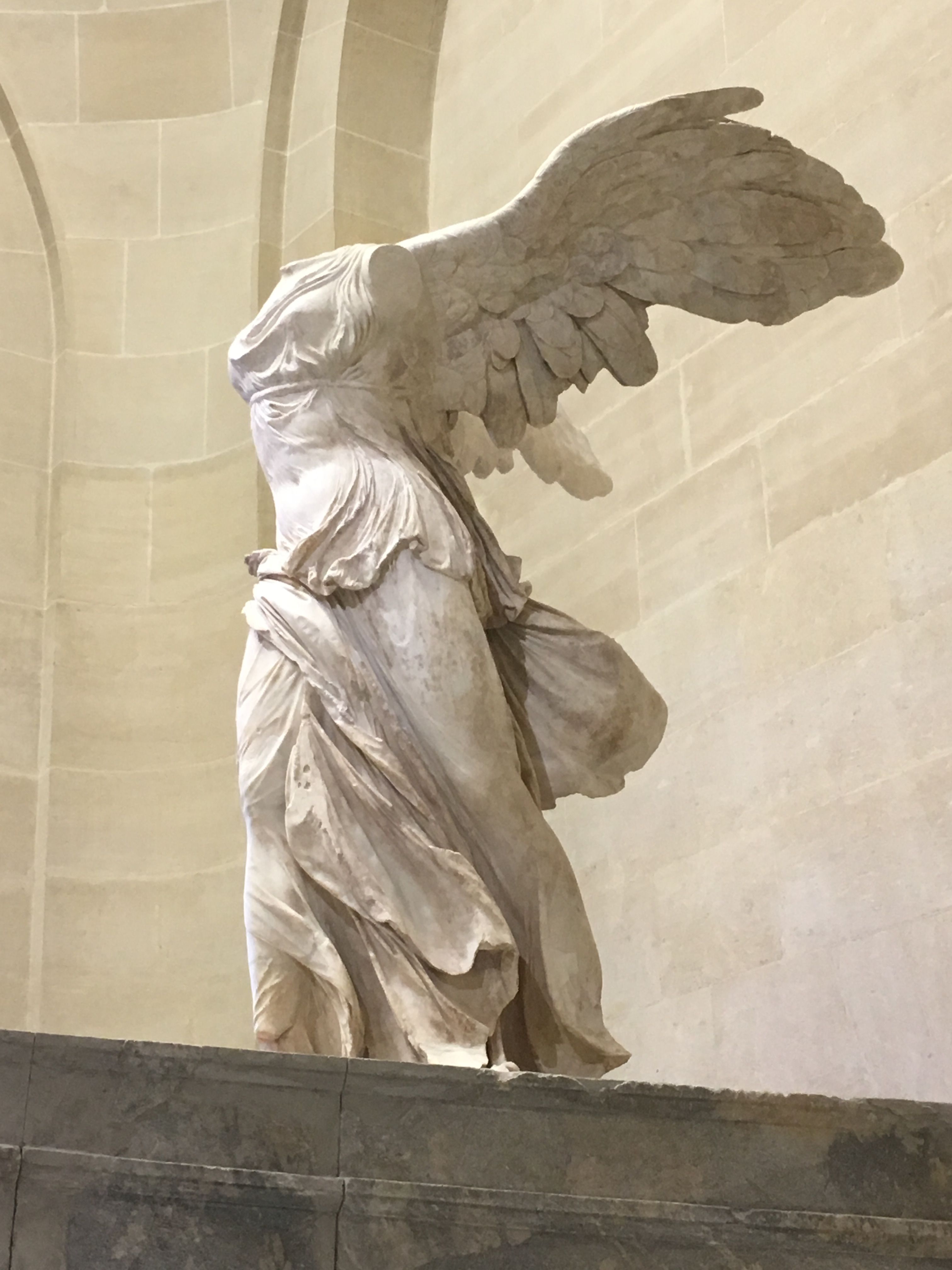


What work is this?
Winged victory of Samothrace
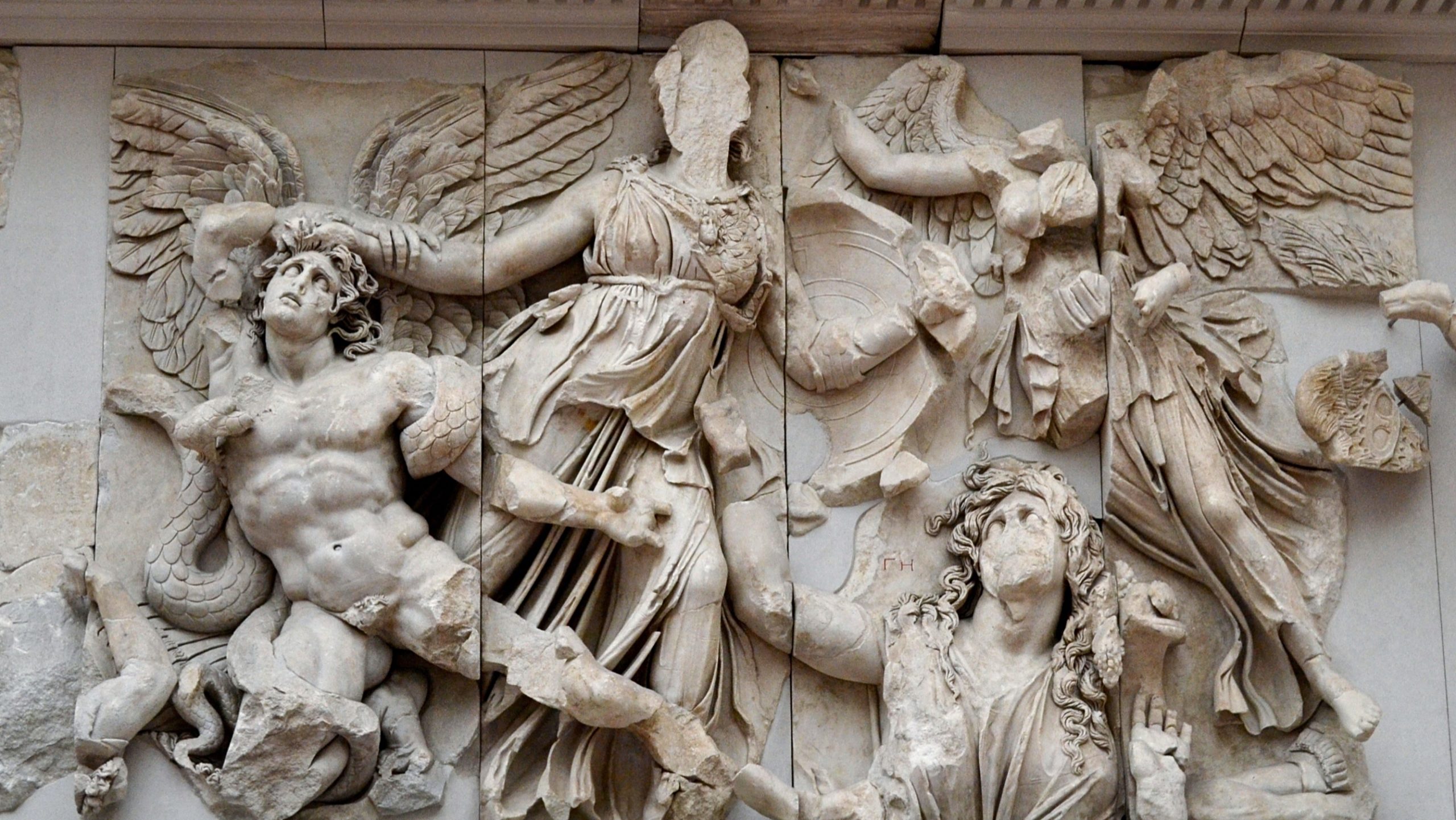
Athena from the Pergamon Altar
This is along the frieze of a temple worshipping both athena and Zeus
Shows the victory of athena over the titans
Nike crowns her victorious
Gaia pleads for her sons to be saved
175 B.C.E.

Seated Boxer
Moving away from the idealized body
The statue seems to have been completely and utterly injured
Might have been a good luck charm for athletes
Blood represented through copper and copper highlighted features
Found in Roman bath and might have been of several works
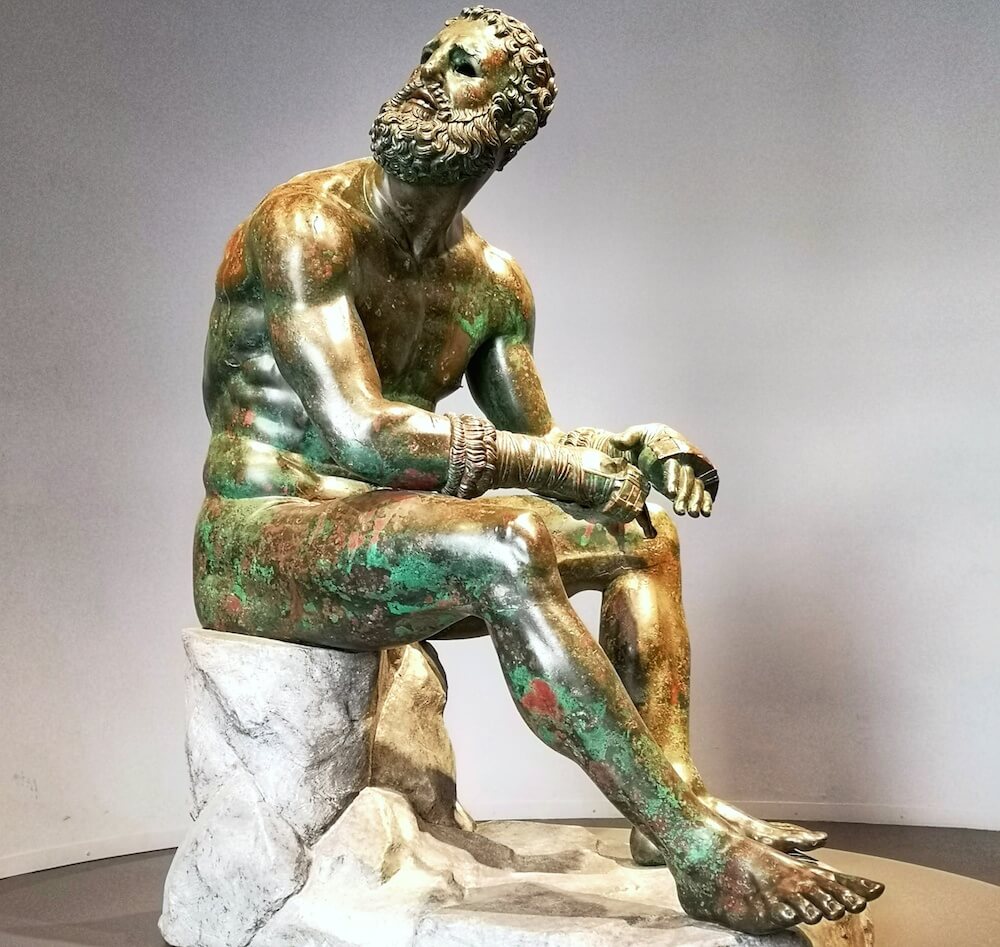

What is this work?
Seated Boxer

Athenian Agora
Pantheonic Festival cut through here (honored Athena)
Considered the birthplace of democracy
Had spaces for male voting and senators
Also there was a theatre
600 - 150 B.C.E.
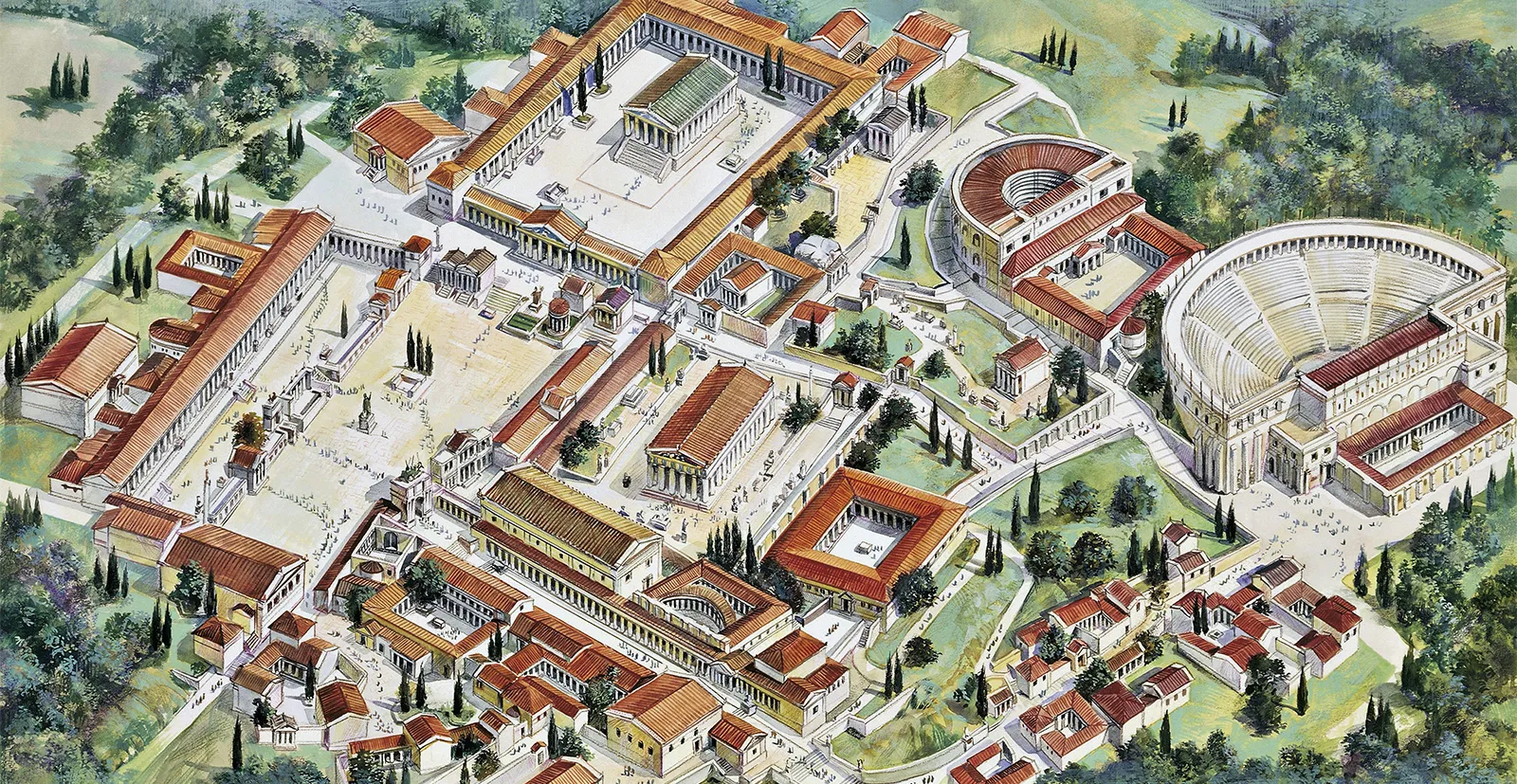
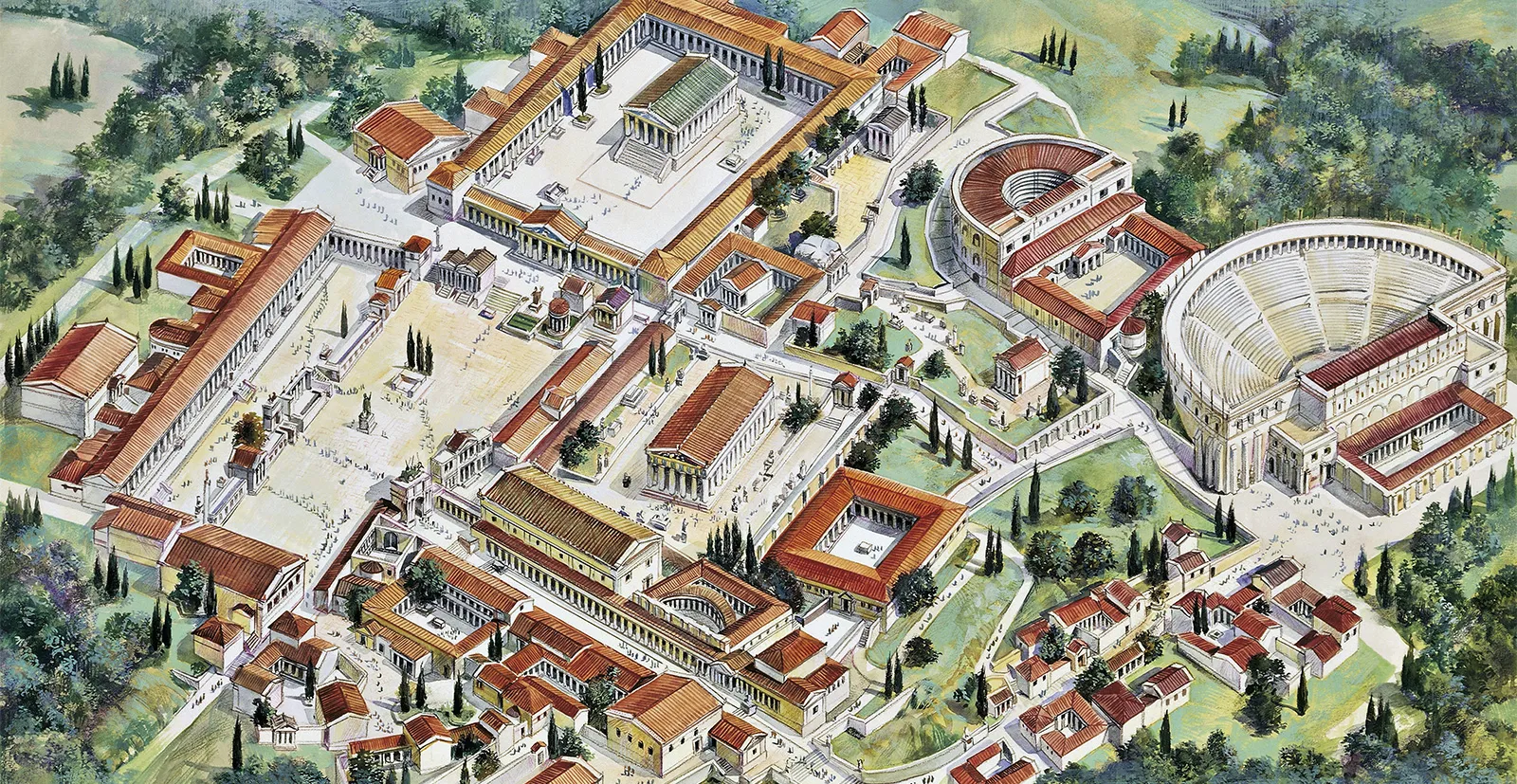


What work is this?
Athenian Agora
The Parthenon
Created by Iktinos and Kallikrates
Columns calculated using x=2y+1
Proportion of the building are 9:4
Altered the shape of various things to make it look more even
Ionic elements (ionic capitals, frieze)
447-438 B.C.E.
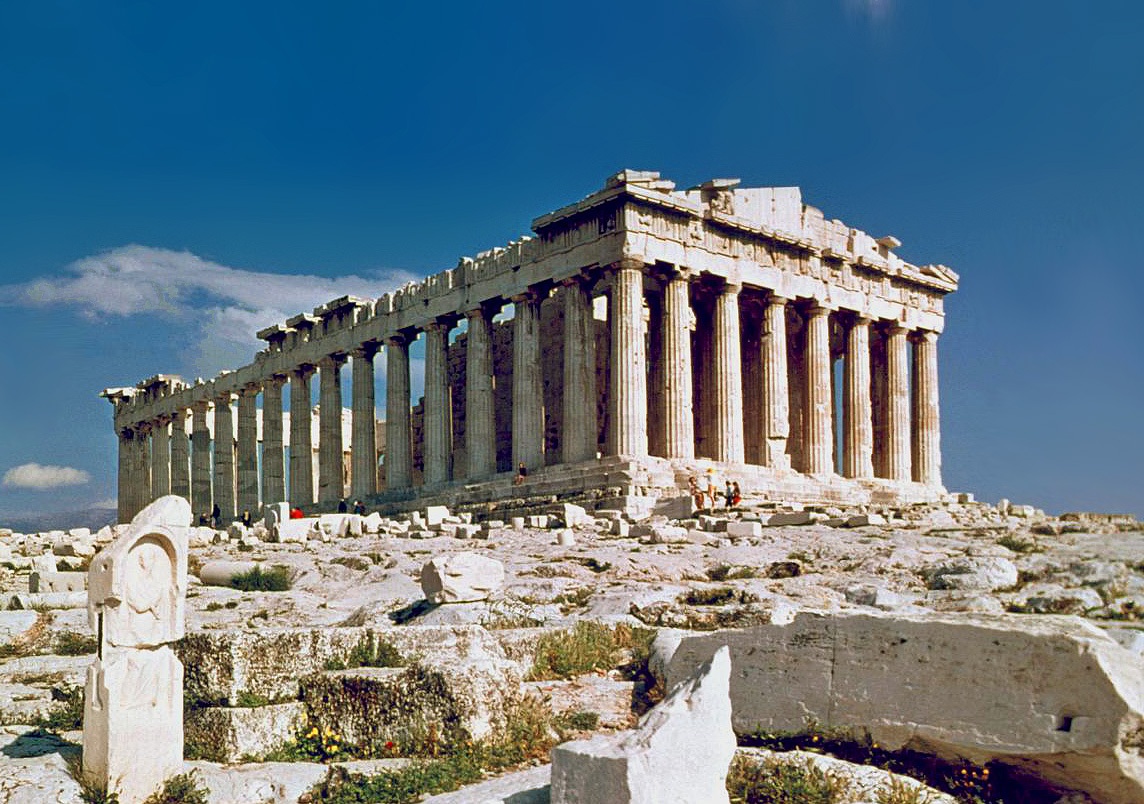
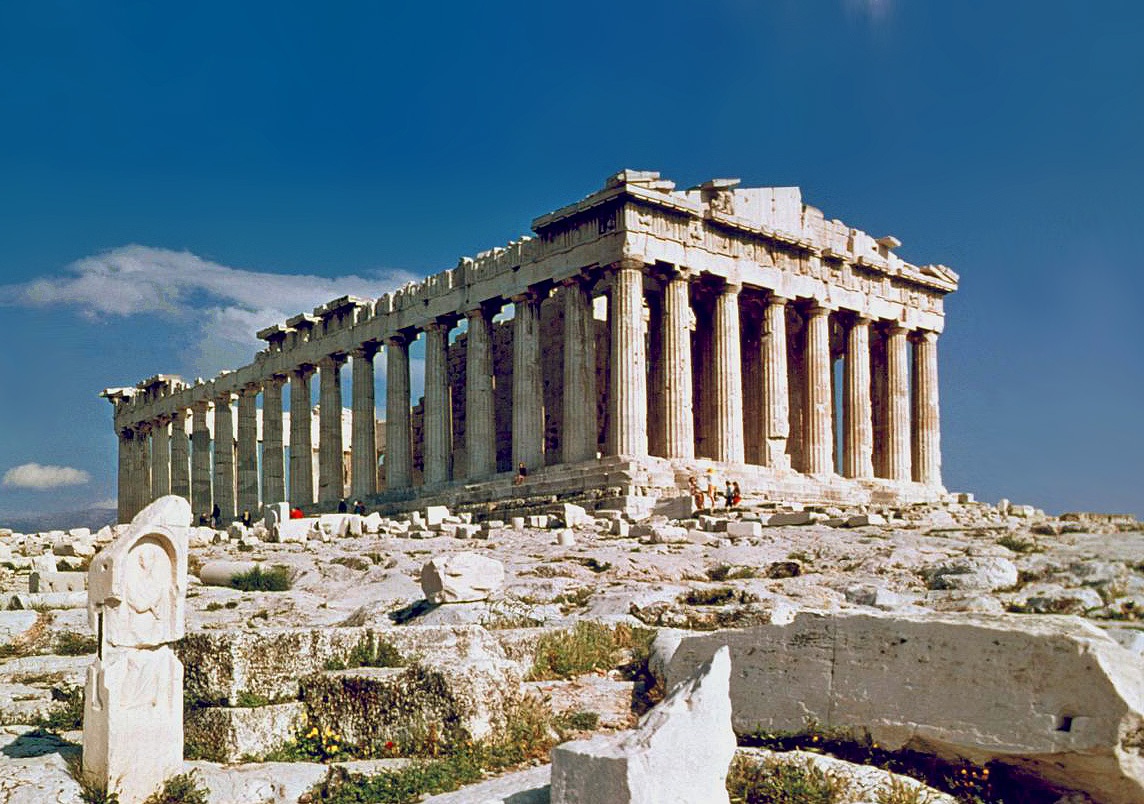


What work is this?
Parthenon on the acropolis
Temple of Athena Nike
Commemorates Greeks beating Persians
Ionic columns that don’t wrap around
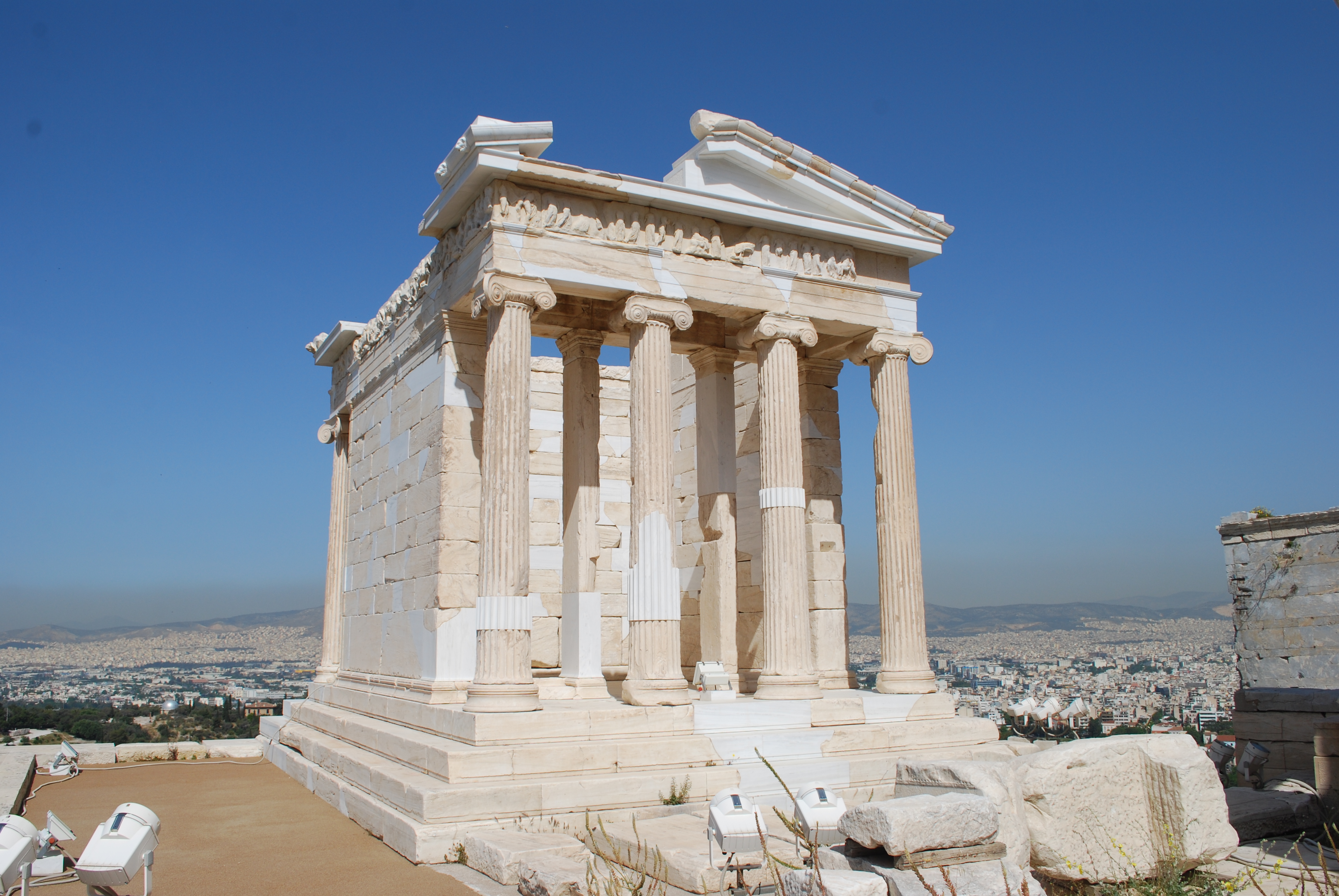


What work is this?
Temple of Athena Nike
Altar of Zeus and Athena at Pergamon
For both Zeus and Athena
Use of Ionic features
Outside was more important because greeks did not go inside for worship
175 B.C.E.
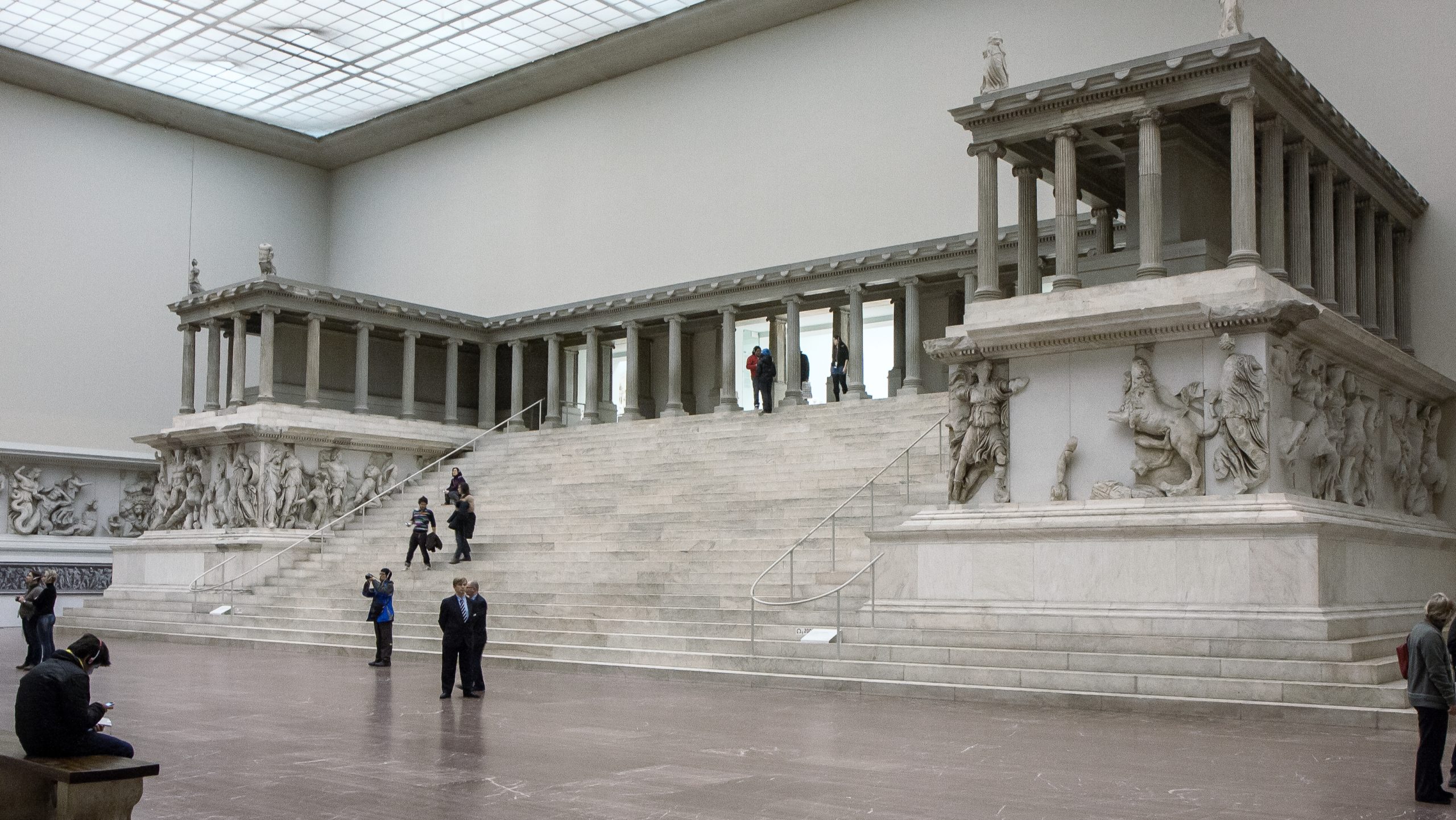


What work is this?
Temple of Zeus and Athena at Pergamon
Niobid Painter
High classical
No longer heads at the same level
Shows the killing of Niobe’s kids (Apollo and Artemis killed her children)
Other side may be Hercules in the arms of athena with heroes
A krater for mixing wine


What work is this?
Niobid Painter
Alexander Mosaic
Use of foreshortening, reflections, etc.
Was based on a greek painting but found in Roman home
Alexander is on the left
Darius is fleeing whilst his brother sacrifices himself
May be made by Helen of Egypt or Piloxenos of Eretia
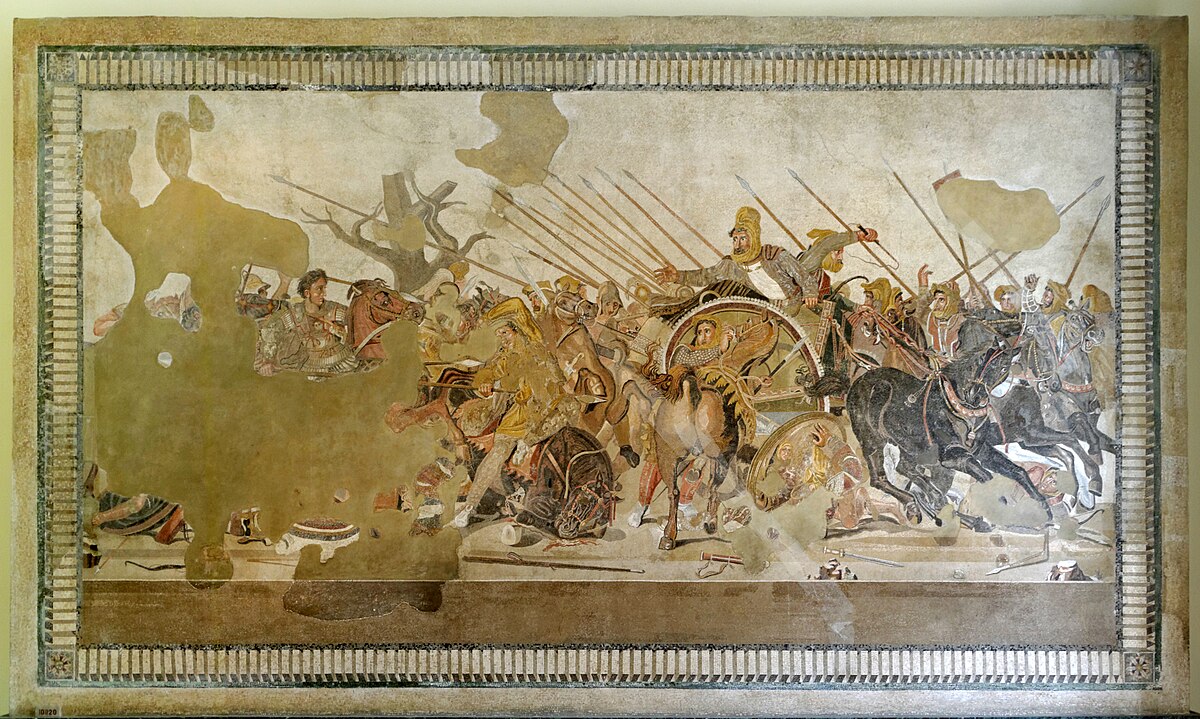
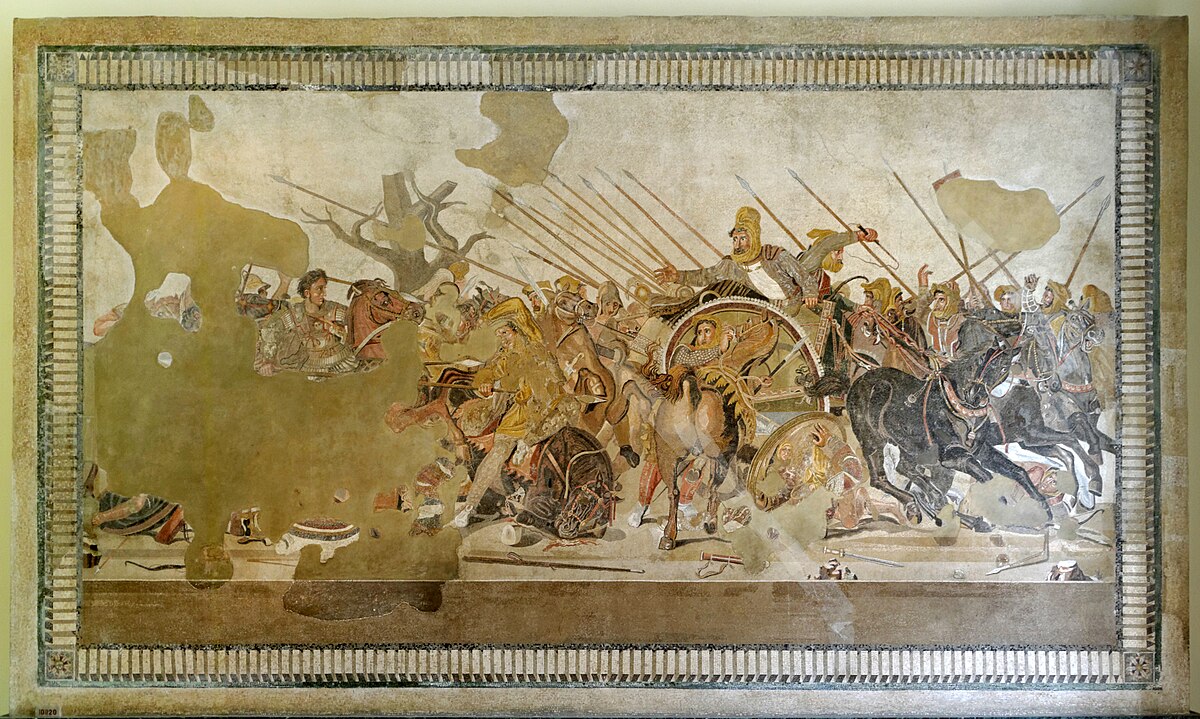


What work is this?
Alexander Mosaic (Maybe by Helen of Egypt, based off Piloxenos of Eretria)
Temple of Minerva
Made off models by Vitruvius
Dedicated to Etruscan Athena
There is an influence from Greek with columns
Has unique etruscan capital
510-500 B.C.E.
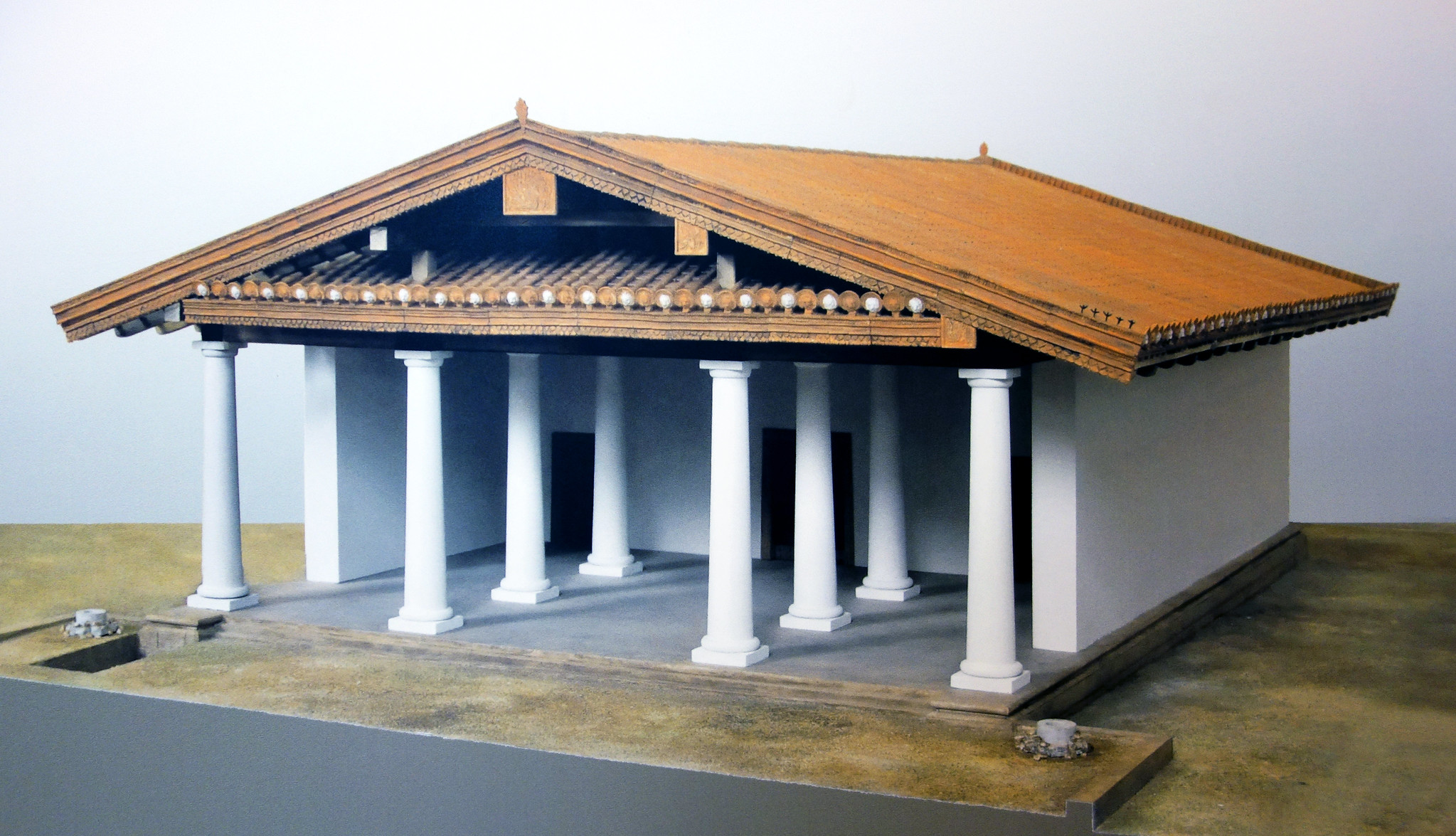
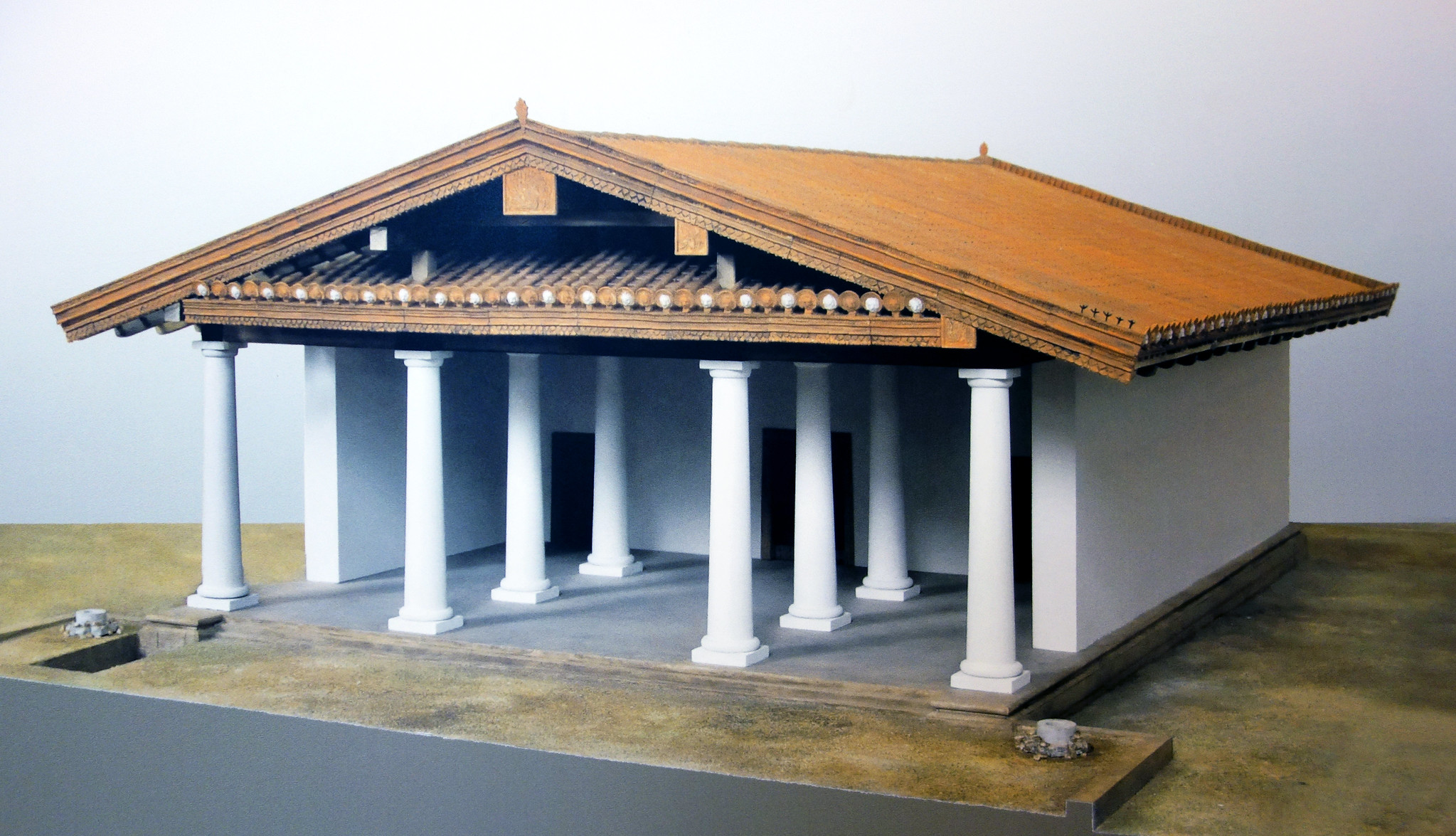


What work is this?
Temple of Minerva
Tomb of the Tricilinium
Men painted darker than the women
The pattern on the roof could refer to either time or to a funerary tent
Likely a funerary banquet with dancing and instruments
Part of the etruscan necropolis
480 - 470 B.C.E.
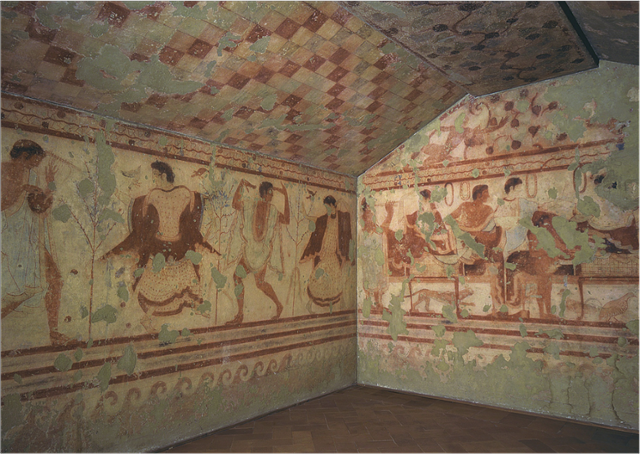
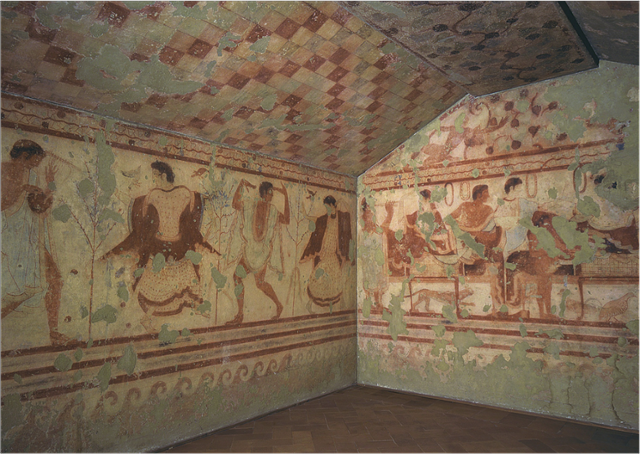


What work is this?
Tomb of the Triclinium
Sarcophagus of a Reclining Couple
Focus on the heads rather than the legs of the figures
Shows a funerary banquet between the two wealthy patrons
Have elongated proportions and stylized hair
Composite view
Made of terracotta
520 B.C.E.
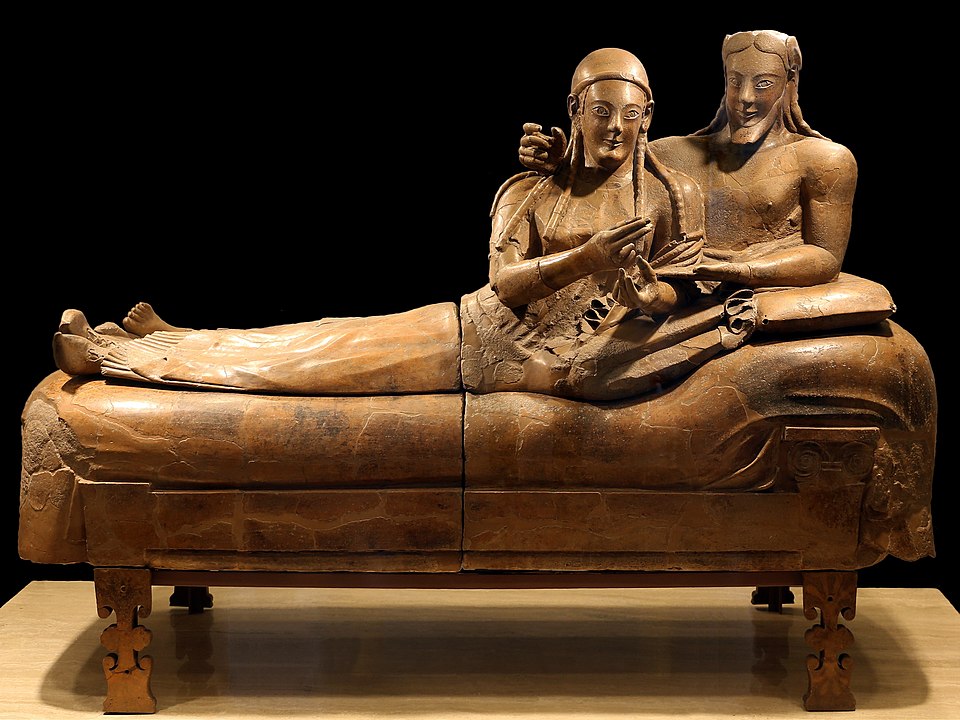
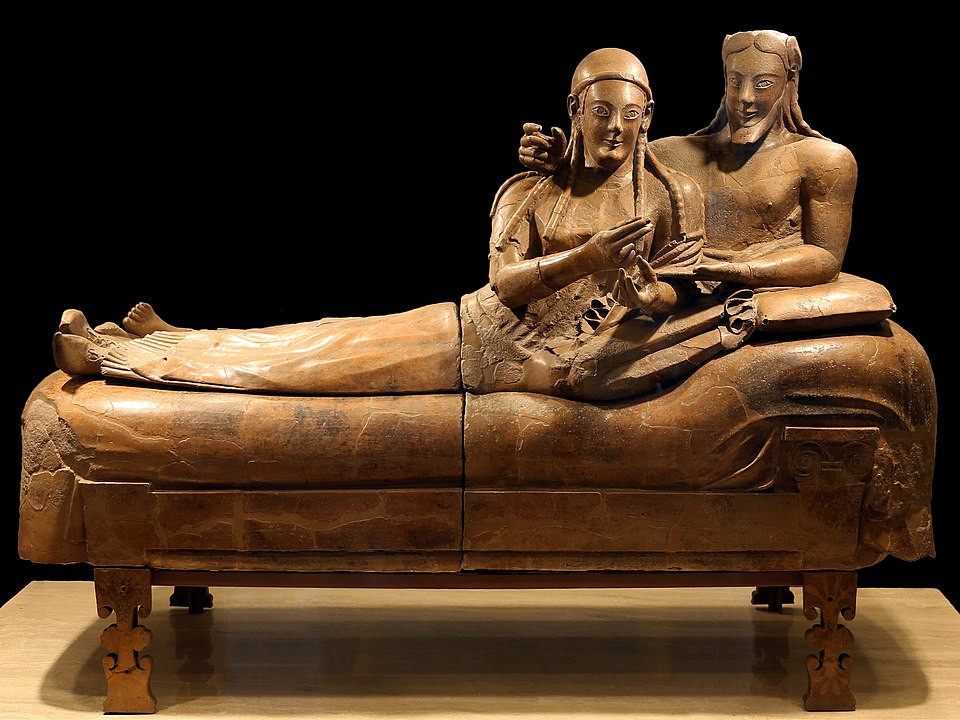


What work is this?
Sarcophagus of a reclining couple
Apollo from Veii
May be made by Vulcan of Veii
Meant to be viewed from below


What work is this?
Apollo of Veii
House of Vettii
Has a basin to catch water located in the middle of the room
Axial symmetry
All light came from the courtyard in the middle
Served as a vacation home for the Vettii family
67-79 C.E.
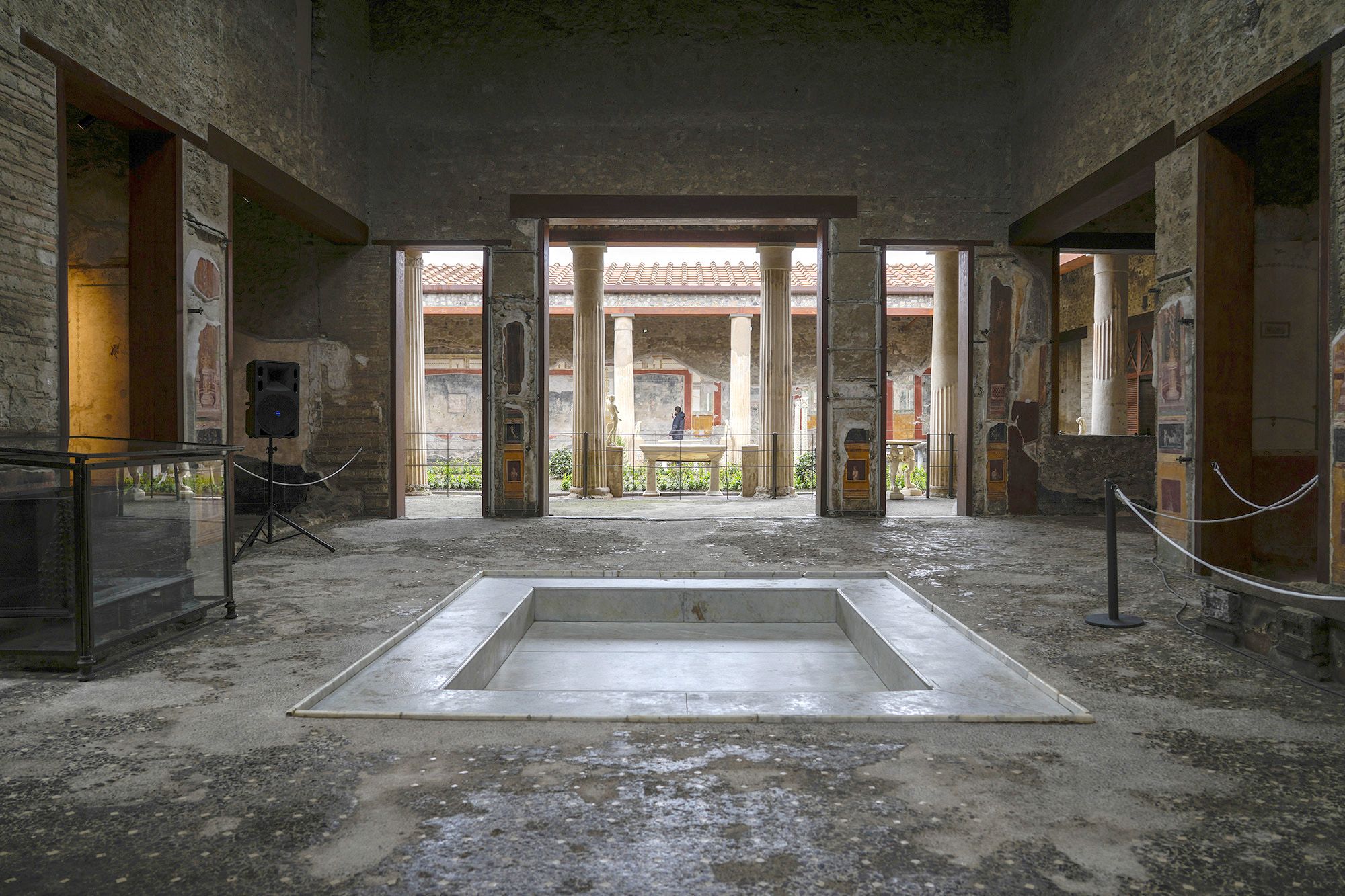
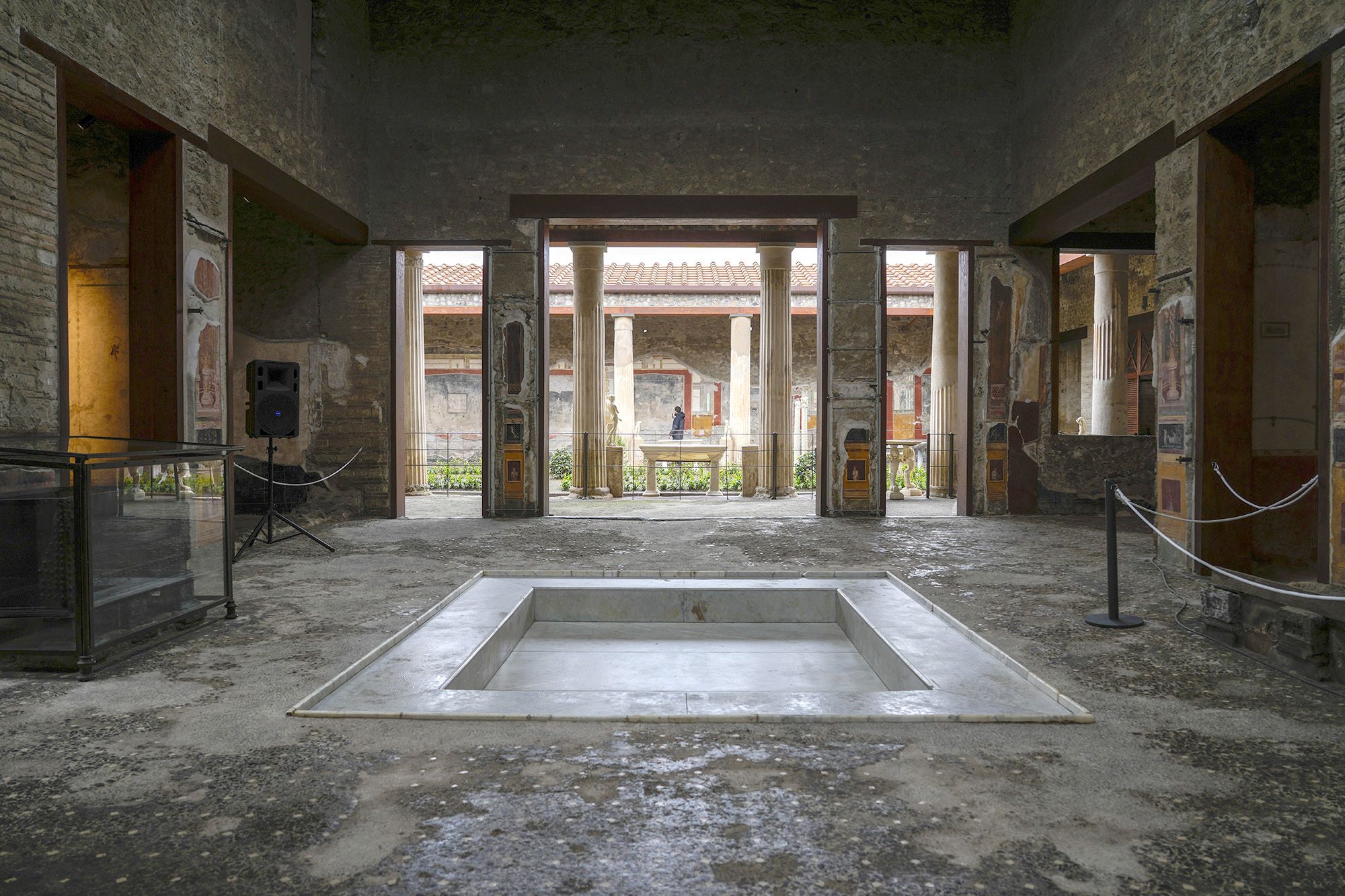


What work is this?
House of Vettii
Flavian Amphitheatre
First story columns are Etruscan, second is iconic, third is Corinthian
There used to be a retractable canvas roof
Replaced statue of Nero with this building
Began by Vespasian, finished by Titus
Used to be covered in marble
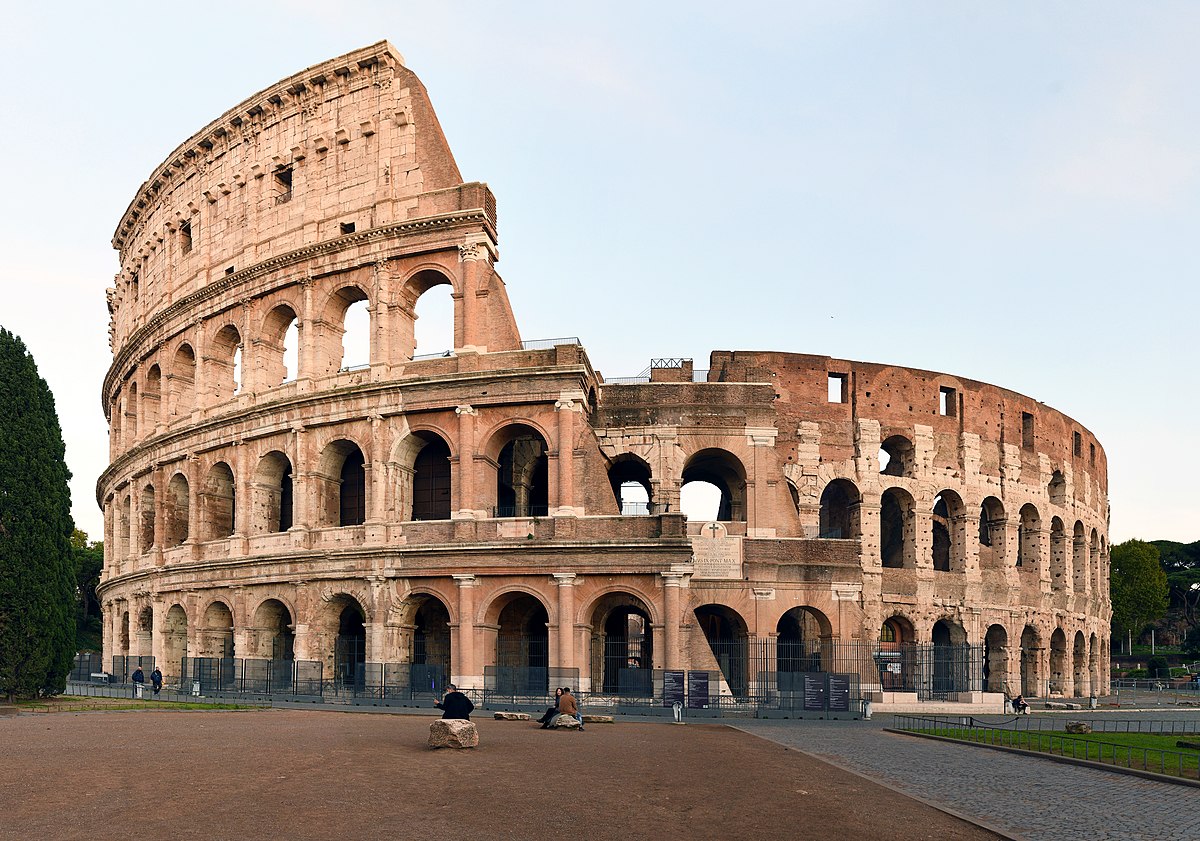
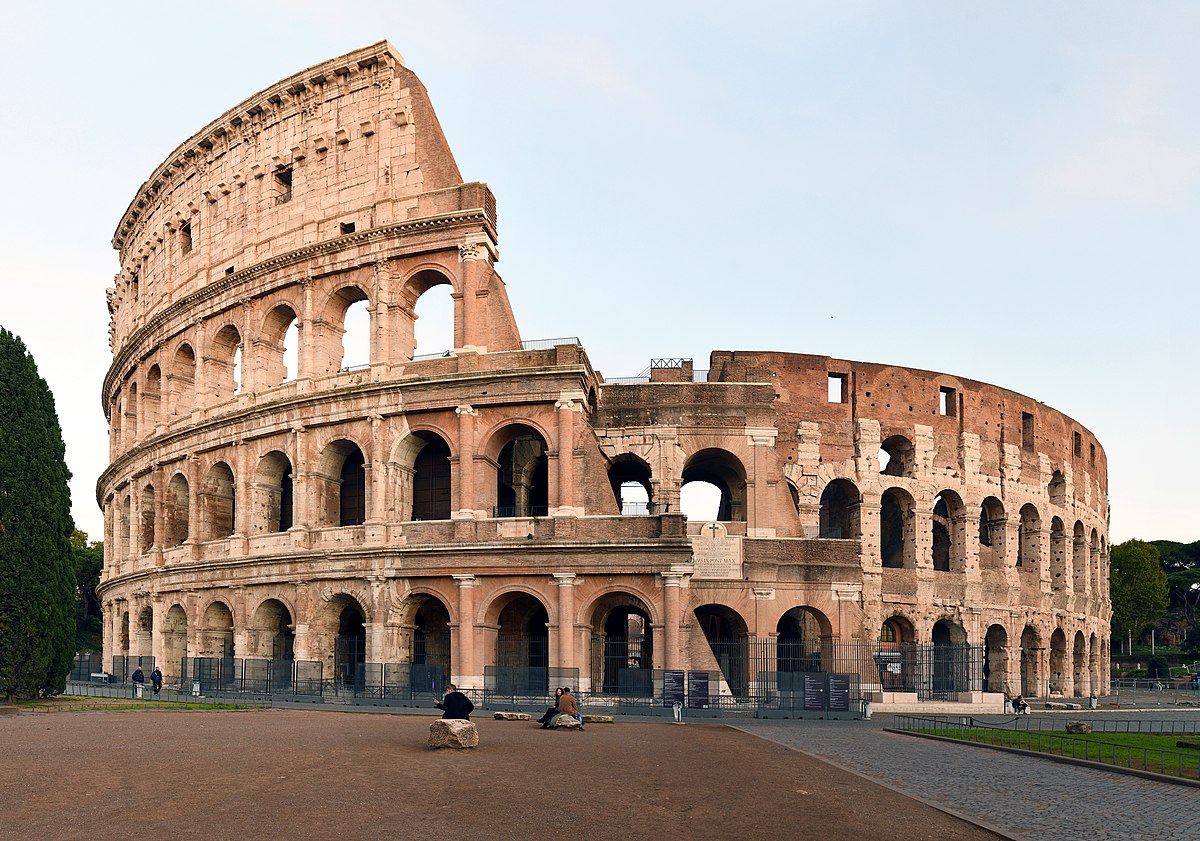


What work is this?
Flavian Amphitheatre (Patron is Vespasian and Titus)
Great Temple of Petra (The treasury)
Located along a caravan route
There were tombs but no bodies were buried inside
Use of Corinthian columns
Broken pediment with central tholos


What work is this?
The Treasury of Petra
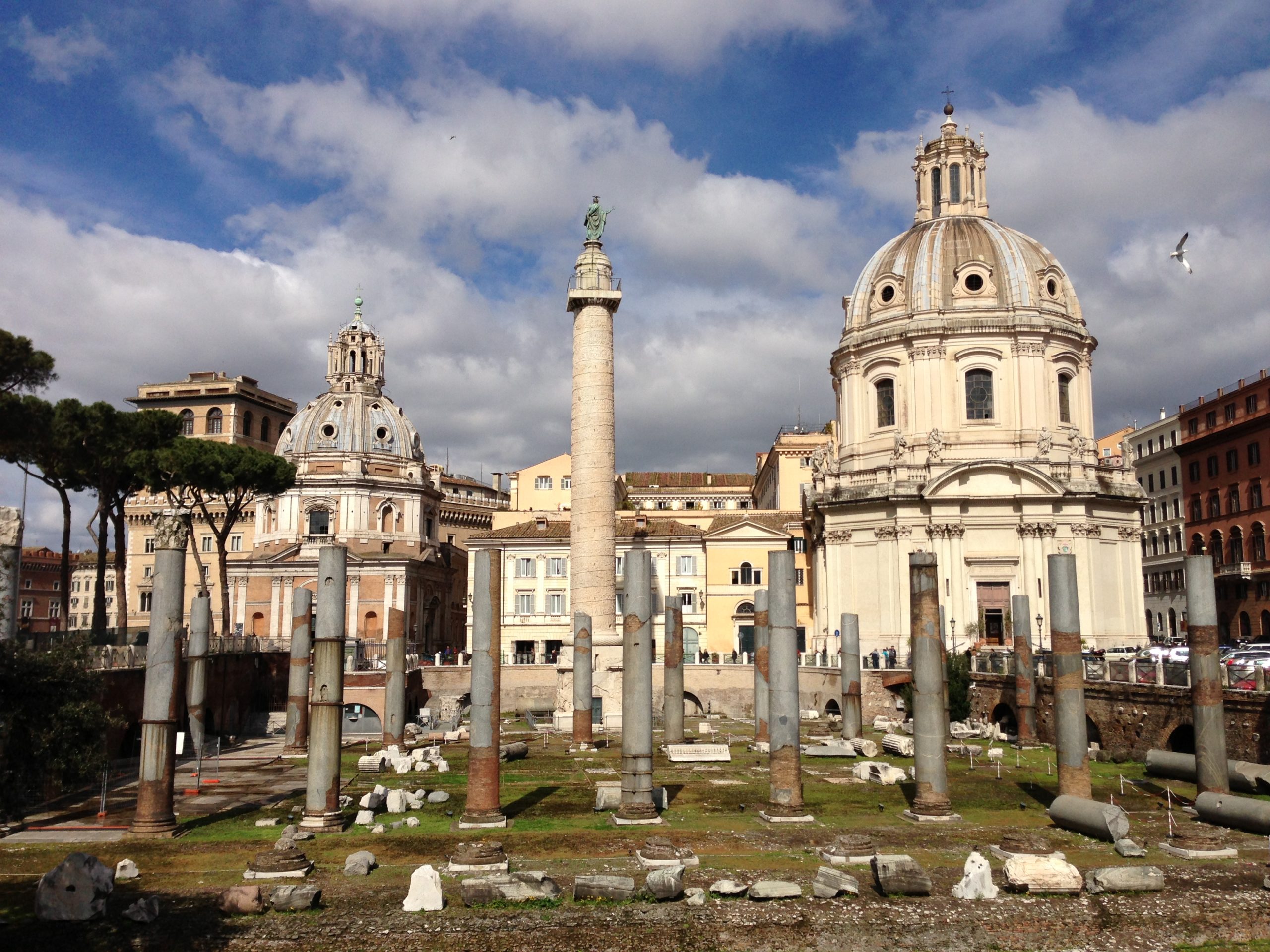
Forum of Trajan
There was an area with shopping center like buildings
Two libraries flanking the column
Basilica has timber roof (for judges)
Military theme —> pavement was shipped from the south
Basically payment after war with the Romanians
112 C.E.
