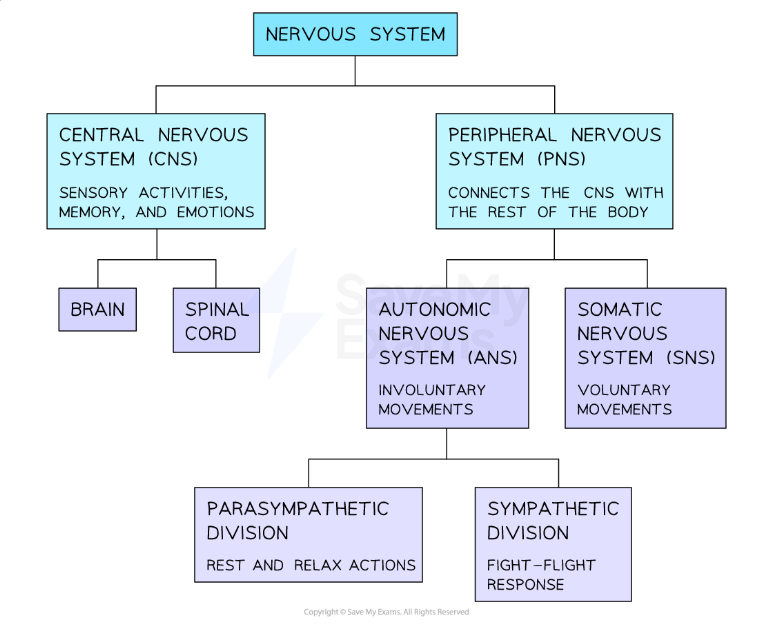
The Divisions of the Nervous System
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
What is the Nervous System?
A specialised network of cells in the human body and is our primary internal communication system. It has two main functions:
To collect, process and respond to information in the environment
To co-ordinate the working of different organs and cells in the body
What are the two subsystems of the human nervous system?
The central nervous system (CNS)
The peripheral nervous system (PNS)
What is the Central Nervous System (CNS)?
Consists of the brain and the spinal cord. It has two main functions:
Control of behaviour (movement)
Regulate the body’s physiological processes (body temperature, heart rate and breathing)
What is the brain?
The centre of all conscious awareness.
The brain’s outer layer, the cerebral cortex, is only 3mm thick and covers the brain
It’s only found in mammals
The brain is highly developed in humans -distinguishes our higher mental functions from those of other animals
Motor control
Sleep
Regulates bodily processes and maintains homeostasis based on the information from the PNS
What is the spinal cord?
An extension of the brain.
Passes messages to and from the brain
Connects nerves to the Peripheral nervous system (PNS)
Responsible for unconscious movements e.g. reflex actions such as pulling your hand away from something hot
What are the similarities between the brain and spinal cord?
The brain stem and spinal cord both control involuntary processes.
The brain system controls breathing
The spinal cord controls involuntary reflexes
What are the differences between the brain and the spinal cord?
The brain provides conscious awareness and allows for higher-order thinking, while the spinal cord allows for simple reflex responses
The brain consists of multiple regions responsible for different functions, whereas the spinal cord has one main function
How does the CNS control behaviour and regulate the body’s physiological processes?
The brain must be able to receive information from the sensory receptors (eyes, ears, skin, etc.) and be able to send messages to the muscles and glands of the body - this involves the spinal cord, a collection of nerve cells that are attached to the brain and run the length of the spinal column.
What is the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)?
Transmits messages (nerve impulses), via millions of neurons (nerve cells), to and from the central nervous system. The PNS is further sub-divided into the:
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
Somatic Nervous System (SNS)
What is the Automatic Nervous System (ANS)?
Transmits information between the CNS and the internal organs, such as:
Heart rate
Breathing
The stress response
Digestion
Sexual arousal
What is the Somatic Nervous System (SNS)?
Controls muscle movement and receives information from sensory receptors.
Therefore the role of the SNS is to carry sensory information from the outside world to the brain and provide muscle responses via the motor pathways
What can the Automatic Nervous System (ANS) be further subdivided into?
The sympathetic nervous system (SPNS)
The parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS)
What is the Sympathetic Nervous System (SPNS)?
Generally sympathetic functions increase bodily activity to prepare for action. E.g. flight or fight response.
How does the Sympathetic nervous system (SPNS) prepare the body for physical activity?
It prepares the body for physical activity when the hypothalamus (in the brain) detects a stimulus which requires attention/action, e.g.
Running away from a threat
Standing and facing the threat
Preparing to fight the threat
When is the Sympathetic nervous system (SPNS) triggered?
When the body is in an 'alert' state, e.g.
When crossing the road
When a noise is heard late at night
What happens when the Sympathetic nervous system (SPNS) is triggered?
Adrenaline is released from the adrenal glands to fuel any physical activity required of the body along with other physiological changes, e.g.
Accelerated heart rate
Widened bronchial passages for increased breathing capacity
Decreased activity of the large intestine
Pupil dilation
Sweating
The SPNS thus enables a fast, automatic response to a possible threat or dangerous situation (but it can also occur when someone is highly elated or excited).
What is the parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS)?
Known as the ‘rest and digest’ system, it’s the body at its usual state. It decreases bodily activity to conserve energy which may be needed later.
What happens when the PSNS is dominant (effects are stronger than the SNS at that moment)?
Bodily functions like digestion and urination are regulated
Heart and breathing rates are slowed
Blood pressure lowers as body enters a state of relaxation
Relaxation enables the body to go into 'standby' (recovery mode)
The more time spent in a PSNS state, the healthier a person is likely to be
What does it mean when the SNS or PSNS is dominant?
Only one part of the autonomic nervous system has more control at a time.
Danger / stress → SNS is dominant (fight or flight)
Calm / safe → PSNS is dominant (rest and digest)
After danger passes, PSNS becomes dominant to return the body to its resting state
Outline of the divisions of the human nervous system.