Lab Quiz
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Know which nerve triggers the dive reflex
trigeminal nerve
The brainstem then sends efferent (motor neurons) signals via the
vagus nerve (& other pathways) to target organs
Know the different responses of the dive reflex
Parasympathetic nerves reduce heart rate and gastric mobility.
- The vagus nerve: bradycardia (heart rate <60BPM)
- Slower HR conserves oxygen
- Sympathetic nerves will cause splenic contractions and peripheral vasoconstriction.
How does an increase in motor units increase contraction force? Is there a limit to this (i.e., is there a point at which all possible motor units can be recruited?)
Maximal Stimulus: Activates all motor units to produce maximum contraction force. A muscle under maximal contraction stimulus can only contract for a short time
complete vs unfused tetanus
Incomplete Tetanus: Multiple action potentials leading to complete tetanus.
- Complete Tetanus: Multiple and rapid action potentials causing muscle tissue to fully
contract and seize up.
Different parts of a muscle twitch (latency, contraction, relaxation), where are they on the muscle twitch
Latency phase starts from the action potential and ends when the muscle begins to contract.
- Contraction phase is the time it takes for the muscle to contract. This is the shortest phase.
- Relaxation phase is the time it takes for the muscle to relax. This is the lonest phase.
What ion is released from t-tubules that triggers sliding of myosin and actin?
calcium
reflex arc
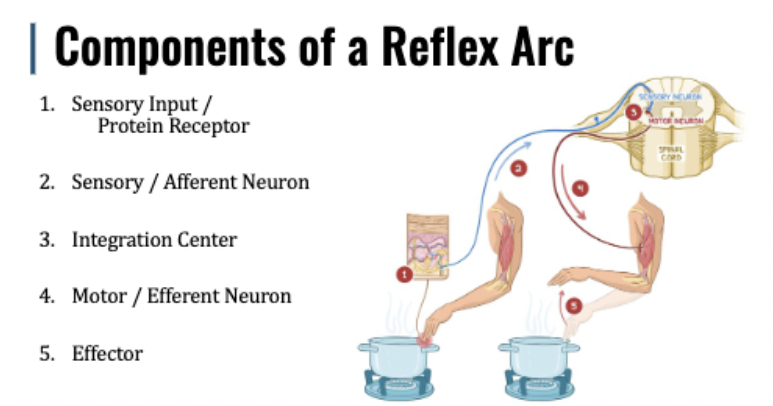
intrinsic vs learned
In= inborn, ex dive reflex
Learn= acquired
somatic vs autonomic
som= skeletal muscle, patellar reflex
auto= smooth muscle, glands ; pupillary reflex
cranial vs spinal
cran= requires brain input, blushing
spin = no input, plantar reflex
monosynaptic vs polysynaptic
mono= A/E neuron synapse is integration center, patellar reflex
poly= 1+ interneurons as integration center, flexor reflex