Chapter 13 - Plant Kingdom: Processes
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
The proper order for the movement of water in plants?
Water comes in through the root hair, root, xlyem, and then the stomata.
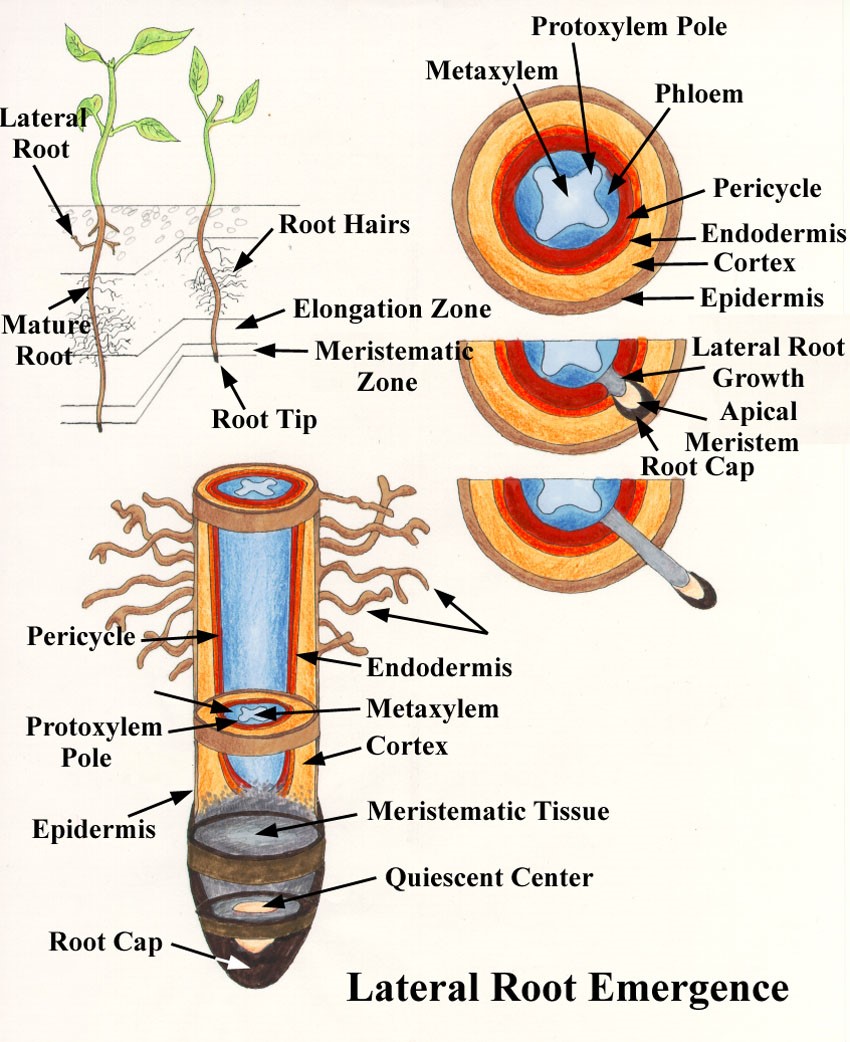
What are some parts of the roots?
root tip, root cap, epidermis, xylem, and root hairs
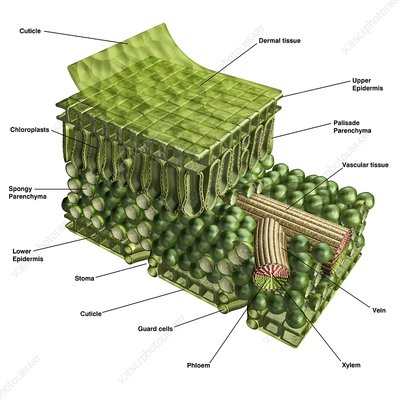
guard cells
regulate the size of the somata
What could happen if the cells malfunction?
The plant might suffer excessive water loss.
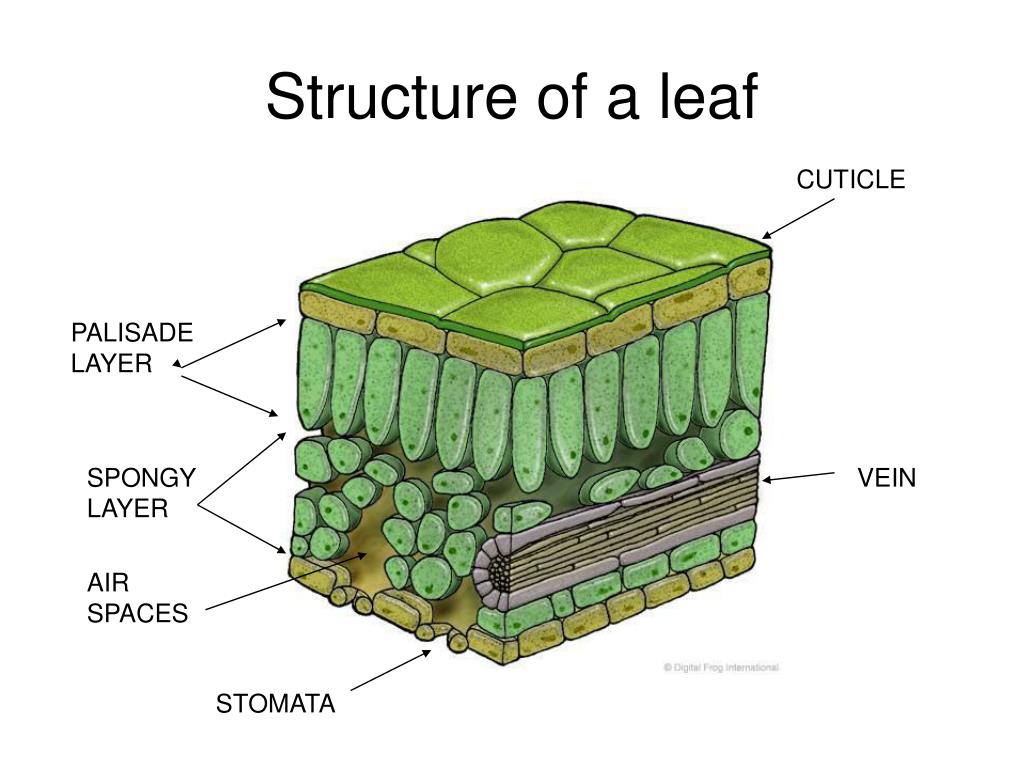
palisade layer
Made up of tall, thin, closely packed cells and is under the upper epidermis
What are plant hormones used for?
kill weeds, control fruit ripening, and for root cuttings.
What do nearly all plant CELLS have in common?
They carry on aerobic cellular repiration.
What things do plants store for their energy?
SUGAR and if they have a lot of sugar, they store the rest as STARCH. Some plants also convert the sugar to LIPIDS. So, plants can store energy as sugar, starch or lipids.
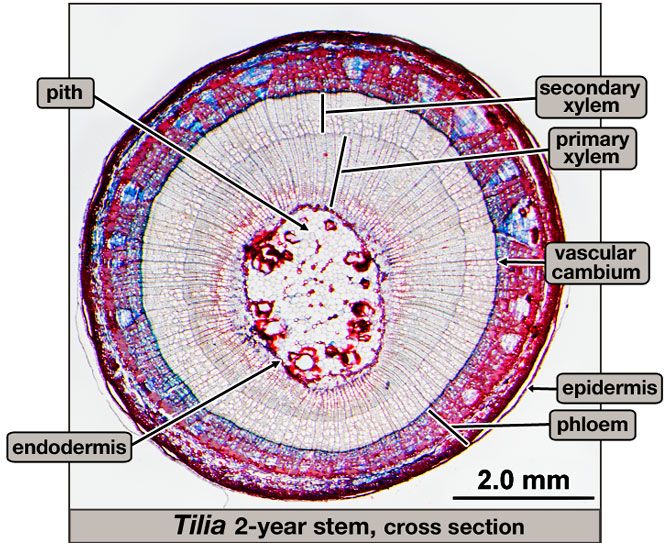
vascular cambium
a growth region in plants between the plant’s xylem and phloem.
What does a plant’s stem exhibit (show)?
negative gravitropism
How do plants move?
One of the most typical ways that plants move is through a process known as phototropism. Essentially, they move and grow toward the light.
phytochrome
proteins that respond to LIGHT.
tropisms
a growth response of plants to their ENVIRONMENT.
negative tropisms
a plant’s response of growing away from a factor
positive tropism
a plant’s response of growing toward a factor
nastic
reversible, repeatable plant movements
gravitropism
a plant’s growth response to gravity
phototropism
a plant’s growth response to light
short-day plants
plants that bloom when NIGHTS are long
long-day plants
plants that bloom when DAYS are long
elongation
a plant’s response to auxin
photoperiodism
a plant’s response to the length of time it is exposed to light
day-neutral plants
plants that bloom whenever moisture and temperature are acceptable
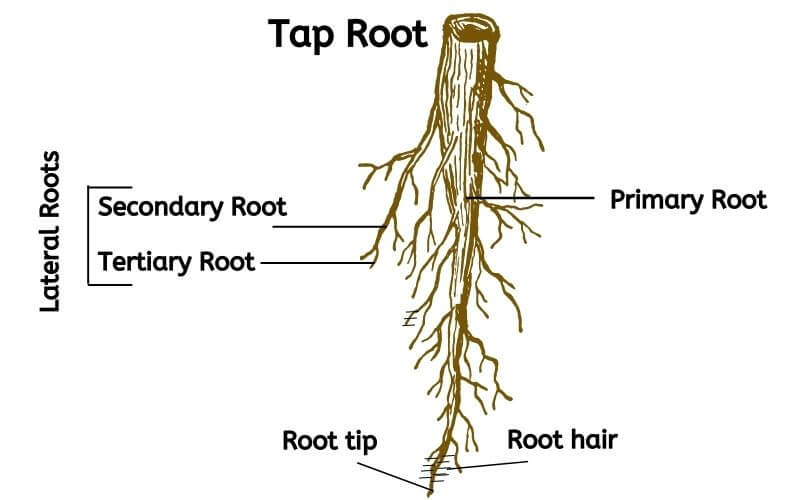
root hairs
The tiny EXTENSIONS in the epidermis cells of the root that help them to ABSORB WATER.
transpiration
occurs when water vapor passes OUT of the leaf THROUGH the stomata.

lenticles
Tiny openings in the bark (stems) that exchange gases in the woody areas of plants.
carbon dioxide
The gas that enters the leaf from the atmosphere during photosynthesis.
Where are stomata found?
In the lower epidermis surface.
auxin
a type of plant hormone
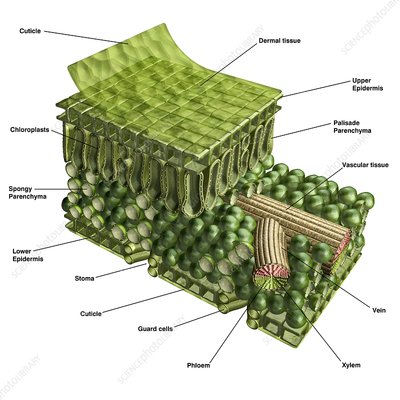
cuticle
outermost layer of plants
chloroplast
produce energy through photosynthesis and oxygen-release processes.
upper epidermis
On the top of the leaf, this is known as the upper epidermis. This is a single layer of cells found directly below the cuticle.
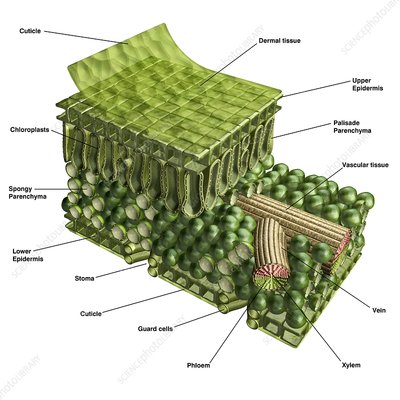
xylem
transports water from roots to stems and leaves, but it also transports nutrients. It’s INSIDE the vein.
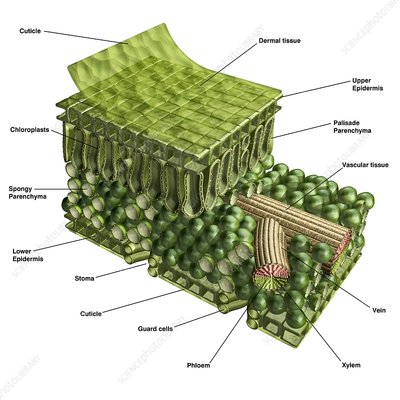
vein
providing an efficient transport route to transfer sugar, water, and nutrients throughout the plant.
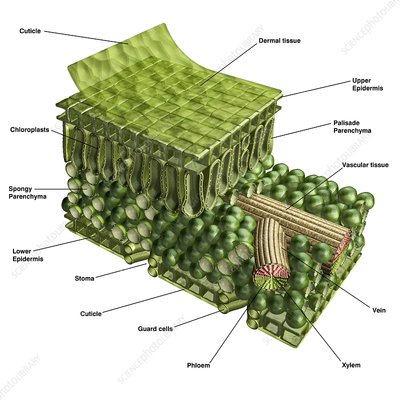
phloem
The vascular tissue in charge of transport and distribution of the organic nutrients. It’s INSIDE the vein.
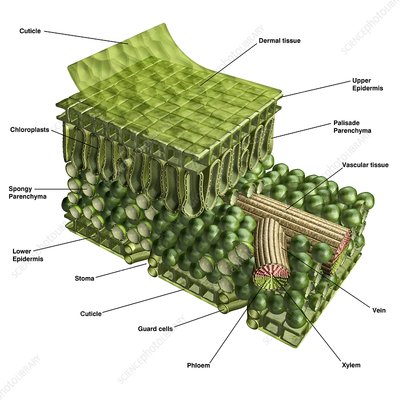
stoma
Regulate gas exchange between the plant and environment and control of water loss by changing the size of the stomatal pore.
aerobic cellular respiration
A process that converts sugar produced by photosynthesis into usable energy for the plant.
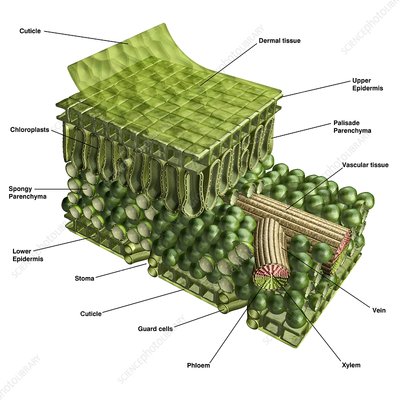
spongy layer (Shown in the picture as the area with the spongy parenchyma)
The layer below the palisade layer in plants. It contains chloroplasts.
What do some plants convert sugar into for energy?
lipids
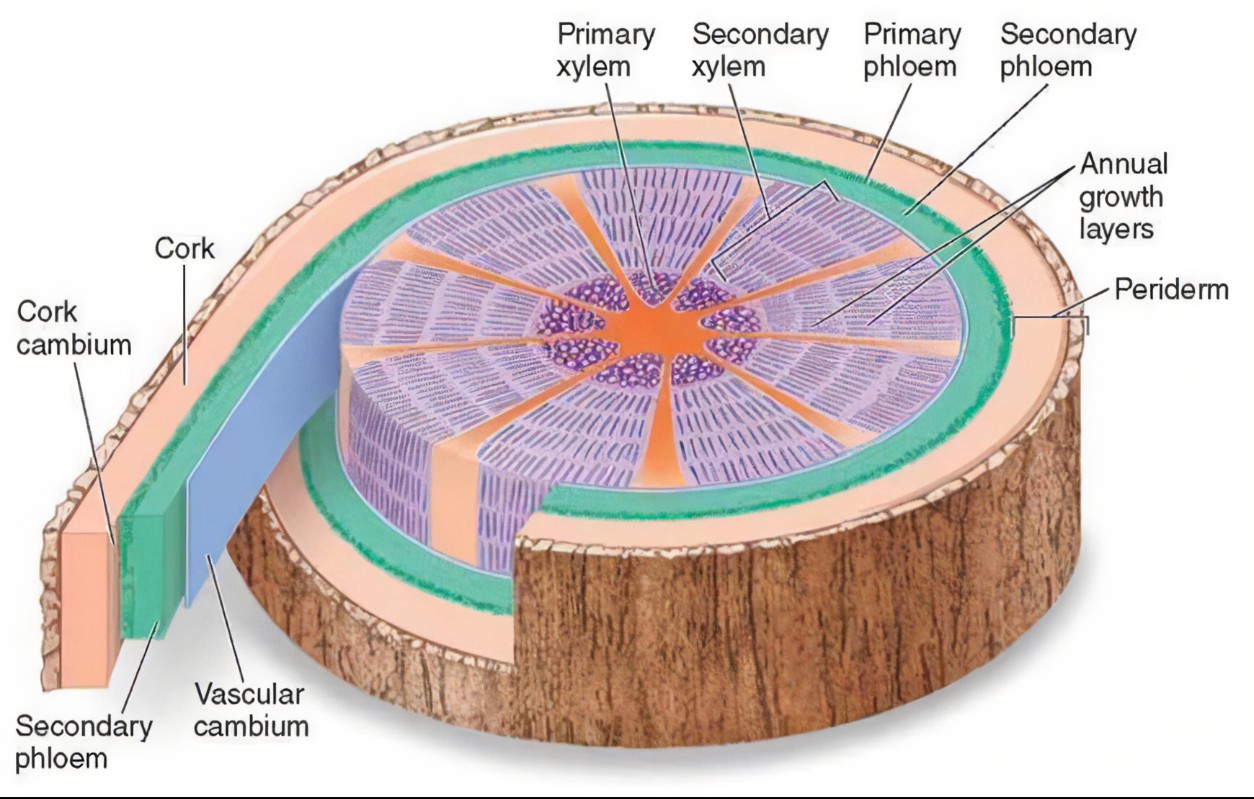
cork cambium
produces cork cells that protect the outside of a plant’s stem.
hormones
chemical substances that are made by plants and that affect how plant tissues grow.
What plant organ carries on transpiration?
the leaf
day-neutral plants
The bloom regardless of long or short days. They just need the right amount of moisture and temperature.
What plant organ absorbs water?
the roots