Ch. 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 7:26 AM on 9/3/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
1
New cards
Neuroembryology: developmental stages
1. Preembryologic
2. Embryonic
3. Fetal
2
New cards
Preembryologic
(1st stage)
(1st stage)
Occurs: conception to 2 weeks
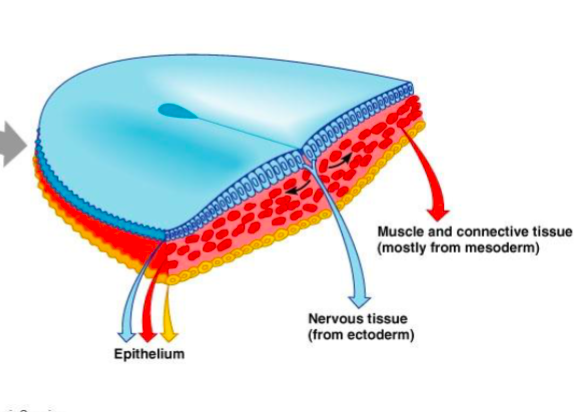
Three layers from the embryonic disc (embryo)
1. Ectoderm (forms nervous tissue (blue)
2. Mesoderm
3. Endoderm
Three layers from the embryonic disc (embryo)
1. Ectoderm (forms nervous tissue (blue)
2. Mesoderm
3. Endoderm
3
New cards
Embryonic
(2nd stage)
(2nd stage)
occurs 2-8 weeks
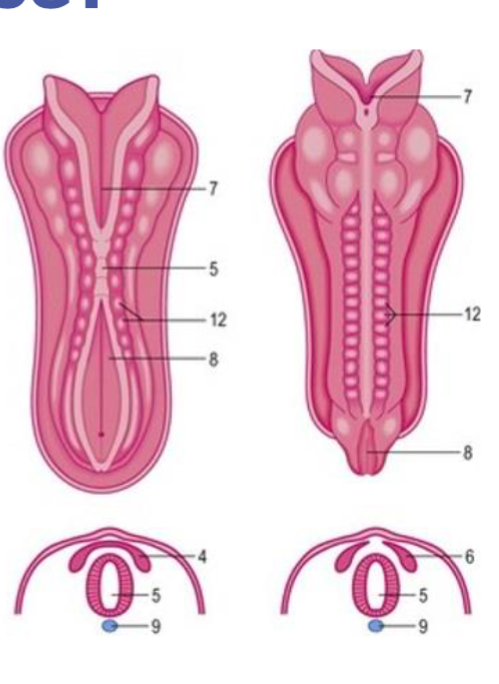
days 18-26 (3 weeks) happens:
* Ectoderm will start to fold and thicken forming a neural plate running along the dorsal side of the developing embryo
* neural plate folds to forms neural groove
* edges fuse to form neural tube
* cells that seperate from the neural tube form autonomic ganglia and most of PNS (neural crest)
days 18-26 (3 weeks) happens:
* Ectoderm will start to fold and thicken forming a neural plate running along the dorsal side of the developing embryo
* neural plate folds to forms neural groove
* edges fuse to form neural tube
* cells that seperate from the neural tube form autonomic ganglia and most of PNS (neural crest)
4
New cards
The neural tube forms how many layers ?
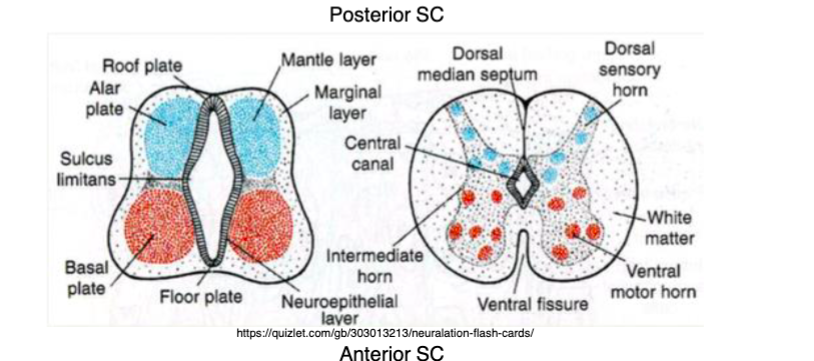
2 layers
1. Mantle layer (inner layer)
* Alar plate- forms dorsal gray matter
* Basal plate -forms ventral gray matter
2. Marginal layer (outer layer)
* become white matter of the spinal cord
1. Mantle layer (inner layer)
* Alar plate- forms dorsal gray matter
* Basal plate -forms ventral gray matter
2. Marginal layer (outer layer)
* become white matter of the spinal cord
5
New cards
How is the central canal formed ?
the neural tube narrows to form the central canal of the spinal cord
6
New cards
Anencephaly
anterior neuropore fails to close leading to a neural tube defect
* the brain cannot form
* can occur day 28 (4 weeks)
* the brain cannot form
* can occur day 28 (4 weeks)
7
New cards
Spina bifida
Failure of the posterior neurpore to close leads to neural tube defect
* area of the spinal cord doesn’t form properly
* day 30
* area of the spinal cord doesn’t form properly
* day 30
8
New cards
the developing brain has how many prominent swellings?
Three
1. Prosencephalon
2. Mesencephalon
3. Rhombencephalon
1. Prosencephalon
2. Mesencephalon
3. Rhombencephalon
9
New cards
Cephalic flexure
between brain and brain stem
10
New cards
cervical flexure
end of brain stem to spinal cord
11
New cards
Fetal
(3rd stage)
(3rd stage)
* occurs 8 weeks to birth
12
New cards
Brain stems consist of _____ (three things)
* midbrain
* pons
* medula
* pons
* medula
13
New cards
cranial nerve development
* 14 week -sucking and swallowing
* 25 weeks- vision
* 28 weeks - hearing
* 31-32 weeks - olfaction (sense)
* 25 weeks- vision
* 28 weeks - hearing
* 31-32 weeks - olfaction (sense)
14
New cards
Meninges
three membranous protective layer covering the entire CNS
* encompass the spinal Cord
* encompass the spinal Cord
15
New cards
layers of the meninges
PAD
* Pia mater
* arachnoid mater
* dura mater
* Pia mater
* arachnoid mater
* dura mater
16
New cards
Cerebrospinal fluid
CNS is bathed in CSF formed by the choroid plexus
* provides stable chemical environment
* provides stable chemical environment
17
New cards
dendrites
short processes which receive inputs
18
New cards
axon
long process which carry outputs
19
New cards
Multipolar
several dendrites and axons
20
New cards
Bipolar
single dendrite and axon
* most sensory neurons
* most sensory neurons
21
New cards
Myelin
formed by glial cells to insulate axons
22
New cards
Oligodendrocytes
myelin forming glial cells in CNS
23
New cards
Schwann cells
myelin forming glial cells in PNS
24
New cards
Unipolar
both axon and dendrite arise from a single process coming off the cell body
25
New cards
Primary CNS neurotransmitters (NT)
* excitatory- glutamate
* inhibitory- GABA
* inhibitory- GABA
26
New cards
primary ANS neurotransmitters (NT)
acetylcholine (parasympathetic) and norepinephrine (sympathetic)
27
New cards
Primary PNS neurotransmitter
acetylcholine
28
New cards
Gray matter
* cell bodies
* most local synaptic communication between neurons in CNS
* most local synaptic communication between neurons in CNS
29
New cards
Cerebral cortex
\-outermost layer
* gray matter that cover the surface of cerebral hemispheres
* gray matter that cover the surface of cerebral hemispheres
30
New cards
White matter
transmit signals over long distance in the CNS
* myelinated axons- carry and send out signals to and from the brain
* myelinated axons- carry and send out signals to and from the brain
31
New cards
white matter names
* tract- long
* commisure- connect right and left sides
* commisure- connect right and left sides
32
New cards
peripheral nerves
bundles of axons in the peripheral nervous system (PNS)
33
New cards
Afferent pathway
toward the structure, to brain
34
New cards
Efferent pathway
Away from structure, to muscle
35
New cards
where does the spinal cord end?
L1-L2 vertebrae column
36
New cards
Conus Medullaris
end of spinal cord
37
New cards
sulci
infolding of cerebral cortex
38
New cards
gyri
ridges of cerebral cortex
39
New cards
central sulcus
seperates frontal and parietal lobes
40
New cards
sylvian (lateral fissure)
superior border of temporal lobe
41
New cards
Parieto-occipital sulcus
separate parietal and occipital lobes
42
New cards
Precental gyrus
anterior to central sulcus
43
New cards
postcentral gyrus
posterior to central sulcus
44
New cards
corpus callosum
giant commissure between hemispheres
consist of :
* rostrum
* genu
* splenium
* body
consist of :
* rostrum
* genu
* splenium
* body
45
New cards
Calcarine fissure
occipital lobe
46
New cards
parahippocampal gyrus
temporal lobe
47
New cards
insular cortex
deep to lateral/ sylvian fissure
“ finger like”
“ finger like”
48
New cards
primary motor cortex (precentral gyrus)
movement on opposite side of the body
49
New cards
primary sensory cortex (postcentral gyrus)
sensation from opposite side of the body
50
New cards
primary visual cortex
posterior occipital lobes
51
New cards
primary auditory cortex
transverse gyri of Heschl (posterior part of insular cortex)
52
New cards
Somatotopic maps
are called sensory or motor homunculus
homunculus= “little man”= HAL
homunculus= “little man”= HAL
53
New cards
(Lateral) corticospinal tract
function: major motor pathway responsible for voluntary movement
Begins in the pre central gyrus (primary motor cortex)
controls movement on the opposite side of the body
two neuron pathway AKA pyramidal tract
Begins in the pre central gyrus (primary motor cortex)
controls movement on the opposite side of the body
two neuron pathway AKA pyramidal tract
54
New cards
Brodmann’s areas
divides cortex into functional areas based on microscopic appearance
* 52 areas identified
* Areas 3,2,1 primary somatosensory cortex
* Area 4- primary motor cortex
* Area 17- primary visual cortex
* 52 areas identified
* Areas 3,2,1 primary somatosensory cortex
* Area 4- primary motor cortex
* Area 17- primary visual cortex
55
New cards
main long tracts of the nervous system
* lateral corticospinal tract
* posterior columns
* anterolateral pathways
* posterior columns
* anterolateral pathways
56
New cards
lateral corticospinal tract
* voluntary motor movement
extending from precentral gyrus (primary motor cortex) to skeletal muscle
extending from precentral gyrus (primary motor cortex) to skeletal muscle
57
New cards
posterior (dorsal) column pathway
sensory
* vibration, joint position (proprioception), light touch) from opposite side of the body
* location and intensity
* axons cross over in the medulla (internal arcuate fibers)
* vibration, joint position (proprioception), light touch) from opposite side of the body
* location and intensity
* axons cross over in the medulla (internal arcuate fibers)
58
New cards
anterolateral pathways
sensory
* Spinothalamic tract
* pain, temperature, crude touch (for those who have a spinal cord injury)
* axon crosses over a few levels above the dorsal sensory root from which it entered (anterior commissure) in the spinal cord
* all axons do NOT cross over together at the same spot
* Spinothalamic tract
* pain, temperature, crude touch (for those who have a spinal cord injury)
* axon crosses over a few levels above the dorsal sensory root from which it entered (anterior commissure) in the spinal cord
* all axons do NOT cross over together at the same spot
59
New cards
pyramidal decussation
where the (lateral corticospinal tract) crosses
at the bottom of the medulla
at the bottom of the medulla
60
New cards
upper motor neuron
motor neuron that projects from cerebral cortex to the spinal cord targeting lower motor neuron
61
New cards
lower motor neuron
makes up a peripheral nerve
front portion of grey matter in spinal cord
innervate skeletal muscle to fire
front portion of grey matter in spinal cord
innervate skeletal muscle to fire
62
New cards
Lesion above the decussation
contralateral opposite sided weakness or paralysis
63
New cards
lesion below decussation
ipsilateral same side weakness or paralysis
64
New cards
Cerebellum
“biggest snoop in town”
* little brain
* dorsal/posterior to pons
* responsible for refining movement
* lesion- ataxia “lack of order” uncoordinated movement
* little brain
* dorsal/posterior to pons
* responsible for refining movement
* lesion- ataxia “lack of order” uncoordinated movement
65
New cards
Thalamus
* right above the brain stem
* 2nd biggest snoop in town
* multiple nuclei located deep in the cerebrum
* major relay center for pathways traveling to the cortex
* 2nd biggest snoop in town
* multiple nuclei located deep in the cerebrum
* major relay center for pathways traveling to the cortex
66
New cards
Basal Ganglia
stop or start movement
lesion- problems with start and or stopping movement
Ex: parkinson’s disease, huntington’s disease
lesion- problems with start and or stopping movement
Ex: parkinson’s disease, huntington’s disease
67
New cards
two main sensory pathways
posterior (dorsal) column pathway
anteriorlateral pathway (spinothalamic tract)
* three neuron pathways
anteriorlateral pathway (spinothalamic tract)
* three neuron pathways
68
New cards
Monosynaptic stretch reflex
* reflex-arc providing local feedback for motor control
* sensory neuron (afferent) synapses on lower motor neuron
* responsible for motor responses
* testing - motor and sensory neuron integrity of PNS
* sensory neuron (afferent) synapses on lower motor neuron
* responsible for motor responses
* testing - motor and sensory neuron integrity of PNS
69
New cards
CN I
olfactory nerve
function: olfaction (smell)
function: olfaction (smell)
70
New cards
CN II
optic nerve
function: vision
function: vision
71
New cards
CN III
oculomotor nerve
function: eye movements; pupil constriction
function: eye movements; pupil constriction
72
New cards
CN IV
trochlear nerve
function: specific eye movements that its involved with
* acts as a pulley
function: specific eye movements that its involved with
* acts as a pulley
73
New cards
CN V
trigeminal nerve
function: facial sensation (pain, temperature, proprioception) ; muscle of mastication (chewing)
function: facial sensation (pain, temperature, proprioception) ; muscle of mastication (chewing)
74
New cards
CN VI
Abducens nerve
Function: eye movements (abduction)
Function: eye movements (abduction)
75
New cards
CN VII
facial nerve
Function: muscles of facial expression; taste; salivation
Function: muscles of facial expression; taste; salivation
76
New cards
CN VIII
vestibulocochlear nerve
Function: hearing; equilibrium sense
Function: hearing; equilibrium sense
77
New cards
CN IX
glossopharyngeal
function: pharyngeal muscles; carotid body reflexes; salivation
function: pharyngeal muscles; carotid body reflexes; salivation
78
New cards
CN X
vagus nerve (to wonder)
function: parasympathetics to most organs; laryngeal muscles (voice)
(speaking + swallowing)
function: parasympathetics to most organs; laryngeal muscles (voice)
(speaking + swallowing)
79
New cards
CN XI
Spinal accessory nerve
function: head turning (trapezius and sternomastoid muscles)
function: head turning (trapezius and sternomastoid muscles)
80
New cards
CN XII
hypoglossal nerve
function: eye movement
function: eye movement
81
New cards
Brainstem
* contain numerous nuclei and white matter tracts
* contains reticular formation (RF)
* contains reticular formation (RF)
82
New cards
Upper RF
* midbrain and upper pons
* regulating level of consciousness (LOC)
* regulating level of consciousness (LOC)
83
New cards
Lower RF
* lower pons and medulla
* motor, reflex, and autonomic functions (breathing, respiration, cardiac)
* motor, reflex, and autonomic functions (breathing, respiration, cardiac)
84
New cards
Limbic system
Function:
HOME
* homeostasis
* olfaction
* memory
* emotions and drives
HOME
* homeostasis
* olfaction
* memory
* emotions and drives
85
New cards
the association cortex breaks down into what two things ?
1. Unimodal association cortex
2. Heteromodal association cortex
86
New cards
Unimodal association cortex
process a single sensory or motor modality
87
New cards
Heteromodal association cortex
Integrates function from multiple sensory and/or motor modalities
Ex: bring emotions and memories and attach to it
Ex: bring emotions and memories and attach to it
88
New cards
Wernicke’s area
temporal lobe
in left hemisphere
function: language comprehension (understand spoken or written language)
in left hemisphere
function: language comprehension (understand spoken or written language)
89
New cards
Broca’s area
frontal lobe
in left hemisphere
function: language production: write, talk, speak
in left hemisphere
function: language production: write, talk, speak
90
New cards
An impairment in language is called ___?
Aphasia
91
New cards
Parietal lobe function
primary
process a lot of sensory and spacial info
important role in sensory perception and integration and spatial awareness (R>L)
sensation and comprehension of speech and reading
process a lot of sensory and spacial info
important role in sensory perception and integration and spatial awareness (R>L)
sensation and comprehension of speech and reading
92
New cards
Lesion in right parietal lobe
* can exhibit hemineglect (neglect one side of the body)
* anosognosia (unawarness of the deficit) do not realize anything is wrong
* anosognosia (unawarness of the deficit) do not realize anything is wrong
93
New cards
lesion in left parietal lobe
* can exhibit apraxia
* inability to perform a movement in response to a verbal command
* inability to perform a movement in response to a verbal command
94
New cards
frontal lobe function
important role in personality and cognitive functioning
* voluntary movement, motor integration, language production (broca’s area) social functioning, initiative, inhibition of impulses, emotions
* voluntary movement, motor integration, language production (broca’s area) social functioning, initiative, inhibition of impulses, emotions
95
New cards
Lesion in left frontal lobe
effects:
depression- like symptoms
apraxia
depression- like symptoms
apraxia
96
New cards
Lesion in right frontal lobe
effects:
mania-like symptoms (wound up)
hemineglect
mania-like symptoms (wound up)
hemineglect
97
New cards
which two arteries supply the whole brain ?
1. internal carotid arteries - anterior circulation
2. vertebral arteries - posterior circulation
both join at the brain stem form the basilar artery
98
New cards
circle of willis
ring of arteries formed at the base of the brain by the anterior and posterior blood supplies
99
New cards
where is the vertebrobasilar system located ?
brain stem and cerebellum
100
New cards
how does blood get out of the brain?
internal jugular veins
* network of dural sinuses collect blood to drain into the internal jugular veins
* network of dural sinuses collect blood to drain into the internal jugular veins