Acid + Base titrations
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What is a titration
Quantitative determination of the concentration of compounds in a solution
Acid-base titration: An application of acid-base WHAT, reaction WHAT
WHAT
WHAT
WHAT
Acid-base titration: An application of acid-base EQUILIBRIA, reaction STOICHOMETRY
Strong acid - strong base
weak acid - strong base
Strong acid - weak base
How do you follow the progress of titration:
WHAT
WHAT
How do you follow the progress of titration:
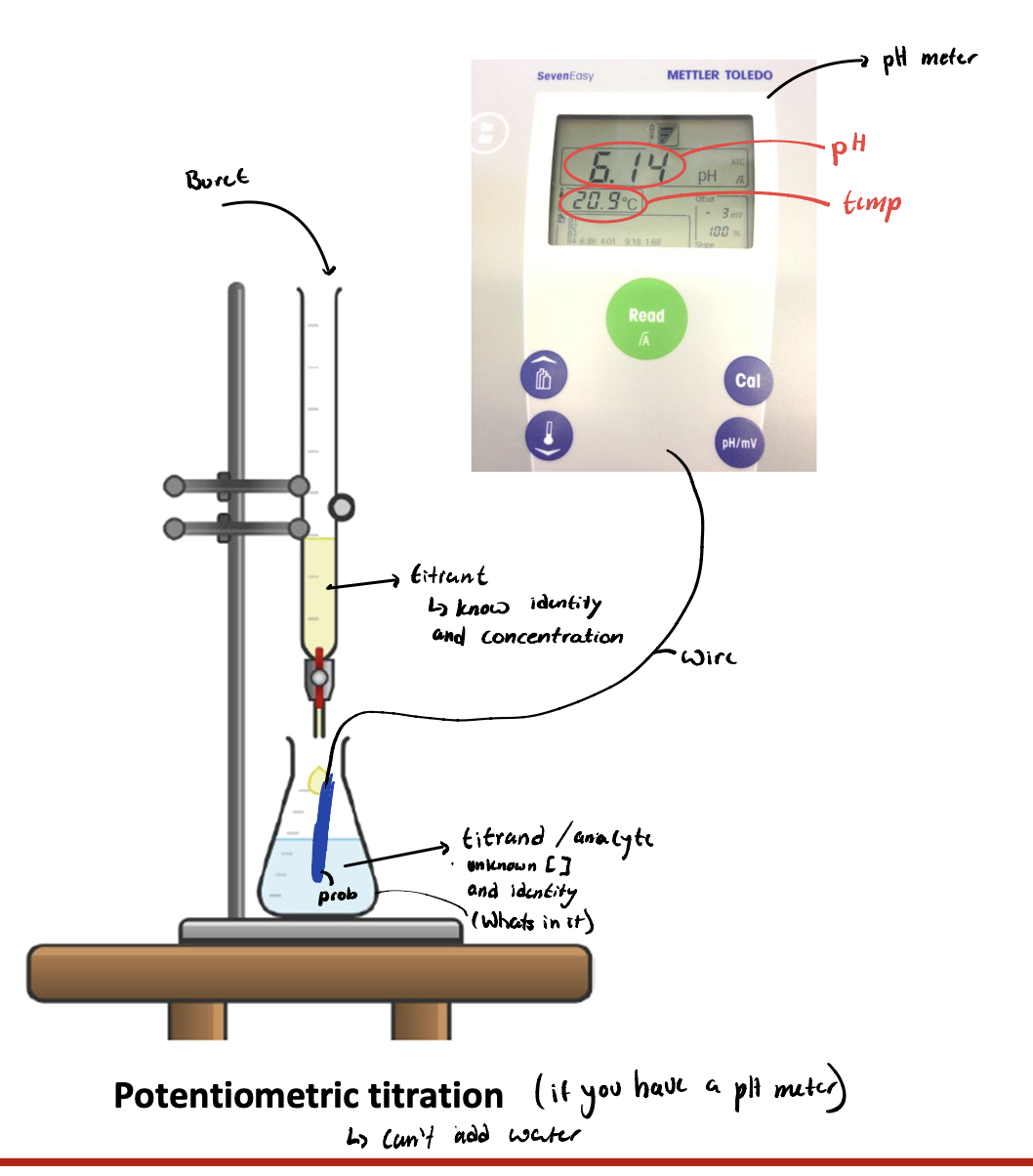
Potentiometric titration
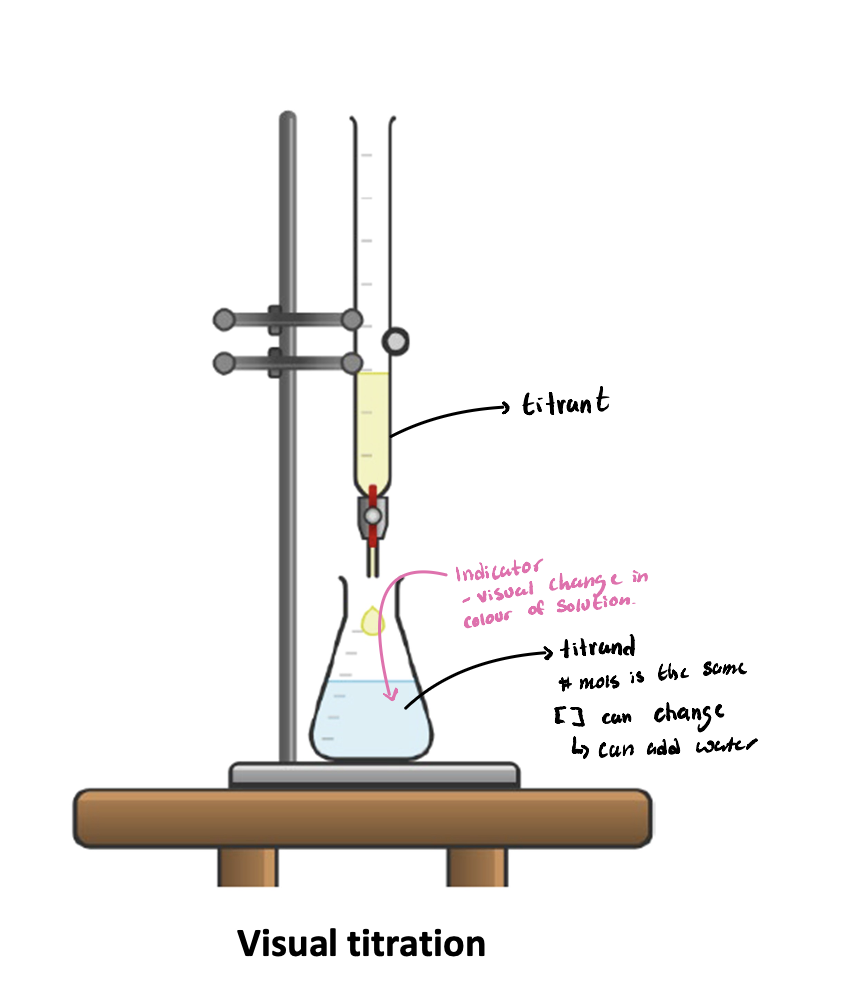
Visual titrations
Potentiometric titration you can add WHAT uses a WHAT
Potentiometric titration you can add WATER uses a pH METER
Visual titrations can add WHAT uses a WHAT
Visual titrations can add WATER (concentration changes NOT moles) uses a INDICATOR
What is a titrant
Solution in which you know the IDENTITY and CONCENTRATION of
What is a titrand / analyte
Unknown CONCENTRATION and unknown IDENTITY
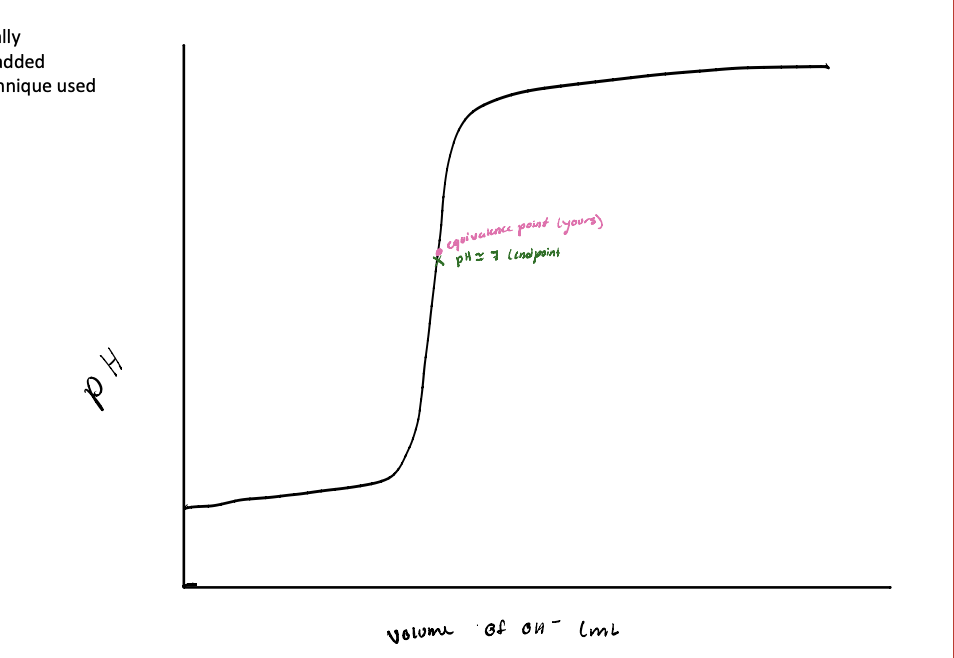
What is an equivalence point:
What is an endpoint:
What is an equivalence point: Ideal, theoretical
No limiting reagent
Exact amount of titrant added
What is an endpoint: Actual, experimental
Determined visually
Value dependent on technique used
What is a ½ equivalence point
nA = nHA
pH = pKa
This can help you identify the identity of the acod
Before equivalence point
Excess H3O+ in solution
pH determined bu [H3O+]
At equivalence point
Acid exactly neutralized
After equivalence point
Excess OH- in solution
pH determine by [OH-]
Which titration would you use for determining concentration of an unknown species
Potentiometric titration
Visual titration
Which titration would you use for determining the IDENTITY of an unknown acid
Potential titration
What factors affect the titration curve shape
[acid]
Identity of acid
[base] (only care about the number of mols)
![<ol><li><p>[acid] </p></li><li><p>Identity of acid </p></li><li><p>[base] (only care about the number of mols) </p></li></ol><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/14d1559f-d780-44db-ba2f-50eec9d22a93.png)
Initial pH can be affected by WHAT
Initial CONCENTRATION of HA (pH = -log[HA])
STRENGTH of HA (Ka)
Volume to reach equivalence point depends on WHAT
Number of MOLES of HA in solution (nH3O+ = nOH-)
CONCENTRATION of STRONG BASE used ([base] + nOH- = nH3O+)
pH at the equivalence point
Slightly basic if titrating a WEAK ACID
The STRONGER the HA, the WEAKER the conjugate base and the closer the pH is to 7
pH at the half-equivalence point depends on WHAT
Strength of the HA (pH = pKa → find Ka - find the identity and strength of the acid)
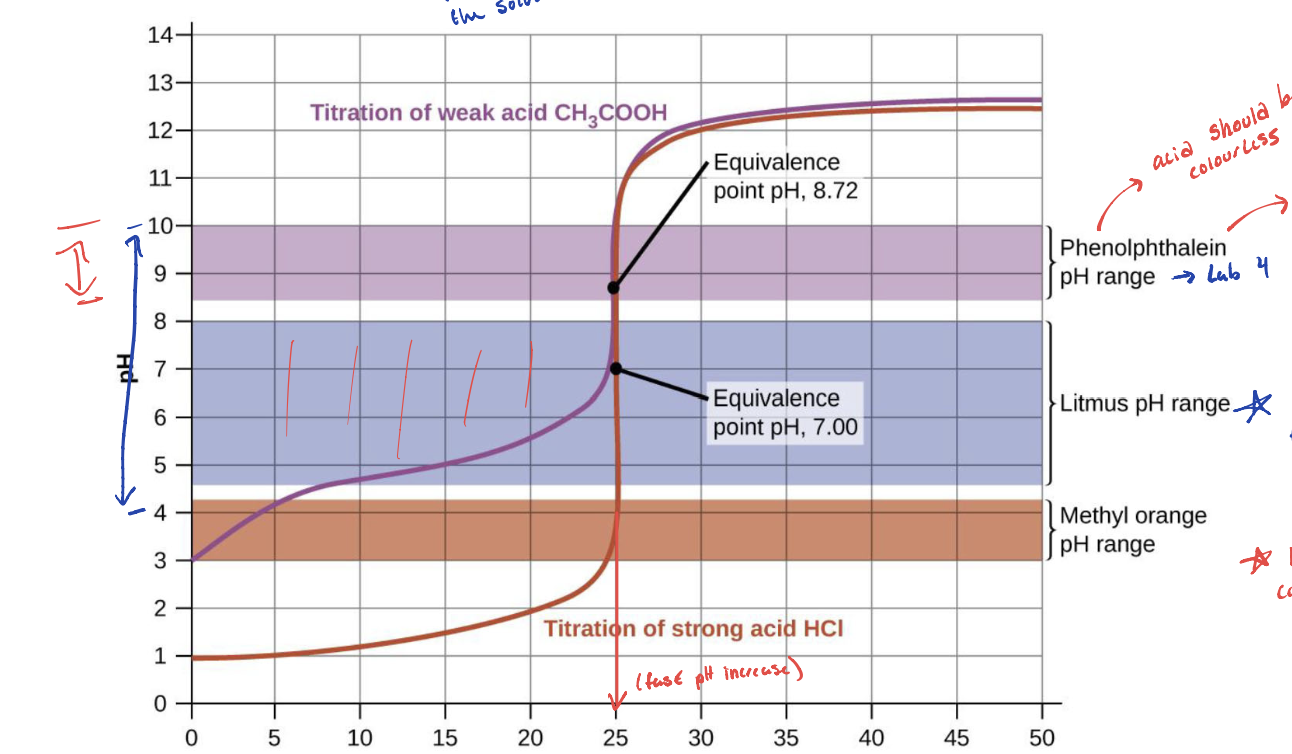
Based on this graph what indicator would you use for a strong acid and for a weak acid
Strong acid = any of the three indicators listed
Weak acid = Phenolphthalein
A good indicator should have a WHAT value close to the expected WHAT at the equivalence point
A good indicator should have a pKa (In) value close to the expected pH at the equivalence point