Hemolytic Anemias: Extracorpuscular Defects (Chapter 14)
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Immune hemolysis
Results from antibodies, complement, or both attatching to the RBC membrane
Diagnosis of immune hemolysis is confirmed by:
A positive direct antiglobulin test (DAT, aka, Coombs test)
Complement
A group of serum proteins that interact with each other to bring about, complete-dependent cell lysis
Immune hemolytic anemia
Patient that produces antibodies to foreign red cell antigens
What can cause autoimmune hemolytic anemia to occur?
Transfusions
Pregnancy
Organ transplantation
Acute hemolytic transfusion reactions (acute HTRs)
Acute intravascular hemolysis that is associated with ABO blood group antibodies
Delayed hemolytic transfusion reactions (delayed HTR)
Associated with antibodies to blood groups other than ABO
Hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn (HDFN)
Fetal or neonatal red cells are destroyed by maternal antibodies
What causes hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn?
Maternal-fetal blood group incompatibility
Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia
Antibodies directed against the patient’s own RBC
Paroxysmal cold hemoglobinuria (PCH)
Not common, representing only 1-7% of patients
Most common in children who had experienced viral disorders
Drug-induced hemolytic anemia
Patients produce antibodies directed at a particular drug, its metabolites, or red cells coated with the drug. These antibodies then destroy the red cells
How may species of malaria can infect humans?
Four
P. falciparum
The most severe species of malaria that causes severe disease with often fatal outcomes
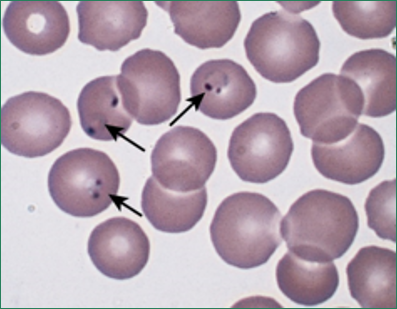
Late stages of Plasmodium vivax malaria produce these, what are they called?
Schüffner’s dots
Babesia
Zoonotic parasitic infection that is usually tickborne but can also be transmitted through blood transfusions
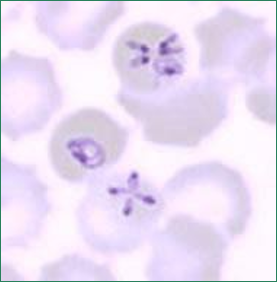
Babesiosis can be distinguish from malaria by formation of these, what are they?
Tetrads of merozoites (Maltese crosses)
Bartonellosis
Caused by any Bartonella bacteria
What are the two primary methods of transmission for Bartonella bacteria?
Sand fly (Bartonella bacilliformis, Carrion’s disease)
Cat (Bartonella henselae “cat scratch fever”)
Hemolytic phase of Bartonellosis
Anemia may be severe; blood smear show many nucleated RBCs and reticulocytosis
Patients in the hemolytic phase of bartonellosis can be effectively treated with:
Antibiotic therapy
Tumor phase of Bartonellosis (aka, verruca peruviana)
Second stage
Verrucous nodes (warty tumors) on face & extremities
Clostridium perfringens
Gram-positive, spore-forming bacillus that is responsible for the development of gas gangrene
What is the preferred locations of clostridium perfringens?
Deep tissues where anaerobic conditions are ideal for the organism
What can occur if a patient has Clostridium perfringens present in deep tissue
Tissue damage from the release of enzymes and toxins
Hemolysis often severe, with hemoglobinemia & hemoglobinuria
Microangiopathic hemolytic anemia (MAHA)
Group of disorders characterized by fragmentation of the red cells as they pass through small, abnormal arterioles (intravascular hemolysis)