AQA GCSE Biology - Inheritance
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Gametes
sex cells
Gametes are made by
Meiosis
Meiosis
Produces non identical cells
Sexual reproduction
-Involves the fusion of Male and female gametes (fertilisation)
-mixing of genetic information so we can see variation in offspring
Asexual reproduction
-one parent
-does not involve gametes and no mixing of genetic information
-offspring are identical
-only involves mitosis
Clones
identical genetic copies
Meiosis
-all chromosomes are copied
-cell divides into two and then one more time, forming gametes
-in the gametes the chromosomes are not in pairs so they have been halved
-produces four gametes from one cell, all genetically different
Meiosis takes place
In reproductive organs, ovaries and testes
Fertilisation
Fusing of a male sex cell with a female sex cell
After fertilisation
The cell divides by mitosis and produces a clump of identical cells (embryo)
As an embryo develops
The cells differentiate forming different cell types eg muscle and nerve cells
Advantages of sexual reproduction
-variation which gives the species more chance of survival because of natural selection (some will survive and reproduce)
Advantages of asexual reproduction
-no need to find a mate
-more efficient and faster
-allows an organism to produce many genetically identical offspring rapidly
Disadvantages of asexual reproduction
-no genetic variation so if conditions become unfavourable they all die
Malaria
-in the human host, parasite reproduces asexually
-in the mosquito, parasite reproduces sexually
Fungi
-produce spores to reproduce asexually
-can also reproduce sexually to create variation
Flowering plants
-reproduce sexually to produce seeds
-strawberry plant reproduces asexually using runners, when it touches the soil it develops into a new plant
Daffodils
-reproduce asexually via bulb division
-parent plant has an underground bulb which produces buds
-these buds eventually form new offspring which are genetically identical
Chromosomes contain
DNA
Structure of DNA
double helix, each strand is a polymer
DNA contains
genes
Each gene
encodes for a specific sequence of amino acids to make a unique protein
Genome
all of an organism's genetic material
Benefits of understanding the human genome
-help us to search for genes that are linked to a disease like cancer
-help us treat inherited disorders like CF
-trace human migration patterns to discover ancestors
DNA structure
polymer of four nucleotides
nucleotides
contain a phosphate group, sugar molecule, base
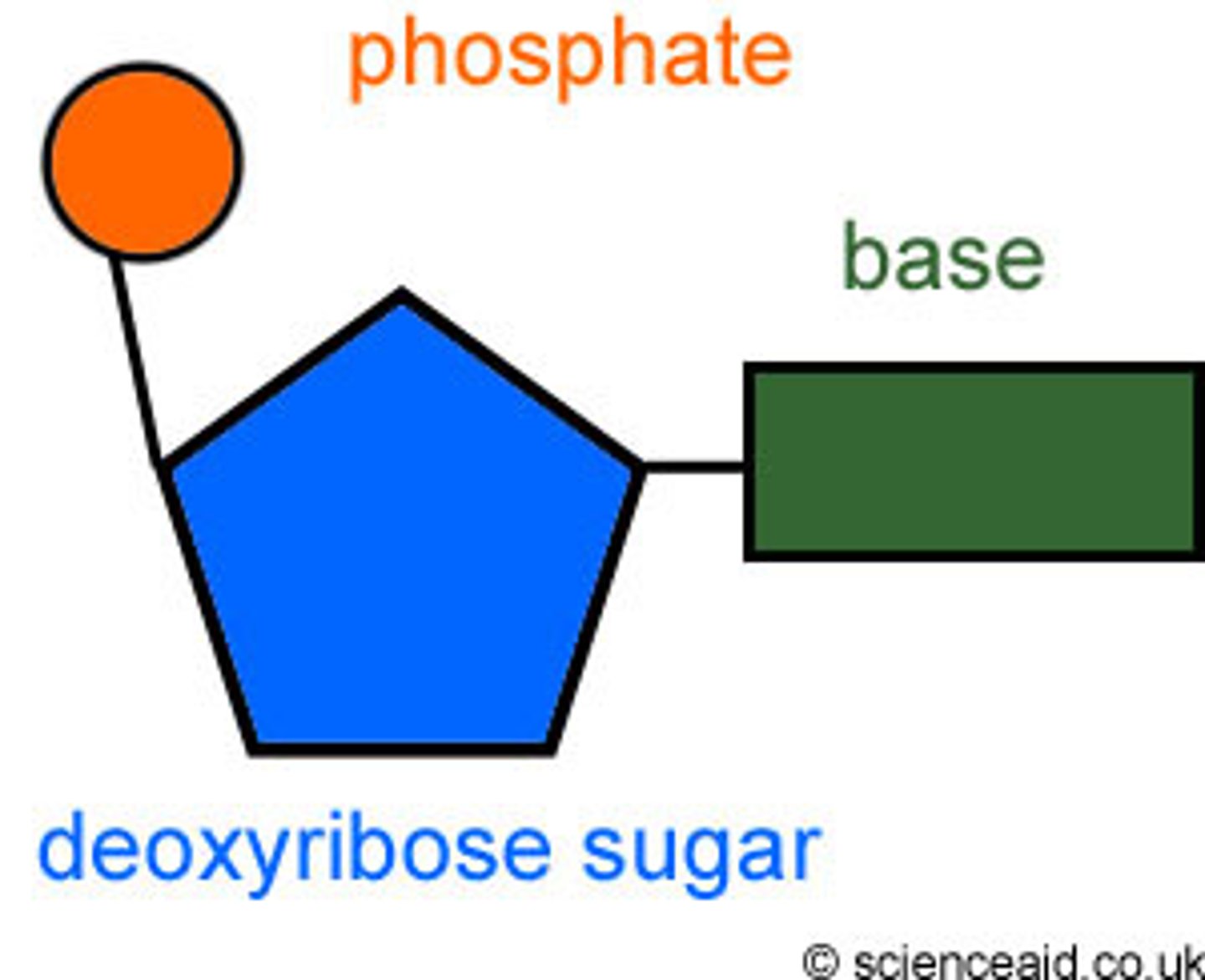
What doesn't change in a nucleotide
the phosphate group and sugar molecule
Bases
complementary and there are four of them
Base pairs
A-T
C-G
Proteinsynthesis
glucose is used to make amino acids for making proteins
Most proteins contain
all 20 amino acids
What does the order of amino acids determine?
the shape of the protein
What does the shape of a protein determine?
its function
Examples of proteins
enzymes and antibodies
How is the order of amino acids determined?
by a sequence of bases in the gene for that protein
Transcription
-the organic process whereby the DNA sequence in a gene is copied into mRNA
-passes out of the nucleus into the cytoplasm
Translation
-mRNA is attached to a ribosome
-amino acids are brought to the ribosome on carrier molecules (transfer RNA)
-ribosomes reads the triplets of bases on the mRNA and uses this to join together the correct amino acids in the right order
-when chain is complete, folds into unique shape
Mutation
A change in DNA structure
Why do some mutations have no effect?
Because different base triplets can sometimes encode for the same amino acid
If an enzyme has a mutation
The substrate may no longer fit into the active site
If a structural protein has a mutation
It may lose its strength
Chromosomes also contain
Non-coding parts of DNA
Gregor Mendel
investigated products of sexual reproduction on pea plants
What did Mendel discover?
-he discovered that characteristics are determined by 'units' that are inherited and do not blend together
-scientists discovered that the 'units' he discovered acted similarly to chromosomes and they were later named genes
Why was Mendel's discovery not recognised in his lifetime?
-he was a monk not a scientist
-he did not publish his work in a well known book
Alleles
Versions of a gene
Genotype
genetic makeup of an organism
Homozygous
Having two identical alleles for a particular gene
Heterozygous
Having two different alleles for a trait
Phenotype
An organism's physical appearance, or visible traits.
Recessive
A recessive allele will only show in the phenotype if two copies are present
Dominant
A dominant allele will show in the phenotype even if there is only one copy present
Cystic fibrosis
-disorder of cell membranes
-controlled by a single gene
-defective allele is recessive
-affects respiratory and digestive system
What is a carrier
heterozygous genotype that carries recessive trait but doesn't express it
Polydactyly
-extra fingers or toes
-caused by a dominant allele
You cannot be a carrier of
A dominant allele because you will have the phenotype
Embryo screening
A process of testing embryos for genetic disorders and rejecting embryos that are at risk
Issues around embryo screening
-expensive
-some healthy embryos are destroyed
Gene therapy
The insertion of working copies of a gene into the cells of a person with a genetic disorder in an attempt to correct the disorder
Family trees show
Phenotypes
How do we know cystic fibrosis is caused by a recessive allele by looking at a family tree?
A person has it but neither of their parents do, so they must both be carriers of the recessive allele