Waste Management
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Laws to follow regarding waste management
Environmental protection act 1990
Special waste regulations (amended) 1996
Hazardous waste regulations 2005
Commercial waste documentation
Section 34(5) of the Environmental Protection Act 1990
Can sometimes be known as Waste Transfer Note
Essential for commercial properties to have evidence on where waste is going
Especially hazardous waste (needs to be a formal document)
But also needed for domestic waste (which can be an invoice of collection)
Types of waste
Non-hazardous
Hazardous
Non-Hazardous waste
Domestic waste
Offensive waste
Pharmaceuticals (non-cytotoxic/cytostatic)
Cadavers (unless harbouring a notifiable disease)
Hazardous waste
Infectious/clinical waste
Sharps
Cytotoxic and cytostatic waste
Photographic/radiographic chemicals
Other (fluorescent light tubes, light bulbs, batteries)
Domestic waste
Waste including: Dry recyclable materials - plastic, metal, glass, paper and card, Food waste, Black bin waste (residual waste)
Internal disposal → Black bin bag or recycle bin or food waste bin
External disposal → landfills for non-recyclable waste and recycled if recyclable
Offensive waste
Waste including: faeces, bedding, clinical material - not infectious
Internal disposal → tiger stipe bag
External disposal → landfill

Pharmaceuticals
Waste including: Empty bottles, syringes, whole drugs, denatured controlled drugs
Internal disposal → Blue topped bin
External disposal → High temperature incineration

Controlled drugs
Regulated by the Misuse of Drugs Regulations 2001
Must be disposed of using a denaturing kit
Liquids – added straight to kit
Tablets – crushed, mixed with water then added
Schedule 2 drugs must have their disposal witnessed
Disposed of in Pharmaceutical waste
Cadavers (a corpse or deceased body)
Non-infectious cadavers → buried at home by owner, buried at a pet cemetery or cremated by a pet crematorium
Cadaver with Notifiable disease → APHA/DEFRA to dispose of
No specific packaging requirement
Infectious/Clinical Waste
Waste including: Animal tissue, body parts, blood or other bodily fluids, Waste from infectious disease and zoonotic patients, Items contaminated with pharmaceuticals
Internal disposal → Yellow clinical waste bag
External disposal → High temperature incineration

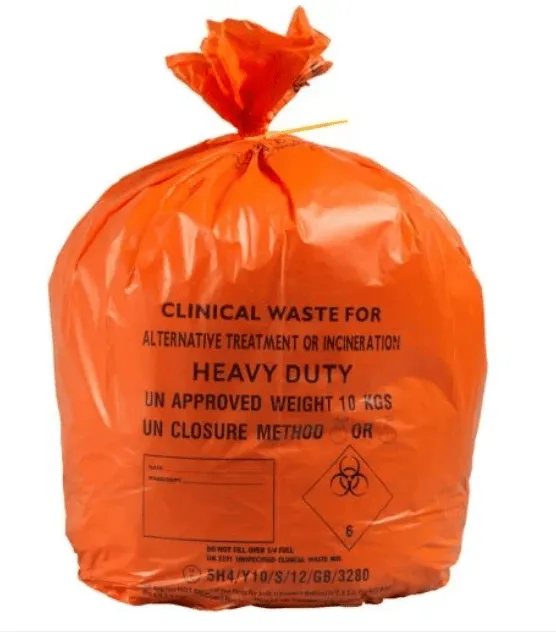
Orange clinical waste bags
No body parts or cadavers
External disposal → Autoclaving for best practice
Sharps - yellow lidded bins
Disposal of surgical needles, scalpel blades, hypodermic needles
Can be contaminated with bodily fluids and pharmaceuticals
Internal disposal → yellow lid sharps bin
External disposal → high temperature incineration

Sharps - Orange lidded bins
Dispose of sharps not contaminated with pharmaceuticals
Internal disposal → orange lid sharps bin
External disposal → autoclaving or disinfection

Cytotoxic means..
Toxic to cells
Cytostatic means..
Inhibition of cell growth and multiplication
Cytotoxic and cytostatic waste
Waste including: anything contaminated with cytotoxic or cytostatic pharmaceuticals
Internal disposal → sharps bin with purple lid, yellow bag with purple stipes or purple bag
External disposal → high temperature incineration

Photographic/Radiographic chemicals
Waste including: fixer and developer solutions
The two solutions should be disposed of separately
No standard packaging requirements
Waste containers must be leak-proof and labelled
Fluorescent light bulbs
Specialised recycling centres
Batteries
Should be taken to local supermarkets for recycling
Light bulbs
Incandescent: regular waste bin
LED or CFL: recycling centre
Consequences of poor waste disposal
Environmental damage
Human injury
Prosecution of organisation and individual
Environmental damage
Infectious/zoonotic diseases
Risk of wildlife health with chemicals
Human injury
Sharps put in plastic bags
Risk of injury from chemicals
Prosecution of organisation and individual
Failure to produce commercial waste documentation
Breach of section 34(5) of the Environmental Protection Act 1990 (£300)