6.3: Control of heart rate
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
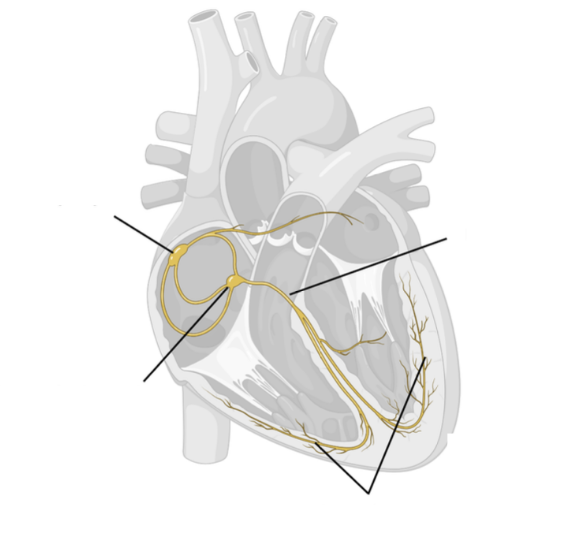
Label the SAN, AVN, Bundle of His, Apex and Purkyne tissue on this diagram
What is the definition of myogenic?
The ability to contract and relax without receiving electrical impulses from nerves
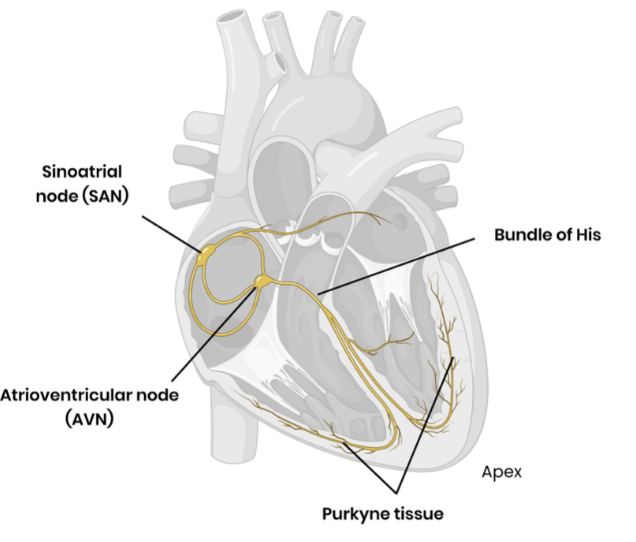
What is the role of the sinoatrial node (SAN)?
Acts as a pacemaker to send regular waves of electrical activity across atria, initiating the heartbeat
What is the role of the atrioventricular node (AVN)?
Delays impulse to prevent immediate contraction of ventricles, allowing the atria to fully contract and empty before ventricles contract
What is the role of the Purkyne tissue in the bundle of His?
Transmits electrical activity to the apex of the heart and along the ventricle walls along Purkyne fibres
Describe the myogenic stimulation of the heart and transmission of a subsequent wave of electrical activity
Sinoatrial node acts as a pacemaker by sending regular waves of activity across atria
Causing atria to contract simultaneously
Non-conducting tissues between atria/ventricles prevents an impulse passing directly into the ventricles
Preventing an immediate contraction of the ventricles
Waves of electrical activity reach the atrioventricular node which delays impulse
Allowing atria to fully contract and empty before ventricles contract
Atrioventricular node sends wave of electrical activity down bundle of His, conducting wave between ventricles to apex where it branches into Purkyne tissues
Causing ventricles to contract simultaneously from the base up
What are the pathways of the autonomic nervous system and what effect do they have?
The sympathetic nervous system (positive effect)
The parasympathetic nervous system (negative effect)
Where are chemoreceptors and pressure receptors located?
Aorta and carotid arteries
What is the role of chemoreceptors, pressure receptors, the autonomic nervous system in increasing heart rate when there is a fall in blood pressure?
Baroreceptors detect a fall in blood pressure
Chemoreceptors detect a rise in blood CO2 conc of fall/rise in blood pH
They send impulses to the medulla/cardiac control centre
Which send more frequent impulses to the SAN along sympathetic neurons
So more frequent impulses are sent from the SAN from AVN
So cardiac muscle contracts more/ frequently
So heart rate increases
What is the role of chemoreceptors, pressure receptors, the autonomic nervous system in decreasing heart rate when there is a rise in blood pressure?
Baroreceptors detect a rise in blood pressure
Chemoreceptors detect a fall in blood CO2 conc of fall/rise in blood pH
They send impulses to the medulla/cardiac control centre
Which send more frequent impulses to the SAN along parasympathetic neurons
So less frequent impulses are sent from the SAN from AVN
So cardiac muscle contracts less frequently
So heart rate decreases
What is the formula for cardiac output?
Cardiac output = heart rate x stroke volume