HOSA Medical Assisting Test
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
Palpation
Physician uses hands and fingers to feel various parts of the body
Percussion
Physician uses fingers to tap various body parts and listen to sounds emitted
Observation
Physician looks at patient closely
Oscultation
Physician uses stethoscope to listen to sounds produced by body organs
opthalmoscope
A lighted instrument for the eyes
Otoscope
Instrument used for visual examination of the ear
Tuning fork
Used to test hearing acuity
Stethoscope
Used to listen for heartbeat
Percussion hammer
used to test tendon reflexes
Ayer blade
Used to scrape cells from cervix
Laryngeal mirror
Used to see down throat
Tongue depressor
Used to look in mouth
Rectal speculum
instrument used to examine the rectum
sigmoidoscope
instrument for looking at the sigmoid colon
Scalpel
Attached to knife blade; used to incise skin and tissue
Surgical scissors
special scissors used to cut tissue; has sharp and dull side.
Hemostats
Used to compress blood vessels to stop bleeding
Tissue forceps
Used to grasp tissue with one or more fine points and no teeth
Retractors
Used to hold or draw back sides of a wound or incision
Needle holder
Used to hold a needle when sutures are being inserted
Splinter forceps
Used to remove foreign objects from skin and tissue
Towel forceps
Used to hold material and separate areas of surgery
Bandage scissors
special scissors with a blunt lower end used to remove dressings and bandages
Horizontal recumbent
(Position) Used to examine the breasts and abdomen
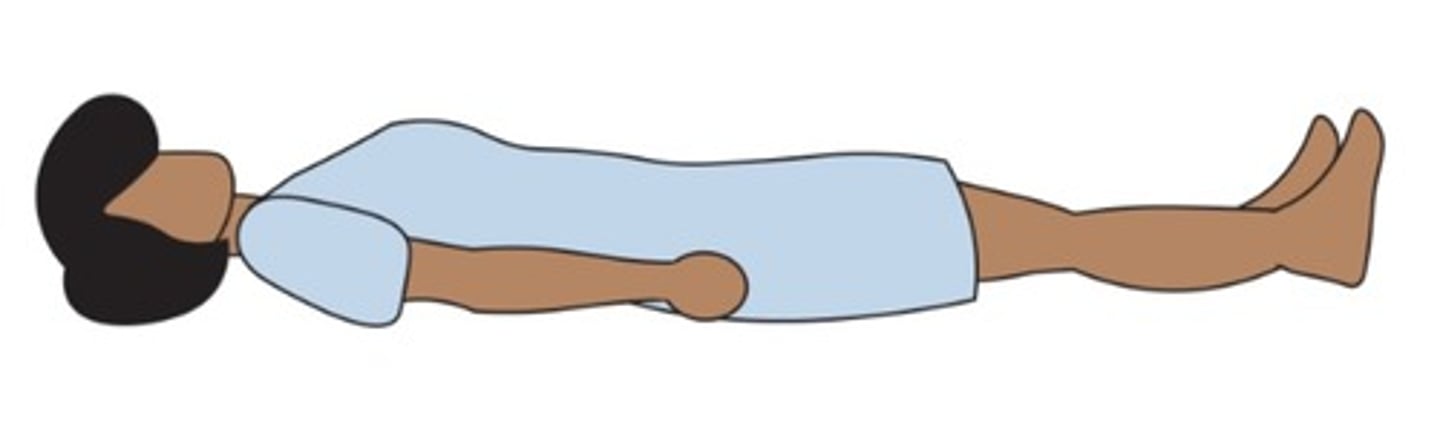
Sims
(Position) Used for enemas and rectal temperatures
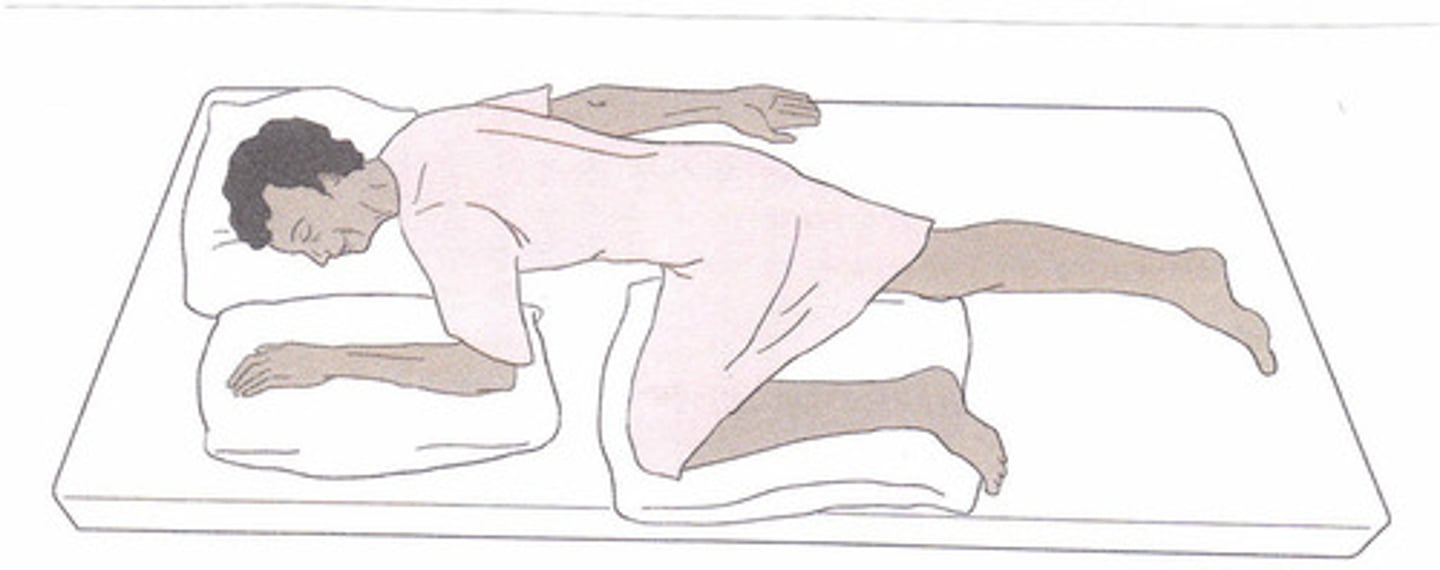
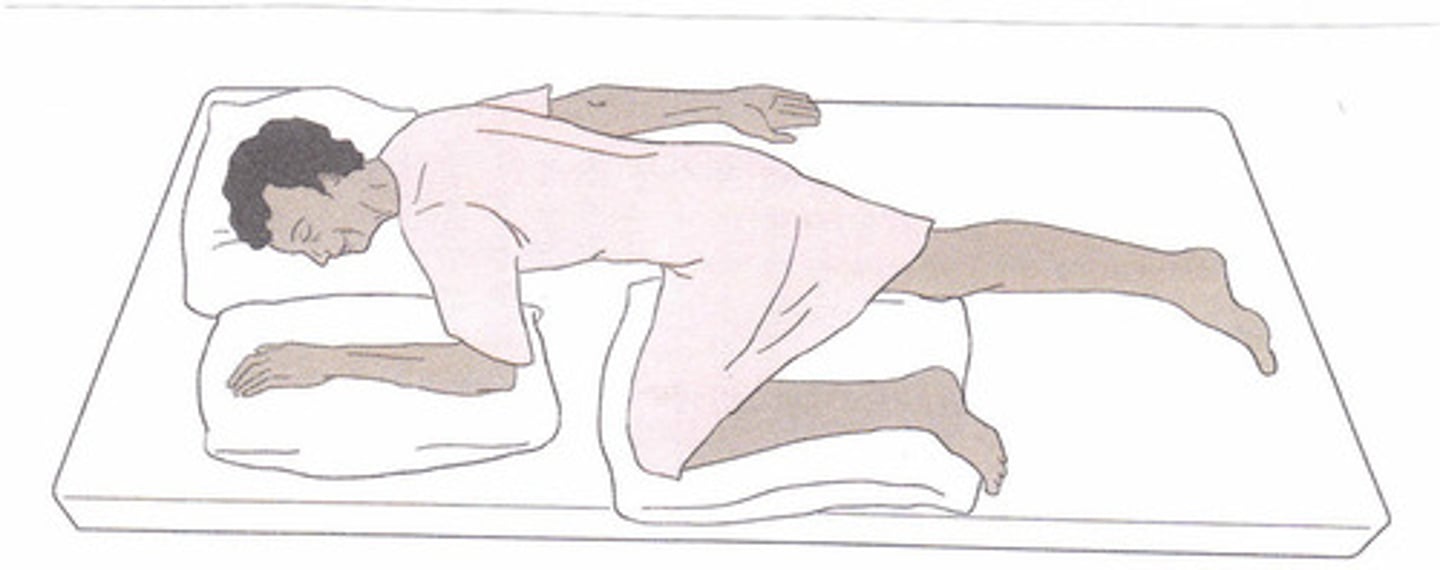
Knee-chest
(Position) Used for sigmoidoscopic examinations
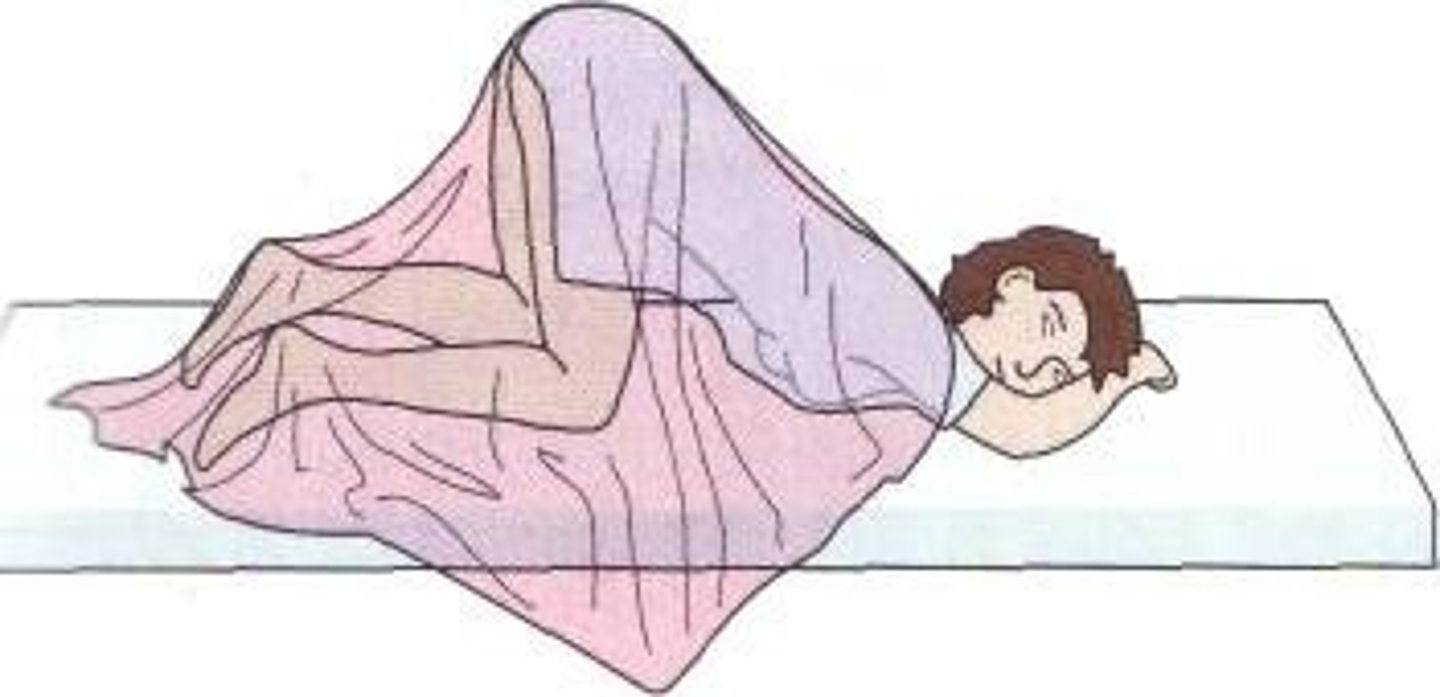
Jackknife
(Position) Used for rectal surgery
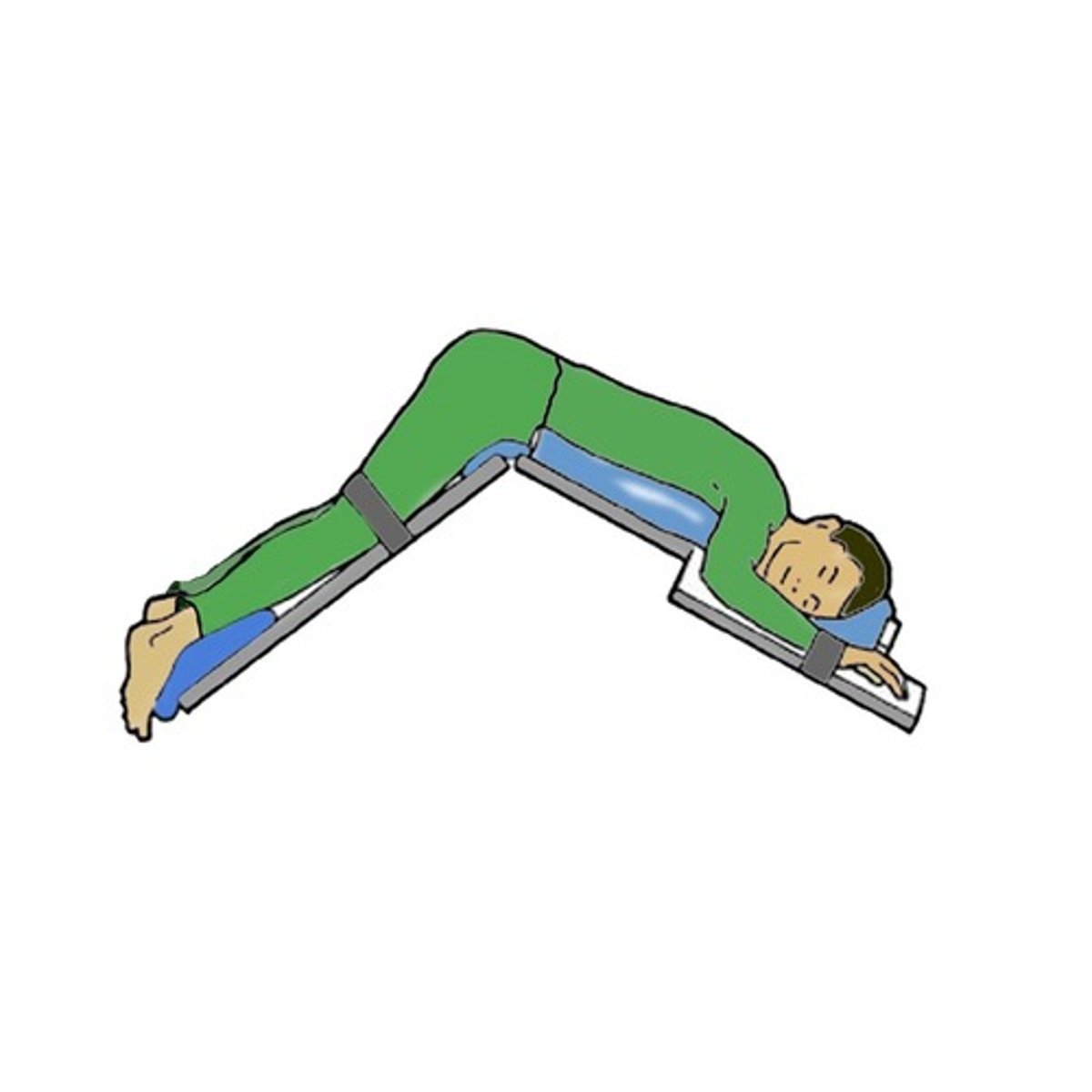
Fowler's
(Position) Used for breathing problems

Prone
(Position) Patient lying flat on abdomen
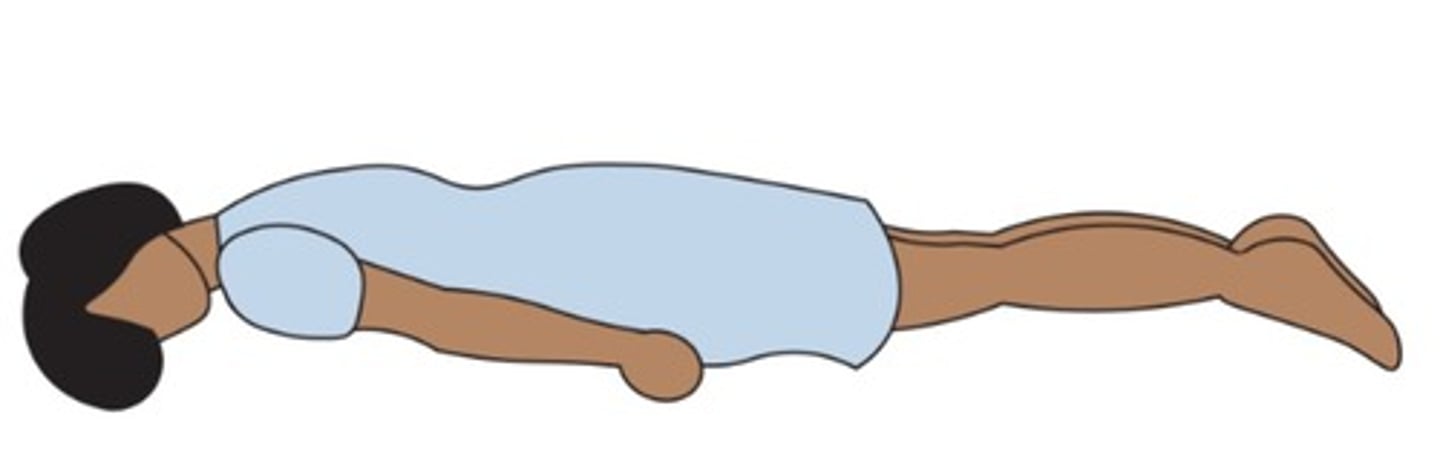
Sims
(Position) Patient lying on left side
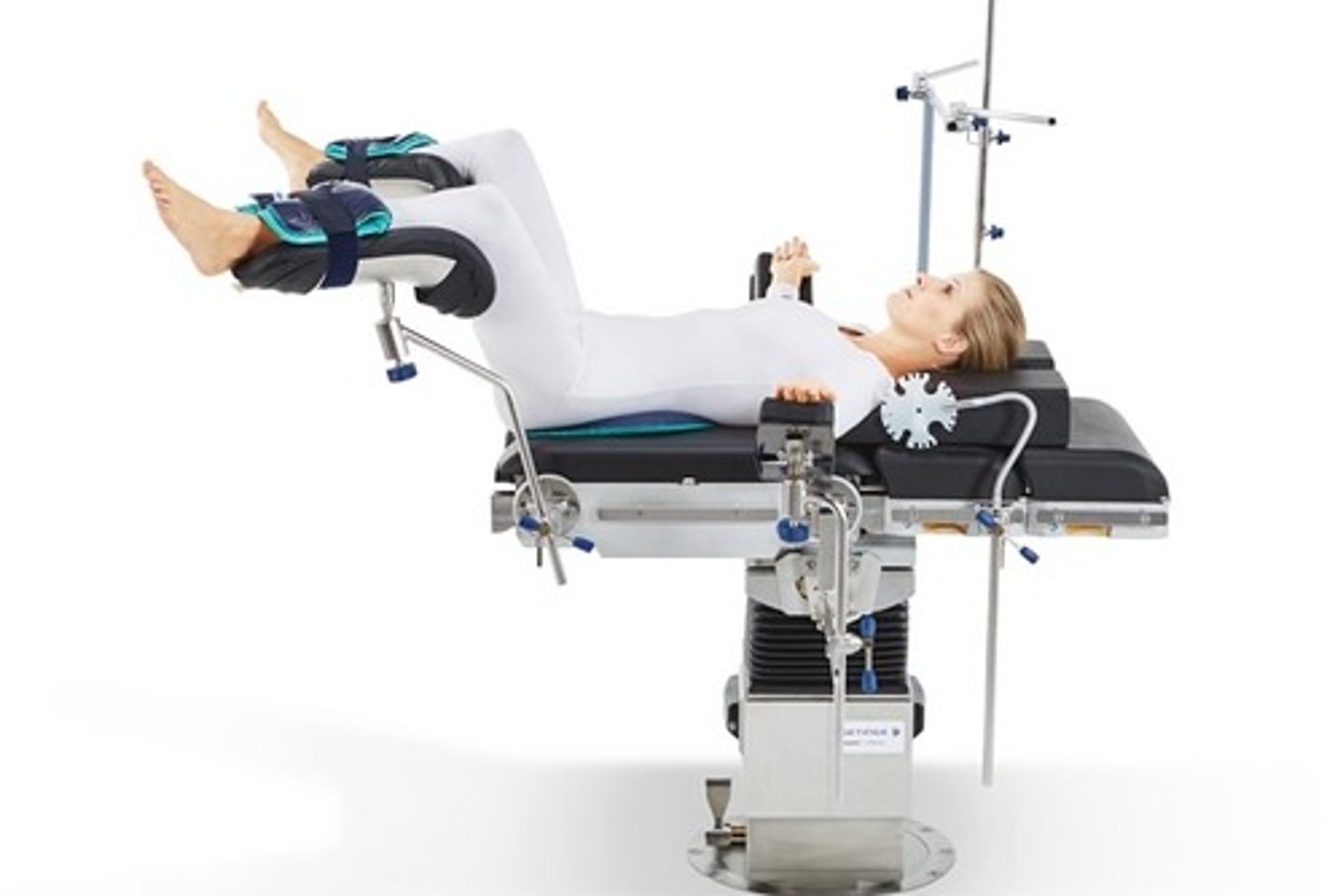
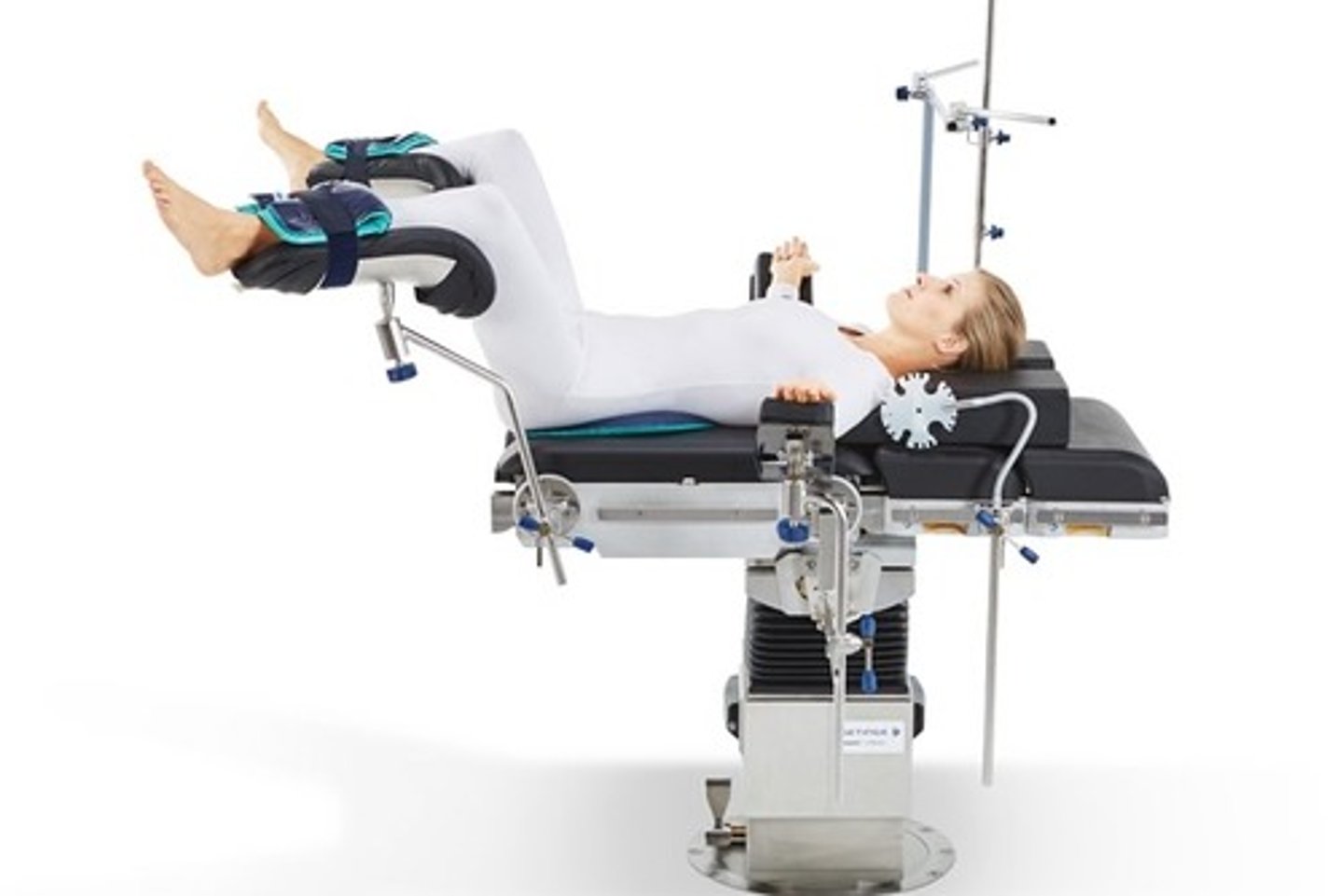
Lithotomy
(Position) Used for Pap tests and vaginal examinations
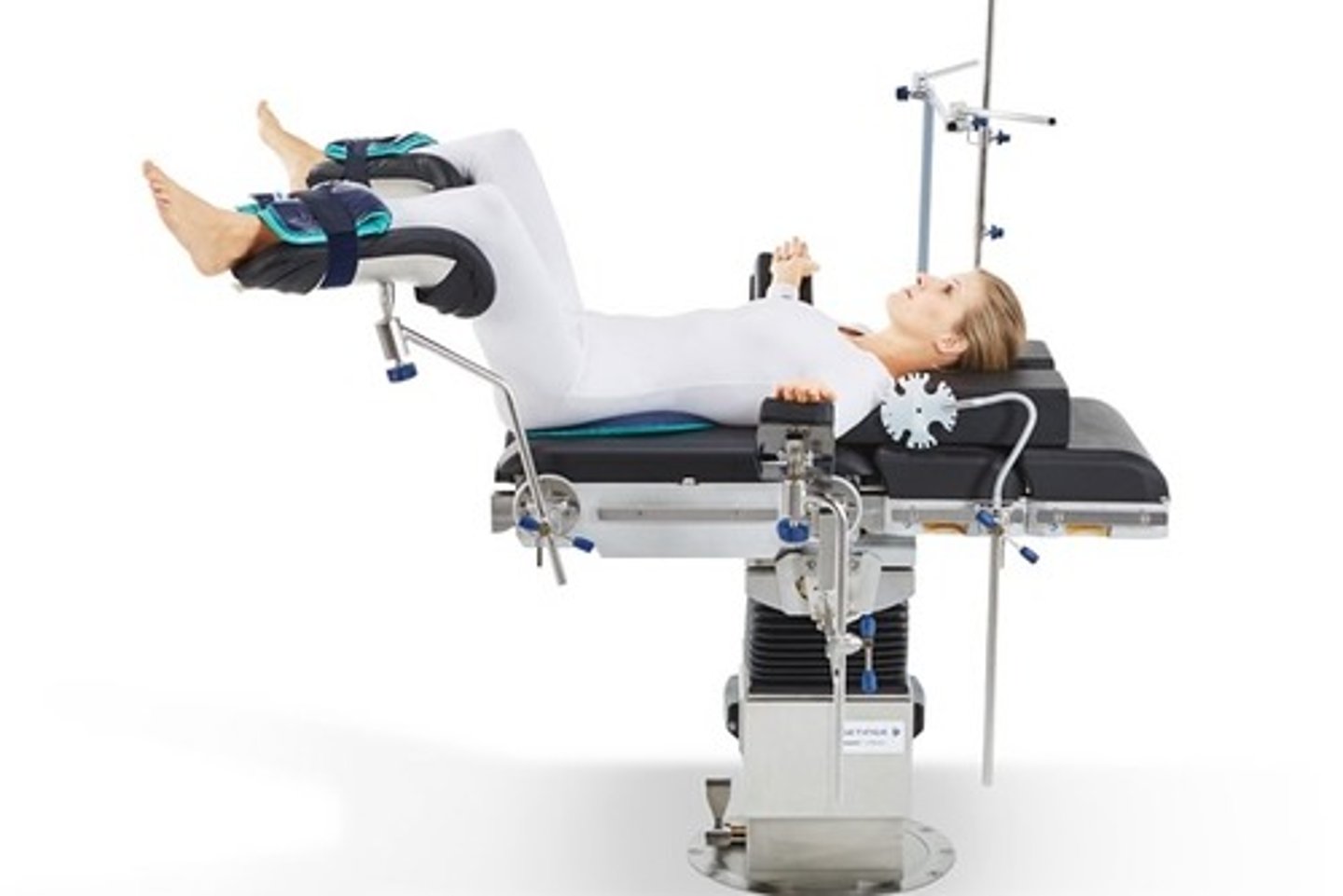
Lithotomy
(Position) Used for pelvic surgery
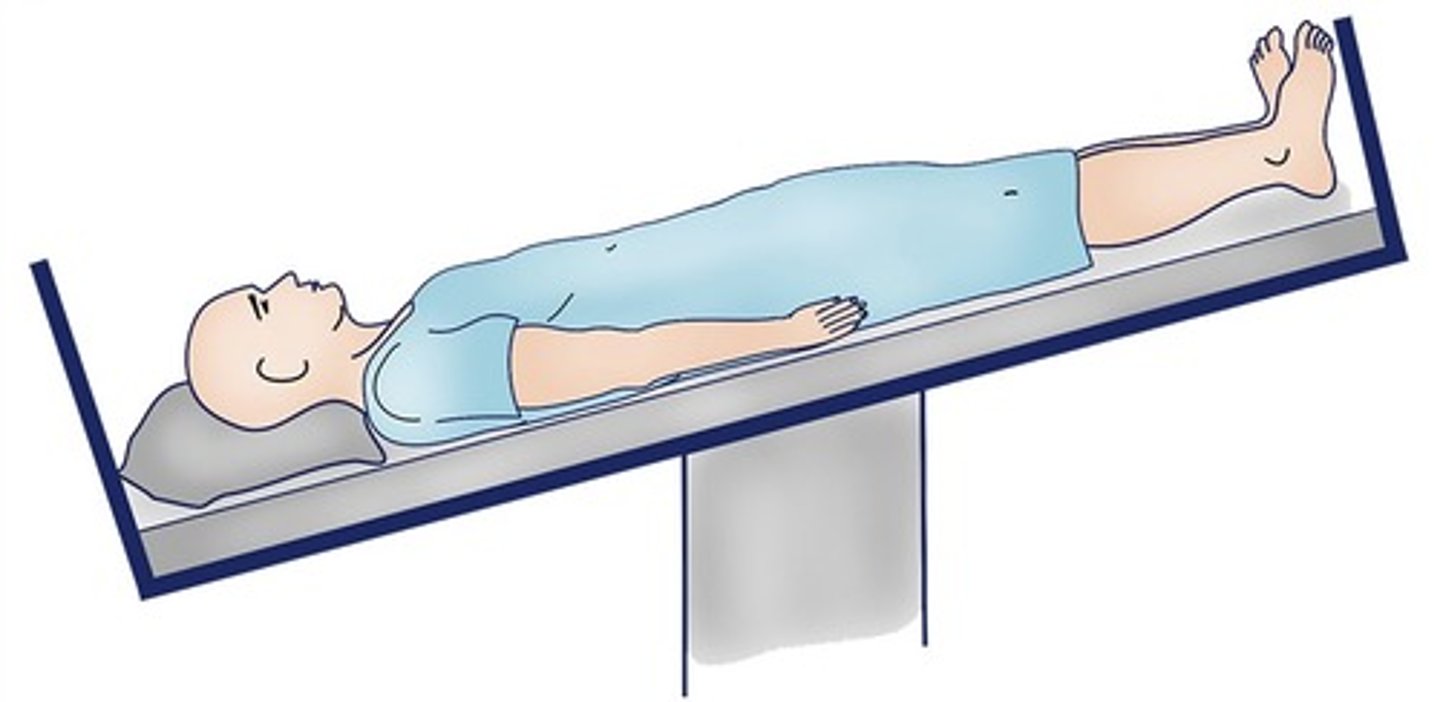
Trendelenburg
(Position) Used for circulatory shock
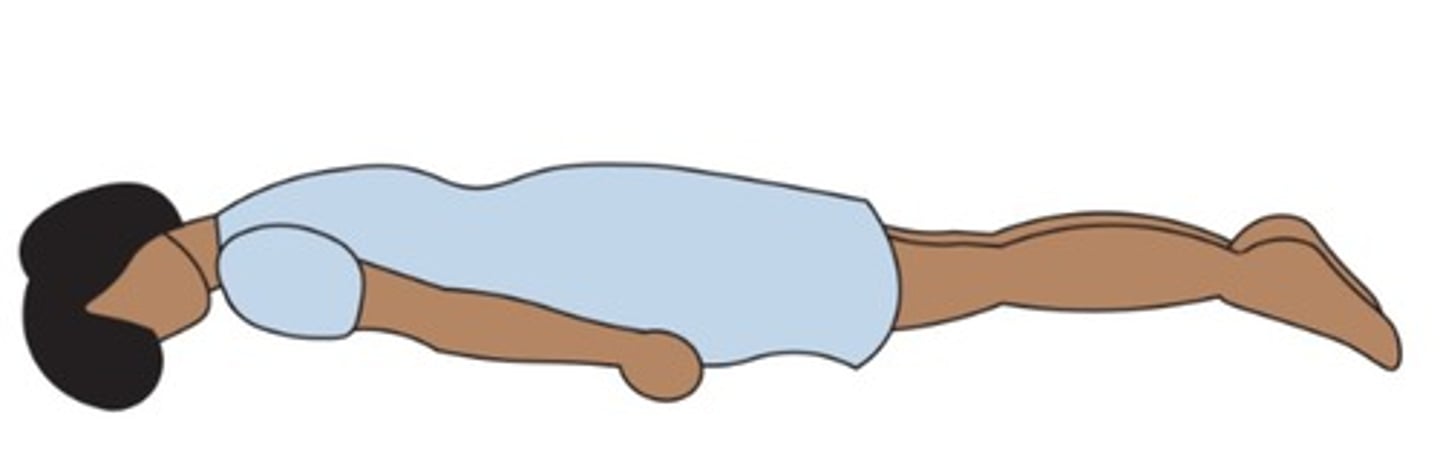
Prone
(Position) Used to examine the back and spine
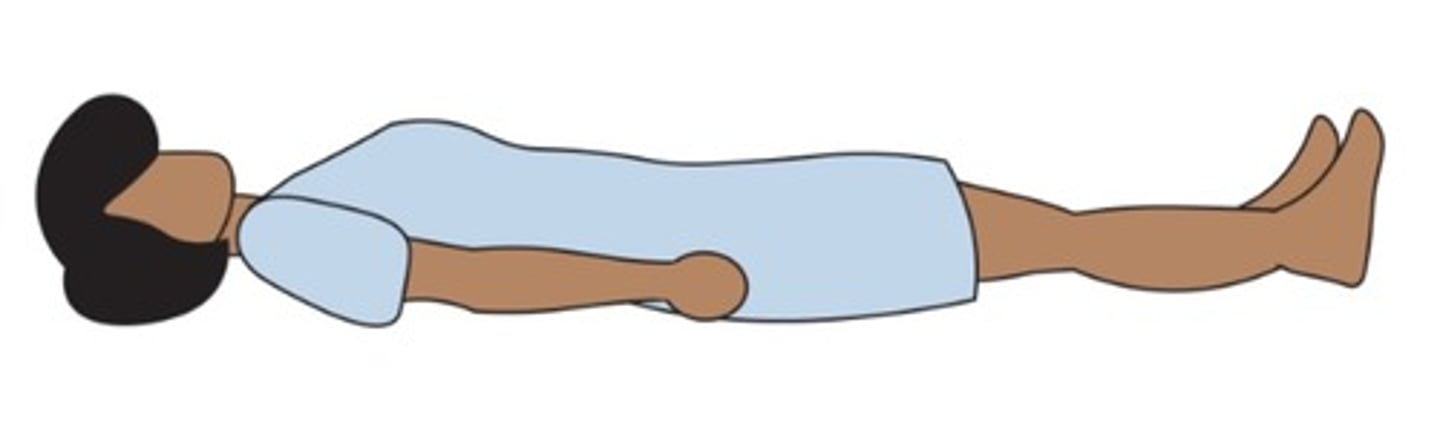
Horizontal recumbent
(Position) Also called the supine position
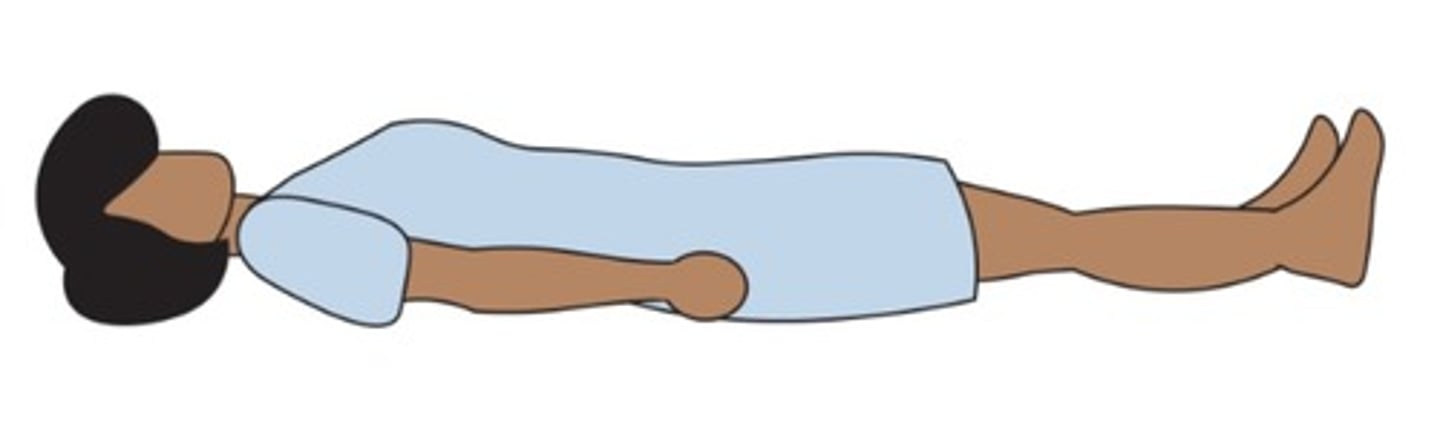
Horizontal recumbent
(Position) Patient lying flat on back
Fowler's
(Position) Used to encourage drainage
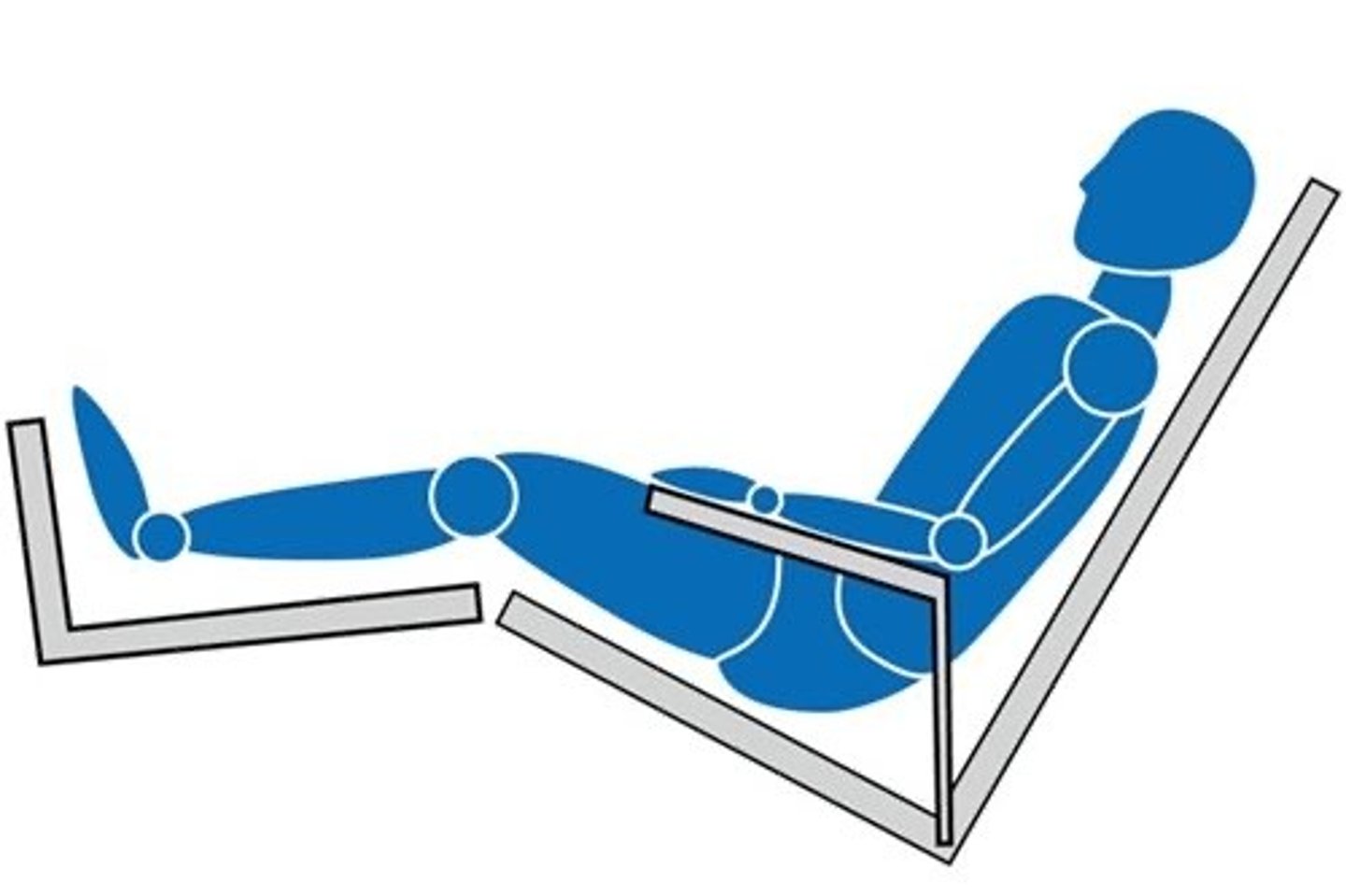
Lithotomy
(Position) Feet elevated in stirrups
Sims'
(Position) Also called the left lateral position
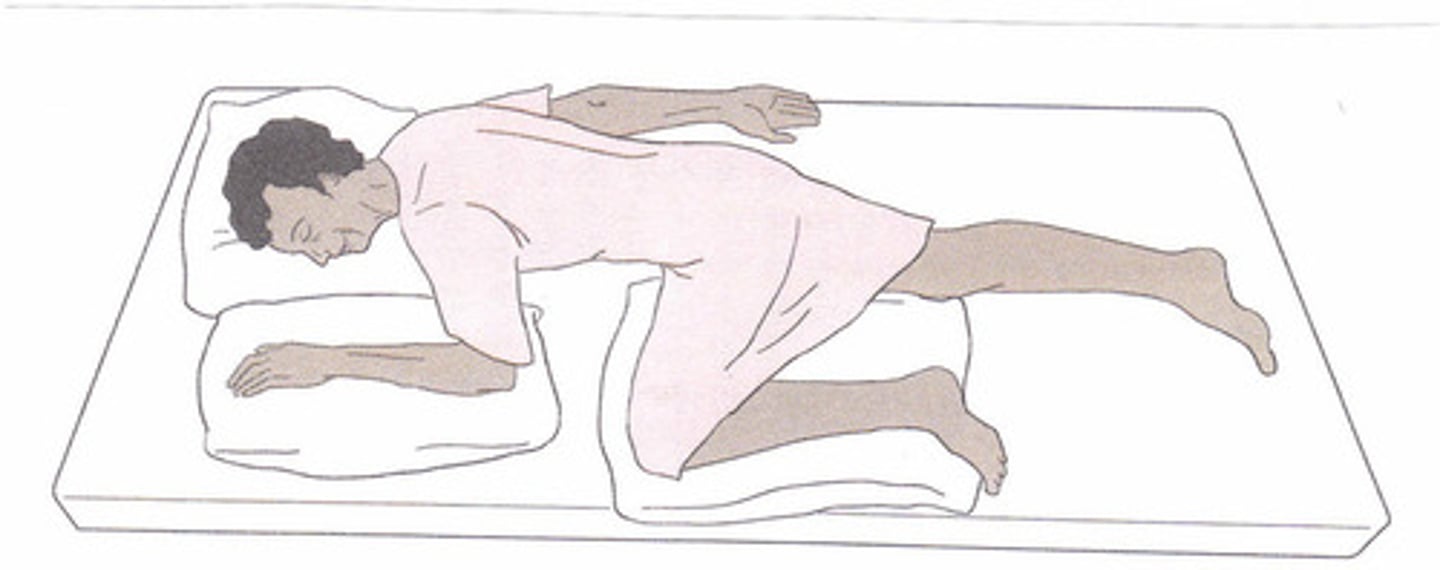
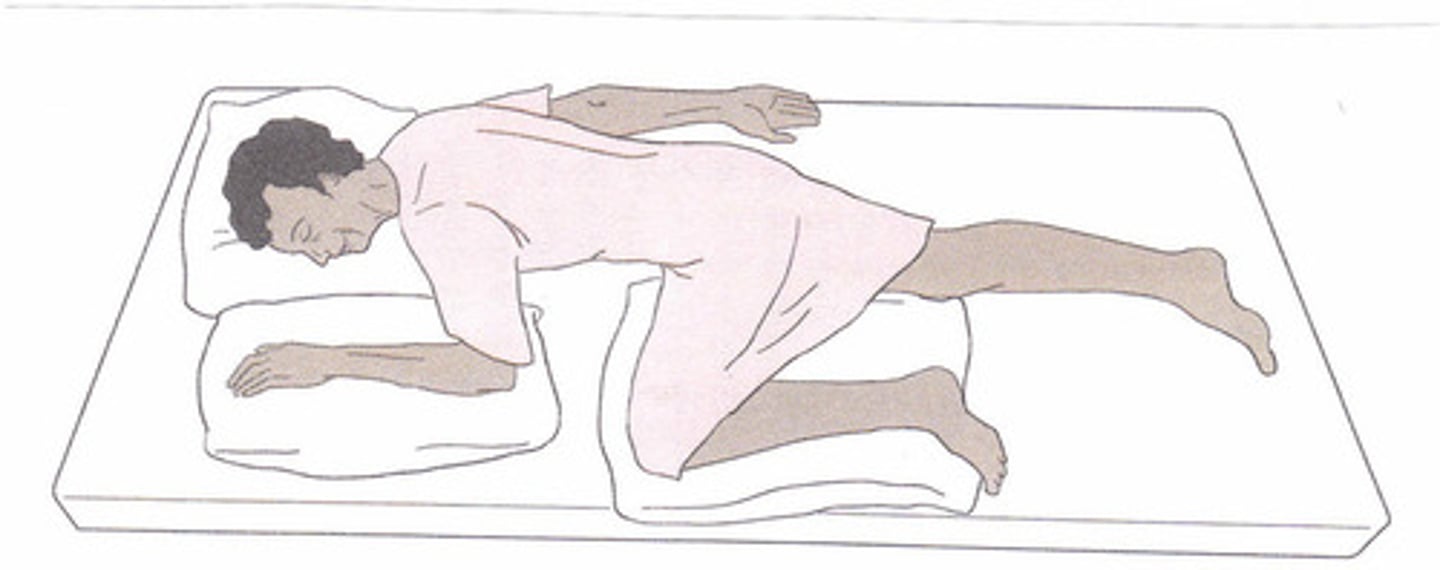
Knee-chest
(Position) Patient rests body weight on knees and chest

Sims'
(Position) Used for rectal examinations and treatments
Fowler's
(Position) Used to examine the chest
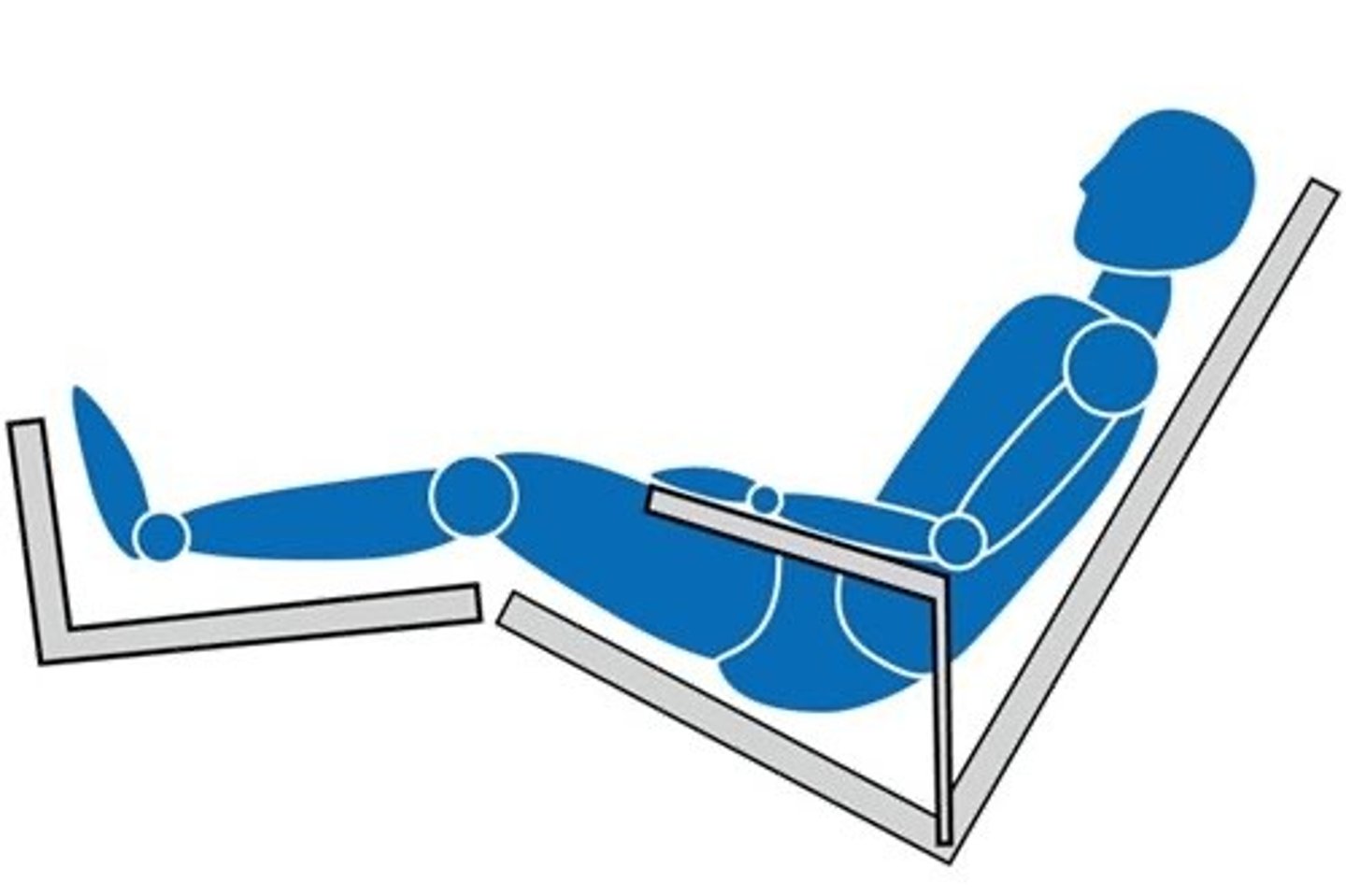
25
How many degrees is low Fowler's position?
45
How many degrees is mid Fowler's position?
90
How many degrees is high Fowler's position?
Snellen chart
Used to test for myopia (nearsightedness). The top indicates how far you are, while the bottom is the size of the characters.

Jagger test
A card that has a paragraph with different millimeter height. The card is held 14 inches away from the face. Tests for hyperopia (farsightedness).

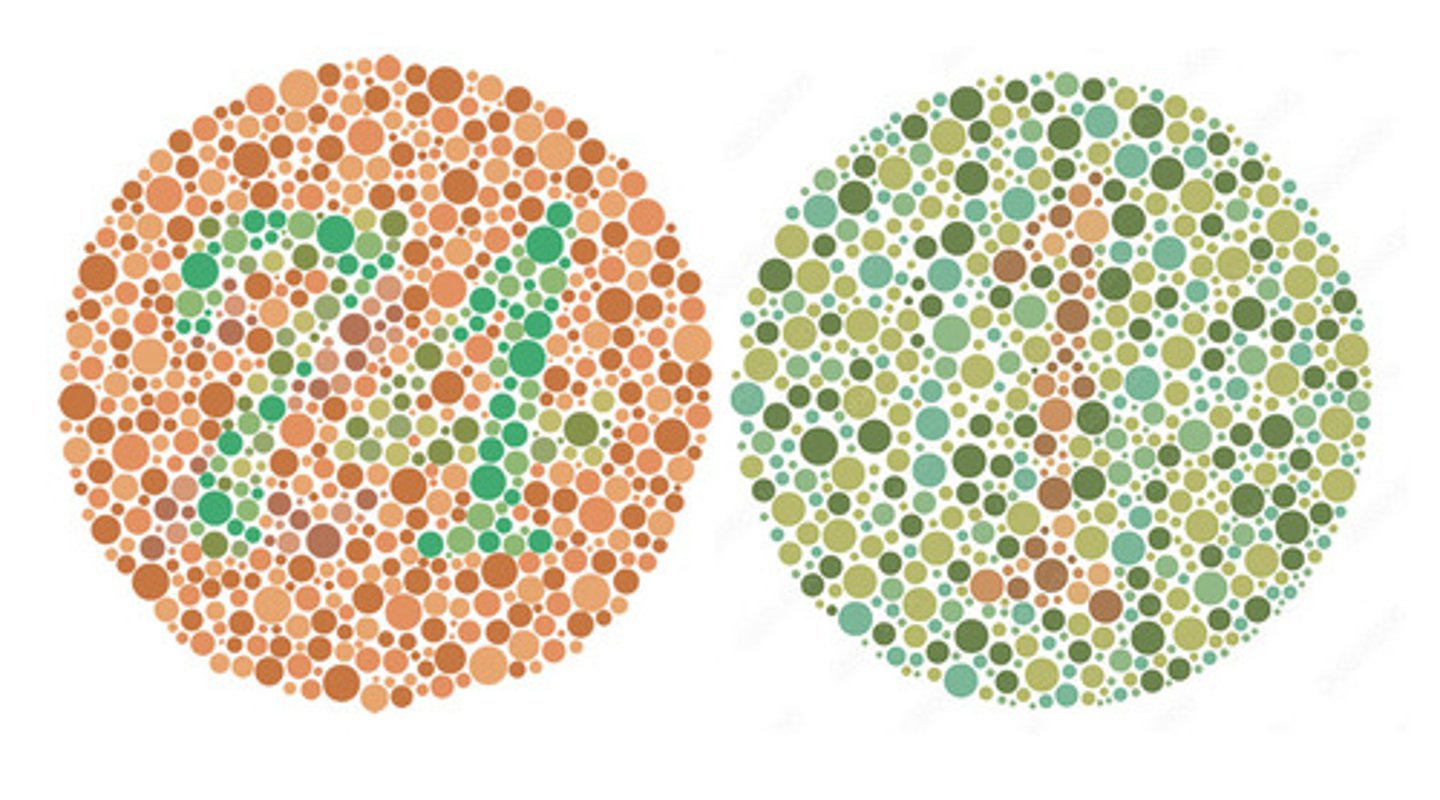
Ishihara Test
Booklet of dots making up a symbol. The dots are green/orange. This test is done for color blindness.

Tonometer test
Putting eye drops in the eyes and testing ocular pressure. Used to test for glaucoma.
right eye (oculus dexter)
(Abbreviation) What does OD stand for?
left eye (oculus sinister)
(Abbreviation) What does OS stand for?
both eyes (oculus uterque)
(Abbreviation) What does OU stand for?
12
How many heads does a complete EKG have?
6
How many leads are located in between the ribs?
Suspension
(Type of medicine) A mixture of a solid and fluid
Capsule
(Type of medicine) a gelatin shell that can be opened and has powder inside
Enteric coated
(Type of medicine) a pill that has a covering that does not dissolve until it reaches the intestine
Scored tablet
(Type of medicine) a tablet that has a line indented all the way down on one side so you can split it in half
Troche
(Type of medicine) melted into a formed disk. It melts in the mouth
Intramuscular, subcutaneous, intradermal, topical, orifice, inhalation
What are the different types of shots?
Ointment
(Semisolid form of medicine) has fat paste
Paste
(Semisolid form of medicine) an ointment with adhesive substance
Cream
(Semisolid form of medicine) medicine with a water soluble base
Suppository
(Semisolid form of medicine) medicine mixed with cocoa butter and formed to be put in different orifices
Medication, dose, patient, time, route, documentation
What are the six rights to observe when giving medications?
Topical (gums), spinal (epidural) , general (breathe in/IV)
What are the 3 types of anesthesia?
Single channel, multiple channel
What are the two types of EKG machines?
1. It can displace other organs. 2. It can make the patient uncomfortable
Why should you void before an exam? (2 reasons)
Vision test, blood test, height and weight, vital signs
What are 4 tests done prior to a physical exam?