nervous tissue
1/153
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
154 Terms
coordination of voluntary and involuntary actions
what is the function of the nervous system?
neurons and glia
what are the two main types of cells that you would find in the nervous system?
all nervous functions
what is the function of neurons?
to provide for the neurons
what is the function of glia?
neurons
what is the functional unit of the nervous system?
excitability and conductivity
what are the two main characteristics of a neuron?
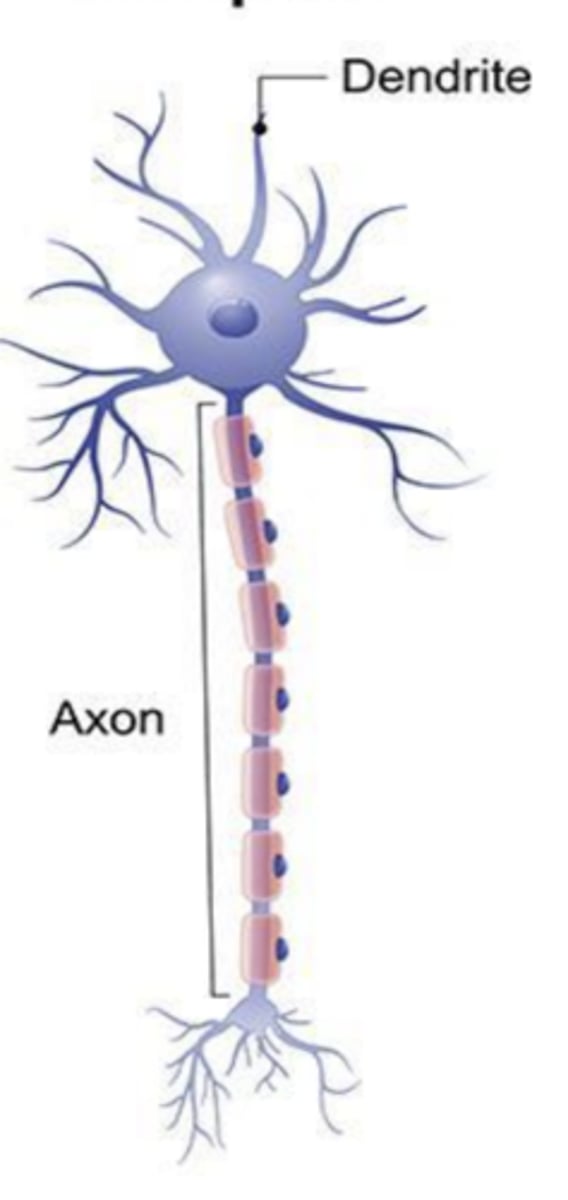
the neural body
what is the soma?
dendrites and axons
what are the extensions of the neuron called?
in the center of the soma, large, with nucleolus inside
where is the nucleus of a neuron? what is it like?
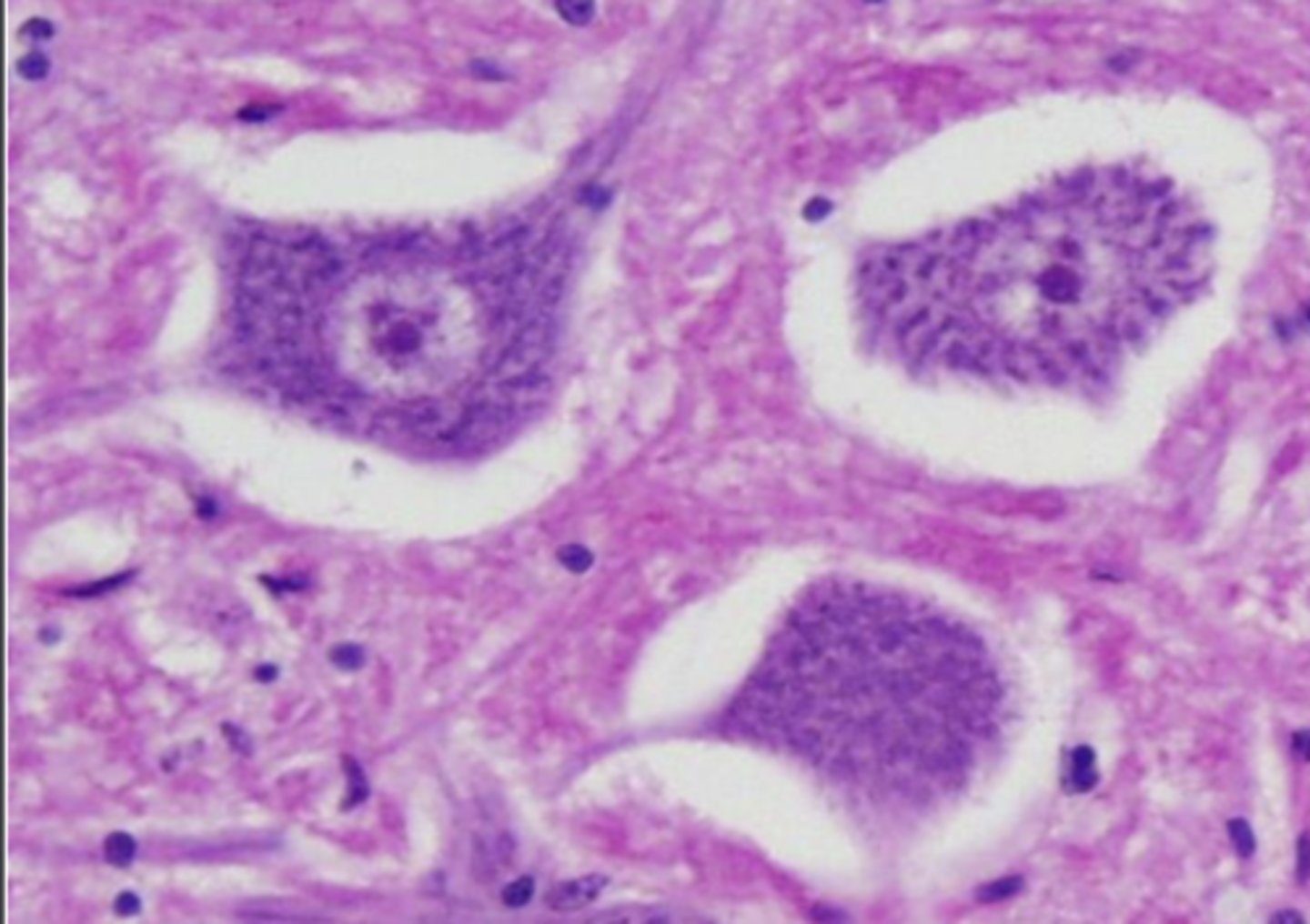
Nissl bodies
SER
Golgi apparatus
mitochondria
what are the four main organelles in the soma of a neuron?
basophilic
contains polyribosomes to synthesize proteins
only in the cytoplasm of neurons
describe a Nissl body
storage of Ca2+
what is the smooth ER for?
transmission of signals between neurons
what is Ca2+ used for in the nervous system?
very developed
what is the golgi apparatus like in a neuron?
a lot
describe the abundance of mitochondria within the neuron
golgi apparatus
what is this organelle?
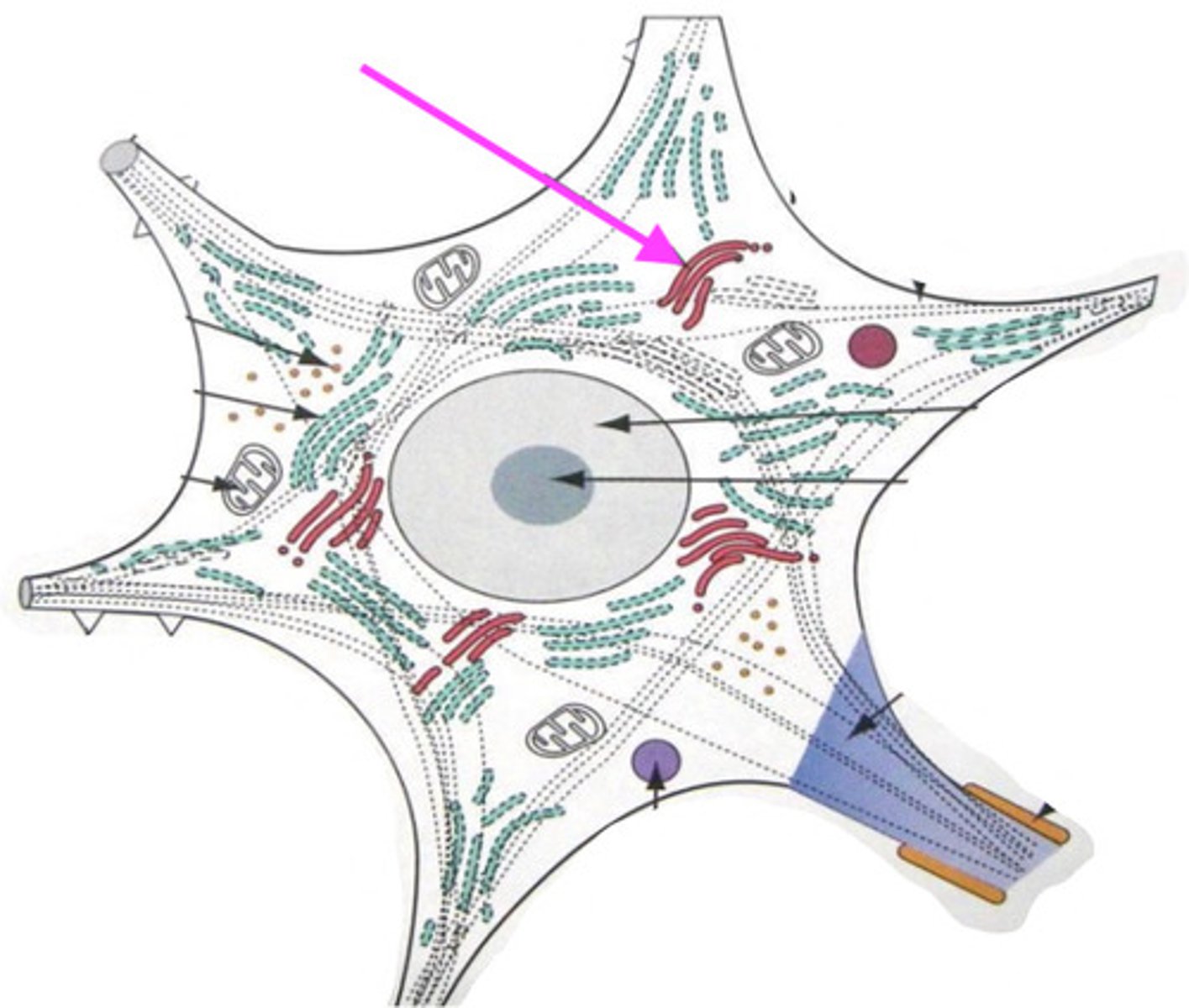
soma (neural body)
what is this?
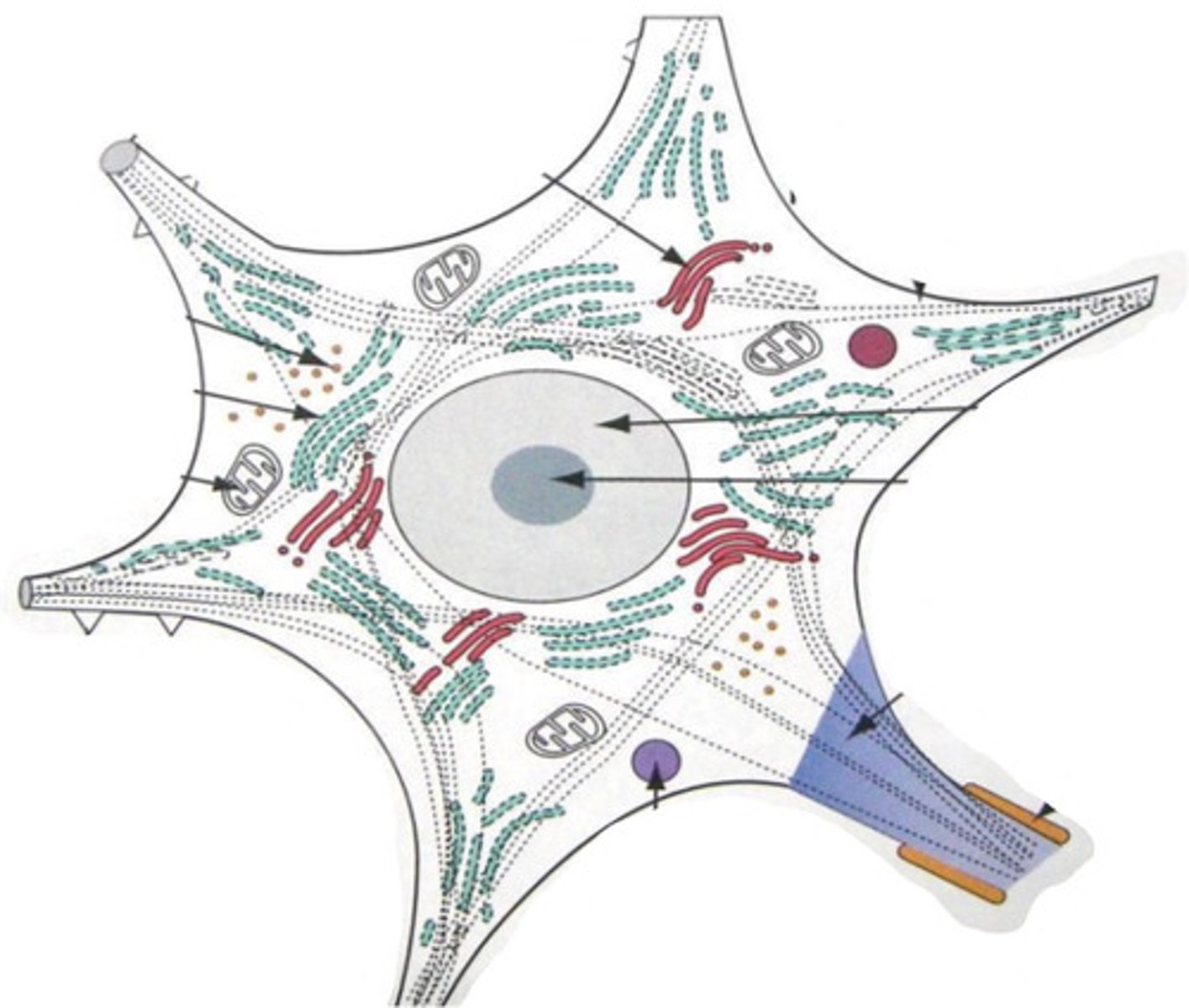
mitochondria
what is this organelle?

Nissl bodies
what is this organelle?
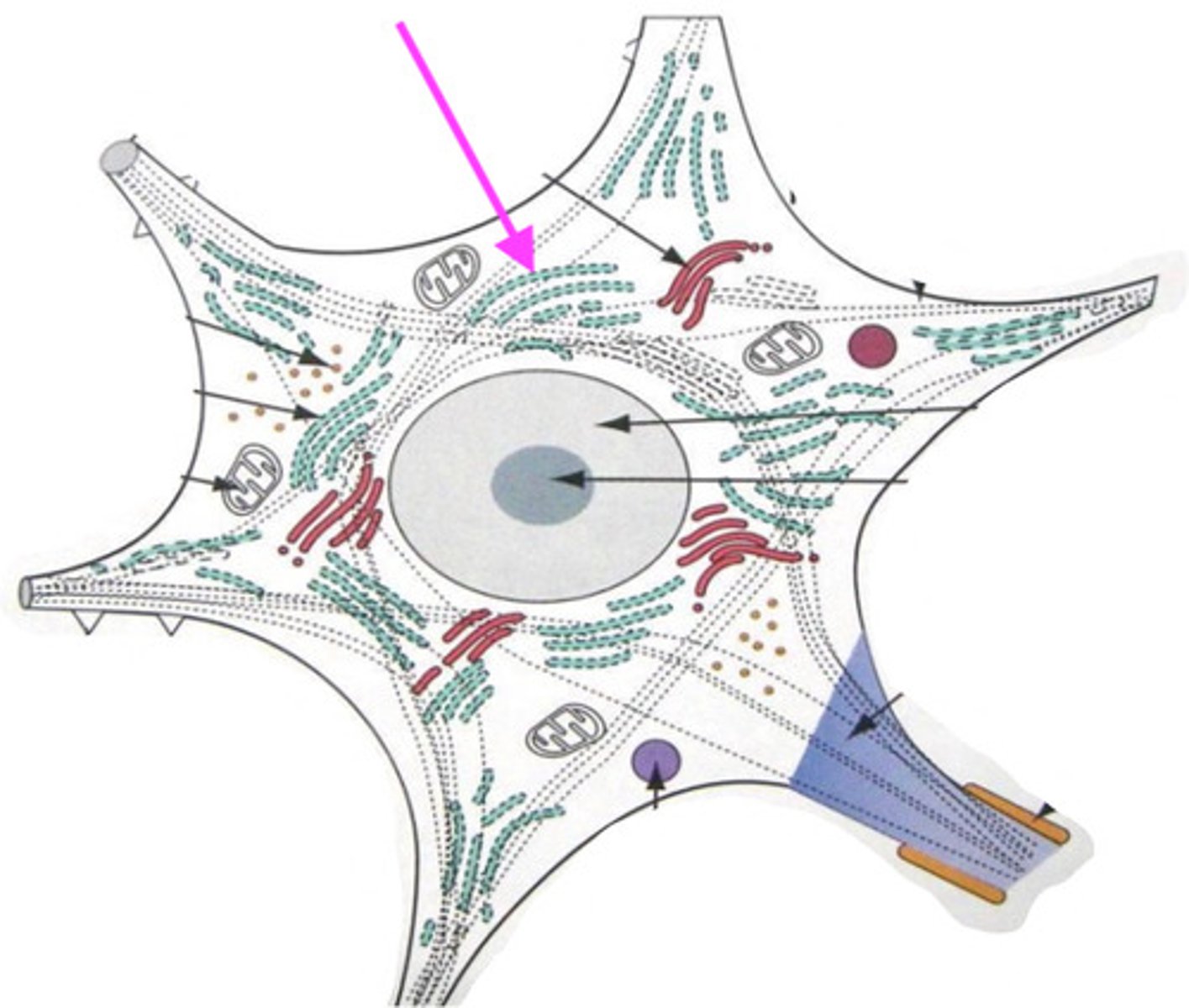
permits neuronal transport
what is the cytoskeleton of the soma for?
dendrites
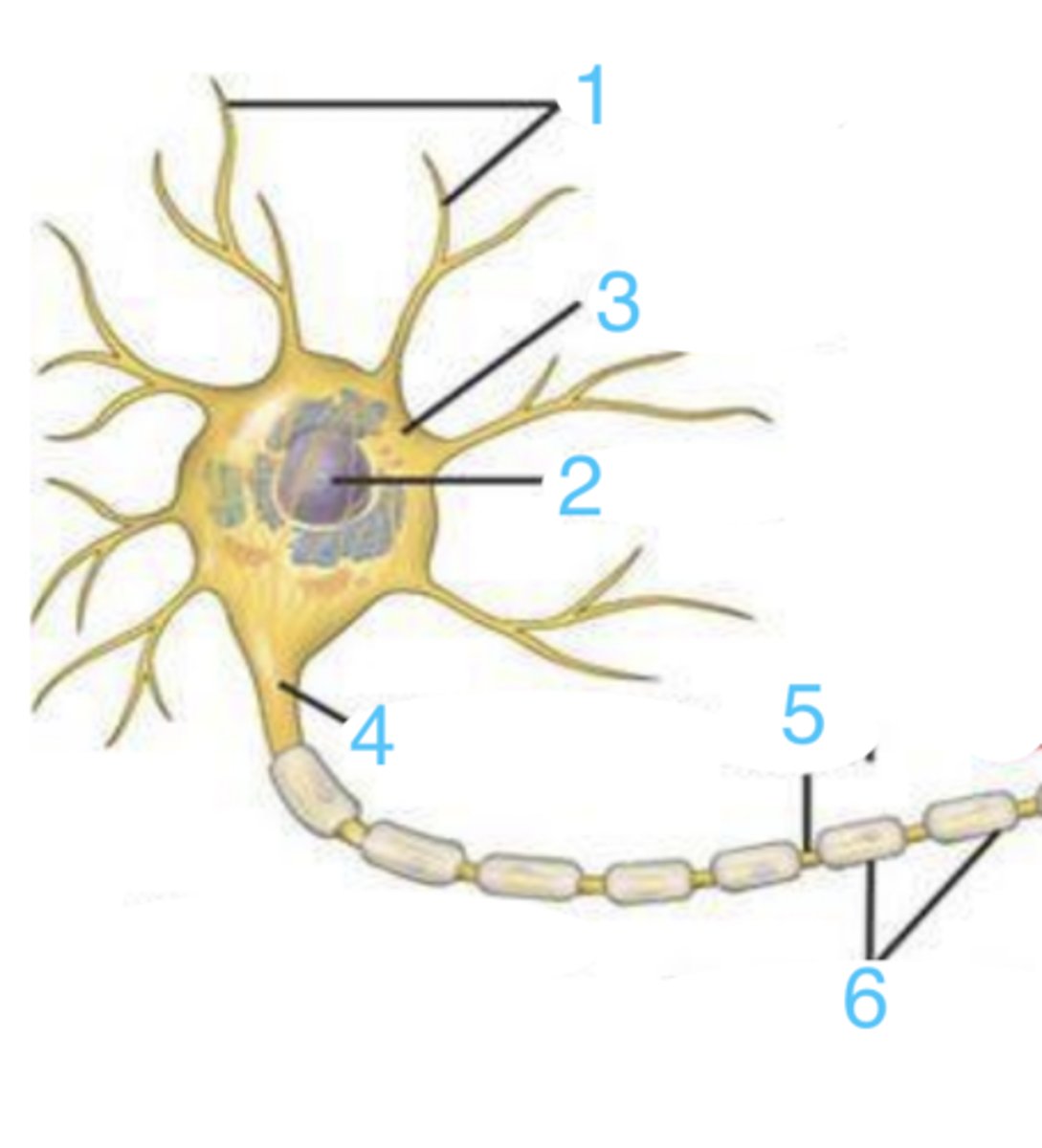
what part of the neuron is 1?
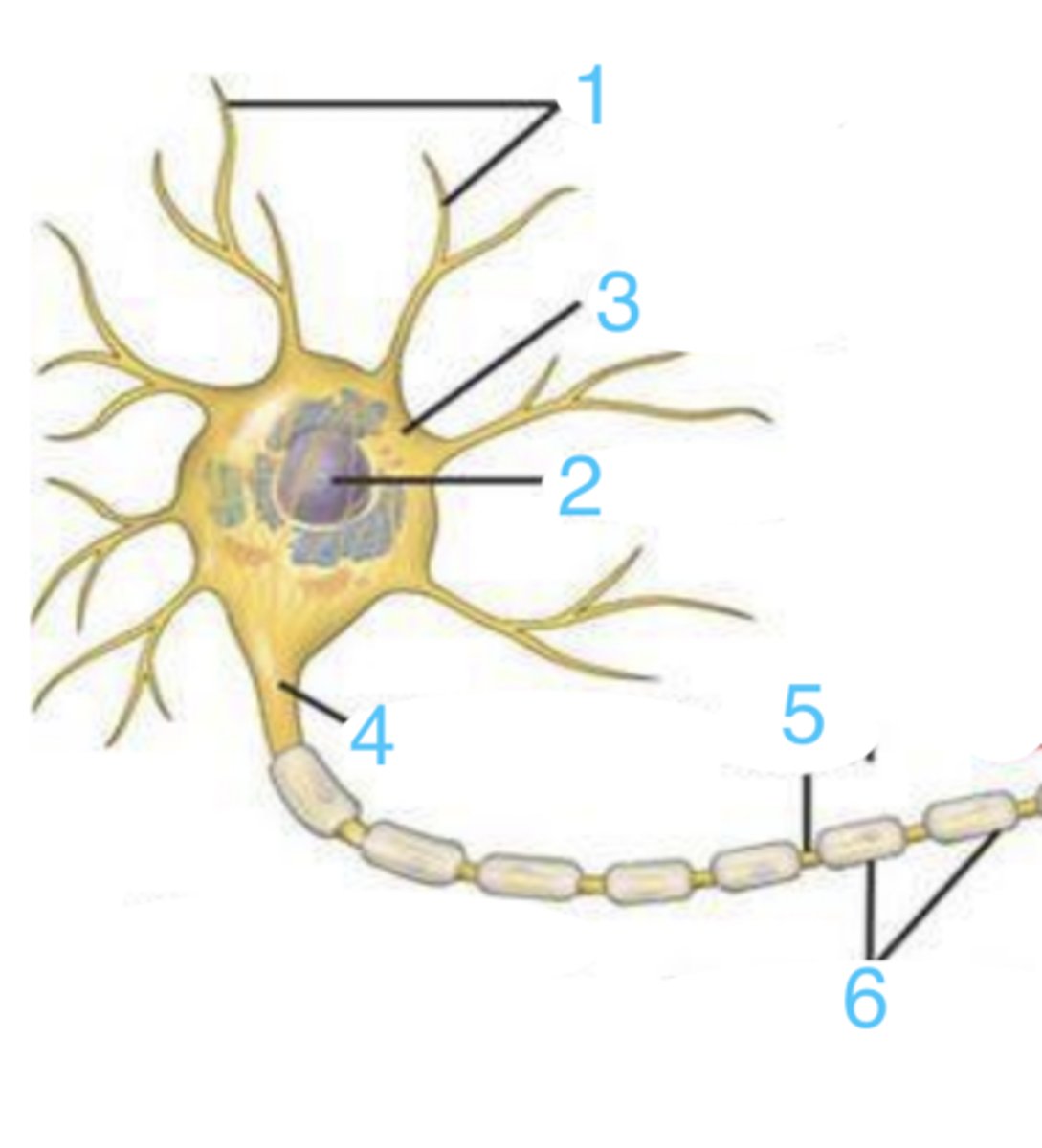
2
where is the nucleus?
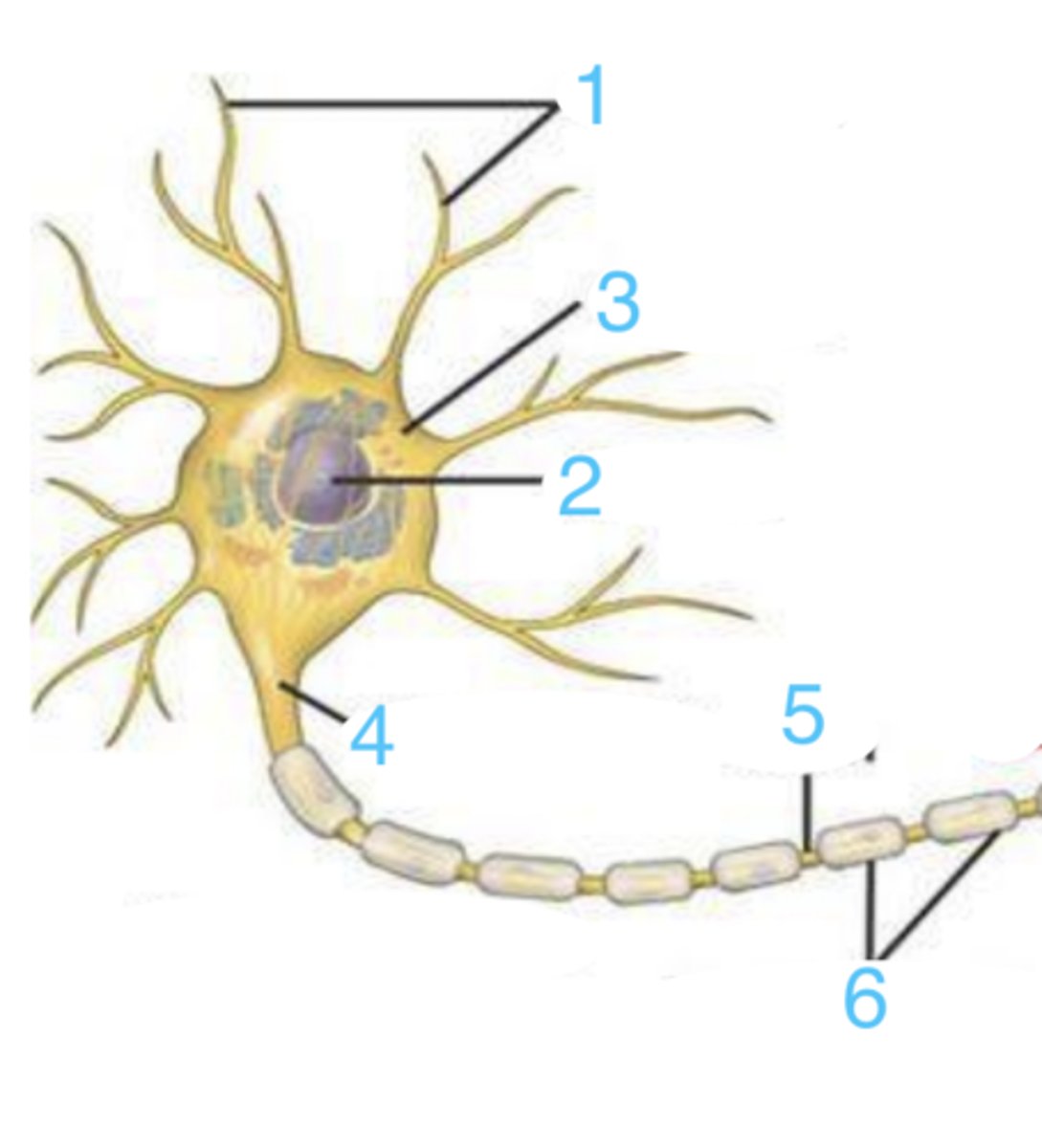
the neural body (soma)
what is 3?
6
where is the myelin sheath?
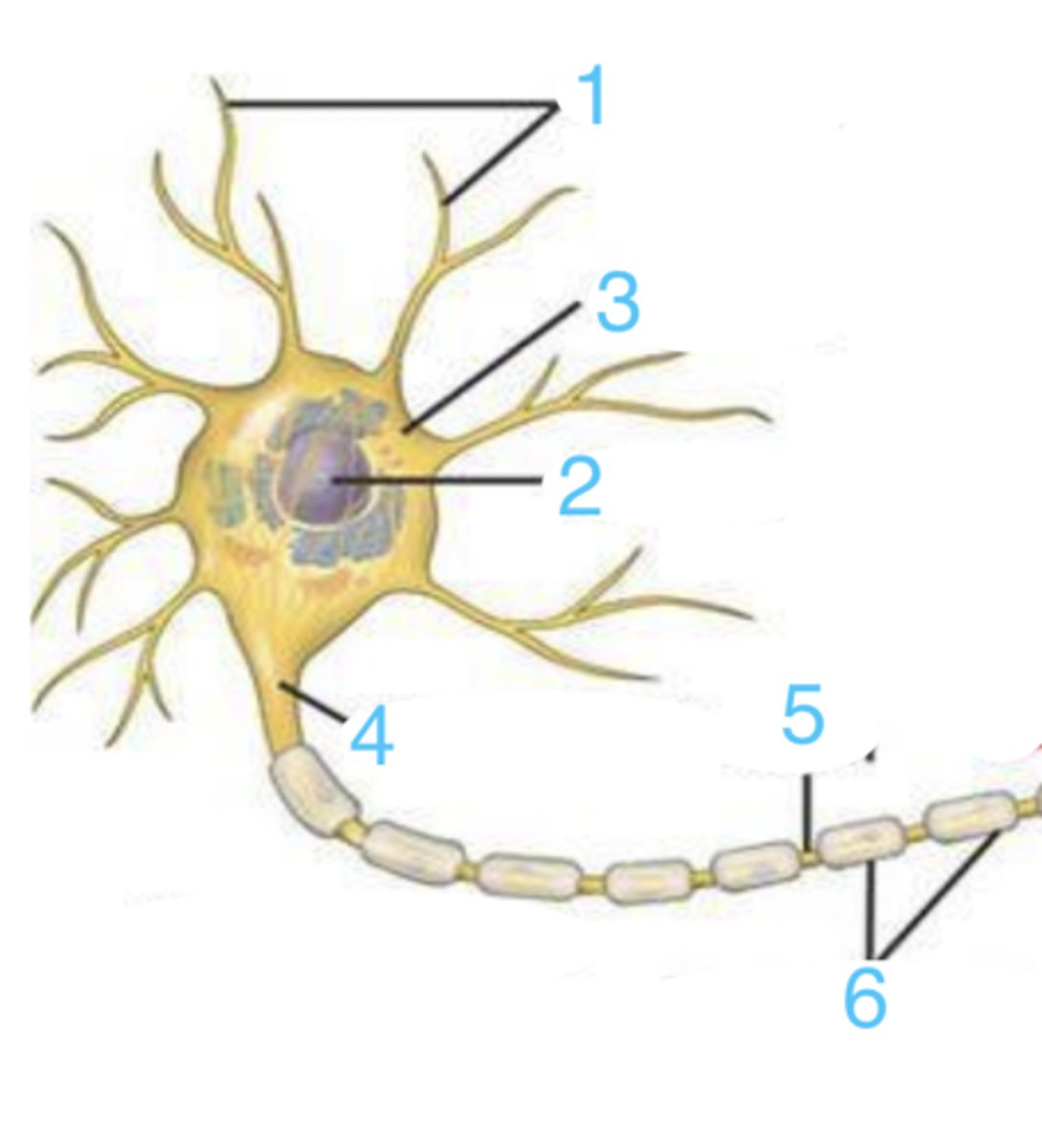
the axon
what does 5 point to?
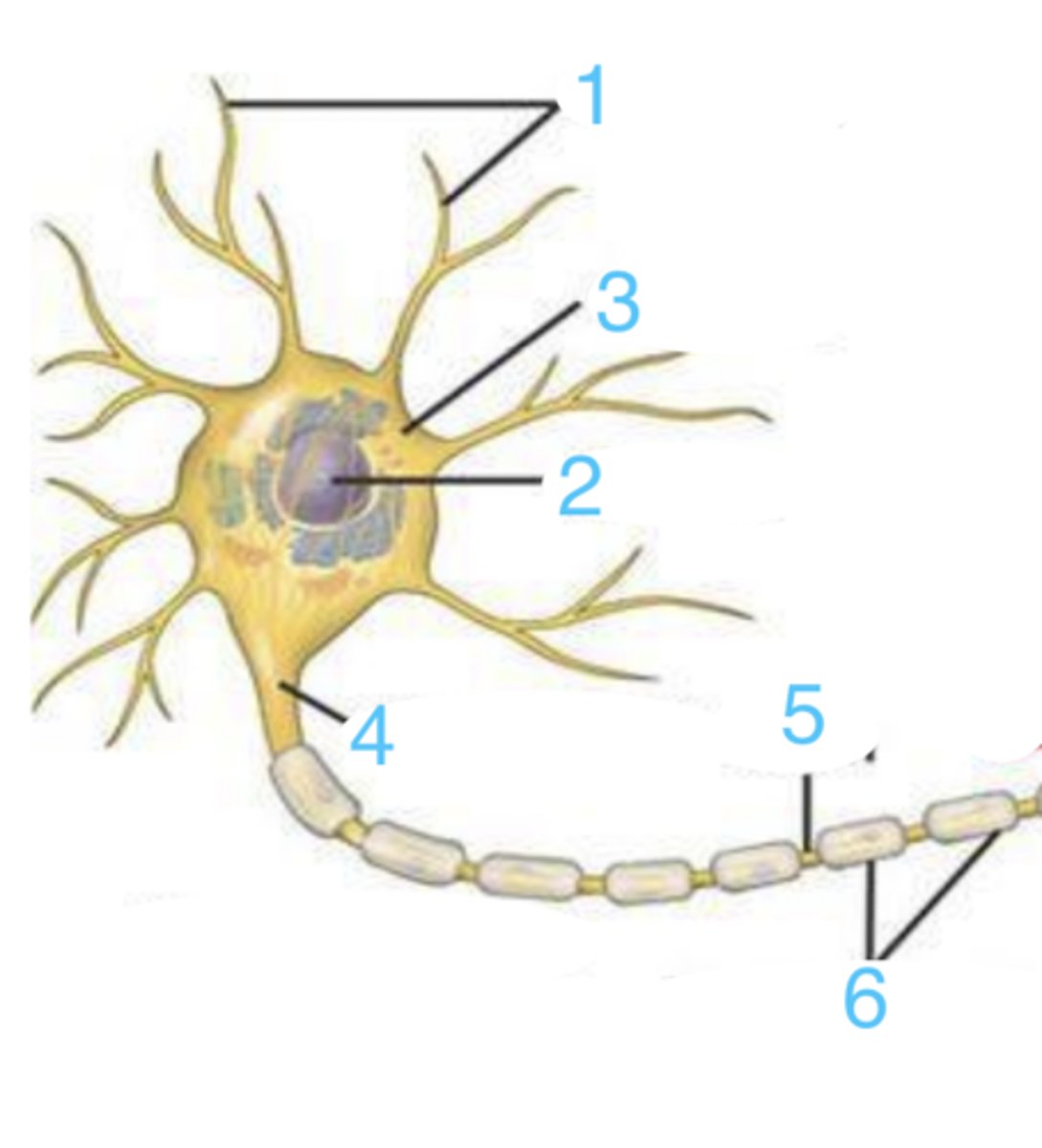
neural bodies
what are these?
to detect a stimulus
what is the function of dendrites?
short, branched, many, thicker when closer to soma
what is the appearance of dendrites?
spine
what is the last point of the dendrite called?
dendrite spine
what is the specific point on the dendrite that is responsible for detecting the stimulus?
1
how many axons per neuron?
to transmit the signal
what is the function of the axon?
axon
what part of the neuron has the function of transmitting the signal?
dendrites
what part of the neuron has the function of detecting the stimulus?
the soma
what part of the neuron has the function of containing the organelles?
dendrites
what are all the branches called?

no
does the thickness of the axon vary?
unipolar
bipolar
pseudounipolar
multipolar
what are the four types of neurons?
unipolar
which type of neuron has no dendrites?
unipolar
which neuron is abundant during the embryonic stage?
olfactory epithelium, retina, vestibular and cochlear ganglion
where are bipolar neurons found?
2 branches, one for transmitting the signal and one for receiving the signal
describe a pseudounipolar neuron
multipolar
which type of neuron is the most abundant?
one axon and many dendrites
describe a multipolar neuron
unipolar
what type of neuron is this?
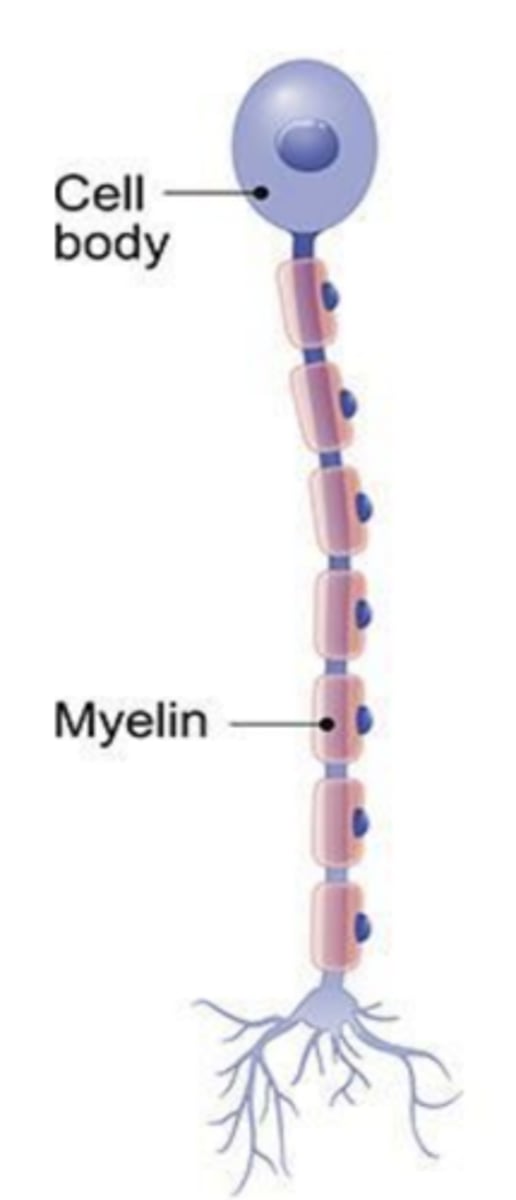
bipolar
what type of neuron is this?
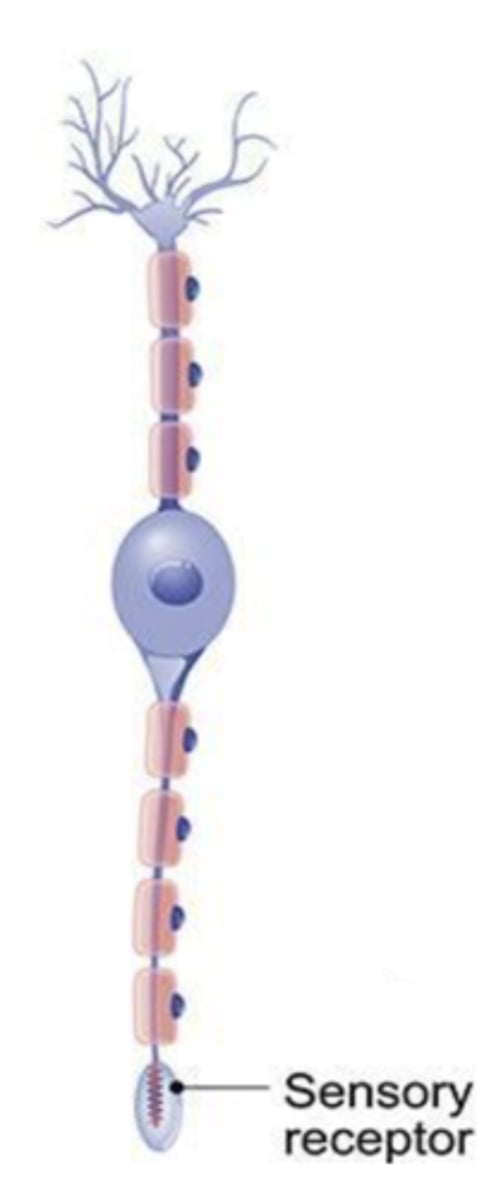
pseudounipolar
what type of neuron is this?
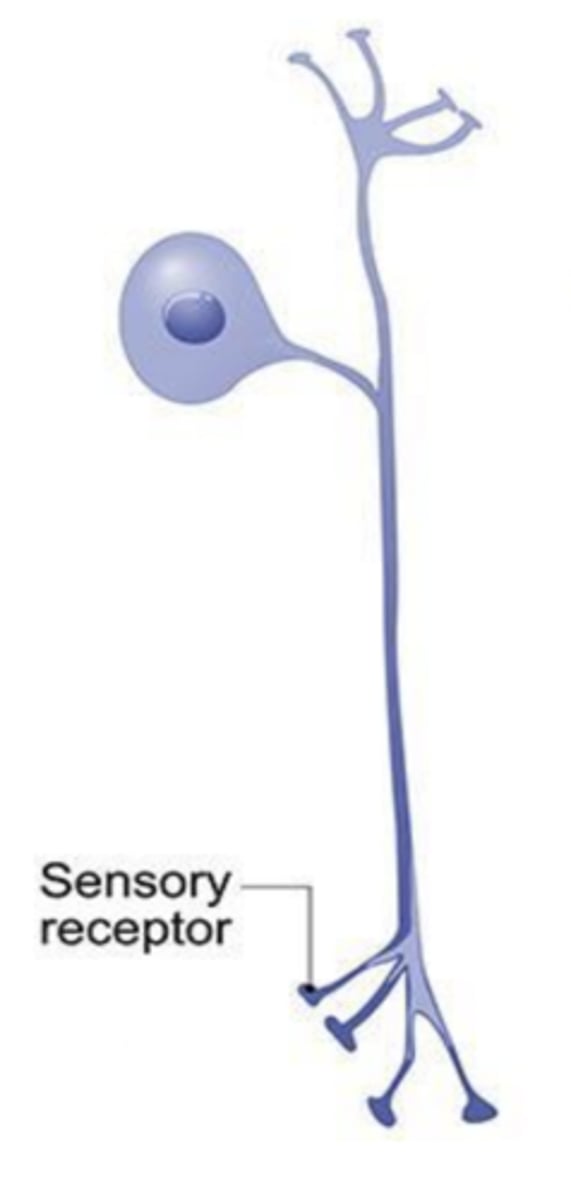
multipolar
what type of neuron is this?
pseudounipolar
which type of neuron would be found in cranial nerve ganglia?
electrical signals
glia cannot generate _____
glia
90% of the cells in the nervous system are ___
glia
which are more abundant, neurons or glia?
astrocytes
oligodendrocytes
microglia
ependymal cells
which are the 4 types of glia that you would find in the central nervous system?
schwann cells
satellite cells
what are the 2 types of glia found in the peripheral nervous system?
PNS
is a schwann cell in the PNS or CNS?
PNS
is a satellite cell in the PNS or CNS?
CNS
is a ependymal cell in the PNS or CNS?
CNS
is a oligodendrocyte in the PNS or CNS?
CNS
is an astrocyte in the PNS or CNS?
CNS
are microglia in the PNS or CNS?
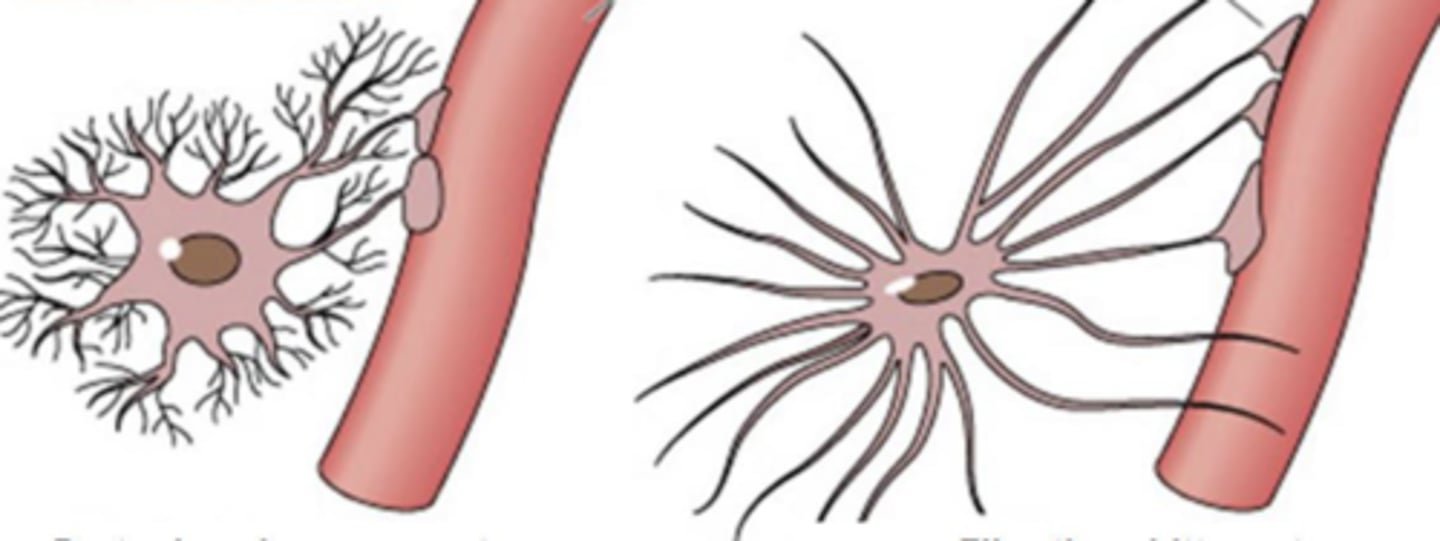
a protoplasmic astrocyte
when an astrocyte is located in the grey matter, is is called...
fibrotic
an astrocyte in the white matter is ...
pedicel
if you locate an astrocyte in the blood brain barrier, it is a ____
IHC staining for GFAPs (glial fibrillary acidic protein)
what staining is used to locate astrocytes?
glycogen
astrocytes store___
astrocytes
what types of cells close injuries in the CNS
transport of nutrients
ion uptake and metabolic waste
glycogen storage
injury closing
blood brain barrier
what are the roles of astrocytes in the CNS?
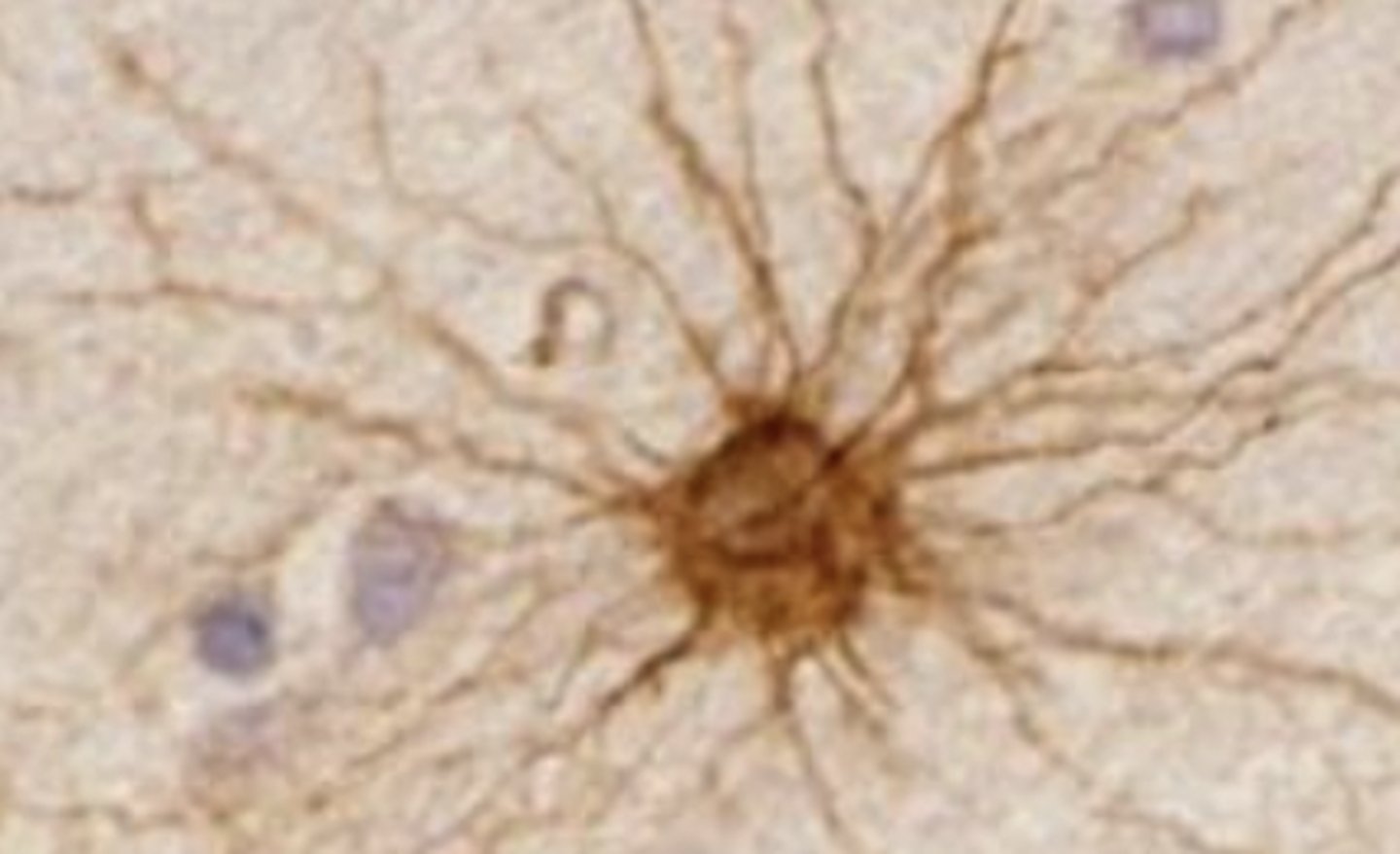
astrocyte
what is this cell in the CNS?
right
which is fibrotic and therefore located in the white matter? left or right?
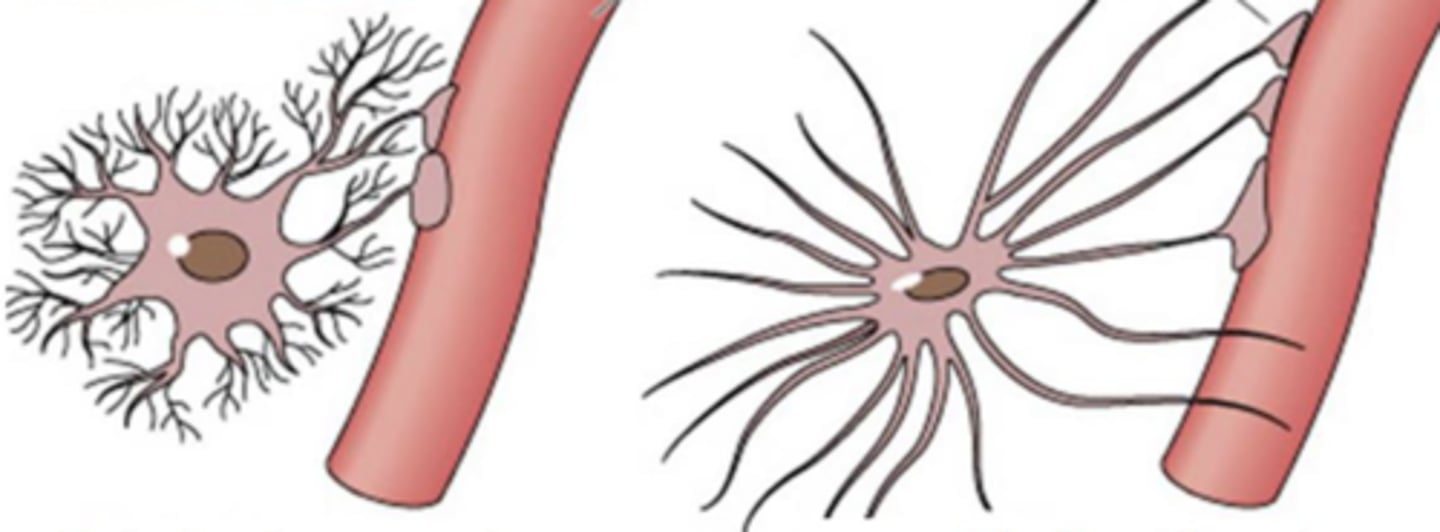
left
which is protoplasmic and therefore located in the grey matter? left or right?
astrocytes
what are the star-like cells?
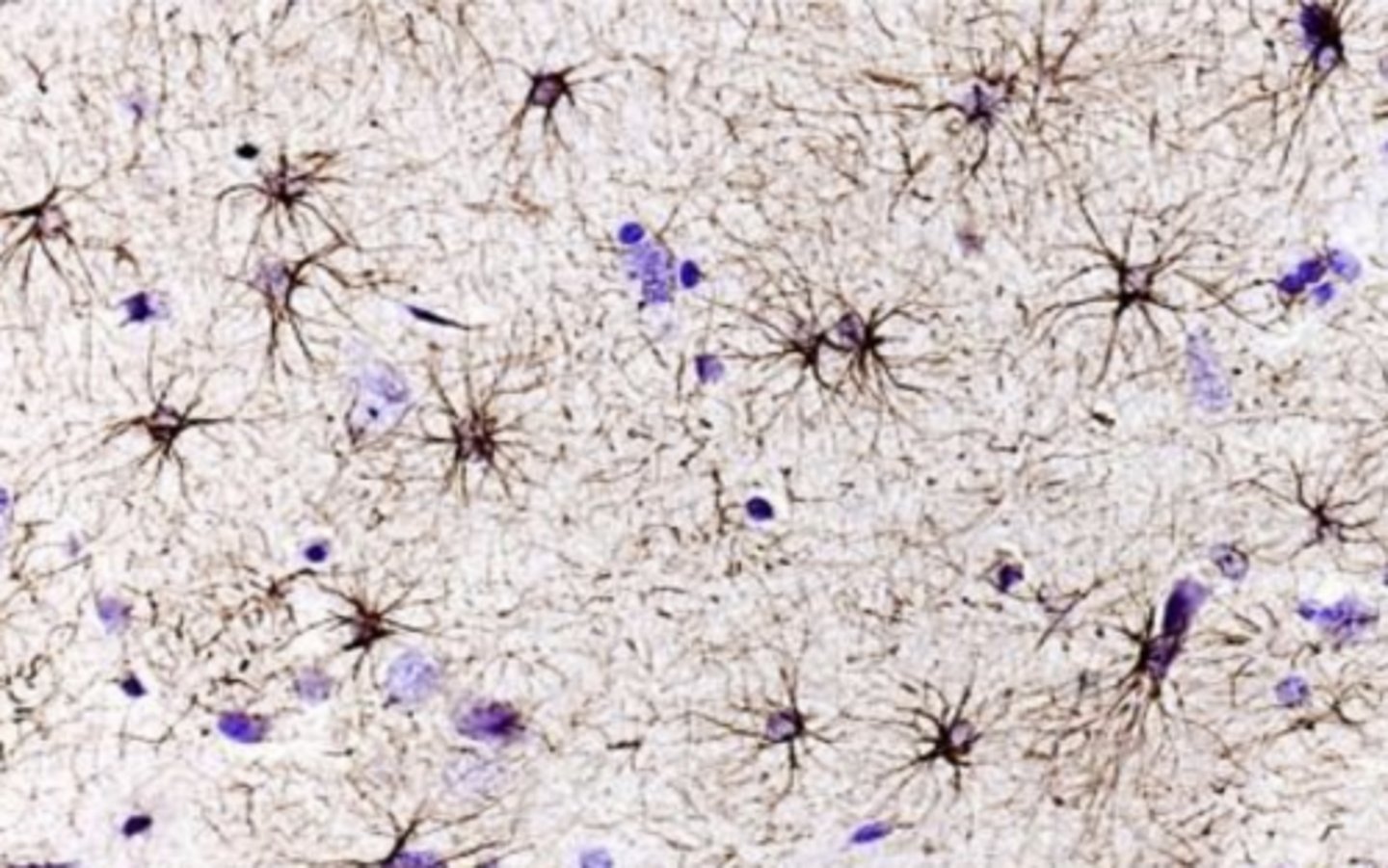
IHC staining for GFAPs (glial fibrillary acidic protein)
what staining was used in order to see the astrocytes?
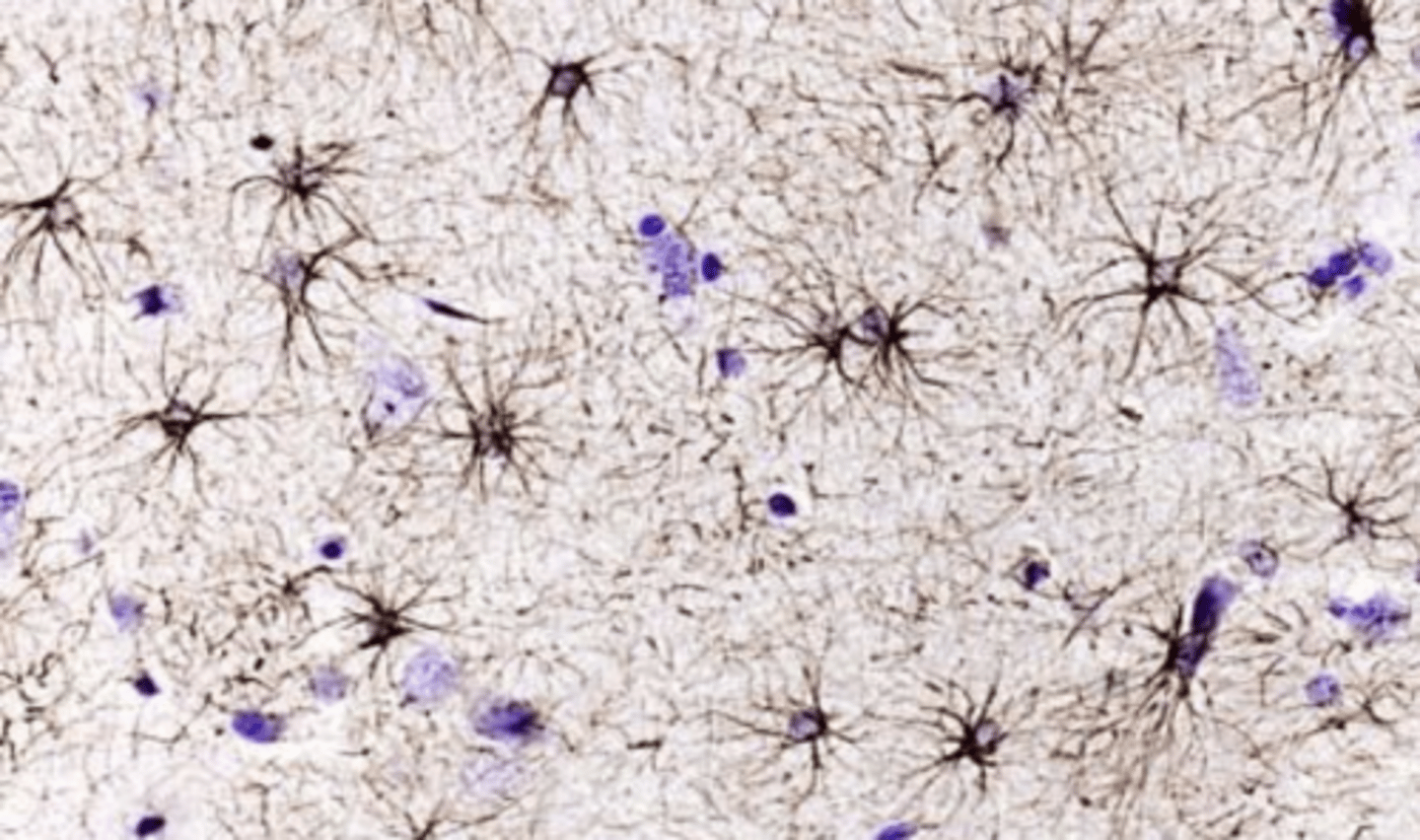
oligodendrocytes
which is the most numerous glial cell in the CNS?
compact
how is the nucleus of an oligodendrocyte?
basophilic
are oligodendrocytes basophilic or eosinophilic?
infrafascicular
satellites
what are the two types of oligodendrocytes?
oligodendrocytes
what are all the purple dots?
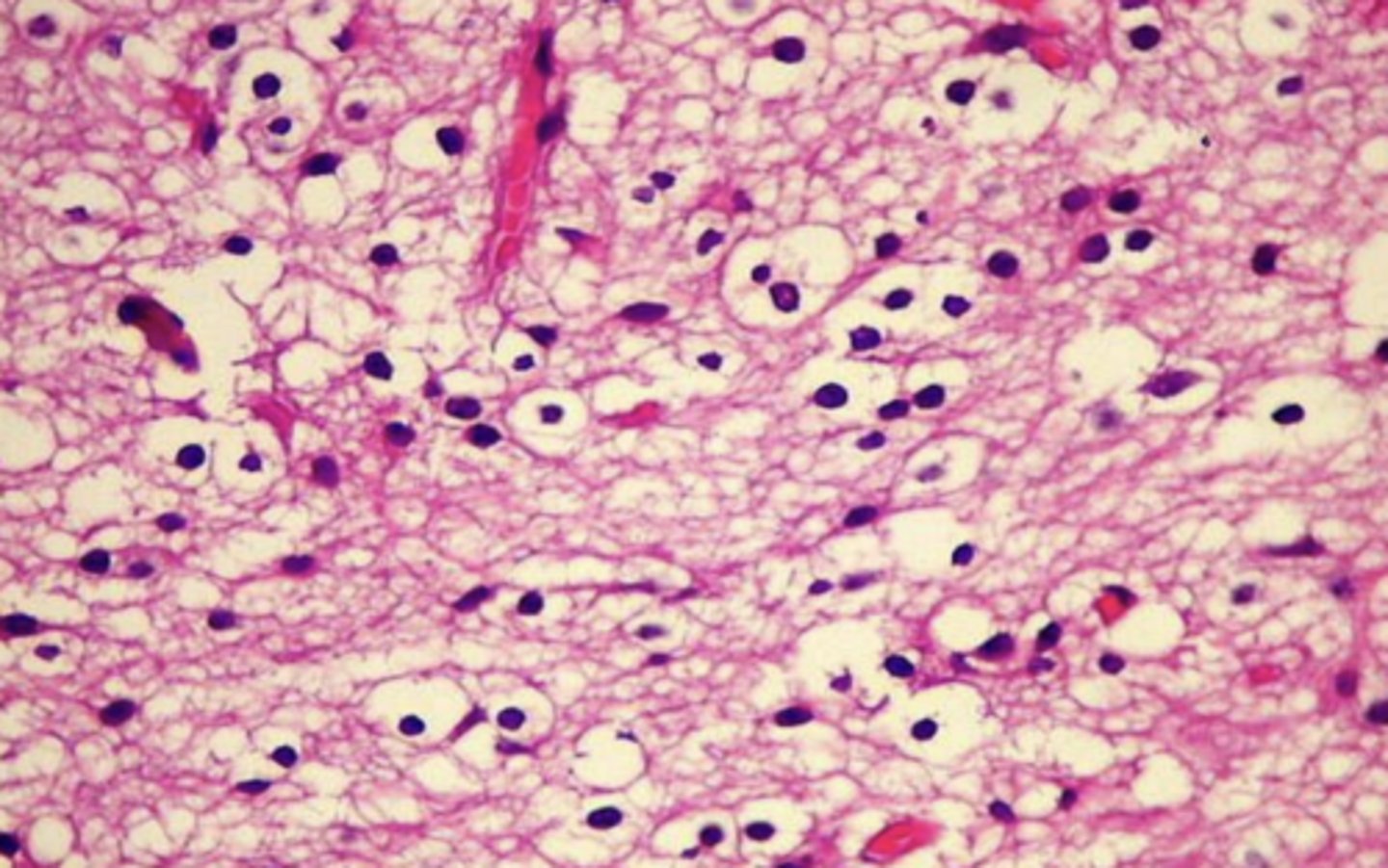
70
____% of glial cells are oligodendrocytes?
mesoderm
microglia originate from which embryonic structure?
fixed
microglia are _____ macrophages
both grey and white
which matter can you find microglia in?
to clean by engulfing waste
what is the function of microglia?
IHC stain
what is the only way to distinguish between microglia and oligodendrocytes?
in the center of the spinal cord
where are ependymal cells located within the CNS?
cuboidal/columnar
what is the shape of ependymal cells
ependymal cells
what glial cells have the function of controlling the passage of substances from the CNS?
since you cannot observe much cytoplasm in the cell, they are microglia
how can you tell if these are oligodendrocytes or microglia?
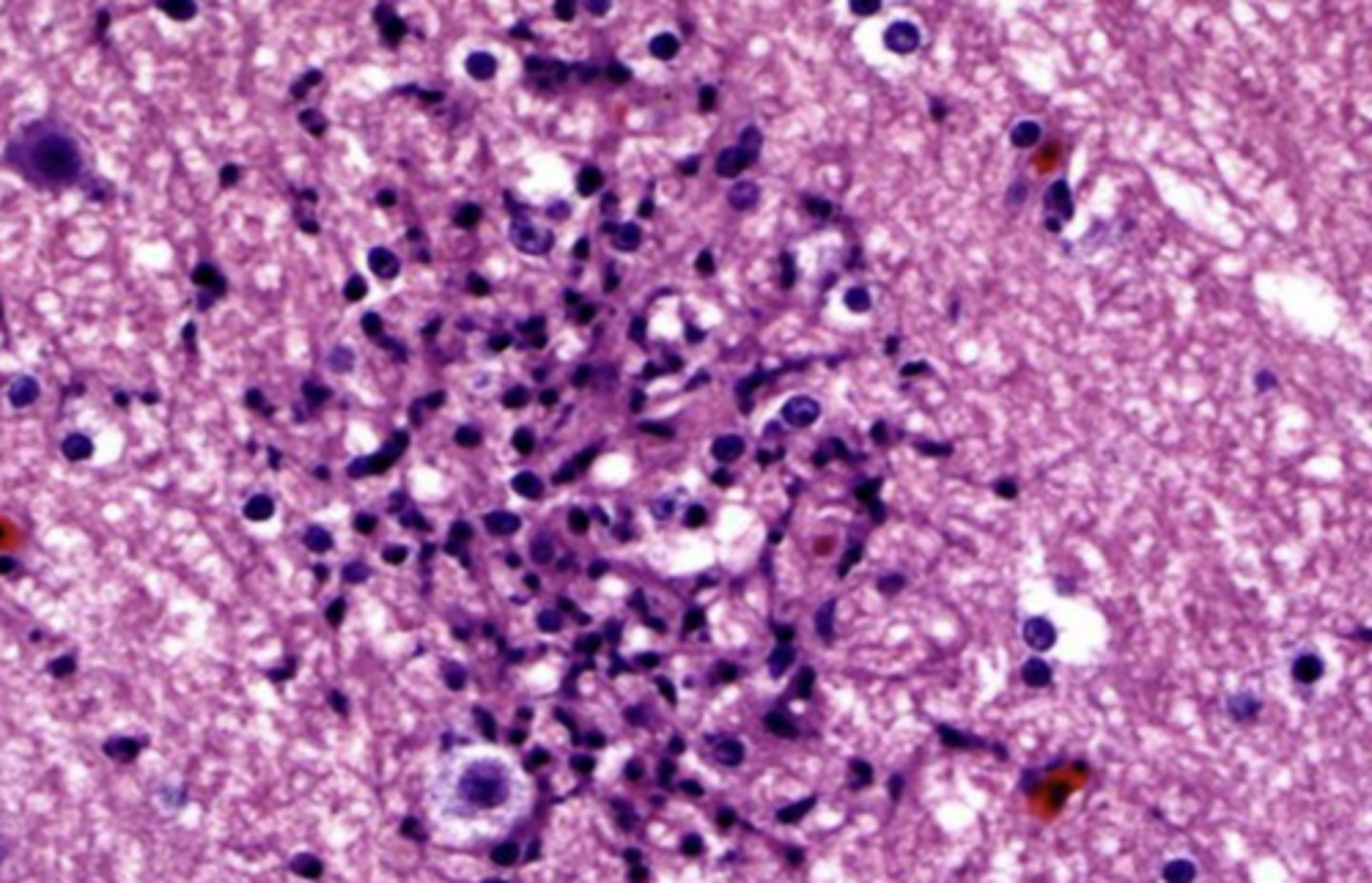
ependymal cells
what are these cells surrounding the central spinal cord?
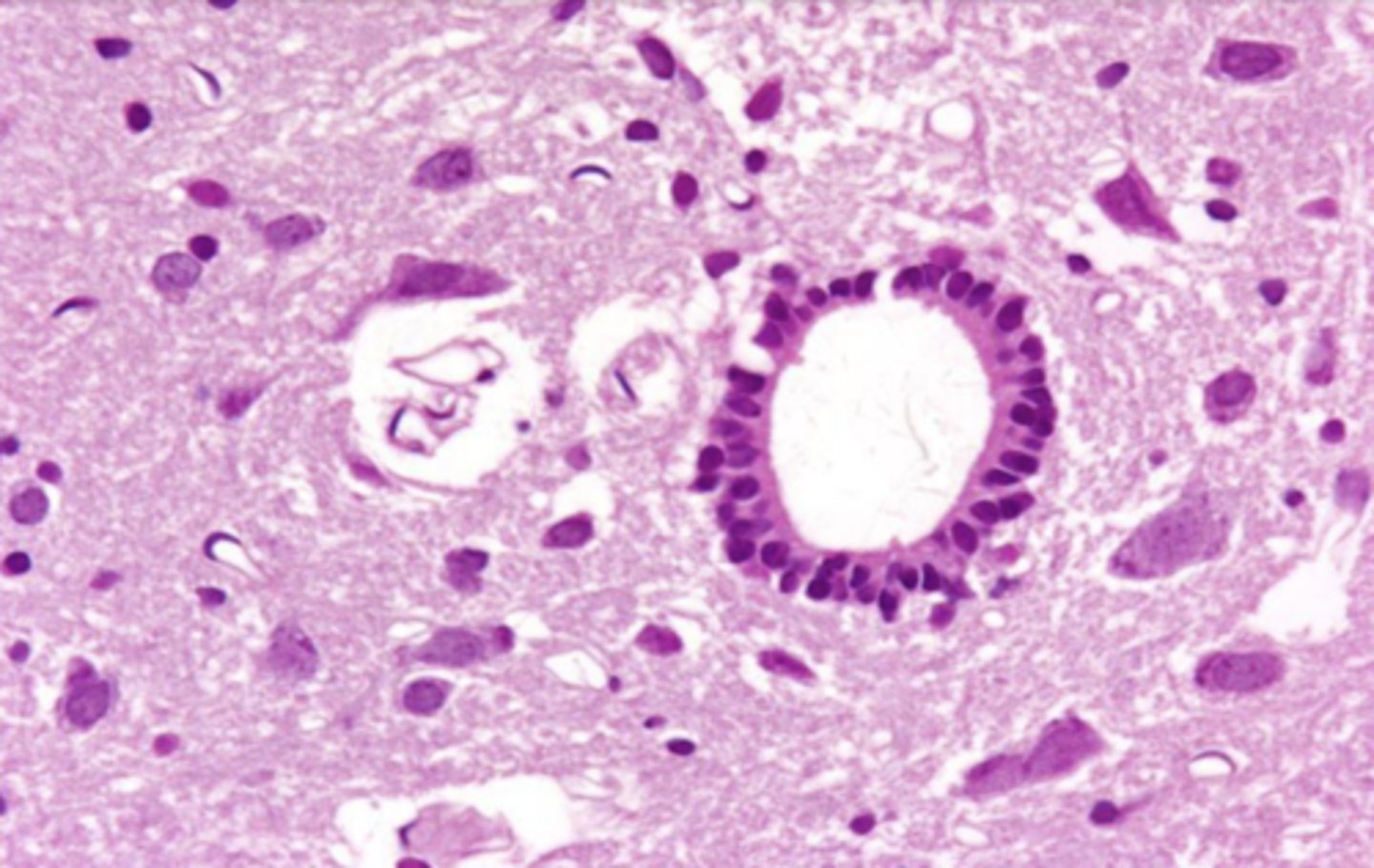
ependymal cells, neurons, olygodendrocytes
what cells can you see in the CNS with an HE stain?
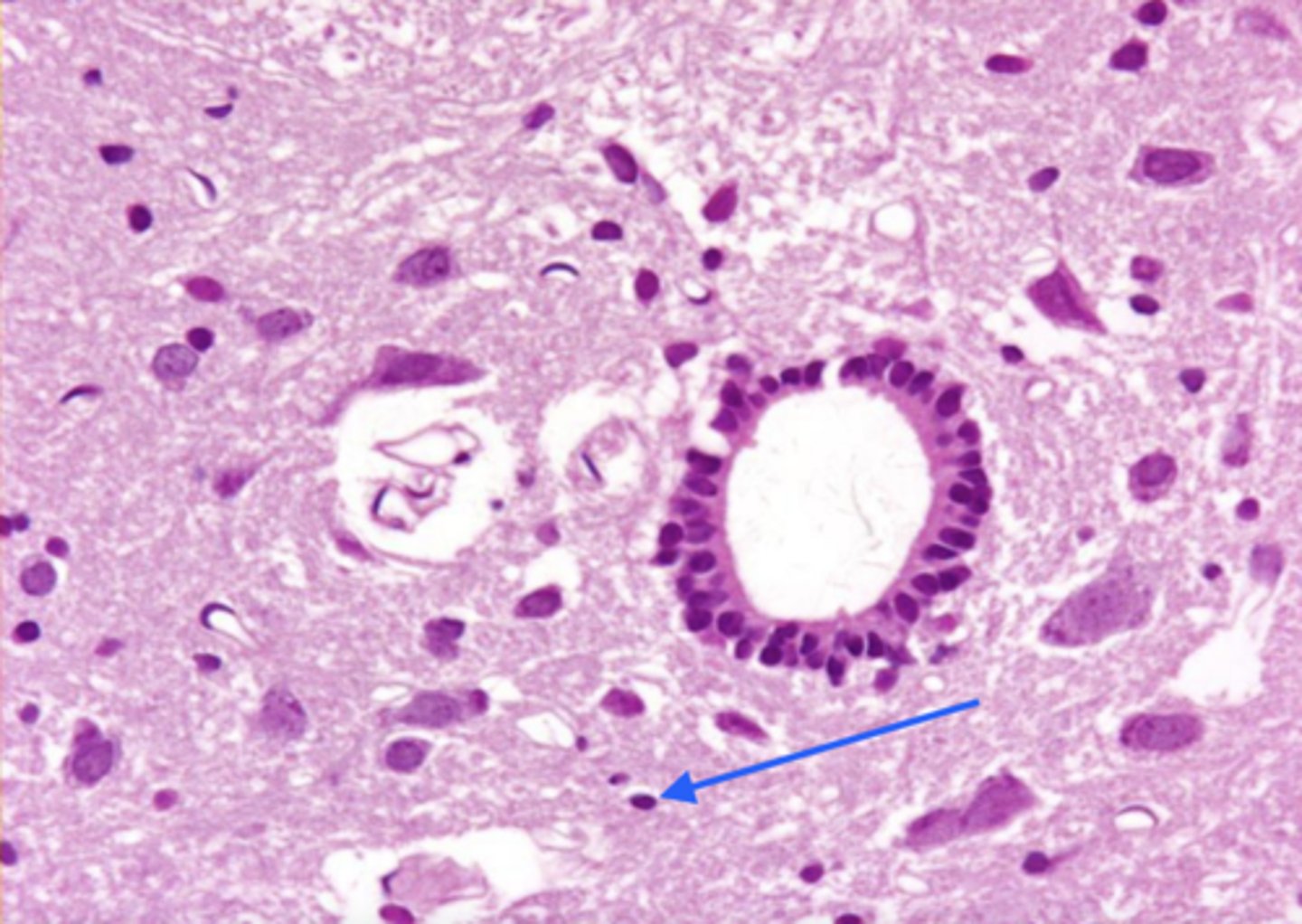
oligodendrocyte
what is this cell?
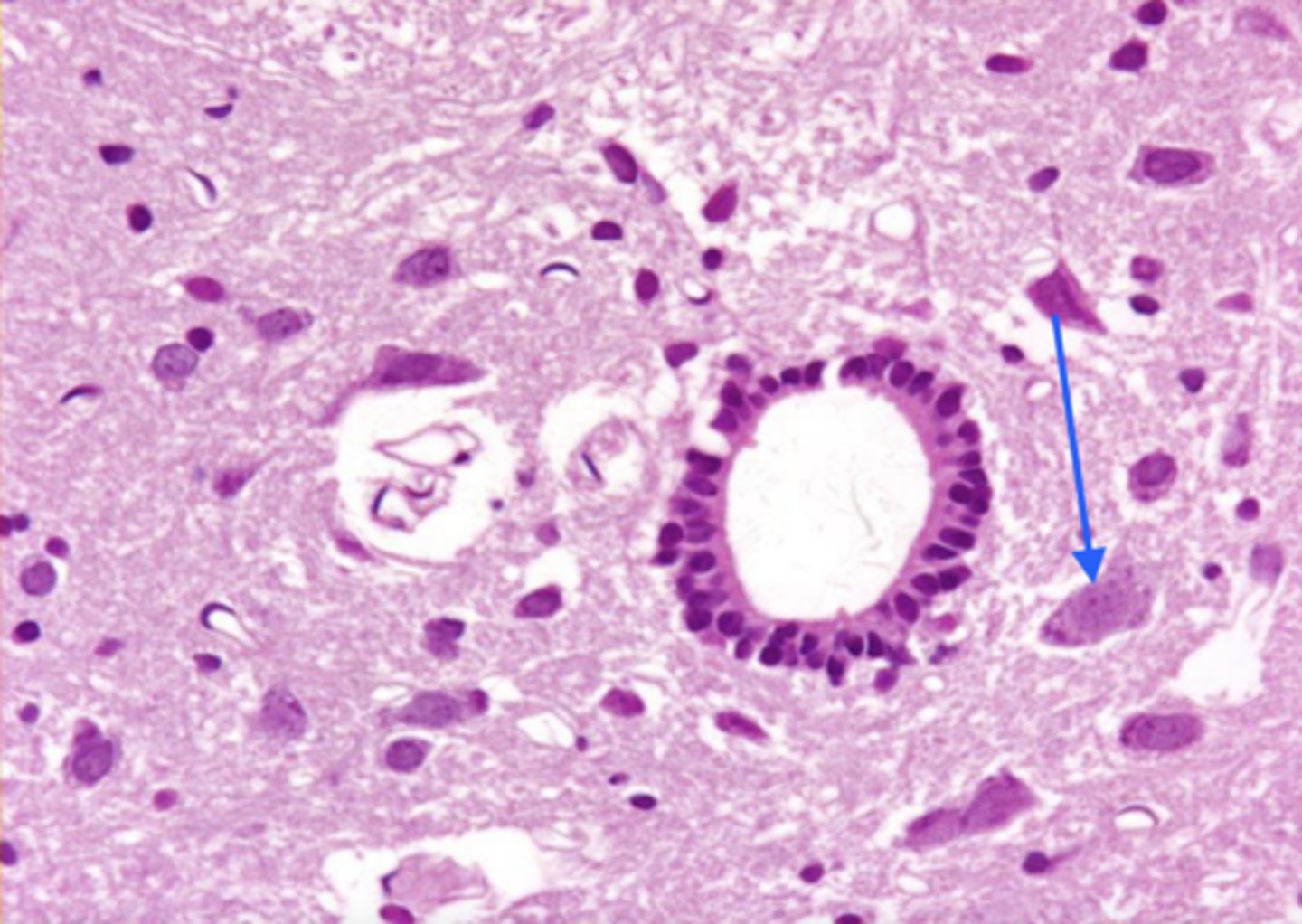
neuron
what is this cell?
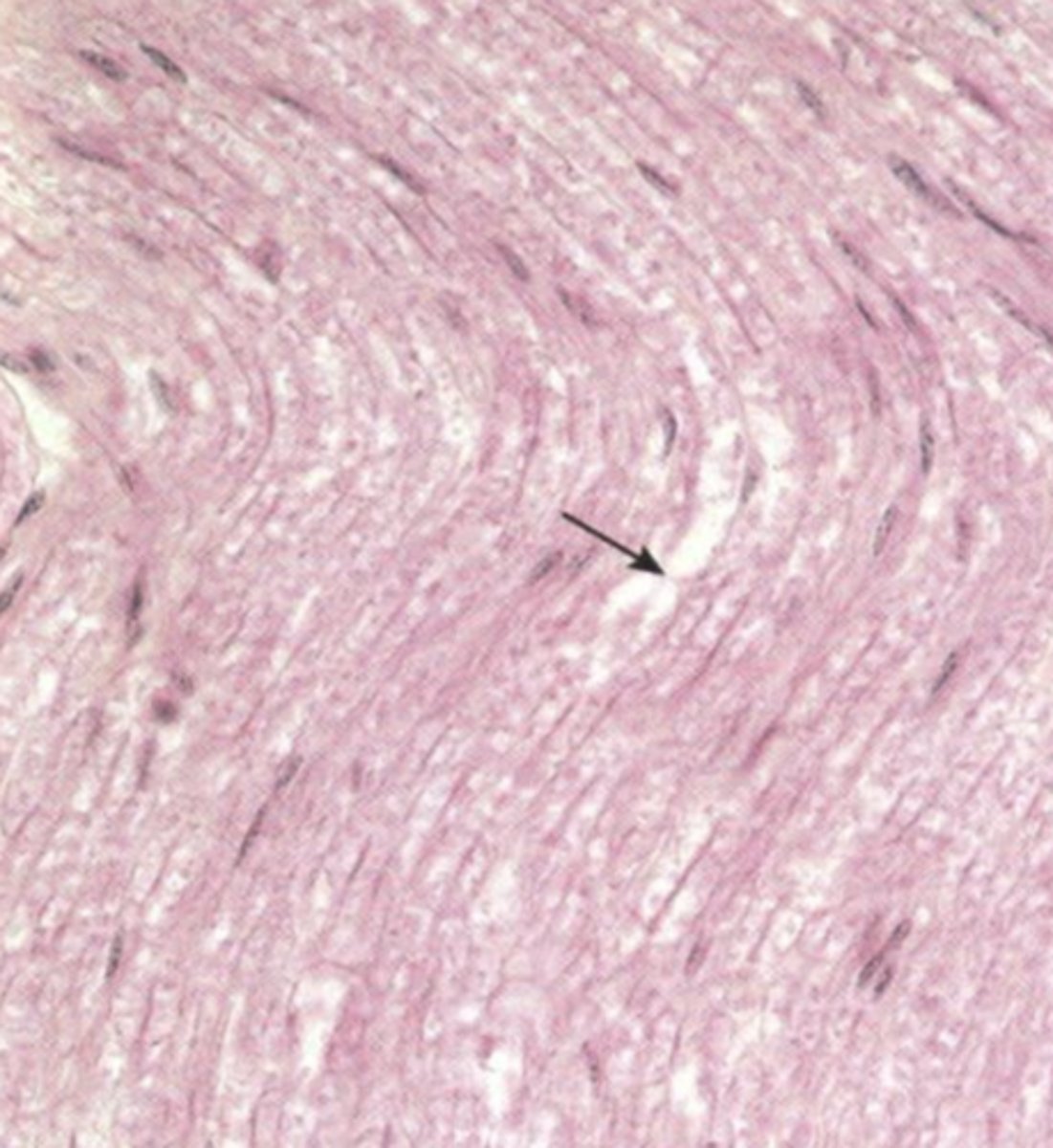
flat
describe the shape of schwann cells
no, very few
do schwann cells have a lot of organelles?
wrap the axon
what is the purpose of schwann cells in the PNS?
surrounding neuronal bodies in the PNS
where can you find a satellite cell in the PNS?
schwann cell
if this is a peripheral nerve, what is this flat cell?
myelinated or unmylenated
what are the two types of schwann cells?
myelinated
which, myelinated or unmyelinated, produces a faster conduction?
brain (including the cerebellum) and spinal chord
what two structures are part of the CNS?
external
where is grey matter located in the brain?