Biochem Lec 16- Fatty Acids and Lipids
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
What are fatty acids (what do they make up)?
Fatty acids are the building block of fuel and structural (membrane) lipids
Fatty acids are amphipathic. What does this mean regarding their structure?
They contain a polar headgroup (carboxyl) and a nonpolar tail (hydrocarbon)
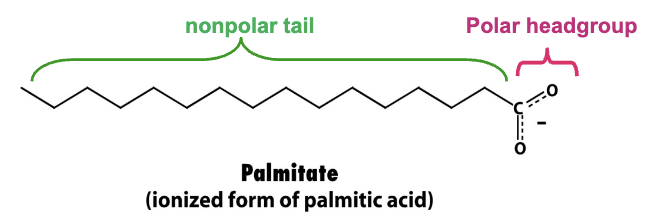
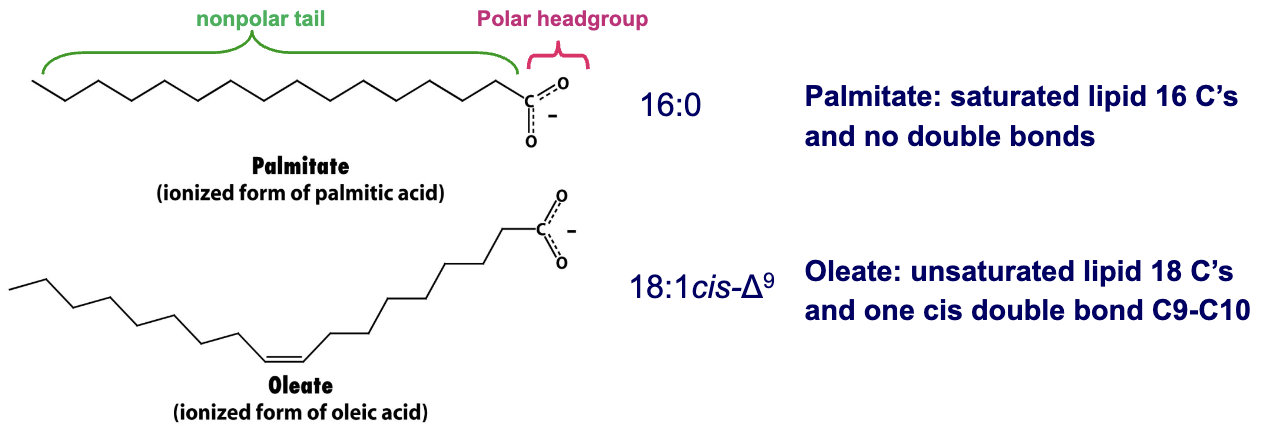
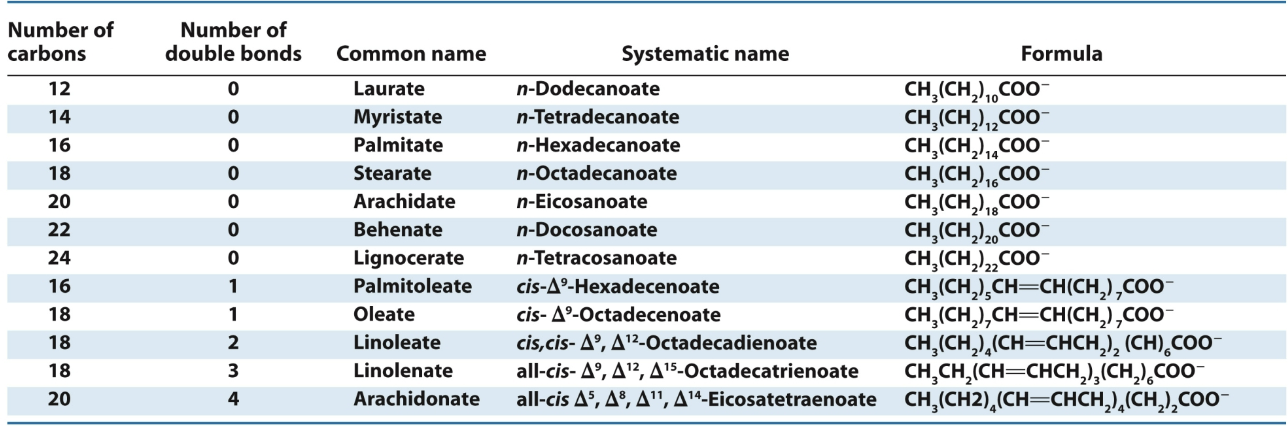
What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated fatty acids? Give an example of a saturated and unsaturated fatty acid.
Saturated- Saturated fatty acids have a carbon chain where every carbon atom is bonded to the maximum number of hydrogen atoms→ no C=C bonds
Unsaturated- Unsaturated fatty acids have one or more double bonds between carbon atoms
Saturated→ Palmitate
Unsaturated→ Oleate
How are fatty acid carbon atoms usually numbered?
Fatty acid carbon atoms are usually numbered beginning with the carboxyl terminal carbon atom
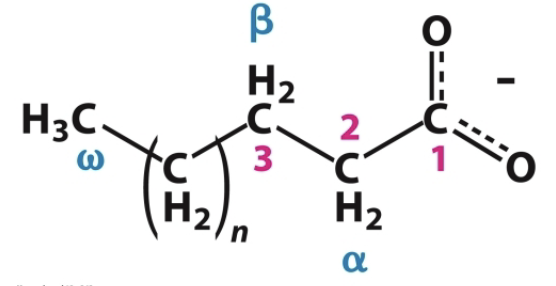
What are carbon atoms 2 and 3 referred to as?
Carbon 2→ α
Carbon 3→ β
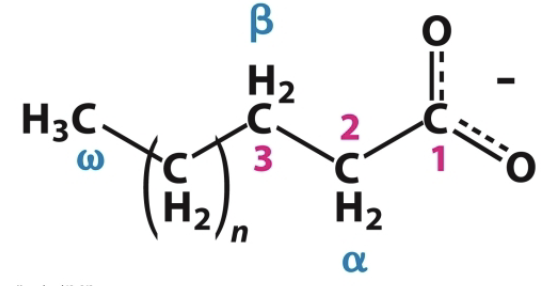
How else can fatty acids be numbered?
Fatty acids can also be numbered from the methyl carbon atom which is called the omega (ω) carbon.
What similar nomenclature can be applied to several fatty acids? Give an example.
A similar nomenclature of C# and unsaturation can be applied to several fatty acids
Ex→ Linoleate (essential fatty acid in the diet) is 18:2 all cis-Δ9 Δ12
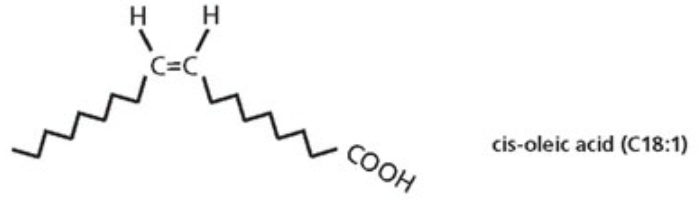
What orientation are double bonds typically found in naturally? What do they do?
Cis orientation→ induce the bending of the acyl chain
Industrial treatment induces an alternative form of the double bond called what? What is the common name for these?
Trans double bonds→ Trans fat is the common name for unsaturated fat with trans-isomer fatty acid(s).
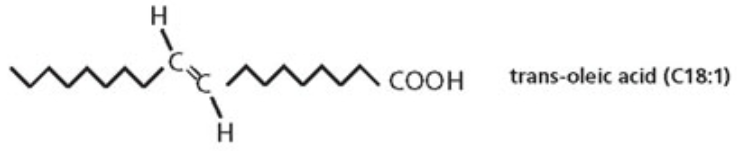
Why are trans fats often considered unhealthy?
Animals do not normally make trans fats. In humans, consumption of trans fats increases the risk of coronary heart disease, inflammation, etc because the human body cannot break down trans fats effectively.
In polyunsaturated fatty acids, how are the double bonds separated?
In polyunsaturated fatty acids, the double bonds are separated by at least one methylene group
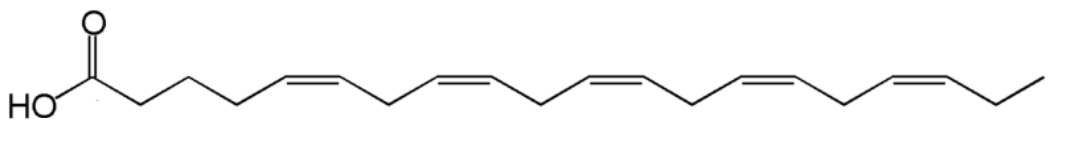
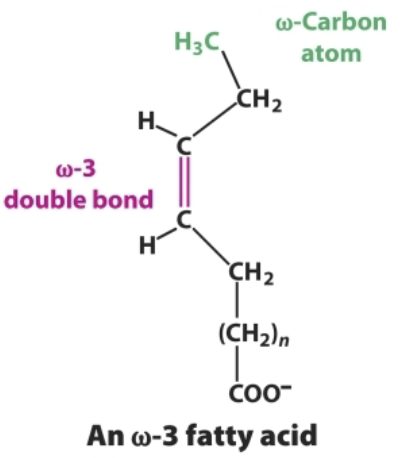
Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) is a fatty acid. How would you name this? Label the alpha and omega carbons.
20:5 all cis- Δ5,Δ8,Δ11,Δ14,Δ17
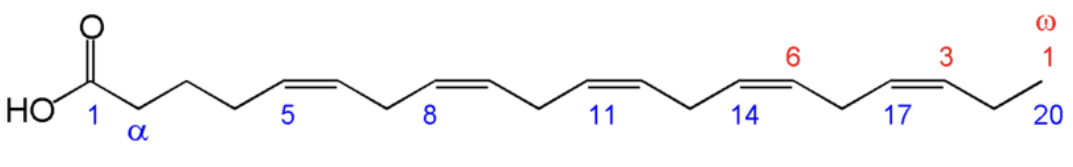
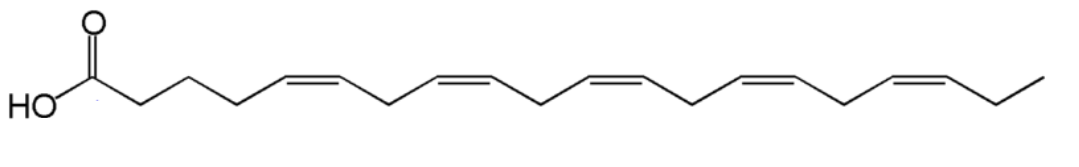
Another way of classify fatty acid is counting from the methyl (tail, or omega) end. What type of fatty acid is EPA based on this?
EPA is an omega-3 fatty acid
What 2 fatty acids are considered essential? Can humans produce them?
Omega-3 and omega-6 are essential fatty acids→ humans cannot produce them
In aqueous media, describe the behavior of the nonpolar tails of fatty acids. What do they form?
In aqueous media, nonpolar tails of fatty acids sequester away from water and form a “micelle”→ remember hydrophobicity and the hydrophobic effect
Membrane lipids are _______ of an _____ backbone and _____
Membrane lipids are amphipathic esters of an alcohol backbone and fatty acids.
What are the three common types of membrane lipids?
Phospholipids
Sphingolipids
Cholesterol
What do most common membranes use as the backbone alcohol?
Most common membrane lipids use glycerol as the backbone alcohol
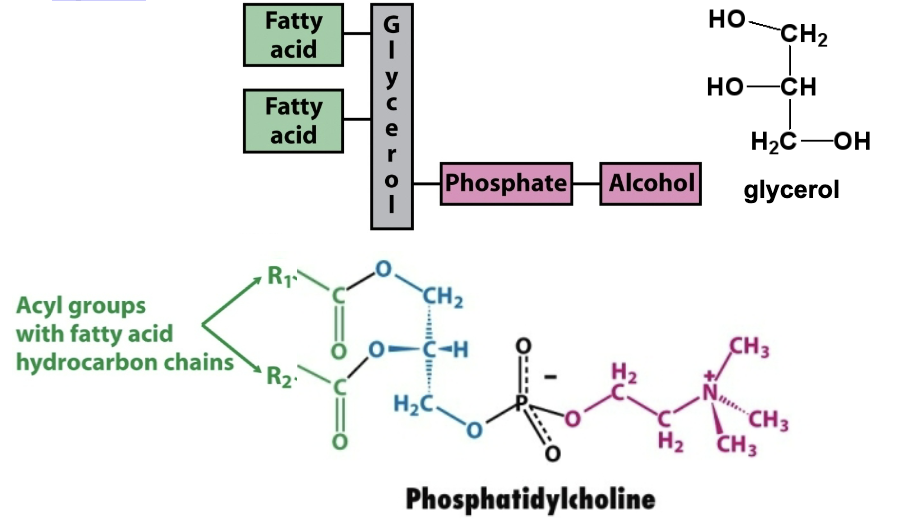
The structure of glycerophospholipids contain what? Give an example.
Glycerophospholipids contain two nonpolar fatty acid esters and a polar phosphate head group.
Ex→ phosphatidyl choline-one of the most common membrane lipids
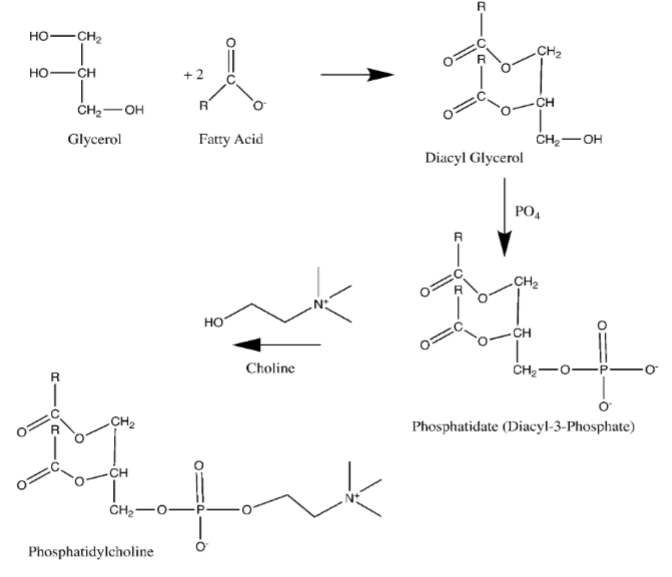
Describe the reaction that forms phosphatidylcholine.
Glycerol reacts with 2 fatty acids to form diacyl glycerol. Diacyl glycerol reacts with PO4 (phosphate) to form phosphatidate (Diacyl-3-Phosphate). Phosphatidate reacts with choline to form phosphatidylcholine.
What are 5 common examples of glycerophospholipids?
Phosphatidylserine
Phosphatidylcholine
Phosphatidylethanolamine
Phosphatidylinositol
Diphosphatidylglycerol (caridolipin)
SCIE 2G
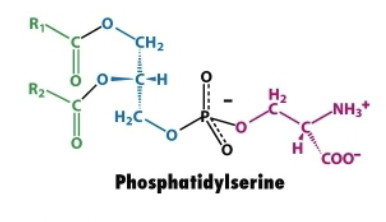
Describe the structure of phosphatidylserine.
Glycerol backbone
Two fatty acid chains→ attached to carbon 1 and 2 via ester bonds
Phosphate group linked to serine
Describe the structure of phosphatidylcholine.
Glycerol backbone
Two fatty acid chains attached to carbons 1 and 2 via ester bonds
A phosphate group linked to choline ([(CH₃)₃NCH₂CH₂OH]⁺)
![<ol><li><p>Glycerol backbone</p></li><li><p>Two fatty acid chains attached to carbons 1 and 2 via ester bonds</p></li><li><p>A phosphate group linked to choline (<span>[(CH₃)₃NCH₂CH₂OH]⁺)</span></p></li></ol><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/a4f69d46-579d-4bc9-8a35-76738745967f.png)
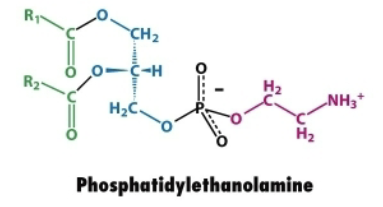
Describe the structure of phosphatidylethanolamine.
Glycerol backbone
Two fatty acid chains attached to carbons 1 and 2 via ester bonds
Phosphate group attached to ethanolamine (NH₂CH₂CH₂OH)
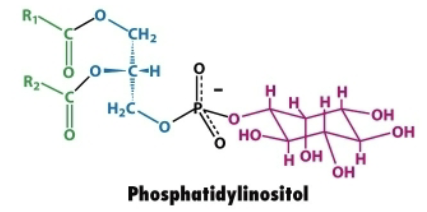
Describe the structure of phosphatidylinositol.
Glycerol backbone
Two fatty acid chains attached to carbons 1 and 2 via ester bonds
Phosphate group linked to inositol (C6H12O6)
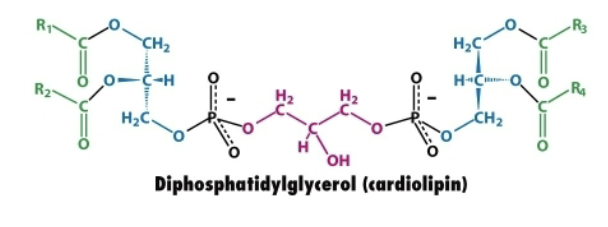
Describe the structure of diphosphatidylglycerol (cardiolipin).
Glycerol backbone (central core)
4 fatty acid chains connected to carbons 1 and 2 of each chain via ester bonds
Two phosphate groups→ connected to central glycerol forming a diphosphatidylglycerol head group.
Sphingolipids are a smaller component of _____, but this depends on _____.
Smaller component of biological membranes, but this depends on the tissue.
Sphingolipids contain a backbone of what alcohol? What is a key property of this alcohol?
Sphingosine→ amphipathic (contains a polar and a nonpolar component)
How does sphingomyelin compare to phosphatidyl choline?
Sphingomyelin is similar to phosphatidylcholine but with a sphingosine backbone rather than a glycerol backbone
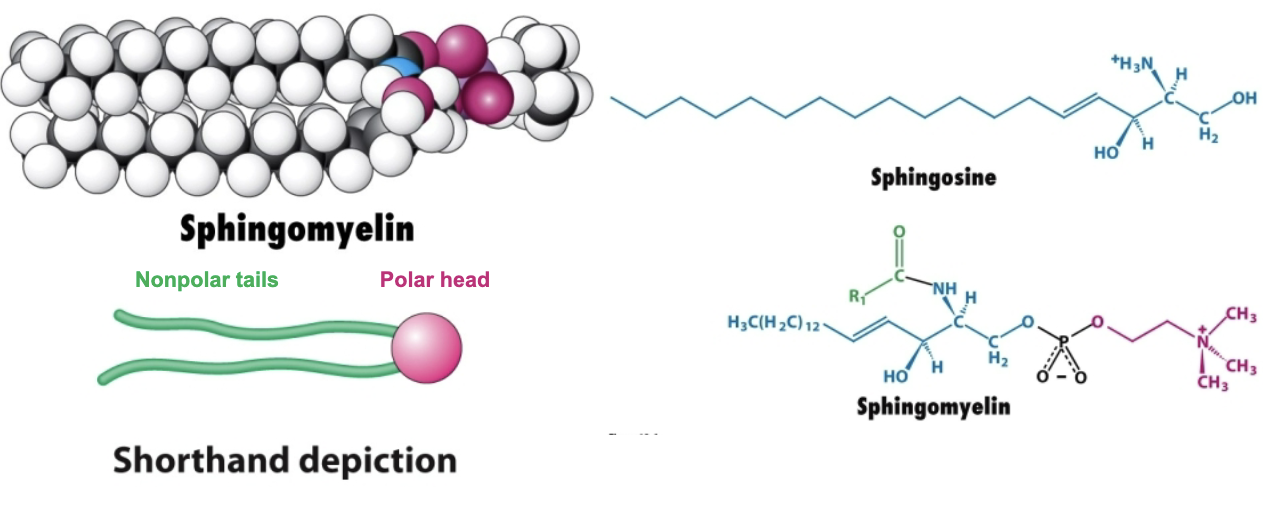
Some sphingolipids have a ____ head group consisting of ______.
Some sphingolipids have a polar headgroup consisting of an O-linked sugar group.
Where are sphingolipids with a polar head group consisting of an O-linked sugar group especially plentiful?
These are especially plentiful in neural tissue
Cerebroside typically contains what sugars?
Cerebroside typically contains either a glucose or galactose group.
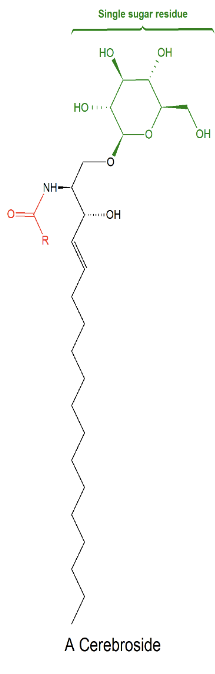
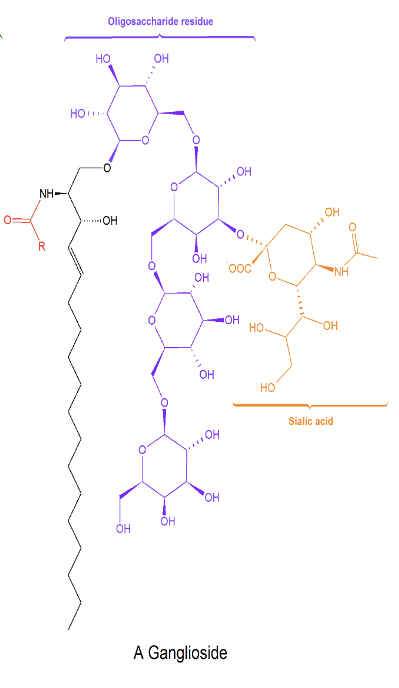
What are gangliosides?
Gangliosides are a type of sphingolipid that is involved in cell recognition and can contain as many as 7 sugar residues.
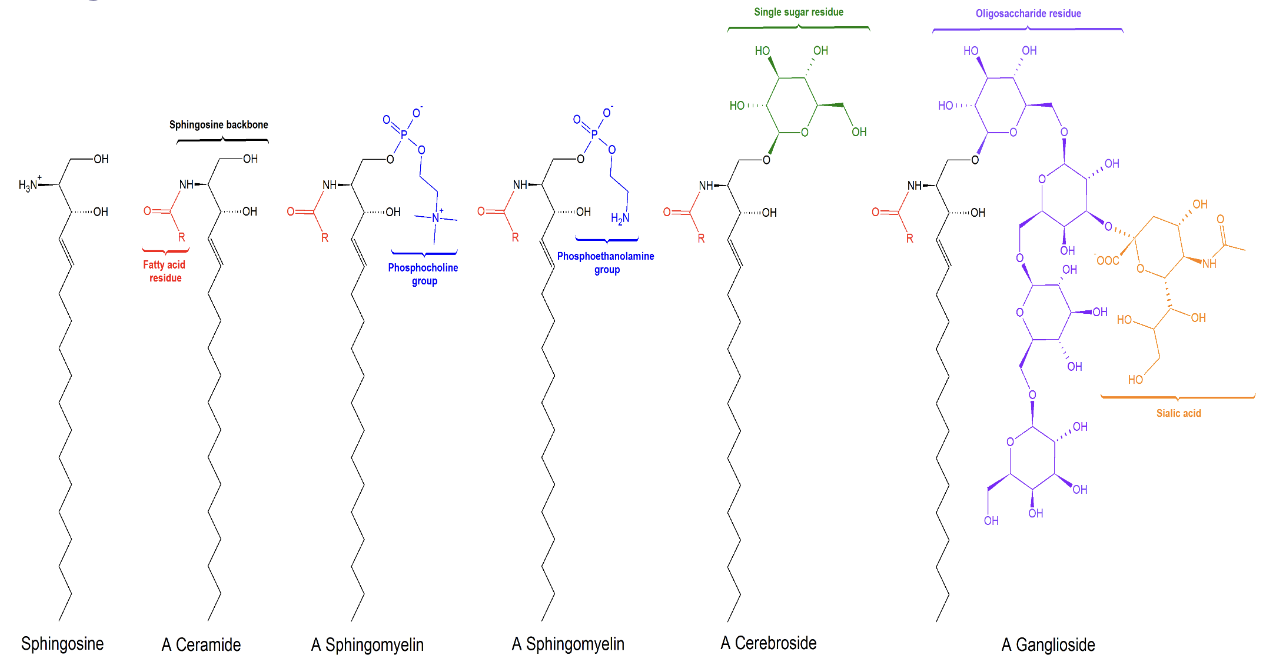
What is the difference between sphingosine, a ceramide, a sphingomyelin, a cerebroside, and a ganglioside?
Sphingosine→ backbone with no fatty acid residues
Ceramides→ Sphingosine backbone with a fatty acid residue
Sphingomyelins→ Sphingosine backbone with a fatty acid residue and a phosphocholine group or a phosphoethanolamine group
Cerebrosides→ Sphingosine backbone with a fatty acid residue and a single sugar group (either glucose or galactose)
Gangliosides→ Sphingosine backbone with a fatty acid residue and up to 7 sugar groups
Cholesterol is quite different from other lipids. Describe its structure.
Cholesterol is a steroid built from 4 linked hydrocarbon rings. It contains a hydroxyl group (-OH), and this is its only polar element.
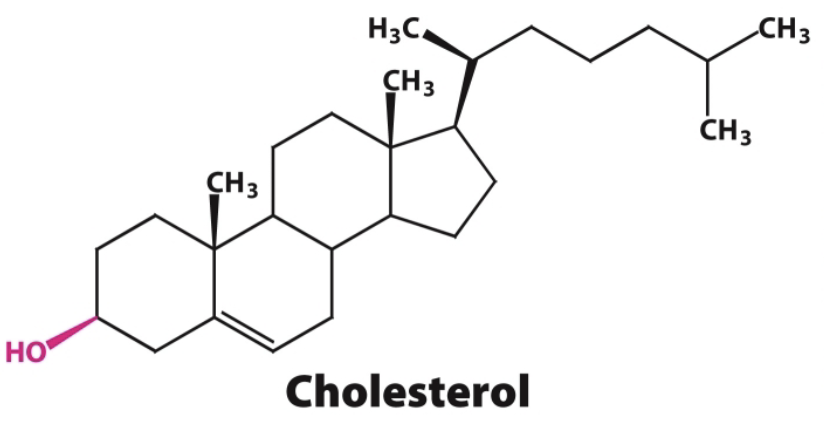
What type of cell is cholesterol most often found in?
It constitutes almost 25% of the membrane lipids in certain nerve cells but is essentially absent from some intracellular membranes→ (Dr. Shelby said could be around 40-50%)
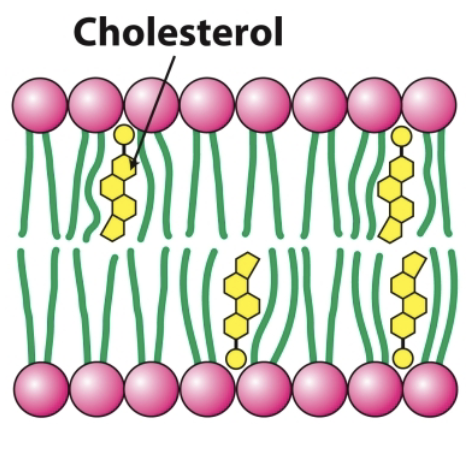
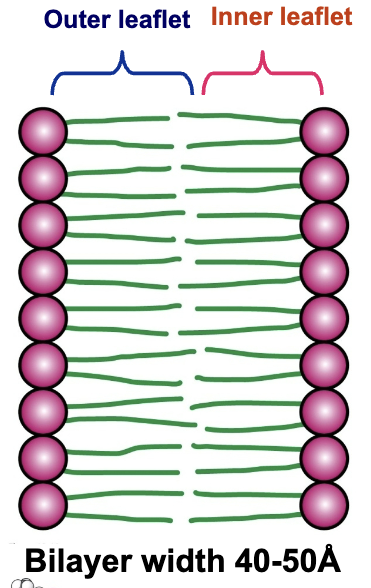
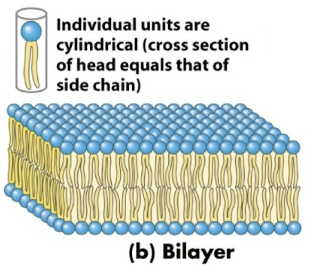
Describe the behavior of phospholipids when in water.
When in water, phospholipids spontaneously form bilayers. The bilayer membrane consists of two layers of phospholipids, with the hydrophobic tails pointing inward toward each other and the hydrophobic heads pointing outward toward either the inner or outer aqueous compartment.
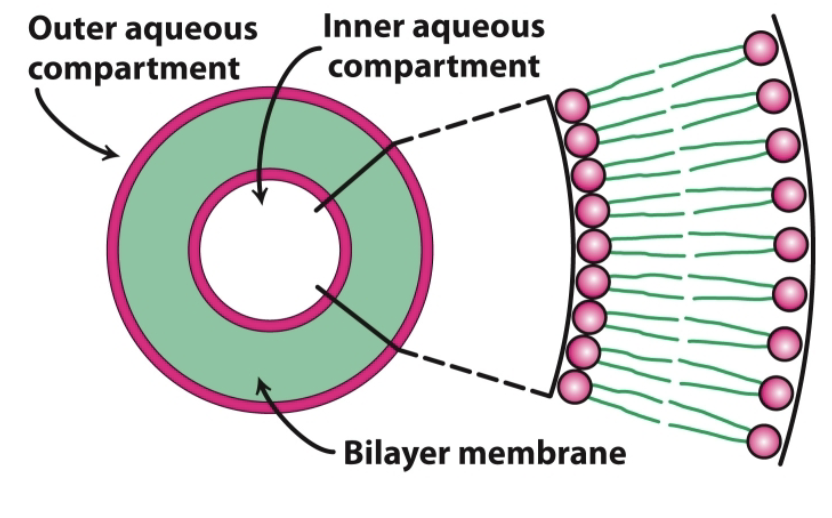
Bilayers are ____ and ______ are the major driving force for the formation of lipid bilayers.
Bilayers are self-sealing and hydrophobic interactions are the major driving force for the formation of lipid bilayers.
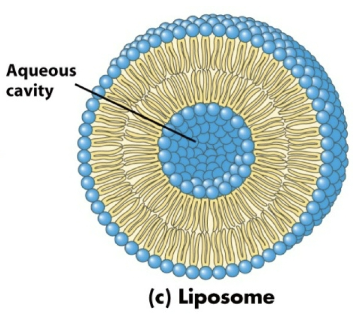
What are liposomes? What is another name for liposomes?
Liposomes, also called lipid vesicles, are aqueous compartments enclosed by a lipid membrane.
What can protein-liposome complexes be used for?
Protein-liposome complexes can be used to investigate membrane protein functions.
What is sonication?
Sonication is a technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to break down larger lipid structures into small, uniform liposomes (tiny spherical vesicles made of lipid bilayers).
Liposomes, formed by _____ a mixture of _____ in aqueous solution, may be useful as ______
Liposomes, formed by sonicating a mixture of phospholipids in aqueous solution, may be useful as drug-delivery
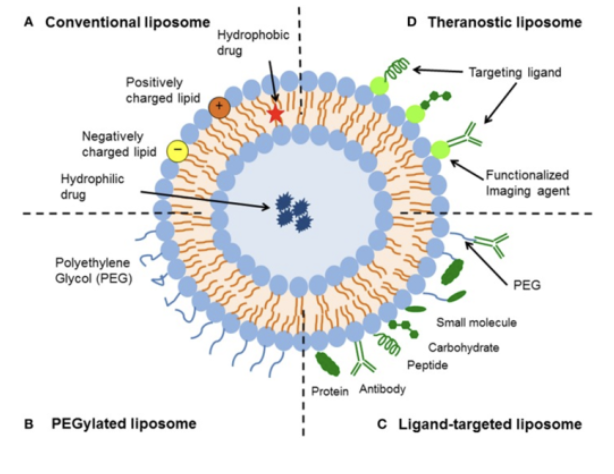
How are lipids important to the COVID-19 vaccine?
The mRNA of the COVID spike proteins are placed into a lipid coating. When the vaccine is injected, the viral spike protein mRNA is interpreted, and copies of the spike protein are produced, so when the virus enters, the protein fragments alert the immune system to produce antibodies.
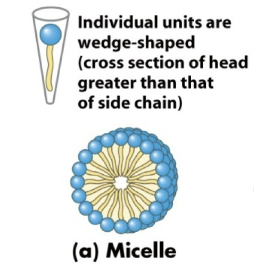
In what structure formed by placing phospholipids in water are the individual units wedge-shaped?
Micelles→ cross section of head is greater than that of side chain
In what structure formed by placing phospholipids in water are the individual units cylindrical?
Bilayers→ cross section of head is equal to cross section of side chain
Describe the structure of liposomes.
Contains a lipid bilayer that forms an aqueous cavity in the center.
Bilayers are self-assembling in water and their formation is driven by the hydrophobic effect. What other non-covalent interactions occur?
Extensive van der Waals interactions between extended fatty acid chains
Polar head groups face aqueous media and form hydrogen bonds and electrostatic interactions
What are the two “leaflets” seen in a bilayer? What is the general width of a bilayer?
Outer and inner leaflet
Width is 40-50 Å