Cystic Fibrosis & Genetic Screening
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
What’s the biggest problem with Cystic Fibrosis
Repeated LRTI (Lower Respiratory Tract Infection) with progressive destruction of lung tissue → bronchiectasis and respiratory failure
What determines life expectancy in CF
CF Pulmonary Infection
Different bacteria cause infection at different stages
Age at which they become permanently colonised/infected with Pseudomonas aeruginosa determines life expectancy
What is a complication seen in 15-20% of infants with CF
Meconium Ileus
Obstruction of the GIT of the infant related to inspissated (thick, dehydrated) material
What determines the risk of developing meconium ileus
Genotype at Cystic Fibrosis Modifier 1 (CFM1) gene on Ch 19
How to confirm CF diagnosis
Define the mutations (targeted mutation panel)
If not a common mutation, then scan exons by PCR amplification and Single Strand Conformation Polymorphism – sequence exons that look different from controls
Explain the CF Mutation Nomenclature
Cystic Fibrosis Carrier = Aa
• A – any CFTR allele that results in a functioning chloride channel (sequence may vary)
• a – any CFTR allele that does not code for a functioning chloride channel
Mutation categories = Class I to V
Explain the difference between CF mutation categories Class I - V
I. Protein production - (no functional protein produced)
II. Protein processing (misfolding)
III. Gating (doesn’t open)
IV. Conduction (faulty channel)
V. Insufficient protein (splice site)
CFTR modulator therapies are designed to do what
Correct the malfunctioning protein made by a mutated CFTR:
Give 3 types of CFTR therapies & what mutations they target
Read-through compounds (non-sense)
Correctors (misfolding)
Potentiators (open channel/increase function)
Give an example of a CF Gating Mutation
G551D (Glycine changed to Aspartic Acid at position 551)
Gating mutations occur in what % of cases of CF
4-5%
What dysfunction does a CF gating mutation cause
The CFTR protein is in place in cell membrane but does not work because the chloride channel does not open
Name a drug used to treat gating mutations
Ivacaftor (Kalydeco)
What type of drug is Ivacaftor (Kalydeco) & what does it do
It is a potentiator - binds to CFTR and allows it to open
Does Ivacaftor (Kalydeco) work for the mutation DF508?
No, but combination drug Orkambi (corrector) does
What is Kaftrio
New Triple Therapy for CF
Comination of Elexacaftor, Tezacaftor (“correctors”) and Ivacaftor (“potentiator”)
Designed to increase the quantity and function of the F508del-CFTR protein at the cell surface
Carrier testing for CF is available to who
Adults over the age of 16 where there is a family history of CF, or where a family member/partner has been found to carry a CF mutation
What kind of diet acts as CF intervention
high energy diet
Newborn Screening for Metabolic Disease is done by what test
Heel prick
Problems associated with IRT (one of the tests done as part of the heel prick)
IRT screening has low specificity
Relatively high false positive rate (better than false negative)
What improves specificity of IRT in testing for CF
Combining the test with mutational analysis
Why is there no CF population carrier screening?

How are adults screened for DF508
Testing just for DF508 is straightforward
Amplify relevant sequence from genomic DNA
Assess for wt or DF508 sequence (restriction enzyme / oliognucleotide probe)
Asses for DF508 during amplification using real time approach
What else do we use to screen for common CF mutations
38 mutation panel detects ~93.5% of the CF mutations found in the Irish population
What is NGS used for
Next-generation sequencing (NGS) is making affordable genetic testing based on the identification of variants in extended genomic regions – ~99% detection rate
NGS also being used to design custom CFTR mutation panels for different geographic regions, with around 95% detection rates
The mutations you screen for depend on what about the person
Ethnic background
Prevalence of deltaF508 in non-Hispanic US Caucasians vs US Hispanics
Non-Hispanic US Caucasians ∆F508 = ~70% carriage rate
US Hispanics = ~46%
Most common CF causing mutation in US Ashkenazi Jew (& %)
W1282X (45.92%)
(high due to founder effect)
Haemochromatosis
Clinical condition characterised by accumulation of Iron in liver, skin & other tissues
When do Clinical manifestations of Haemochromatosis develop
in adult life
Symptoms of Haemochromatosis
Hepatic failure
Cardiac failure
Skin pigmentation
Joint Disease
How is hemochromatosis diagnosed
Elevated transferrin saturation
Elevated serum ferritin levels
Haemochromatosis treatmnet
phlebotomy
Classical Haemochromatosis is associated with variant alleles of what gene
HFE gene 6p21.3
Does haemochromatosis have an autosomal dominant/recessive pattern
Autosomal recessive pattern
Role of HFE
HFE regulates iron absorption from the diet and iron storage.
Deficiency = iron overload
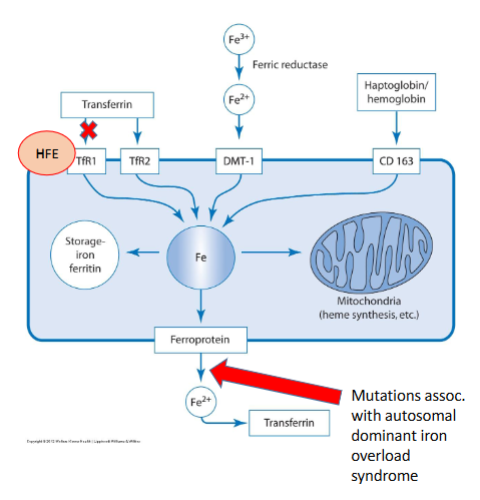
What 2 key mutations can occur with the HFE gene
G to A transition at nucleotide 845 (c.845G>A) - Cysteine to Tyrosine (p.C282Y)
C to G at nucleotide 187 (c.187C>G) - Histidine to Aspartic acid 63 (p.H63D)
The mutation C282Y homozygous is found in what % of hemochromatosis cases and leads to what x increase in iron absorption
Found in 80-85% hemochromatosis cases
3x increase iron absorption
We know that C282Y homozygotes result in clinically manifest haemochromatosis.
Do C282Y & H63D Compound Heterozygotes, and Homozygous H63D result in clinically manifesting haemochromatosis?
Heterozygotes do
Homozygous H63D does not result in clinically manifesting haemochromatosis
Haemochromatosis penetrance
Penetrance may be as low as 1%, even in homozygotes
(It is technically a hereditary disease but outcome is critically dependent on lifestyle factors “exposome”)
Why do we not have a population screening test for Haemochromatosis
Likelihood of discovering undiagnosed patient with HH is <1 in 1000
No evidence of clinical benefit for treatment of asymptomatic carriers
Low positive predictive value – e.g. Haemochromatosis H63D
Low population attributable risk (PAR) – the proportion of total disease risk in the population attributable to the factor being screened for – e.g. G6PDD mutations
Low absolute risk – e.g. FV Leiden thromboembolism relative risk for oral contraceptive users high, but absolute risk low as most of these are young people
No actionable knowledge – no way to improve prognosis
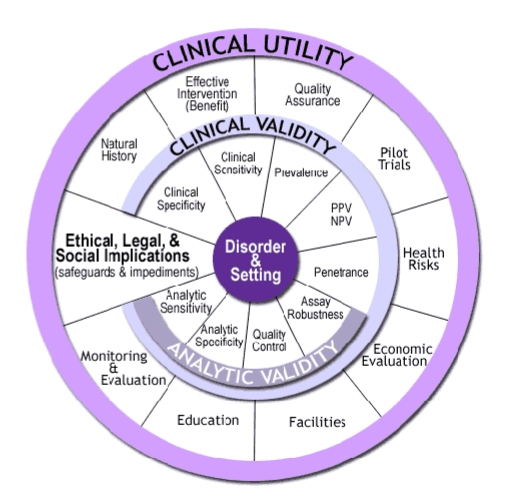
What is CDC’s ACCE framework for Principles of Screening
Analytical validity – how accurate is measurement?
Clinical validity – how accurately does it predict presence/absence of disease?
Clinical utility – how useful are the results (clinical benefit)?
Ethical, legal and social implications?
True/False Screening = diagnosis
False: Screening is not diagnosis and you need to confirm the diagnosis
Genetic drift
the change in allele frequencies in a population from one generation to the next due to chance. These changes are more pronounced in smaller populations than larger populations.