PSC `156 Chapter 1 Lifespan Perspective and SOC
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
True/False: Dementia is a normal part of aging
False
World Health Organization: Dementia
cases will eventually surpass ___ million
worldwide by ___
157, 2050
How is progression of dementia slowed?
Healthy Lifestyle
What is Cognitive Heathspan?
Years without cognitive impairment
What is ageism?
A form of
discrimination against older
adults based on their age. “Old” concept / stereotype: old age = decline
Gerontology
The scientific
study of aging from maturity
through old age
What are the two phases of the lifespan perspective?
Early (infanthood, childhood, adolescence): rapid age-related gains in size & abilities
• Later (young adulthood, middle age, old age): slower changes
Development is complex, and difficult to encompass with one approach/theory
• Lifespan perspective emphasizes that human development takes a lifetime to complete
• → Lifelong development! The entire lifespan is important
Which of the following statements best aligns with the lifespan
perspective in gerontology? A. Aging is primarily a process of inevitable decline in physical and
cognitive abilities.
B. Human development is influenced by a combination of
biological, psychological, and social factors throughout life.
C. Older adults are less capable of learning new skills compared to
younger individuals.
D. Ageism is justified because older adults contribute less to
society.
B.
What are the 4 features of Balte’s Perspective?
Multi-Directionality, Plasticity, Historical Context, Multiple Causation
What is Multi-Directionality from Balte’s Perspective?
Development
involves growth and decline → growth
in one area may mean decline in
another area, and at different rates
Example: Adolescence is a prime example of simultaneous gains and losses in brain function, often termed "selective optimization."
Gain: Improved self-regulation, abstract thinking, and prefrontal cortex development.
Loss: A decline in raw spontaneity, impulsivity, and creativity as the brain becomes more focused on logical decision-making.
What is plasticity from Balte’s perspective?
One’s capacity is not
predetermined. Many skills can
be trained or improved with
practice, even in late life.
Example: Learning an instrument late in life, new language
What is historical context from Balte’s perspective?
Everyone develops
within a particular set of circumstances
determined by the historical time in
which we are born and the culture in
which we grow up.
Example: Living through Covid
What is Multiple Causation from Balte’s perspective?
How people
develop results from a wide
variety of forces (e.g., biological,
psychological, sociocultural, life
cycle forces)
Biological: genetic & health related factors
• Psychological : perceptual, cognitive, emotional, and
personality factors
• Socio-cultural: interpersonal, societal, cultural, and
ethnic factors
• Life-cycle: The same events can affect people
differently depending on timing (cohort effects)
Which example best illustrates multi-directionality, plasticity,
historical context, and multiple causation?
A. A 55-year-old recalls how growing up during the advent of the
internet shaped their communication habits and career
opportunities.
B. A 40-year-old balances work, family, and personal goals,
demonstrating the role of _____ in development.
C. 30-year-old changes careers multiple times, reflecting the idea
that development can take different directions at any age.
D. A 75-year-old learns to use a smartphone, showing that abilities
can adapt with training and effort.
A: Historical context
B: Multiple causation
C: multi directionality
D plasticity
What are some goals of the lifespan perspective?
To delineate the biological, psychological, social, and environmental factors and _____ that are
the foundations of lifespan psychology
• To specify the biological and environmental ______ & _____ that shape development,
including the range of plasticity
mechanisms, opportunities and constraints
What are the key SOC model features?
a) An age-related _____ in the amount /
quality of biologically based resources
b) An age-related _____ in the amount / quality
of culture needed to generate growth
c) An age-related _____ in the efficiency of
using resources, as well as lack of resources
Requirement to shift more resources to maintain the same level of function for optimal aging
decrease
increase
decline
What does SOC Model stand for?
Selection, Optimization, Compensation. Selecting goals, optimizing resources to achieve those goals, and
compensating for losses to maintain functioning
What is Selection in the SOC Model with example?
As people age, they focus on or
select abilities deemed essential for functioning. Adjusting goals in response to loss of resources. Example: An older adult stops attending large parties (LBS) to focus only on small family gatherings. A pianist plays fewer pieces in concert. An older adult focuses only on reading, reducing other hobbies. Focusing energy on fewer, more important goals due to reduced resources (time, energy, health).
What is Optimization in the SOC Model with example?
Individuals then optimize
their behavior by focusing on this more limited
set of abilities. Example: practicing piano daily for two hours to improve proficiency. Practice a few compositions in more depth. Buying a magnifying lamp for better vision. Acquiring resources or refining skills to achieve the best possible results.
What is Compensation in the SOC model with examples?
People learn to
compensate for decline by designing workaround
strategies. Examples: switch to audiobooks or large-print books when eyesight declines further. use voice-to-text features to bypass fine motor skill difficulties, uses walking poles or knee braces, Adjusted relative
tempo to minimize
losses in keying
latency
. Using alternative means or technology to maintain performance despite losses.
What is a population pyramid? Can you analyze this one?
A graphic technique used to
illustrate changes in the age distribution of a population
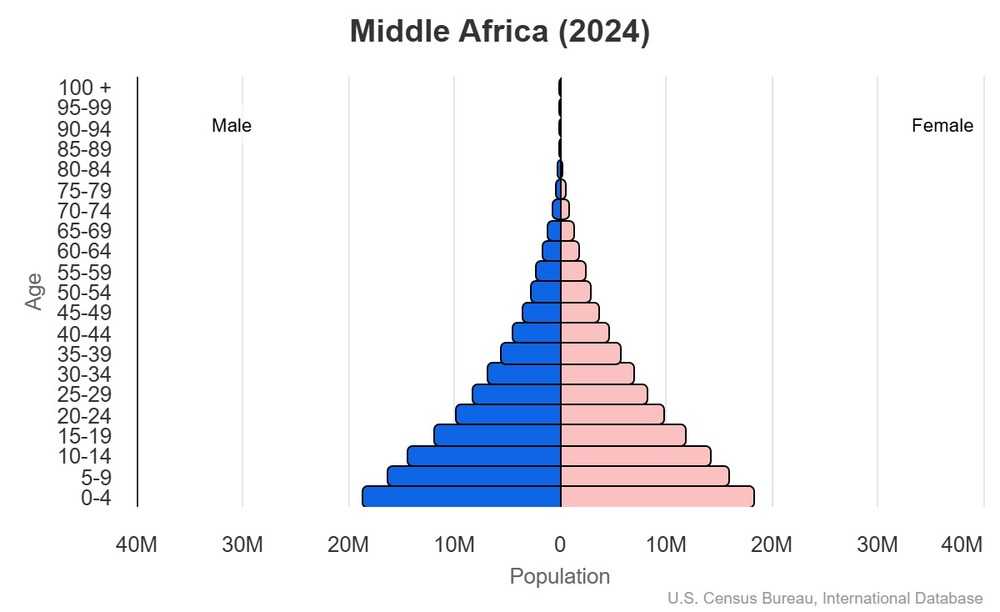
What is culture?
Shared basic value orientations, norms,
beliefs, and customary habits and ways of living.
What is ethnicity?
An individual/collective sense of identity based on
historical and cultural group membership. There are solid and
fluid qualities of ethnic group identities.
Culture vs. ethnicity
Culture could be culture of America for example of personal space and shaking hands, ethnicity is more like ancestry and cultures from that that you may blend with the culture of where you are currently
Normative age-graded influences
Experiences strongly tied to
chronological age that occur to “most”
people at a particular age
Normative history-graded influences:
Events most people within a specific
culture experience at the same time
Non-normative influences:
Random; important for specific
individual
What will population be like in 2100?
Females outnumber males
• Older adults will be better educated
• Better education → longer life expectancy (higher income =
better health)
• Demographic shifts = adaption of social policies
• Countries may become economically strained
• Older adults are increasing across all
cultural groups
• Ageism & racism contribute to intersections
of discrimination in older adulthood
Which of the following statements about the demographics of
aging is TRUE?
A. The majority of older adults worldwide live in developed countries.
B. By 2050, the proportion of the global population aged 65 and older
is expected to double.
C. Older adults have consistently lower levels of education compared
to younger generations, regardless of region or time period.
D. The aging population is decreasing in low- and middle-income
countries due to shorter life expectancies.
B
Match each example with the correct type of influence:
A. Normative age-graded influence
B. Normative history-graded influence
C. Non-normative influence
1. Starting school at age 5 →
2. Living through World War II →
3. Winning a national art competition →
4. Retiring at age 65 →
5. Experiencing a major economic recession →
1. Starting school at age 5 → Normative age-graded
2. Living through World War II → Normative history-graded
3. Winning a national art competition → Non-normative
4. Retiring at age 65 → Normative age-graded
5. Experiencing a major economic recession → Normative history-graded
Which of the following best describes the core principles of the
SOC model (Selection, Optimization, and Compensation)?
A. Selecting one’s goals, avoiding risks, and compensating for
failures.
B. Setting priorities, organizing tasks, and completing them
efficiently.
C. Selecting goals, optimizing resources to achieve those goals, and
compensating for losses to maintain functioning.
D. Strategizing, observing outcomes, and changing behaviors to
align with external expectations
C