OB exam 3 (2nd & 3rd trimester and measurements)
1/255
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
256 Terms
#1 way to check for fetal viability
heart rate/cardiac motion
how do you rule out placenta previa?
examine the lower uterine segment
what all is measured to assess fetal age?
BPD
head cirucmference
femur length
humerus length
abdominal circumference
HC/AC ratio(abnormal head to abdomen size)
humerus length is usually only found in?
MFM (maternal fetal medicine)
what may not be visualized during 2nd and 3rd trimester on the mother?
ovaries
anatomic survey of the fetus includes which structures and what is it ruling out?
Head, spine, stomach, heart, kidneys and bladder
rules out major congenital malformations
what are you looking for when examining the insertion site of the umbilical cord into the abdomen?
3 vessels- 1 umbilical vein and 2 arteries
human pregnancy length
40 weeks or 280 days beginning from LMP
ovulatory age is approx how long?
38 weeks or 266 days
first trimester
0-12 weeks
2nd trimester
13-26 weeks
3rd trimester
27-40 weeks
Nageles Rule
EDC(estimated date of confinement or due date)= LMP - 3 months +7 days (+1 year)
gravidity
sum of all pregnancies
parity
the number of pregnancies in which the patient has given birth to a fetus at or beyond 20 weeks
Example- define G4P2103
4 total pregnancies
2 full term
1 premature
0 abortions
3 living children
Vertex/cephalic fetal presentation
longitudinal lie- fetal head located at level of bladder and lower uterine segments (head down)
fetal occiput
back of fetal head
Breech fetal presentation
fetal head seen in the fundus
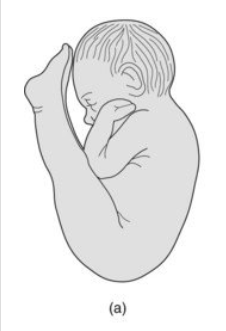
Frank breech
thighs flexed at the hips and lower legs extended in front of head
sometimes the fetus can be turned in this position to ensure safe vaginal delivery
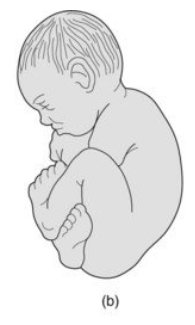
complete breech
both hips and lower extremities are lower than the pelvis, legs crossed
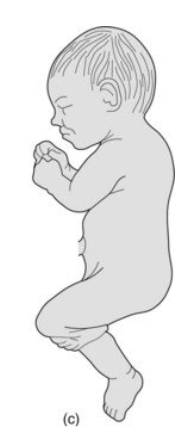
footling breech (incomplete breech)
hips are extended and one or both feet are closest to the cervix-requires C section
transverse lie-what will be seen in a sagittal transducer
a transverse fetus
situs means?
fetal positioning
cranial bones ossify by which week?
12th week
normal brain tissue appears how?
hypoechoic or cystic due to high water content
dura and pia mater appear how?
echogenic
CSF appears how?
cystic
pia later and dura- which one is outer
pia mater=inner most
dura-outermost
brain anatomy and measurements are assessed in which scanning plane?
transverse
as preganancy progresses, why does it become more difficult to visualize the brain?
becasue of increasing calcification of the skill and the position of the fetal head deeper in the pelvis
standard obstetric exam guidelines require you to image and record what structures in the brain?
cerebellum, choroid plexus, cisterna magna, lateral cerebral ventricles, midline falx and the cavum septum pallucidum
why is visualizing the falx important?
because its presence implies that separation of the cerebrum has occured
what can be viewed lateral and parallel to the falx?
deep venous structures (white matter tracts) positioned above lateral ventricles
how does the white matter tracts appear?
2 linear echoes
where is choroid plexus tissue located
within the roof of each ventricle, except at the frontal ventricular horns
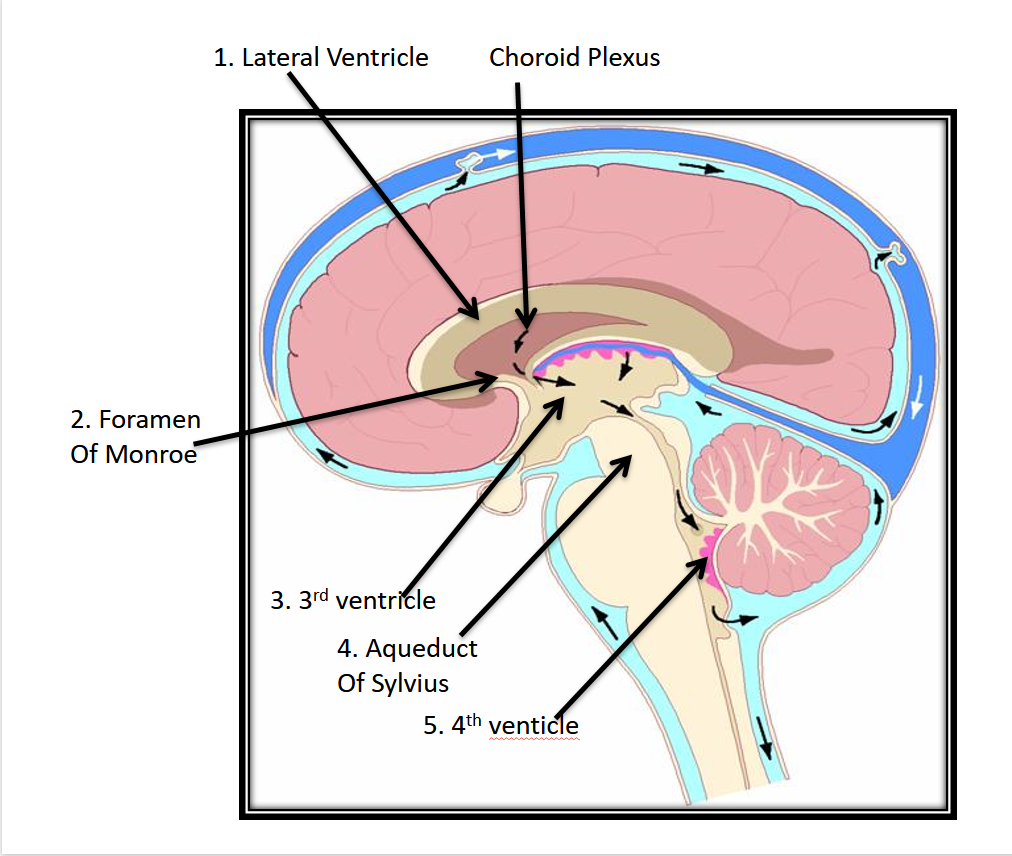
the fetal ventricular system consists of:
2 paired lateral ventricles, a midline third ventricle and a fourth ventricle adjacent to the cerebellum
CSF travel path
travels from the lateral to the third ventricle through the foramen of monroe. from the 3rd ventricle, fluid travels through the aqueduct of Sylvius to the fourth ventricle. from there, it flows into the cerebral and spinal subarachnoid spaces from the interventricular foramina and the foramen of Luschka. after this, it is reabsorbed and enters the venous system
picture of CSF pathway
the most common neural tube defects
ventriculomegaly and hydrocephalus
what is associated with spinal defects?
dilation of the entire system, including the fourth ventricle
lumina of the ventricles may be recognized how?
by the bright reflection of their borders and the presence of hyperehcoic choroid plexus tissue that fills the cavity of the ventricles
how do you measure ventricles
from echogenic line to echogenic line
the lateral ventricle is more easily imaged where?
in the distal hemisphere due to reverberation artifact in the near field
body of the choroid plexus is called
gloms
the gloms mark what?
the site at which the ventricles are to be measured
shape of choroid plexus
tear shaped
the glomus should do what in a normal pregnancy?
fill the entire atria
if the body appears to float or dangle, what should be suspected?
ventriculomegaly
ventricular size should do what throughout the gestation?
remain the same
normal measurement of the ventricle
6.5mm
above 10 mm(1cm) is considered abnormal
3rd ventricle cavity is located where?
between the thalamus
how do you find the midline echo complex?
moving the transducer caudally from the ventricles
what is seen in front of the thalamus
CSP
the frontal horns of the ventricles may be seen how?
as 2 diverging echo free structures within the frontal lobes of the brain
what is the band of tissue between the frontal ventricular horns?
the corpus callosum
what are the pulsatile structures bordering the thalamus posteriorly?
the cisterns
what shape are the cerebral peduncles?
heart shaped, but smaller than the thalamus
where can you see the basilar artery pulsations?
between the lobes of the peduncles and the interpeduncular cistern
How does the Circle of WIllis appear?
triangular and highly pulsatile due to cerebral arteries
what is visualized in the center of the circle of willis?
suprasellar cistern
where is the cerebellum located?
in the back of the cerebral peduncles within the posterior fossa
cerebral hemispheres are joined together by what?
the cerebellar vermis
what lies directly behind the cerebellum?
the cisterna magna(posterior fossa)
normal measurement of cisterna magna
3-11 mm, average is 5-6mm
where do you measure the cisterna magna?
from the vermis to the inner skull of occipital bone
linear echoes within the cisterna magna are?
dural folds that attach the falx cerebri
what is the limit for the measurement of cisterna magna?
1 cm
when scanning inferior to or below the cerebellar plane what can be visualized?
the orbits
facial morphology becomes more apparent in what trimester?
2nd trimester
visualization of the fetal face heavily relies on what?
fetal positioning, adequate amounts of amniotic fluid and excellent acoustic windows
the facial profile view shows the contour of what?
the frontal bone, nose, upper and lower lips and the chin
abnormally small chin is called what?
micrognathia
recognized components of down syndrome in the profile view
small nose and midface hypoplasia
coronal facial view demonstrates what?
both orbital rings, parietal bones, ethmoid bones, nasal septum, zygomatic bone, maxillae and mandible
scan obtained in an anterior plane over the orbits demonstrates what?
eyelids and the orbital lens
when is the oral cavity and tongue frequently outlined?
during fetal swallowing
coronal/axial/tangential views on the face demonstrate what? what is it helpful in diagnosing?
nostrils, nares, nasal septum, maxillae and mandible.
diagnoses cleft lip
how are the fetal ears defined?
as lateral protuberances emerging from the parietal bones
the fetal spine is viewed in what scanning planes?
sagittal, coronal and transverse
in sagittal the spine appears how?
as two curvilinear lines extending from the cervical spine to the sacrum
the double line sign from the spine called what?
the railway sign
cervical spine or sacrum is wider?
cervical. it tapers near the sacrum
how does the spine appear in a transverse scan?
as a closed circle
what does the closed circle indicate?
closure of the neural tube
the circle of echoes in the spine represents what?
the center of the verebral body and the posterior elements
when evaluating the spine it is imperative to do what?
to align the transducer in a perpendicular axis to the spinal elements- incorrect angles could falsely indicate an abnormality or not correctly line up with the skin which could indicate spina bifida
posterior elements of the spine
laminae
what serves aas lateral borders to the heart?
the lungs
what should be assessed in the lungs?
lung size, texture, and location to exclude a lung mass
fluid filled lungs seen as?
solid homogeneous masses of tissue bordered by the heart, diaphragm and ribcage
as pregnancy progresses, fetal lung tissue….
appears denser and more echogenic than the liver
what are bony landmarks of the chest cavity?
ribs, scapulae and clavicles
what creates a “washboard” appearance?
echogenic ribs and intercostal space
when should you be able to view the 4 chamber heart?
15 weeks
what degree is the heart positioned in the chest?
45 degrees
which chamber sits closest to the spine and aorta?
left atrium
the apex of the heart points to where?
the left side
what plane does the heart lie in
transverse
left heart valve
mitral valve