CH 12: Global Challenges (Cyber, Space, & Transnational Threats)
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
cyber-espionage, economic, political
China leverages _______ operations to gather information in support of gaining _______ and _______ advantages over Western countries.
mobile devices, Internet of Things (IoT)
weakest technological components:
Information Technology (IT)
the Digital Silk Road will provide China with long-term access to global _______ _______ networks as the infrastructure for future cyber operations.
(also creates foreign economic dependency)
PLASSF
MSS
China’s cyber elements are divided into two forces:
People’s Liberation Army Strategic Support Forces
PLASSF
Ministry of State Security
MSS

cyber, space, electronic
reorganizing into the Strategic Support Forces combined _______ , _______ , and _______ warfare units into a single organization
operational security, sophistication
Since the reorganization, the PLASSF forces have increased _______ and _______ of their attacks.
Russia, China
_______ and _______ are the US’s main adversaries in cyberspace
asymmetrically
Iran and North Korea can launch disruptive cyberattacks & use cyberspace to _______ respond to perceived challenges.
generate revenue
increase notoriety
disrupt international communication & trade
Non-state actors and cyber criminals continue to use malicious cyberattacks to _______ , _______ , and _______.
state-sponsored, state-directed
although there is a strong presence of cybercriminal actors operating out of Russia, there are not clear ties to their operations being _______ or _______
FSB
SVR
GRU
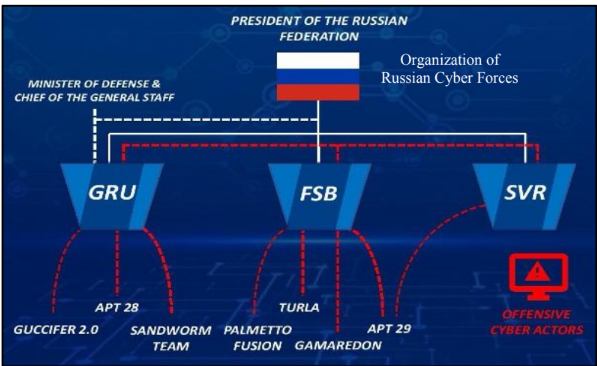
Russia organizes their state-sponsored cyber elements into three organizations:
Federal Security Service
FSB
Foreign Intelligence Service
SVR
GRU
Main Directorate of the General Staff of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation
FSB
counterintelligence operations
SVR
human intelligence
GRU
all other intelligence services (muddled mess)
GRU
Associated with attacking government and defense industries, the ___ is responsible for breaching the Pentagon’s network in 2015 and the DNC’s in 2016
also responsible for disabling power grids in multiple Eastern European countries (Georgia in 2008 & Ukraine in 2015)
assessed to be the best resourced organization for cyber operations.
SVR
In 2020, the United States publicly acknowledged that the ___ was the lead element behind the SolarWinds attack
space domain
area above the altitude where atmospheric effects on airborne objects become negligible

100km
USSPACECOM’s AOR is area greater than ___ above sea level.
near-worldwide coverage, denied
Space capabilities provide combatant commanders (CCDRs) with _______ and access to otherwise _______ areas.
Freedom of action
Overflight
Responsiveness
Multi-user capacity
Speed, reach, and persistence
Global perspective
advantages of space for operational purposes (6)

solar activity
radiation
natural orbital debris
natural threats to satellites (3)

man-made threats to satellites
unintentional
satellite debris
electromagnetic interference (EMI)
intentional
jamming
lasing
cyberspace attacks
antisatellite weapons
space, cyberspace
many _______ operations depend on _______, and a critical portion of cyberspace can only be provided via space operations (unique relationship)
Space Domain Awareness (SDA)
Space Control
Positioning, Navigation, and Timing
Intelligence, Surveillance, Reconnaissance (ISR)
Satellite Communications (SATCOM)
Satellite Operations (SATOPS)
Environmental Monitoring
Missile Warning
Nuclear Detonation Detection
Spacelift
10 space missions
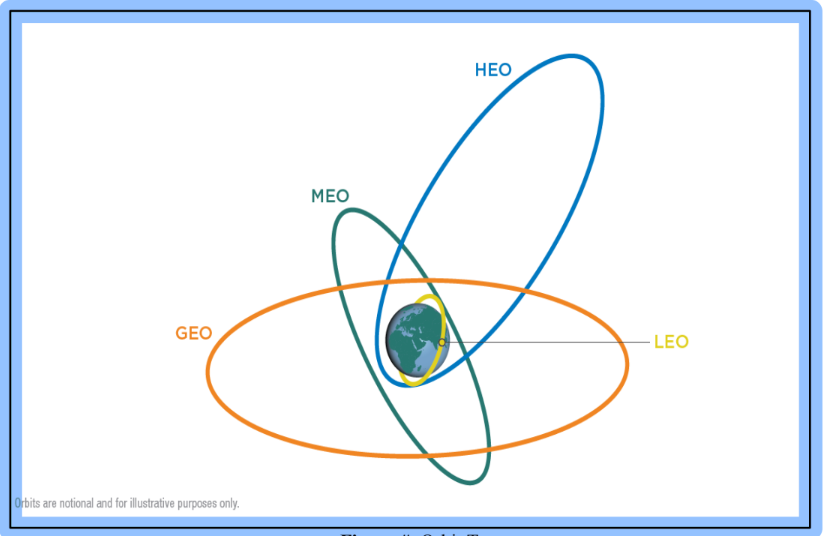
orbit types
HEO (right)
MEO
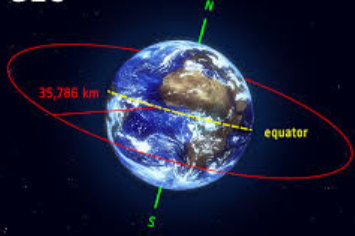
GEO (big oval)
LEO (around earth)
geosynchronous earth orbit (GEO)
circular
nearly hemispheric
disadvantages: far from earth, easier to jam
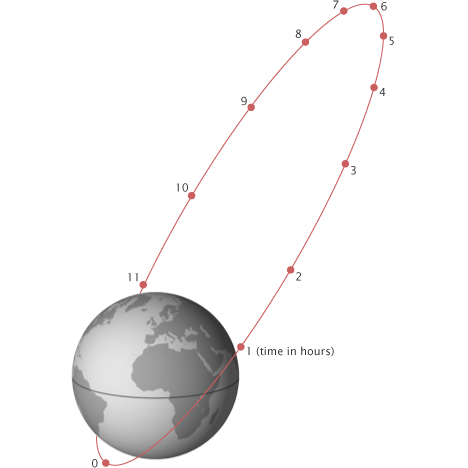
highly elliptical orbit (HEO)
long ellipse
600 miles at point closest to Earth; 25,000 miles at high point
large area; coverage of North or South latitudes; missile warning
disadvantage: requires multiple satellites
medium earth orbit (MEO)
roughly circular, stable orbit, less signal latency
disadvantage: highest radiation environment
1,000 to 22,000 miles
low earth orbit (LEO)
circular, near Earth, high resolution, high signal strength
disadvantage: small coverage area
manned space flight
up to 1,000 miles above Earth’s surface

Space domain awareness (SDA)
info. on operational environment; physical, virtual, information
Space Control
offensive and defensive operations; providing continued, sustainable use of space; contributes to space deterrence; assures the use of space
Positioning, Navigation, and Timing (PNT)
precise & accurate geolocation, navigation, and time reference services; GPS
ISR
space-based intelligence collection; includes overhead persistent infrared (OPIR)
Satellite Communications (SATCOM)
situational awareness, satellites; equatorial coverage or high-latitude coverage;
beyond line-of-sight connectivity

Environmental Monitoring
provides information on meteorological and oceanographic factors that affect military operations

Missile Warning
notifies national leaders of missile attack against North America, multinational partners, or forward-deployed personnel

Nuclear Detonation Detection
sensors to provide warning; place, height of burst, and yield of nuclear detonations

Spacelift
ability to deliver payloads (satellites or other materials) into space
Satellite Operations (SATOPS)
maneuver, configuration, operations and sustainment of on-orbit assets
Network Systems Department
cyberwarfare — its current major target is the United States
Space Systems Department
responsible for nearly all PLA space operations
space launch & support
space surveillance
space information support
space telemetry
space warfare
2022 and 2024
We expect the Chinese space station in low Earth orbit (LEO) to be operational between ____ and ____.
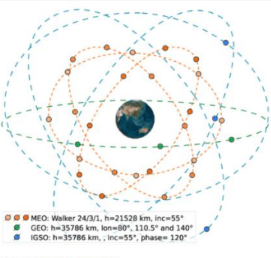
Beidou Navigation Satellite System (BDS)
comprised of 35 satellites in the constellation
27x MEO
3x IGSO
5x GEO
Chang’e
lunar sample return mission that launched on 23 NOV 2020

Yaogan
comprehensive Chinese earth-observing and remote-sensing satellite platform
Russia
_______ focuses on integrating space services into its weapons and command-and-control systems
GLONASS (Global Navigation Satellite System)
consists of 24+ satellites in MEO; owned and operated by the Russian Federation

5.2
more than ___ million refugees have fled Syria since 2011
Nudol
anti-satellite mission
PL-19 (19th system at launch facility)
it is expected that Russian anti-satellite weapons will be aimed at communications satellites and imagery intelligence satellites in low Earth orbit (LEO)

Tiangong
Chinese Space Station; roughly 1/5 mass of International Space Station
chemical, biological
ISIS has _______ and _______ capabilities.
Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi
leader of ISIS in September 2017; killed 2019; long-term strategy of establishing “global caliphate”
(killed by US Special Ops in 2019)

online
ISIS will maintain an expansive _______ presence.
2017, 2018
ISIS suffered significant setbacks in ____ and ____.
unmanned aerial systems (drones)
ISIS uses _______ for surveillance & delivery of explosives
Syria, Yemen
Al-Qaida remains a serious and persistent threat to U.S. interests worldwide. In particular, the group’s exploitation of conflicts in _______ and _______ offers opportunities for reconstituted external attack capabilities.
Ayman al-Zawahiri
2013 guidelines for jihad = “exhaust America and bleed her to death”

Hamza bin Laden
Al-Qaida is preparing for the next generation of leadership with Usama bin Laden’s son, _______, and his call to attack the United States in retaliation for his father’s death.
(son was killed in 2019 by U.S. counterterrorism operation)

Libya
Afghanistan
Philippines
ISIS’s capabilities have been degraded in _______, _______, and _______.
West
ISIS continues to inspire more attacks in major cities throughout the _______ than any other terrorist organization — significant terrorist threat to the United States and other Western nations.
displacement
Conflicts are driving record population _______, resource shortages, demographic shifts, and unplanned expenditures of economic and military assets in countries of strategic interest to the United States.
overtaxed, living standards, labor markets
Many Middle Eastern countries are closing their borders because public service provisions & government finances are being _______ , _______ _______ are declining, _______ _______ are narrowing, and they perceive a lack of burden sharing by countries outside the region.
counter space, strategic intel
overlapping missions of Space Systems Department and Network Systems Department
telemetry, tracking, and control
TT&C
GEO
disadvantage: Far from Earth - resolution and signal limitations - easier to jam signal latency
HEO
disadvantage: continuous coverage requires multiple satellites
MEO
disadvantage: highest radiation level environment
LEO
disadvantage: small coverage area over Earth surface, limited coverage windows for any specific geographic region
MSS
operates a global campaign of cyber espionage for economic, political and strategic purposes
dominance, Western, pro-democracy, global
Russia leverages their cyberspace capabilities to re-establish _______ in its near-abroad, damage ________ and ___-_________ influence, and expand _______ influence.
Al-Qaida affiliates
Somalia, North Africa, the Sahel, Yemen, South Asia
Minister of Defense & Chief of the General Staff
in charge of GRU
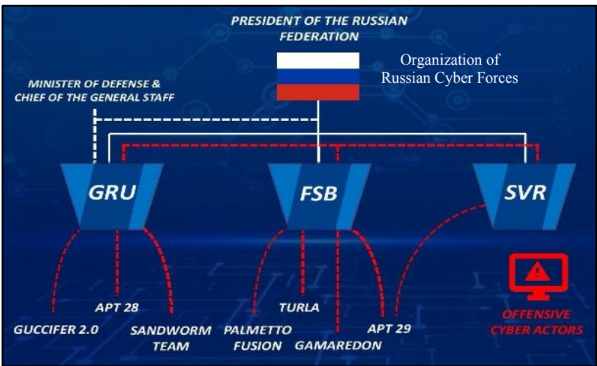
President of the Russian Federation
in charge of GRU, FSB, and SVR
SSF
theater command-level organization
GEO
~23,000 miles
HEO
~600-25,000 miles
MEO
~1,000-22,000 miles
LEO
~1,000 miles
GEO
continuous coverage over specific area; coverage nearly hemispheric
HEO
long dwell time over a large area; coverage of high North or South latitudes
MEO
stable orbit; less signal latency
LEO
Near Earth - high resolution and signal strength
MEO
Position, navigation, & timing; Communication
LEO
manned space flight, weather, communications