Biomechanical Engineering/Zabala
1/147
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
148 Terms
28 years
peak bone density occurs at age...
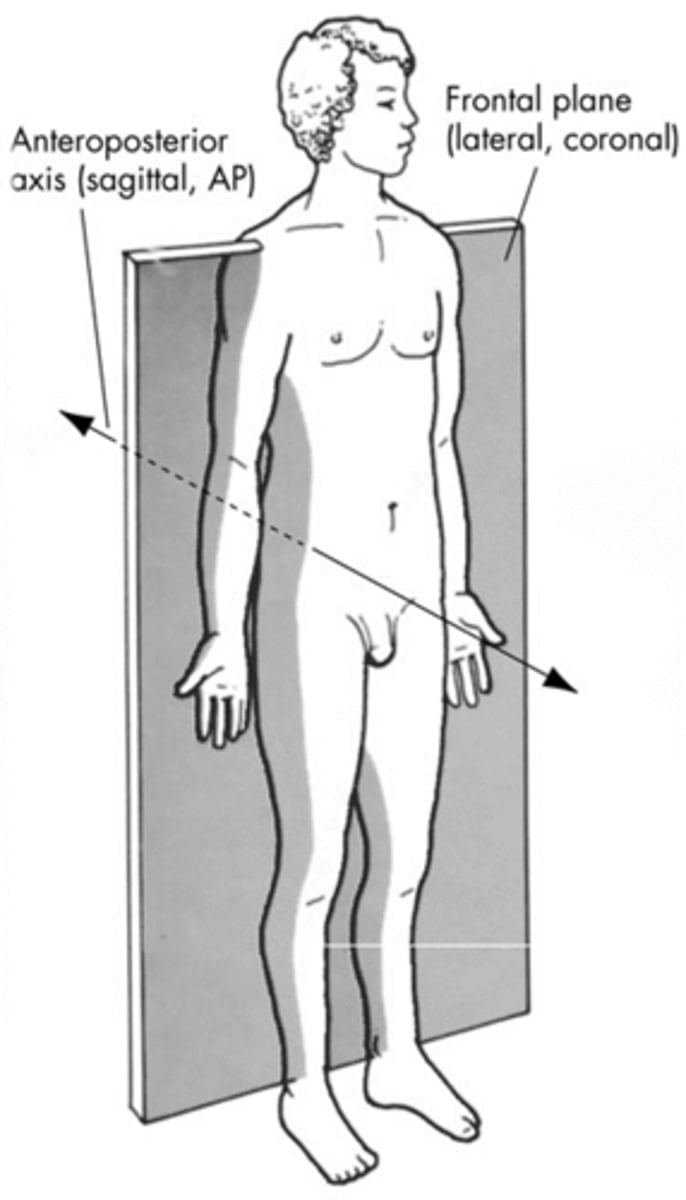
frontal plane (coronal plane)
divides body into anterior and posterior sides

mediolateral axis
perpendicular to sagittal plane
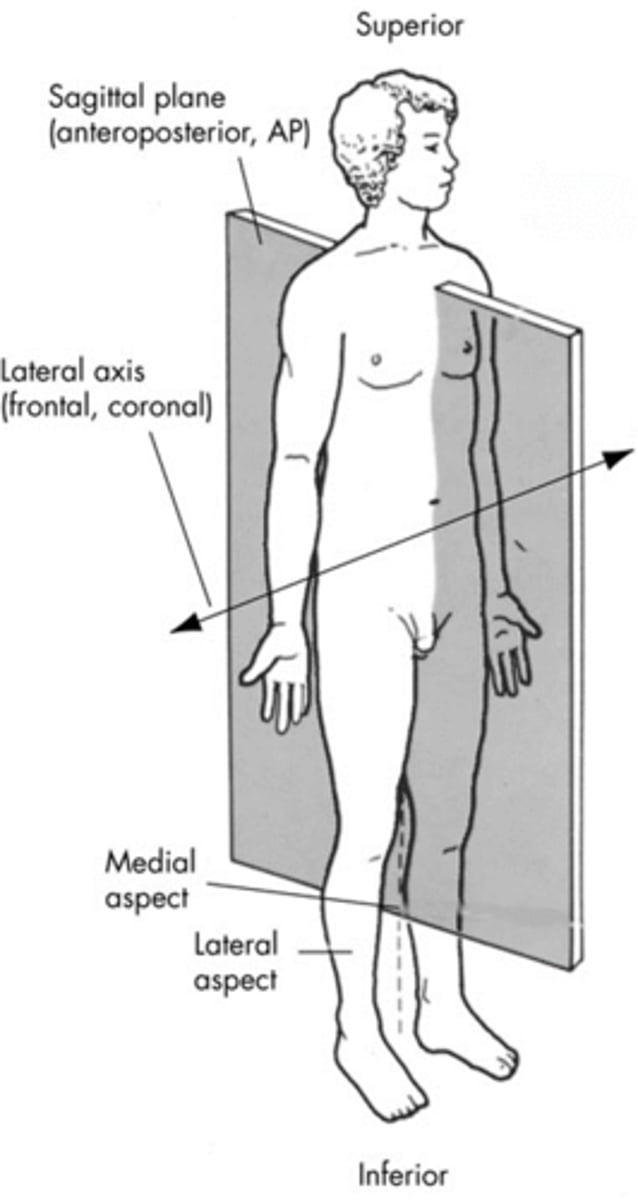
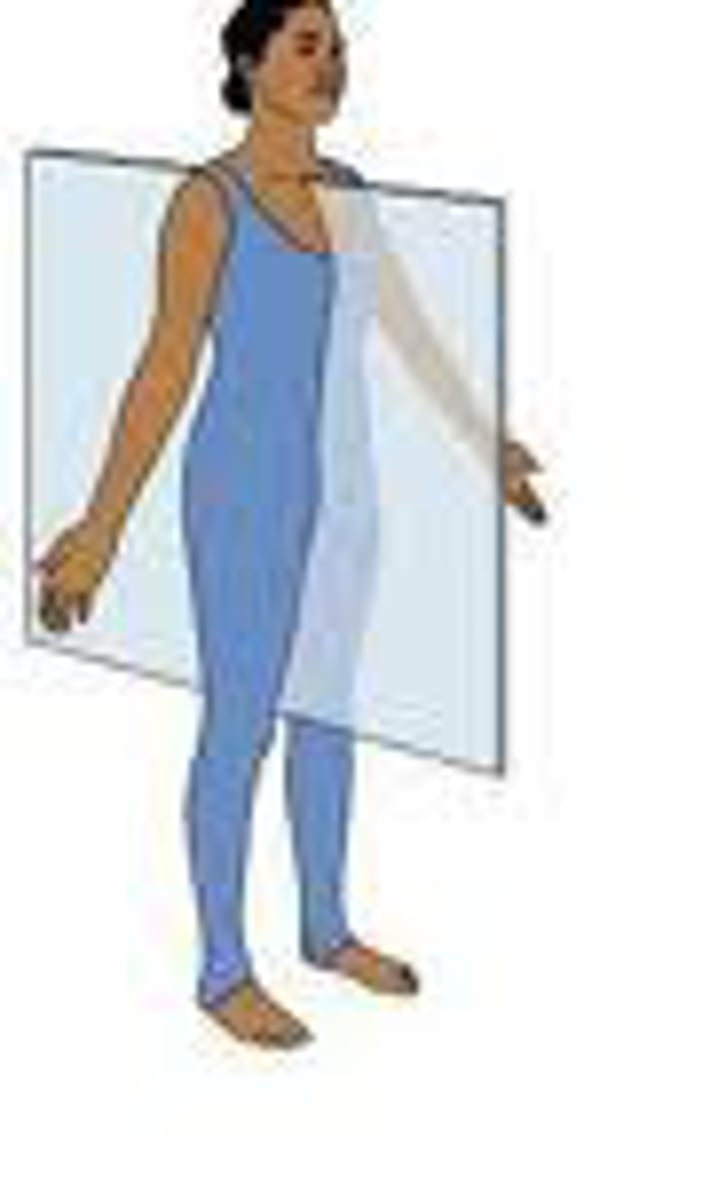
sagittal plane
divides body into left and right
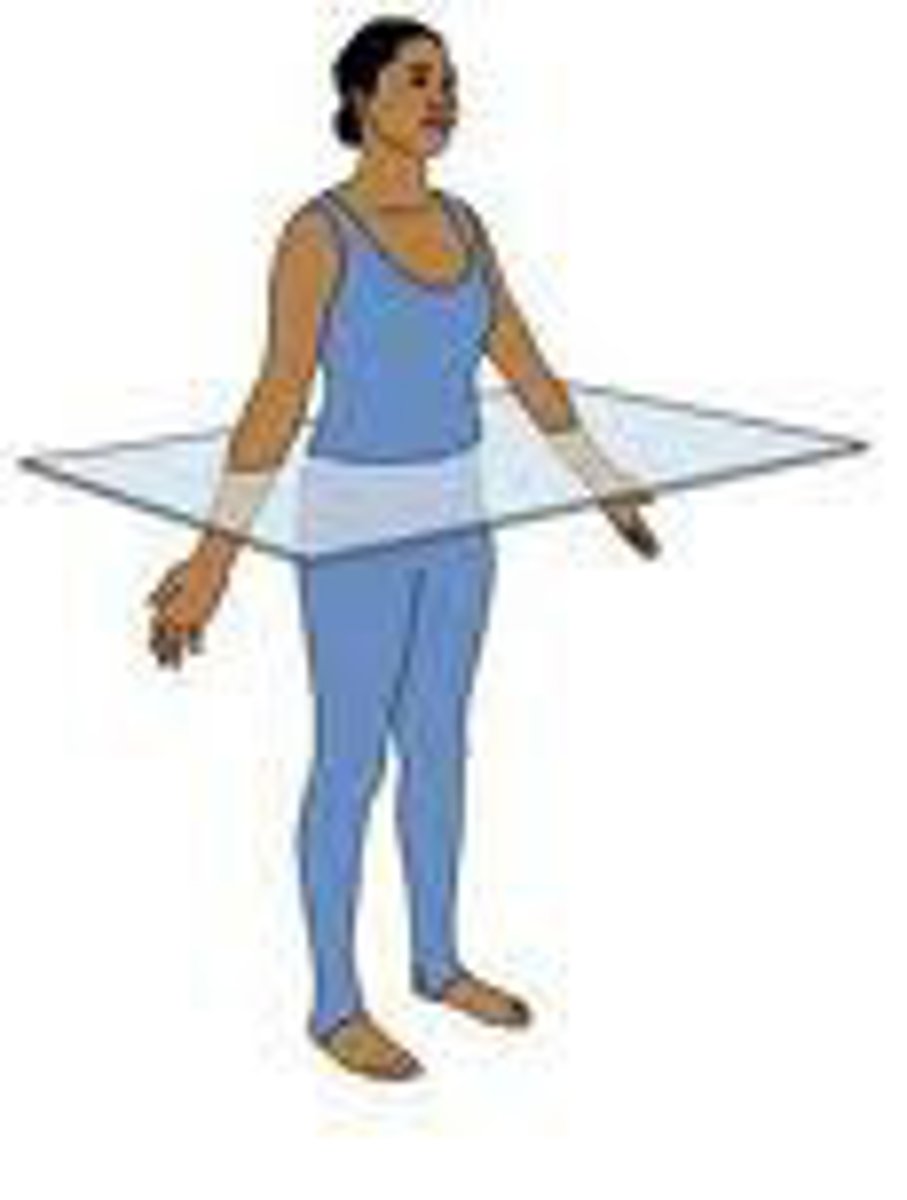
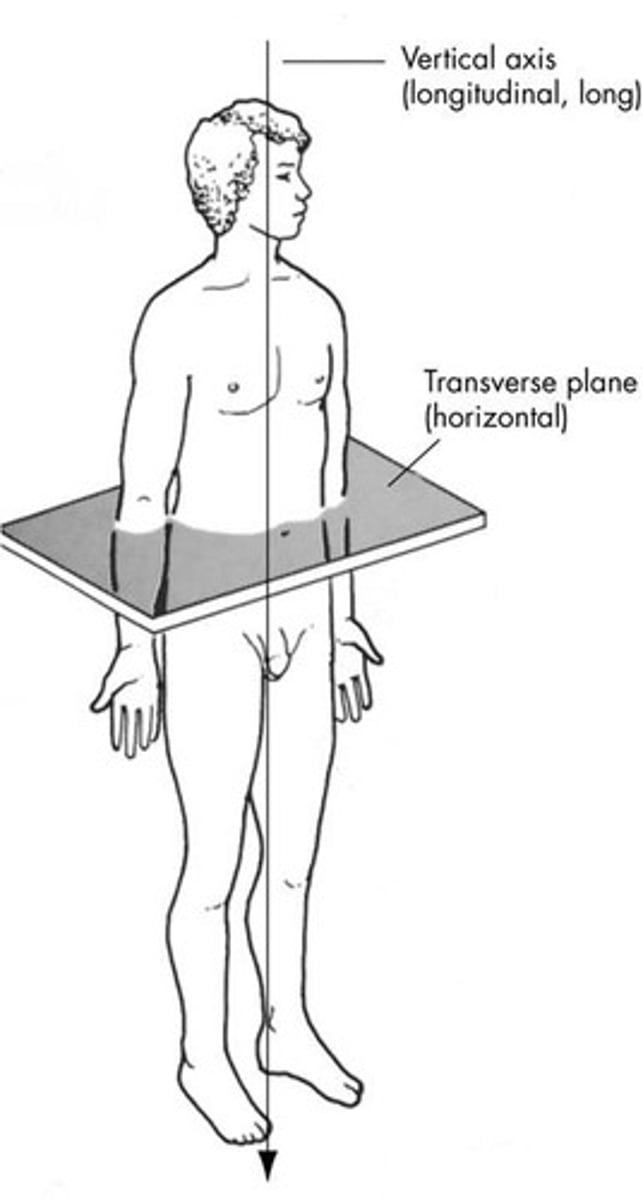
transverse plane
divides the body into superior and inferior parts
anteroposterior axis
perpendicular to frontal plane
longitudinal axis
perpendicular to transverse plane
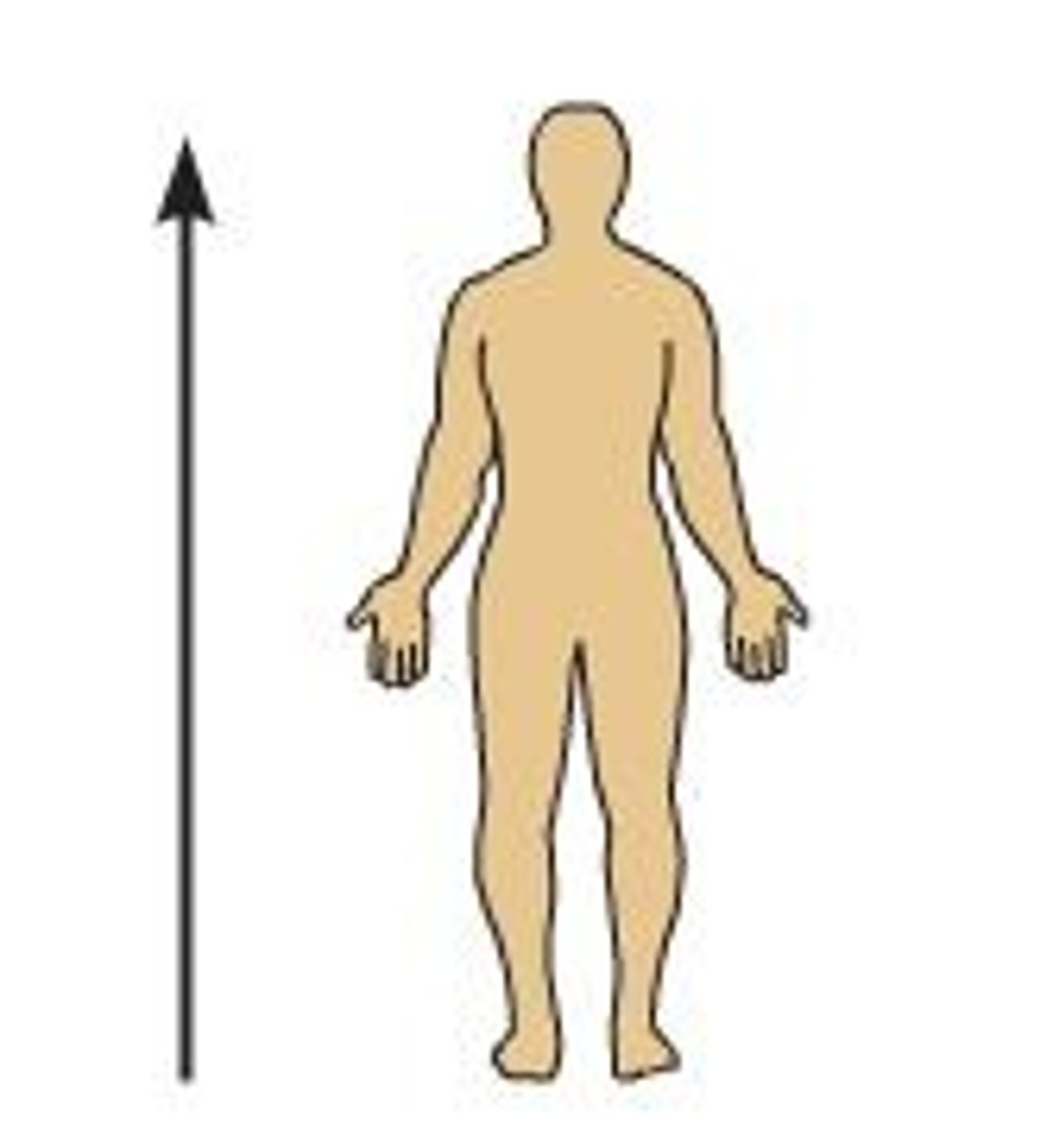
Superior (cranial)
toward the head end or upper part of a structure or the body; above
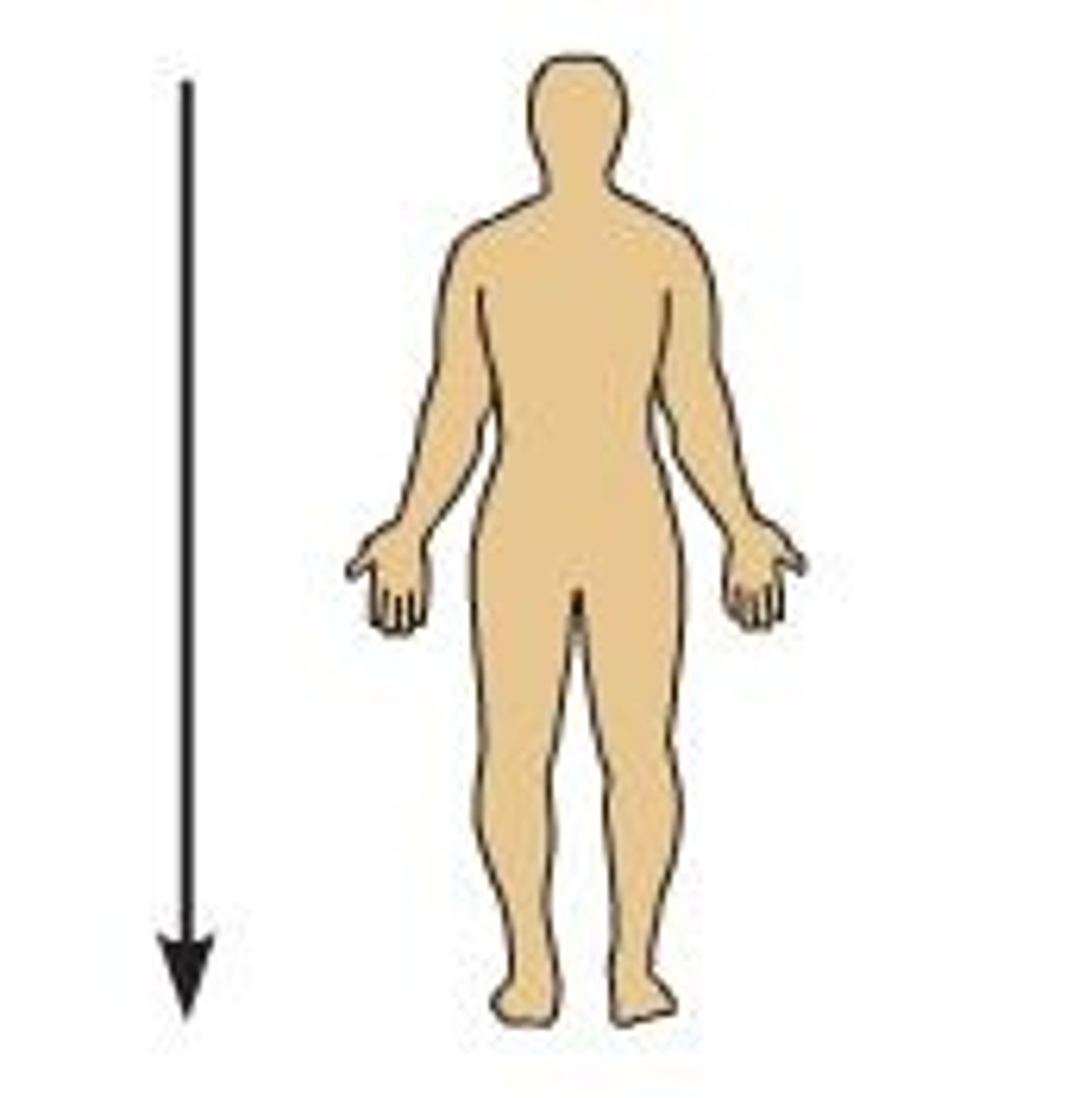
Inferior (caudal)
away from the head end or toward the lower part of a structure or the body; below
anterior (ventral)
toward the front of the body
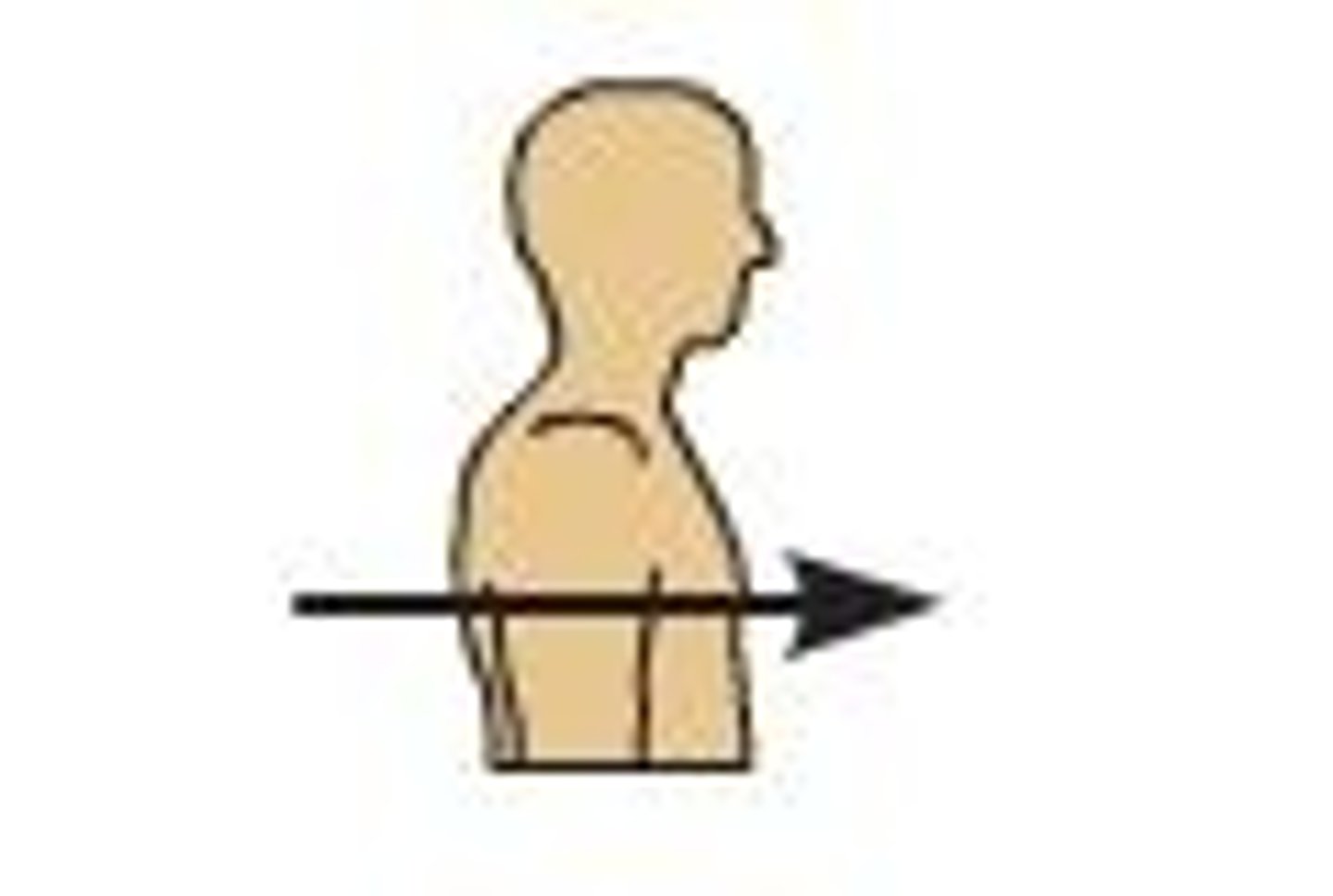
posterior (dorsal)
toward the back of the body
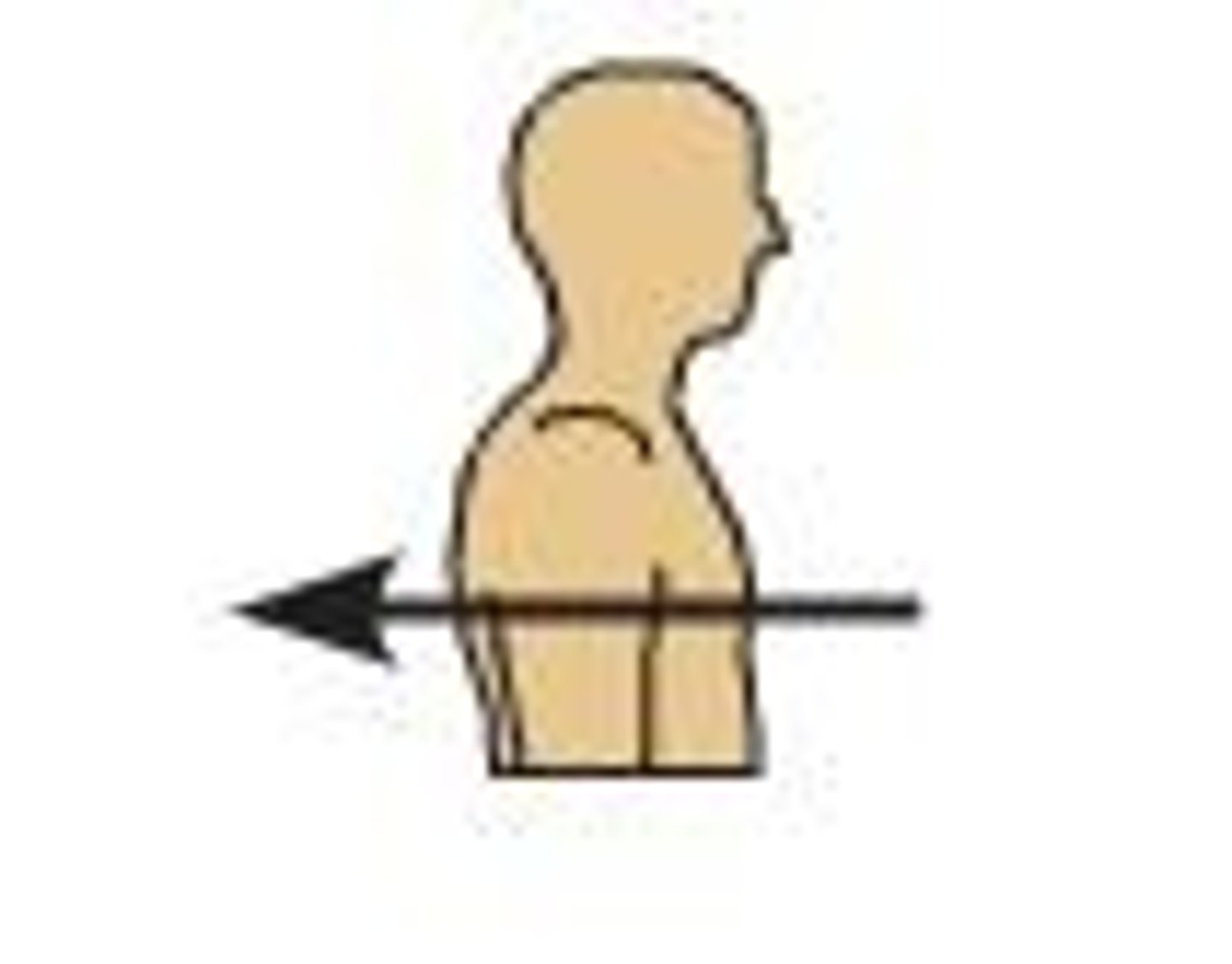
medial
Toward the midline of the body
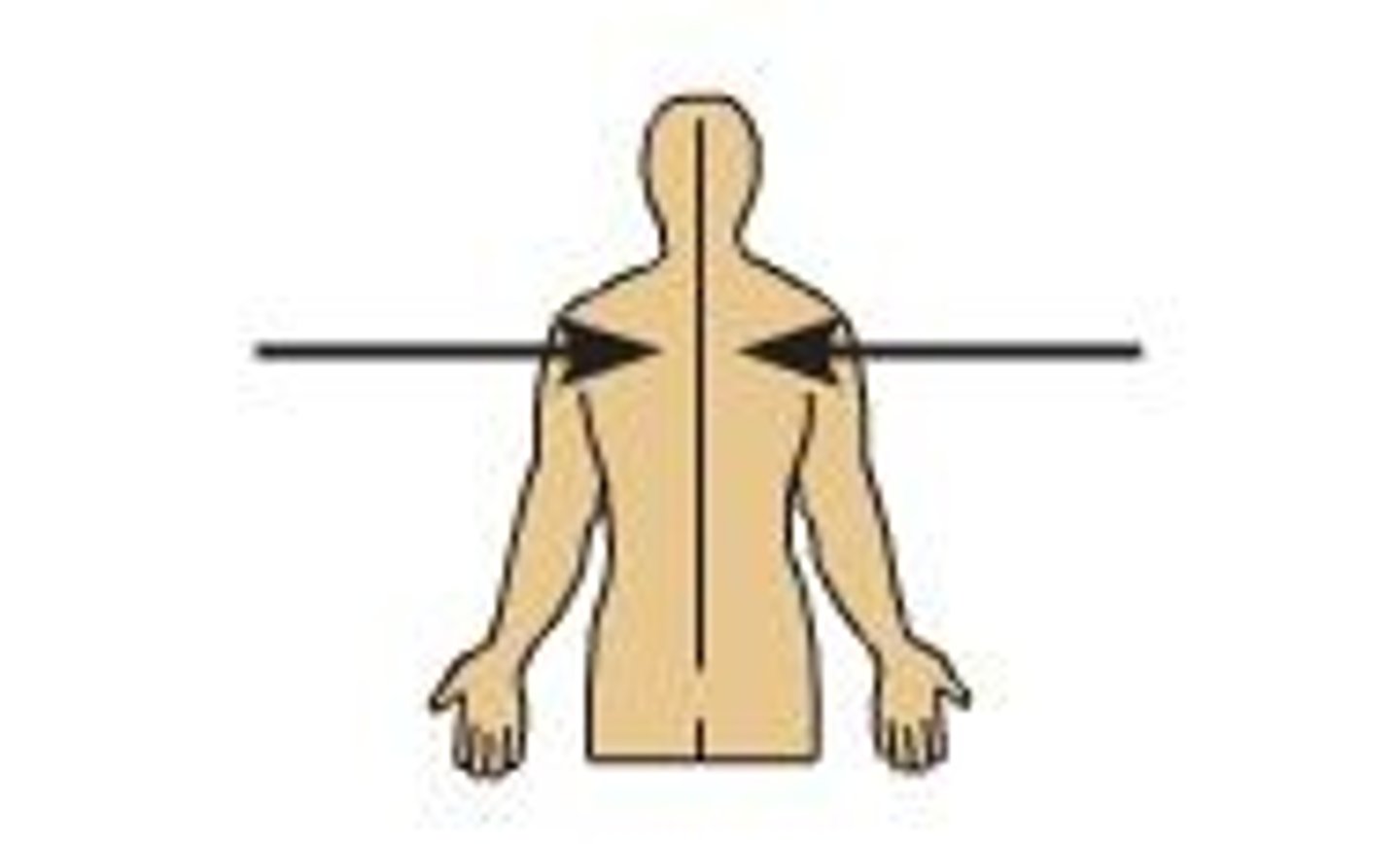
lateral
Away from the midline of the body
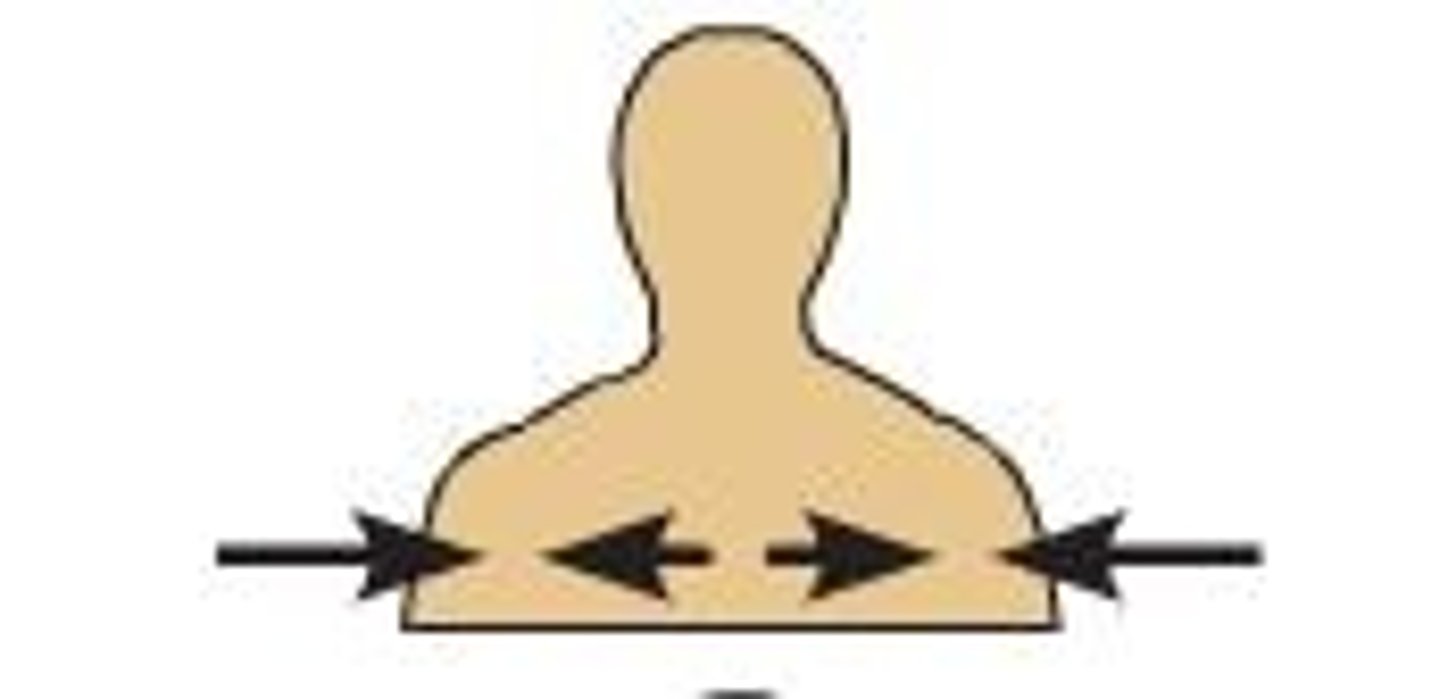
intermediate
between a more medial and a more lateral structure
proximal
Closer to the origin of the body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk
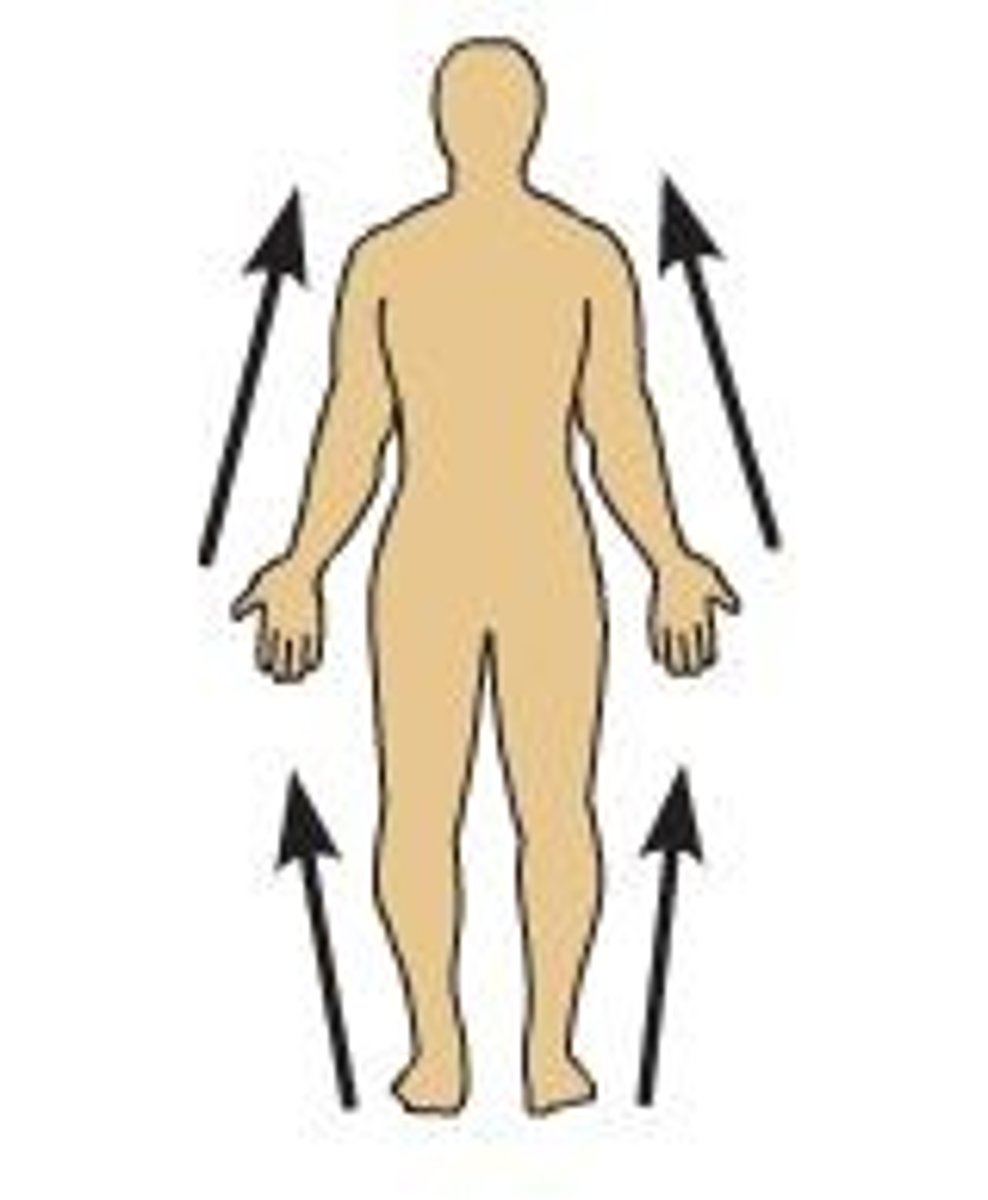
distal
farther from the origin of a body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk
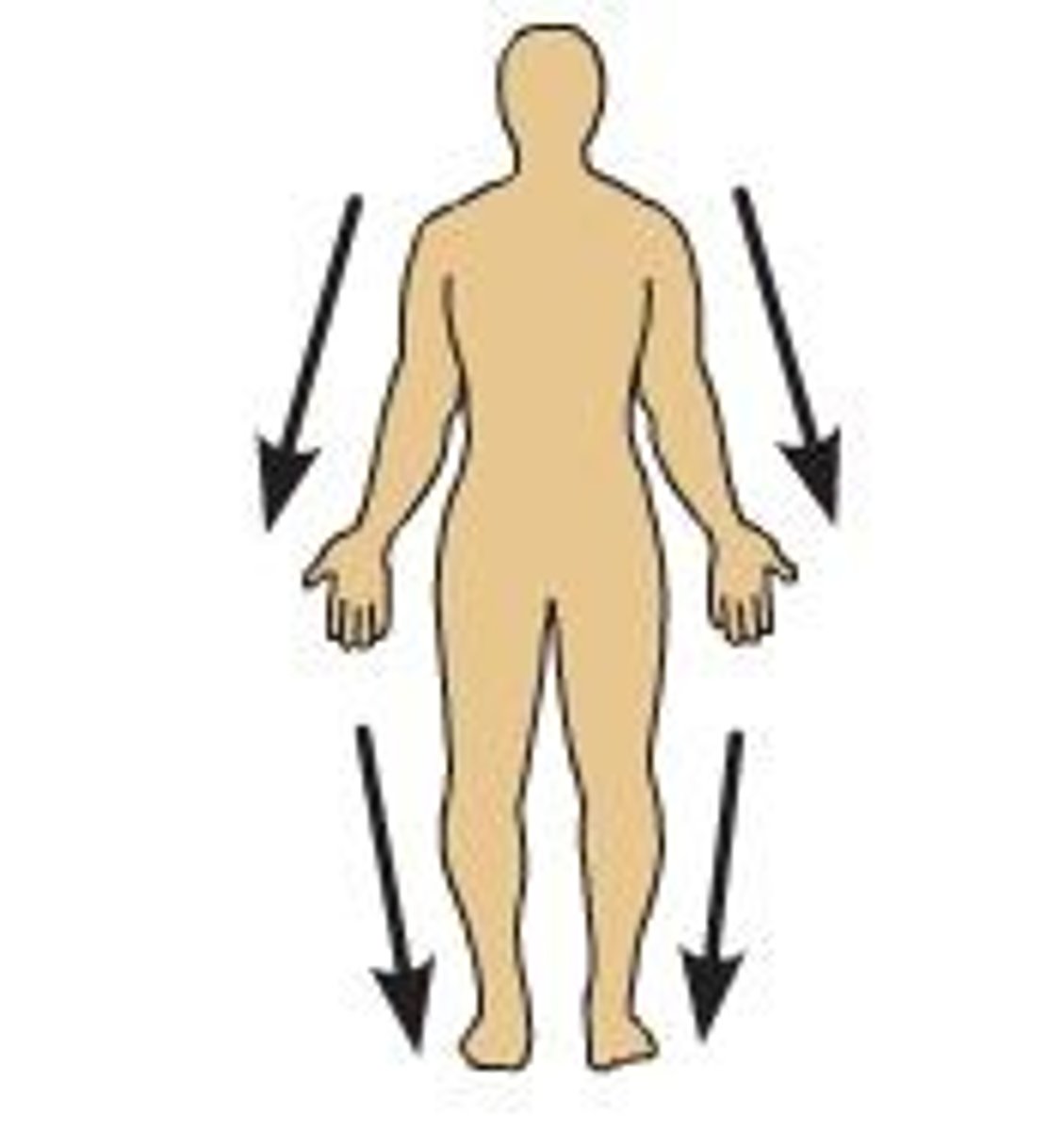
superficial
toward or at the body surface
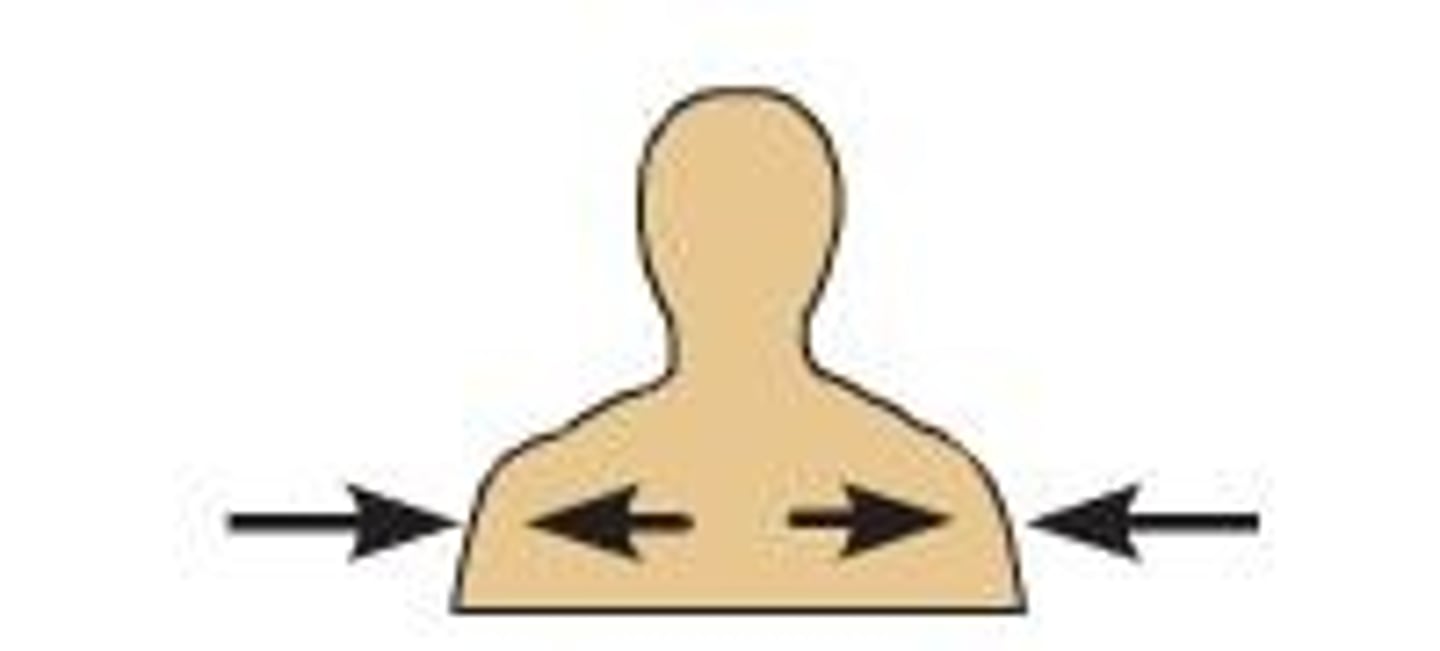
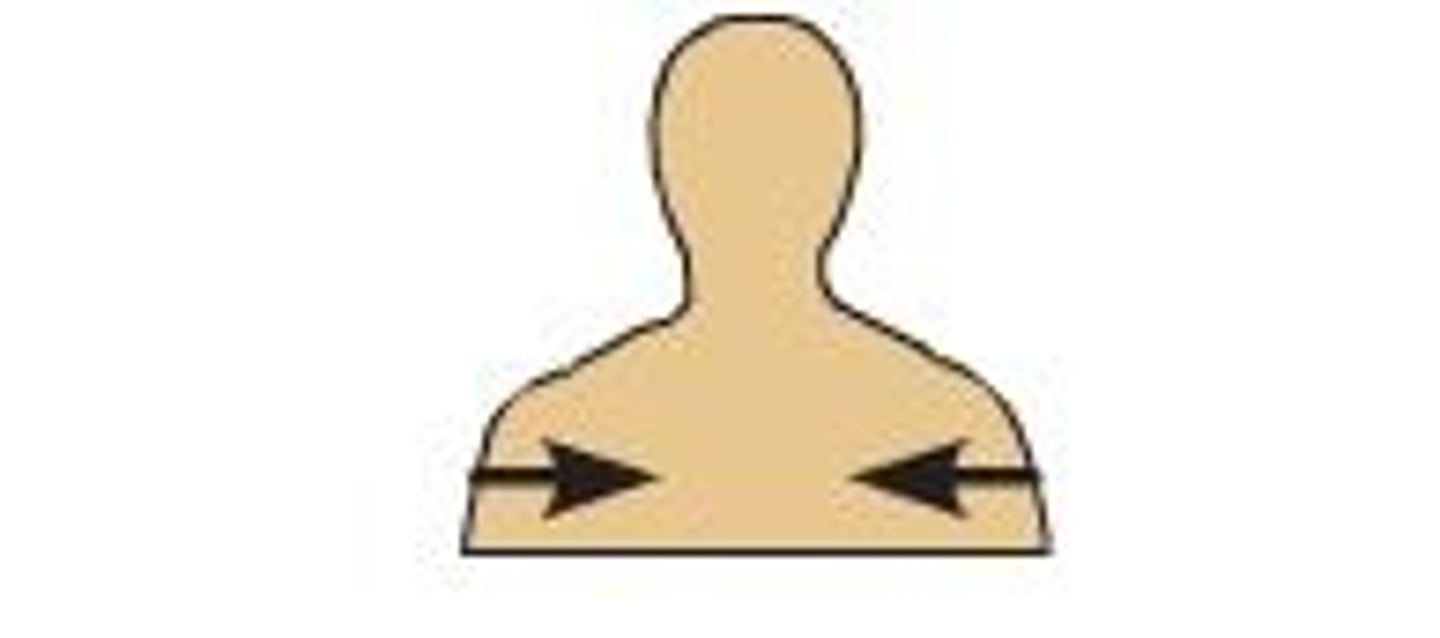
deep
Away from the body surface; more internal
flexion
movement that decreases joint angle
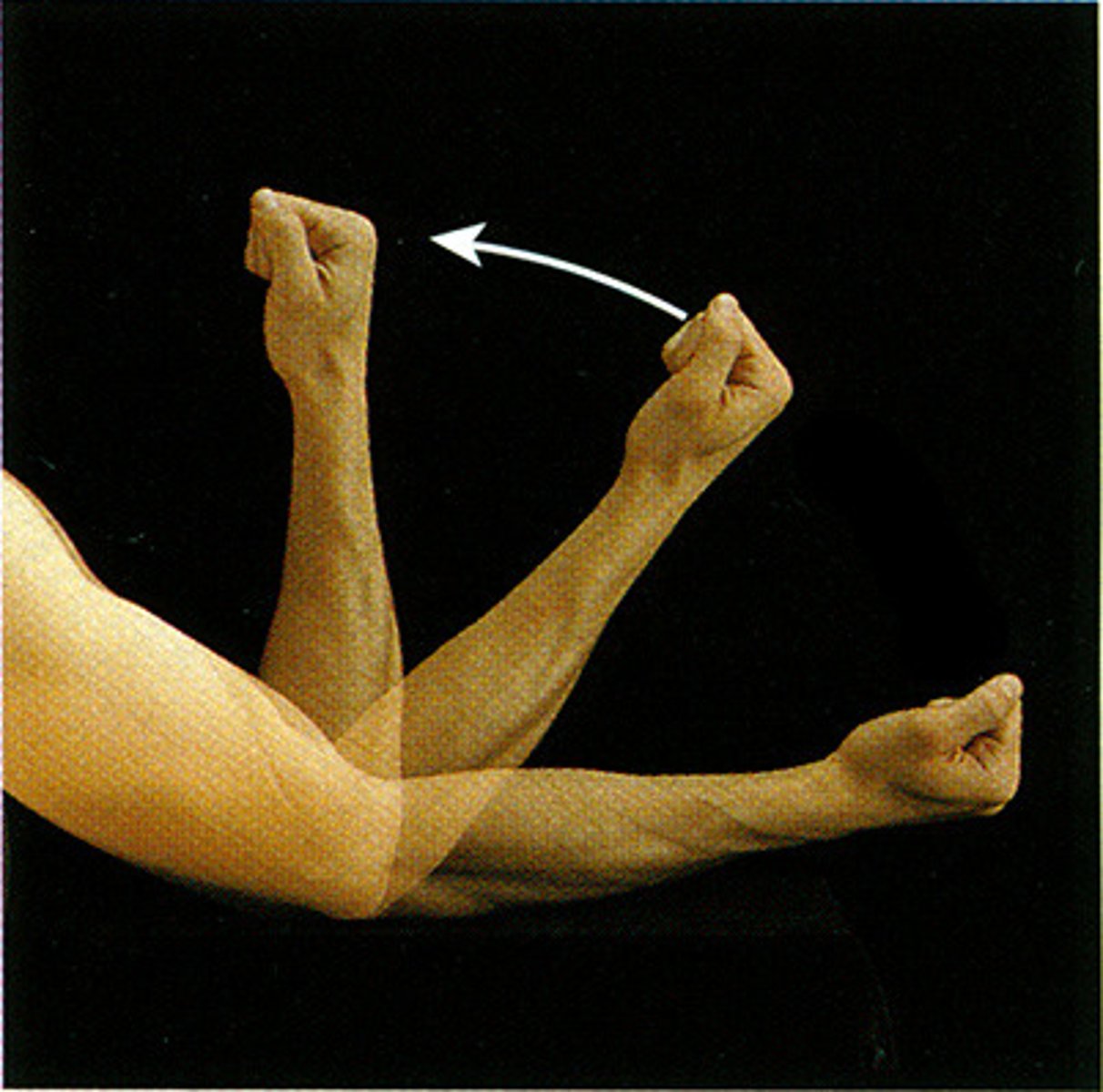
extension
movement that increases the angle of a joint
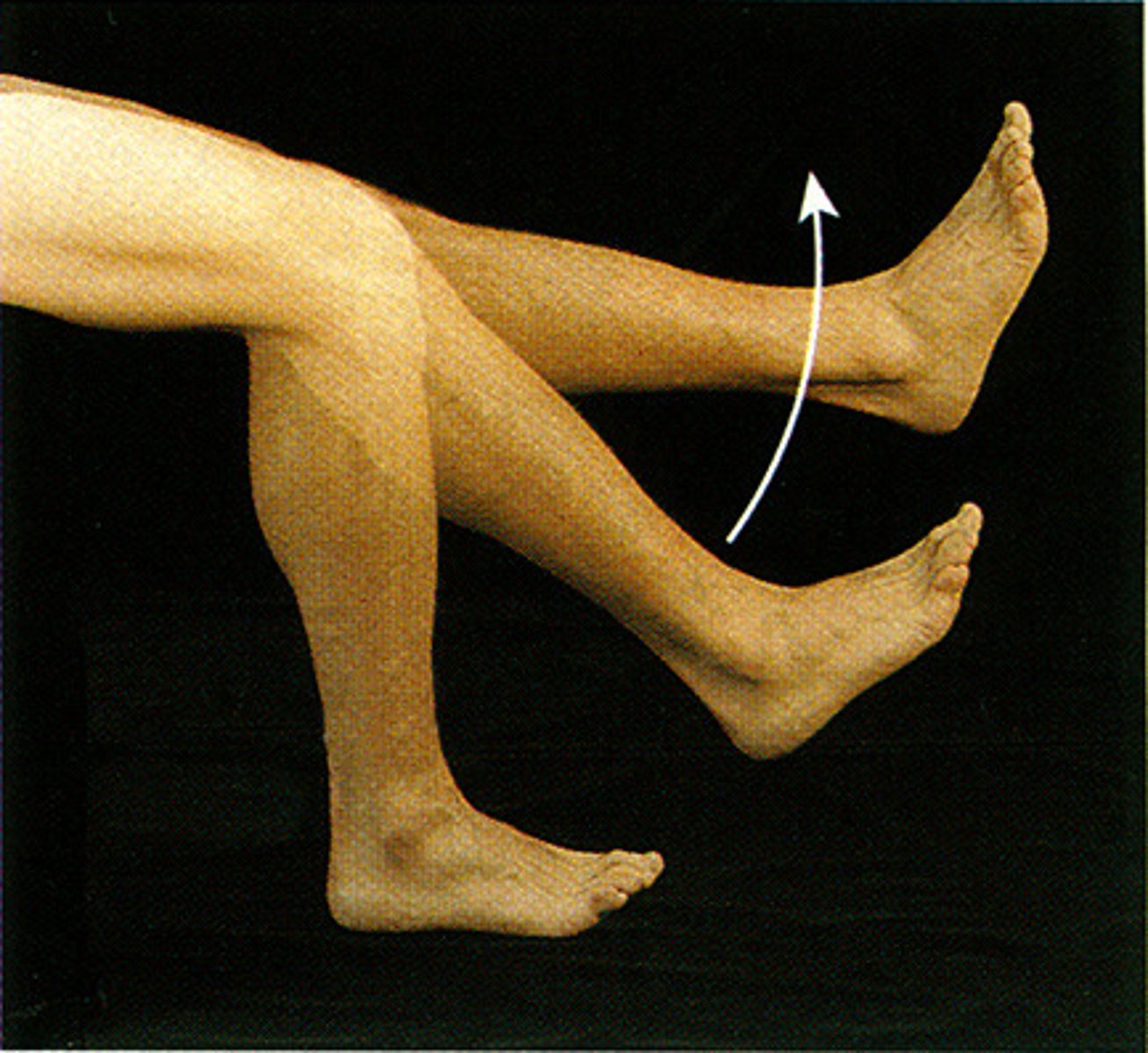
hyperextension
extension that is greater than 180 deg
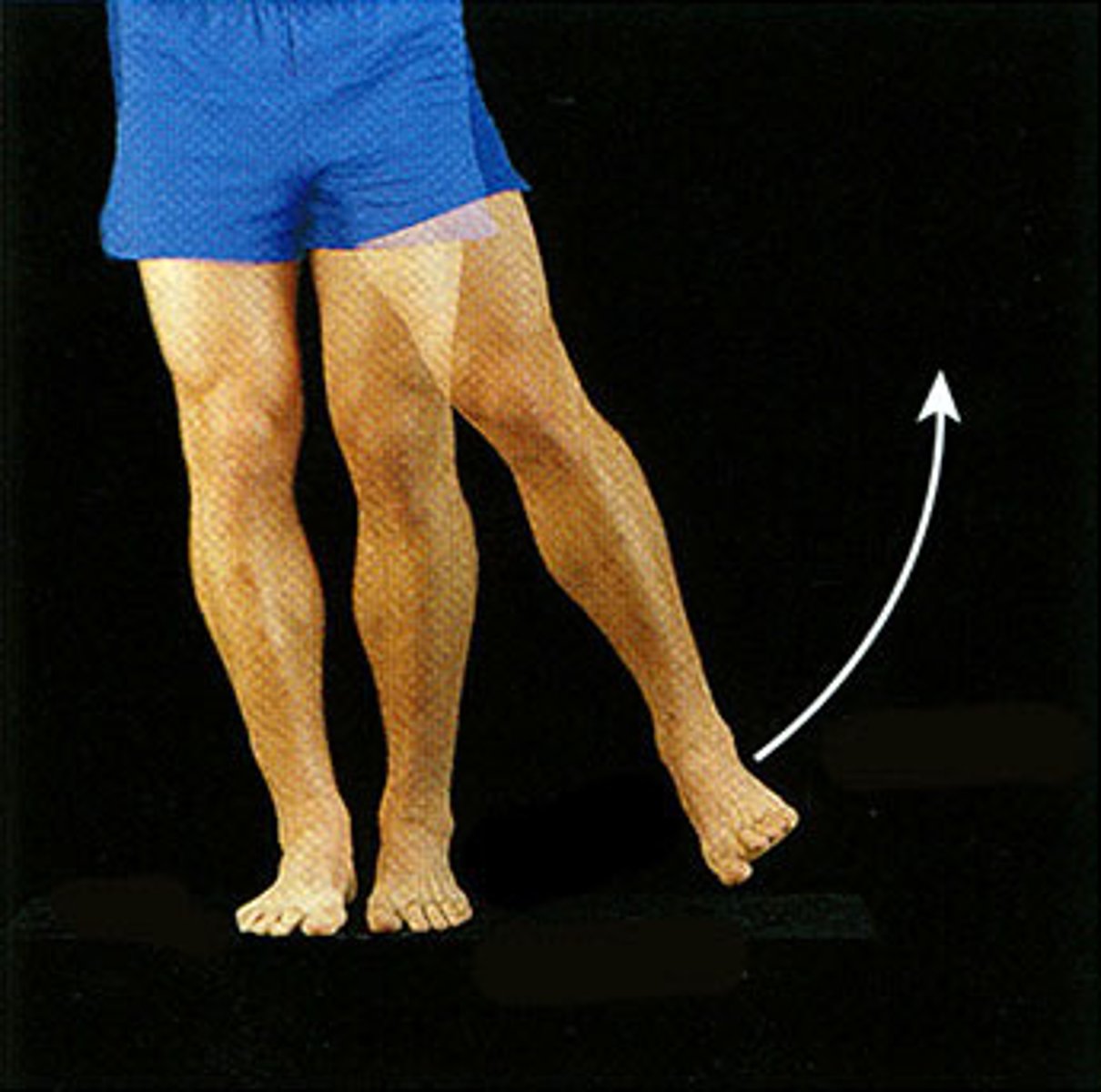
abduction
moving a limb away from the midline of the body
adduction
opposite of abduction; movement of a limb toward the body midline

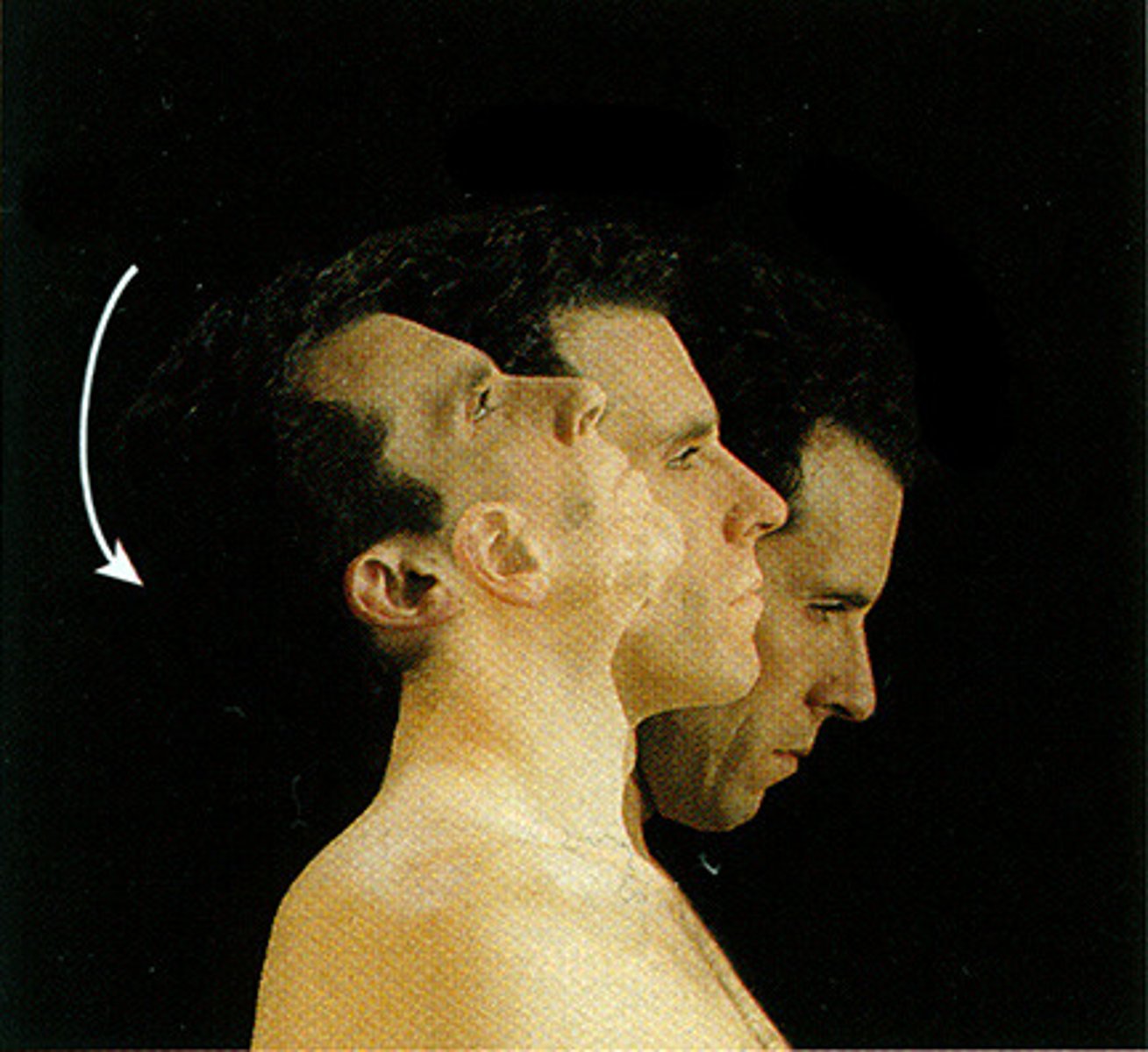
rotation
movement of a bone around its longitudinal axis
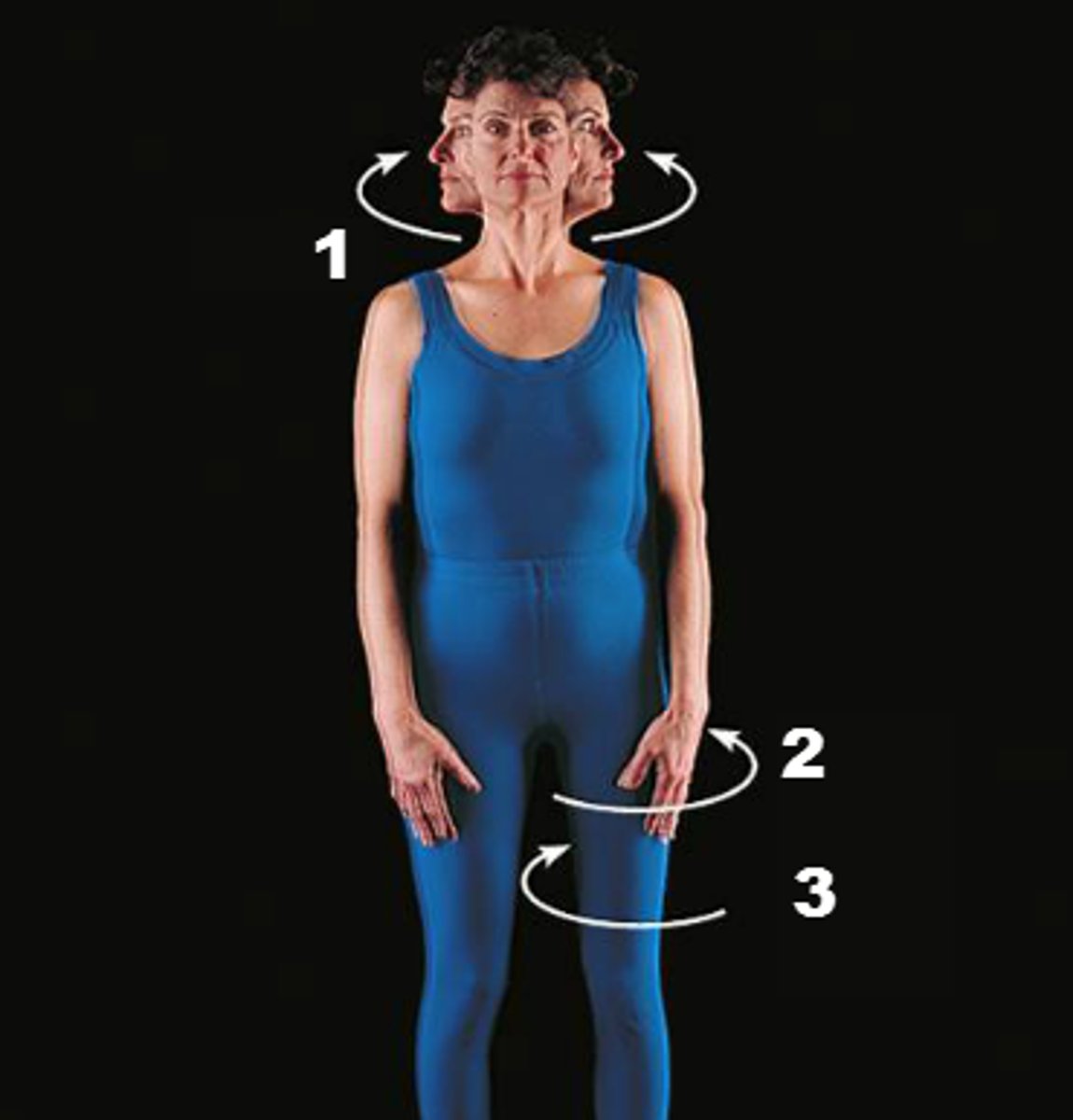
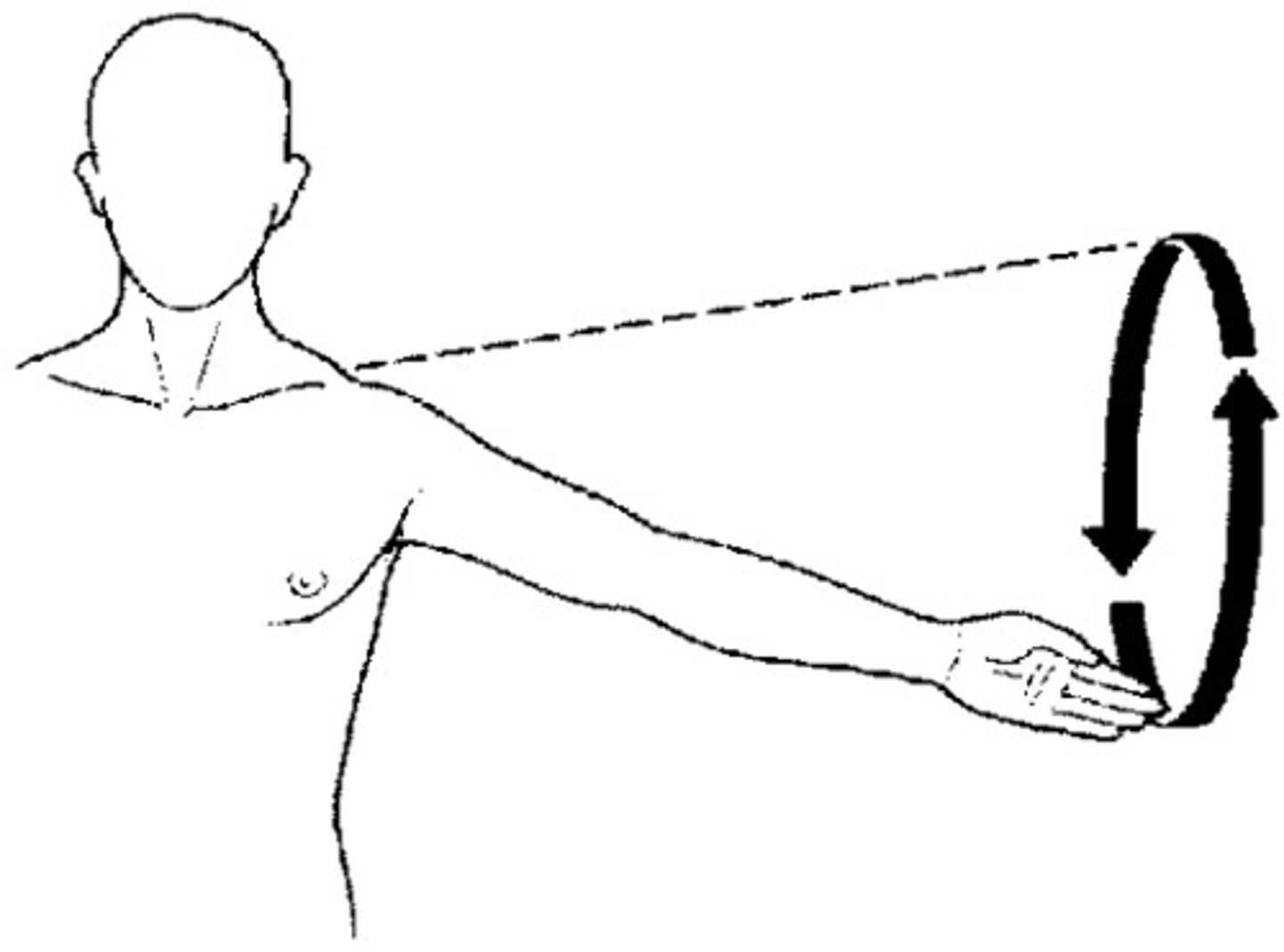
circumduction
combination of flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction
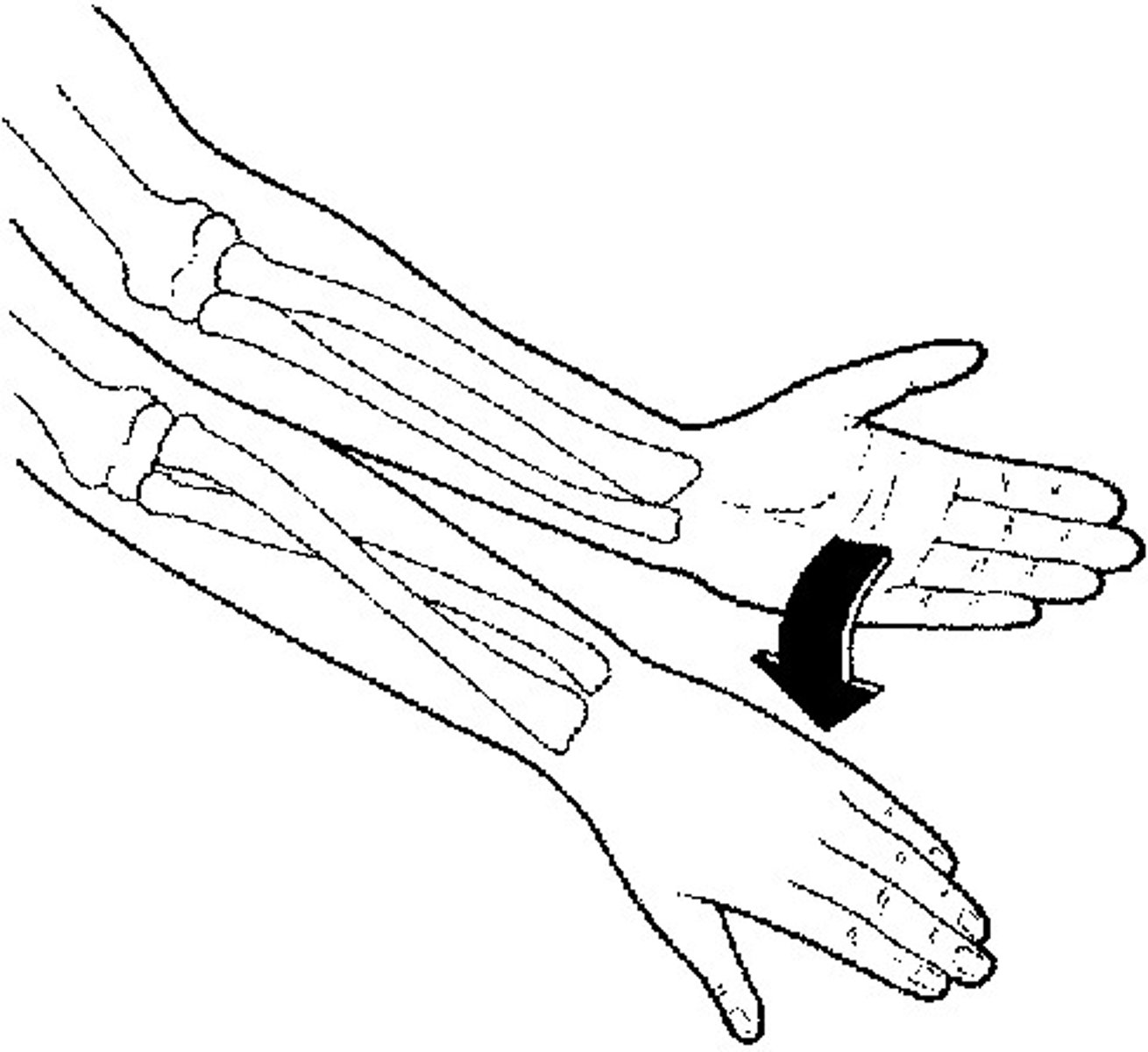
pronation
rotation of the hands and forearms so that the palms face downward
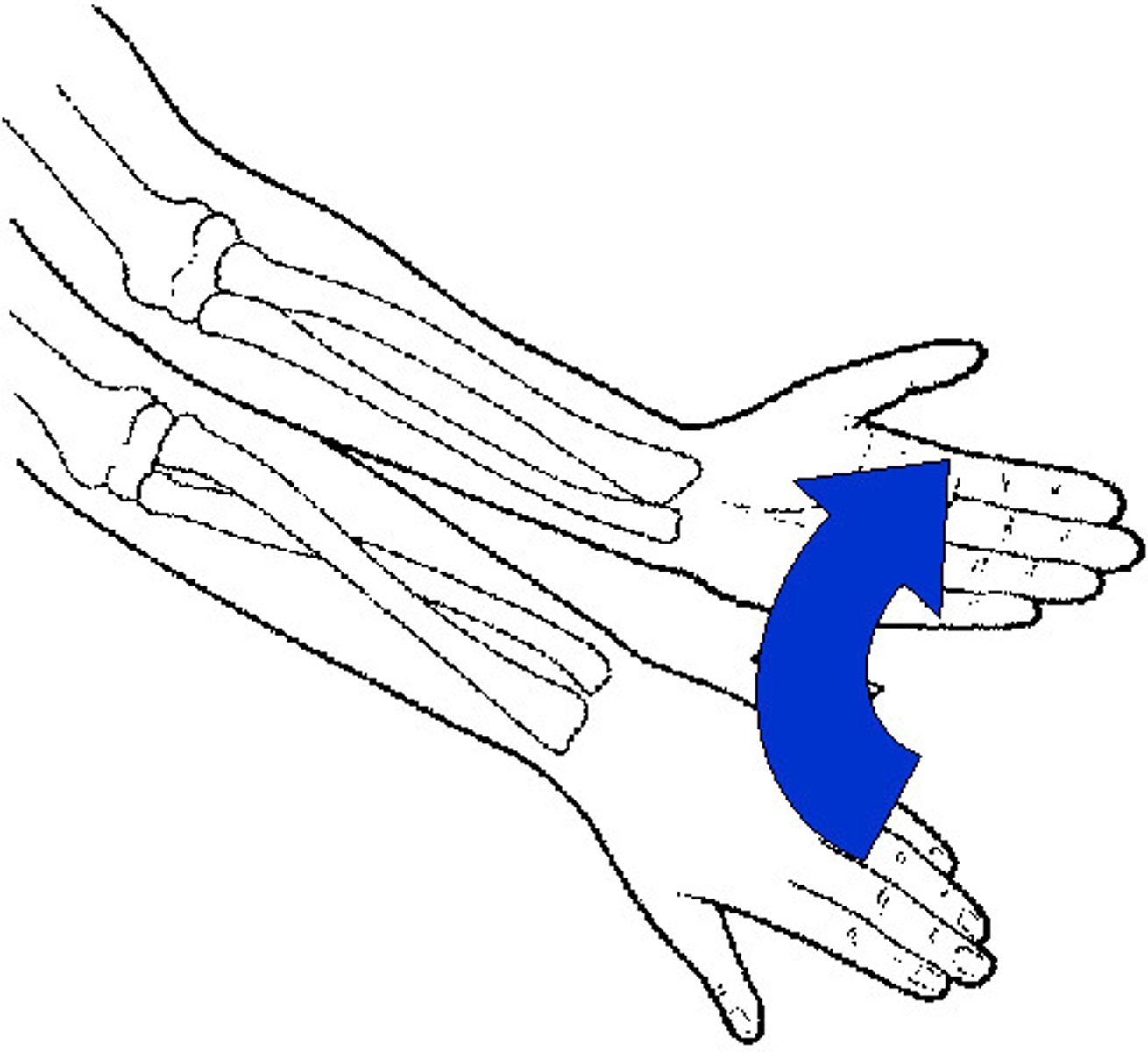
supination
rotation of the forearm and hand so that the palm faces anteriorly
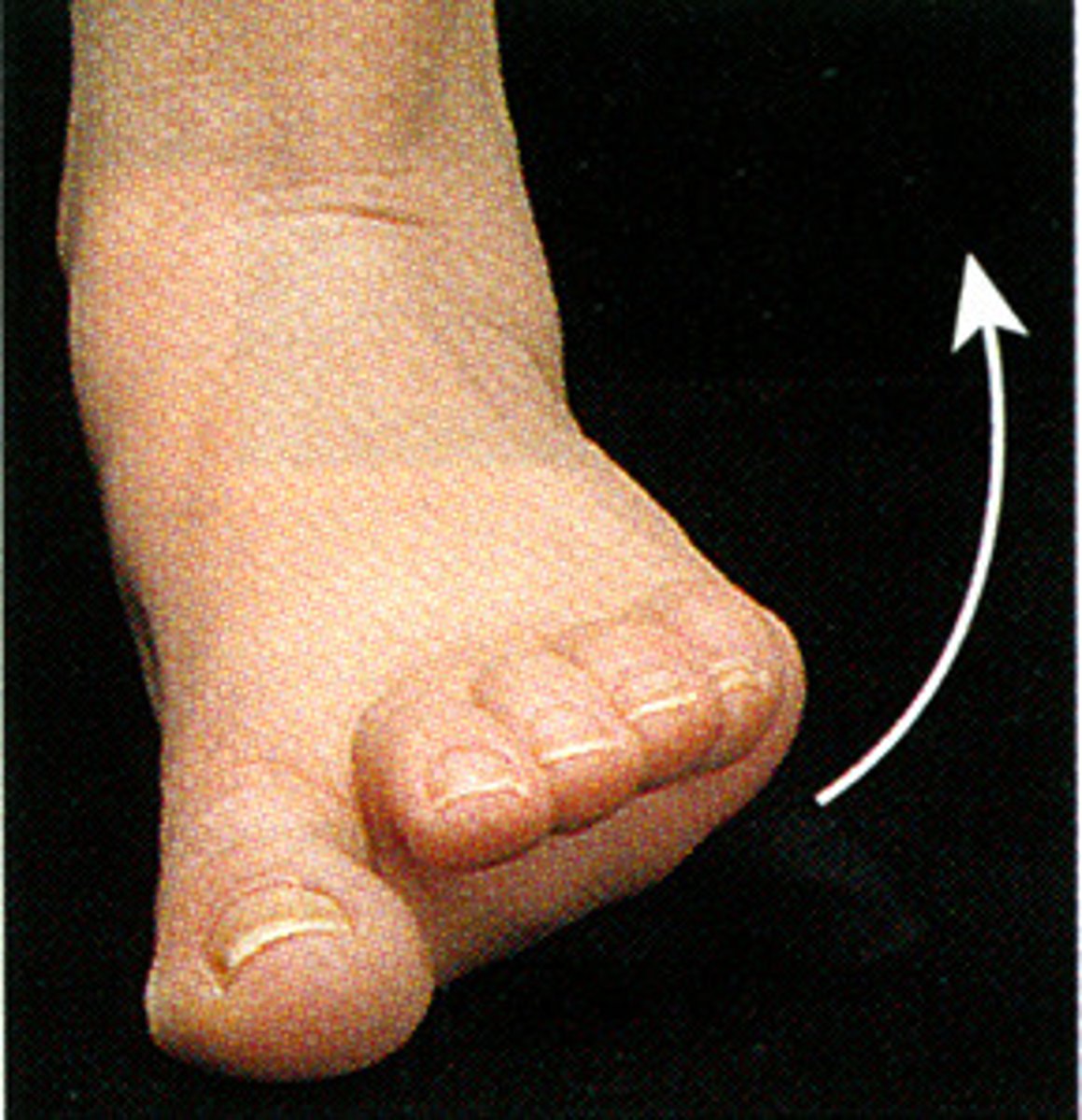
inversion
Turning the sole of the foot inward
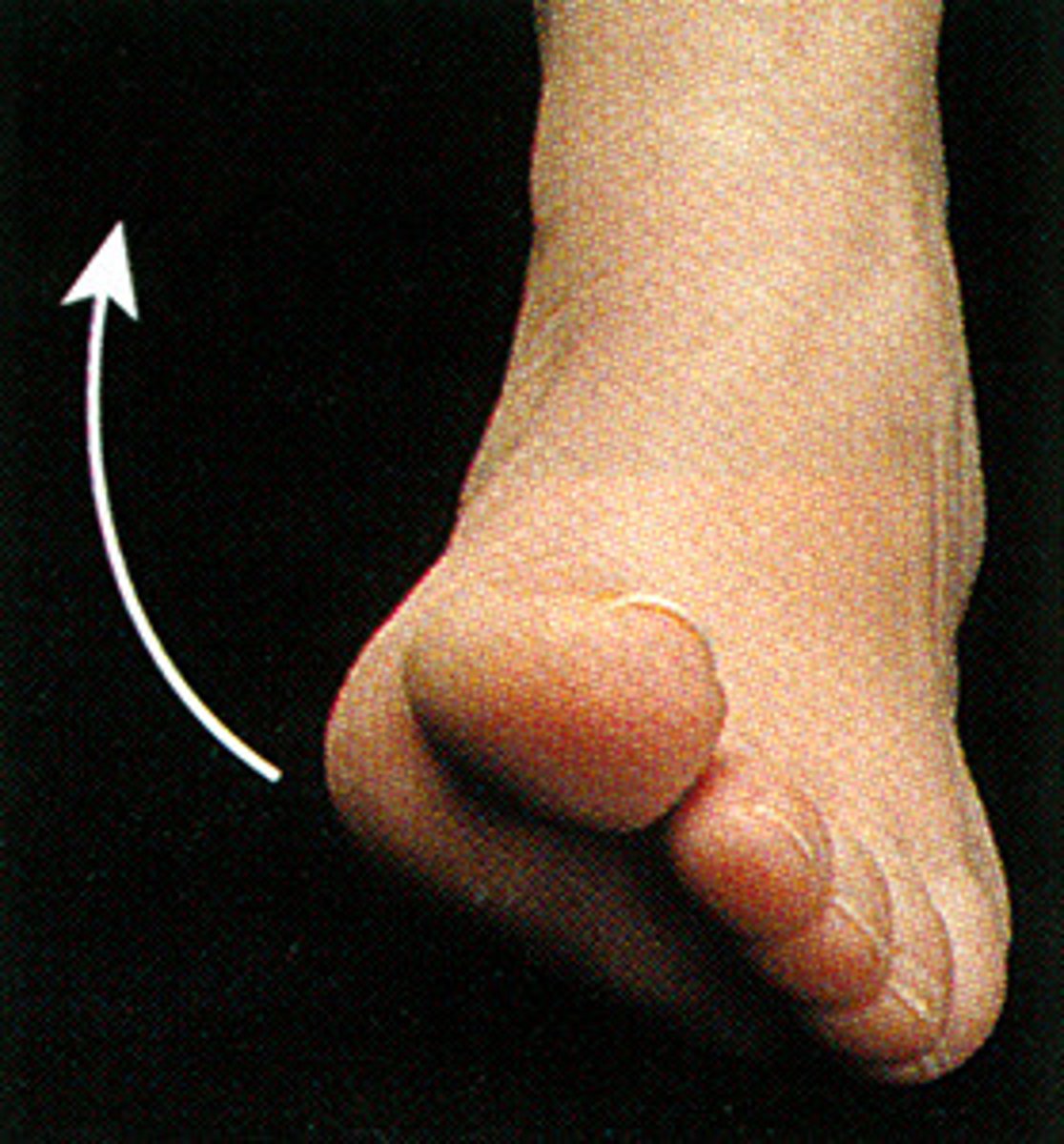
eversion
turning the sole of the foot outward
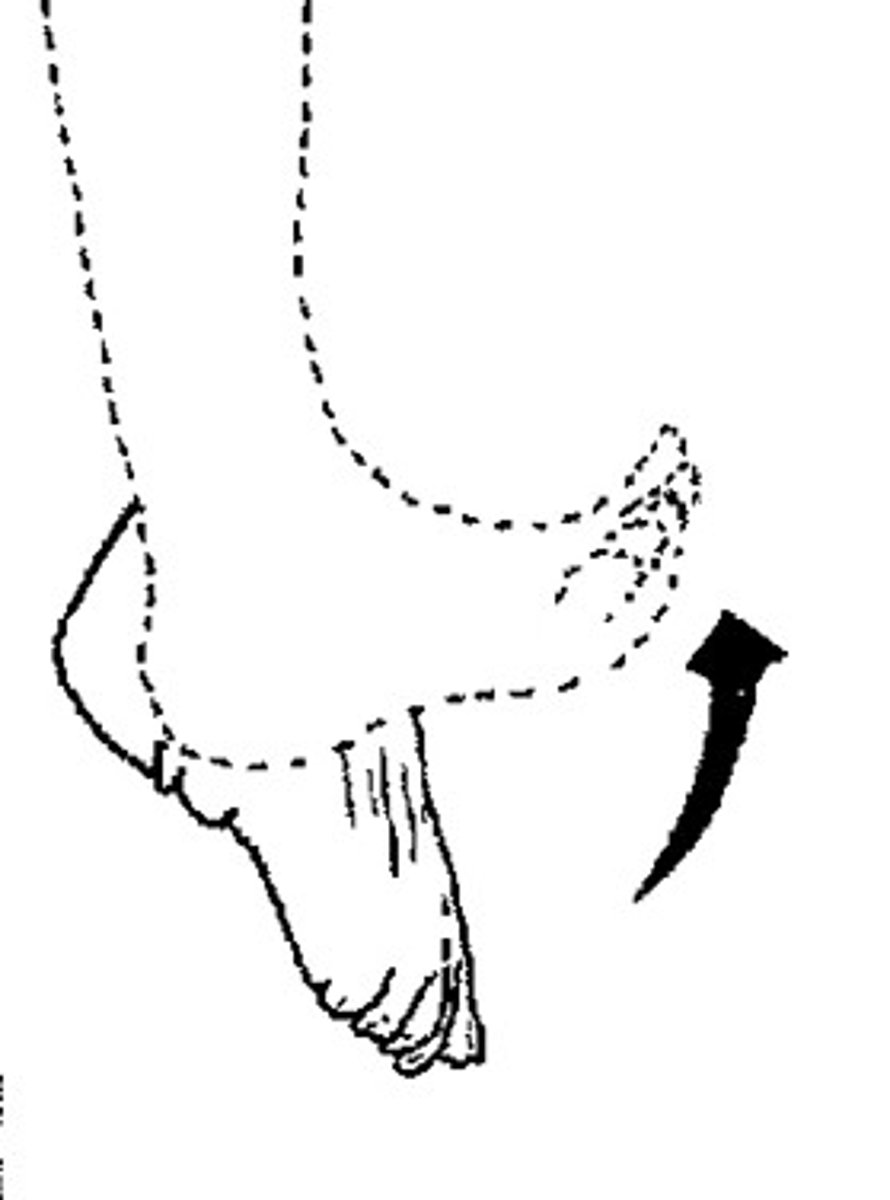
dosiflexion
movement at the ankle that moves the instep of the foot up
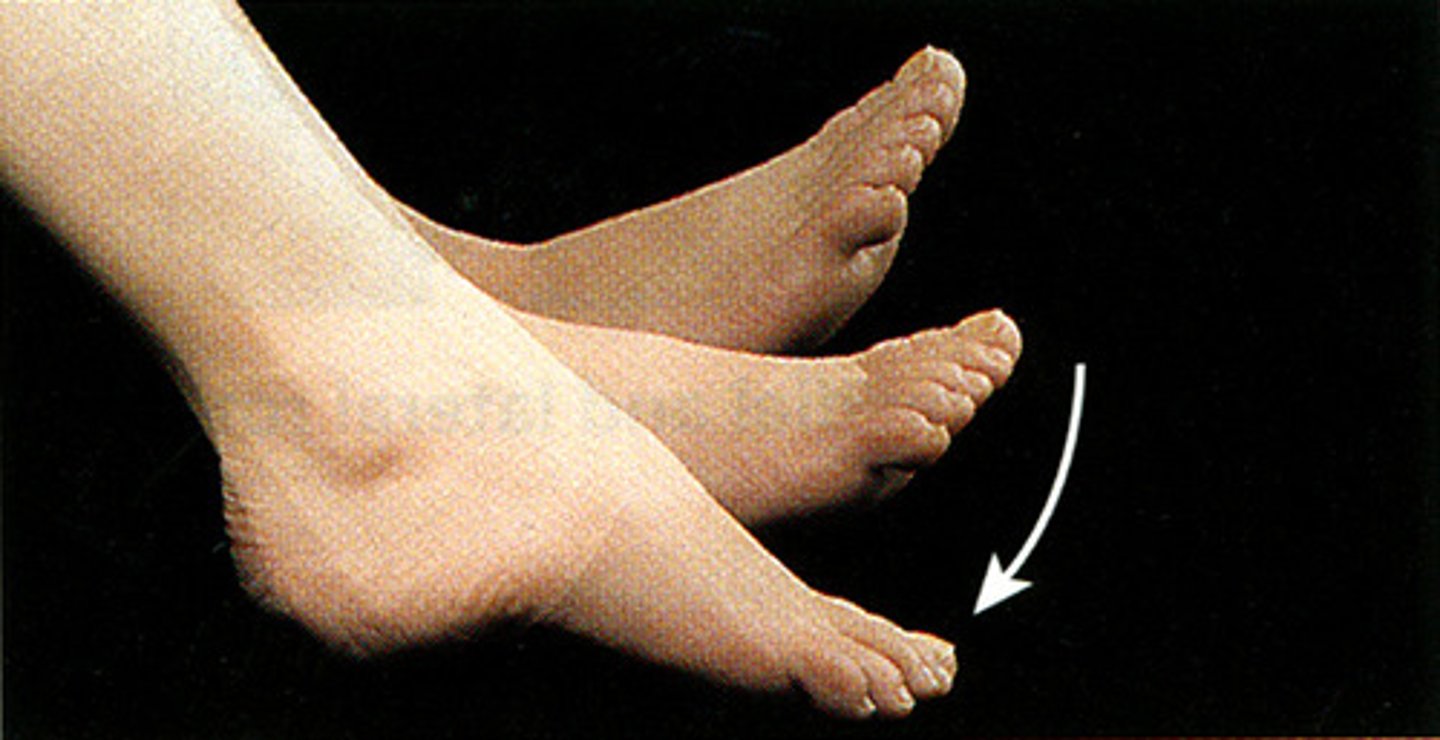
plantar flexion
straightens the ankle joint causing the toes to point downward
functions of bone
support, protection, movement, storage, blood cell formation
clavicle
collar bone
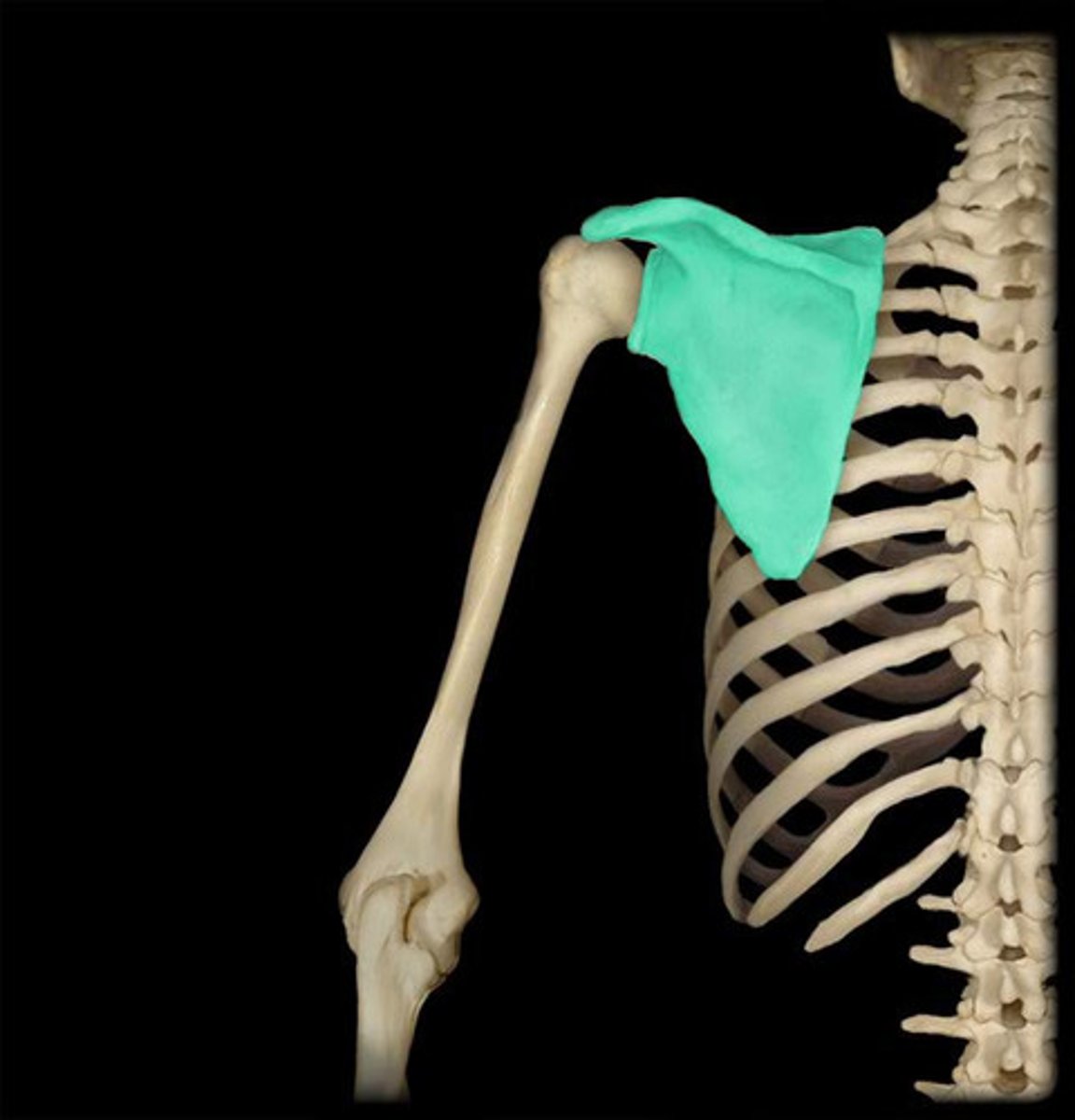
scapula
shoulder blade
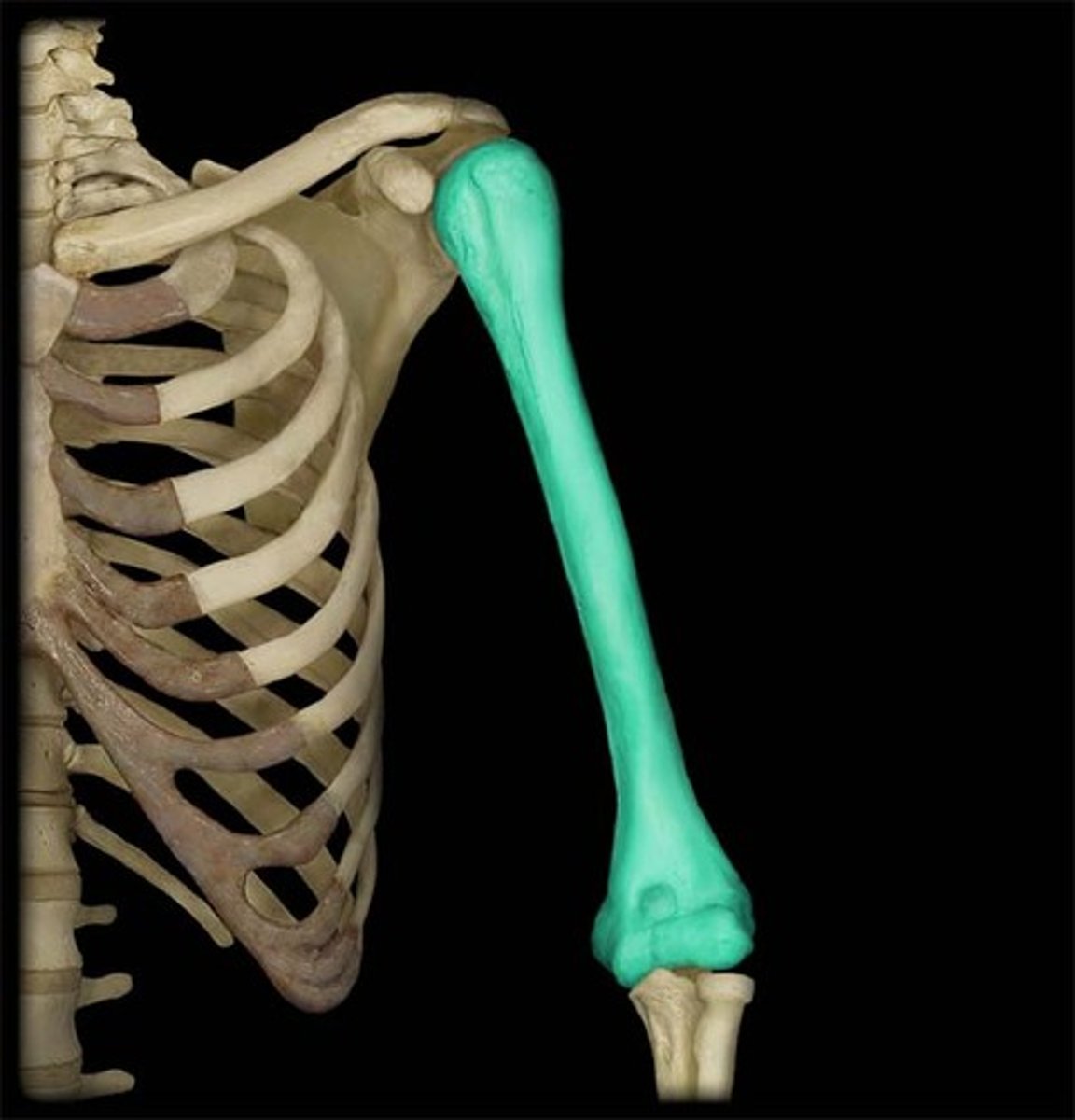
humerus
upper arm bone
ulna
medial bone of the forearm
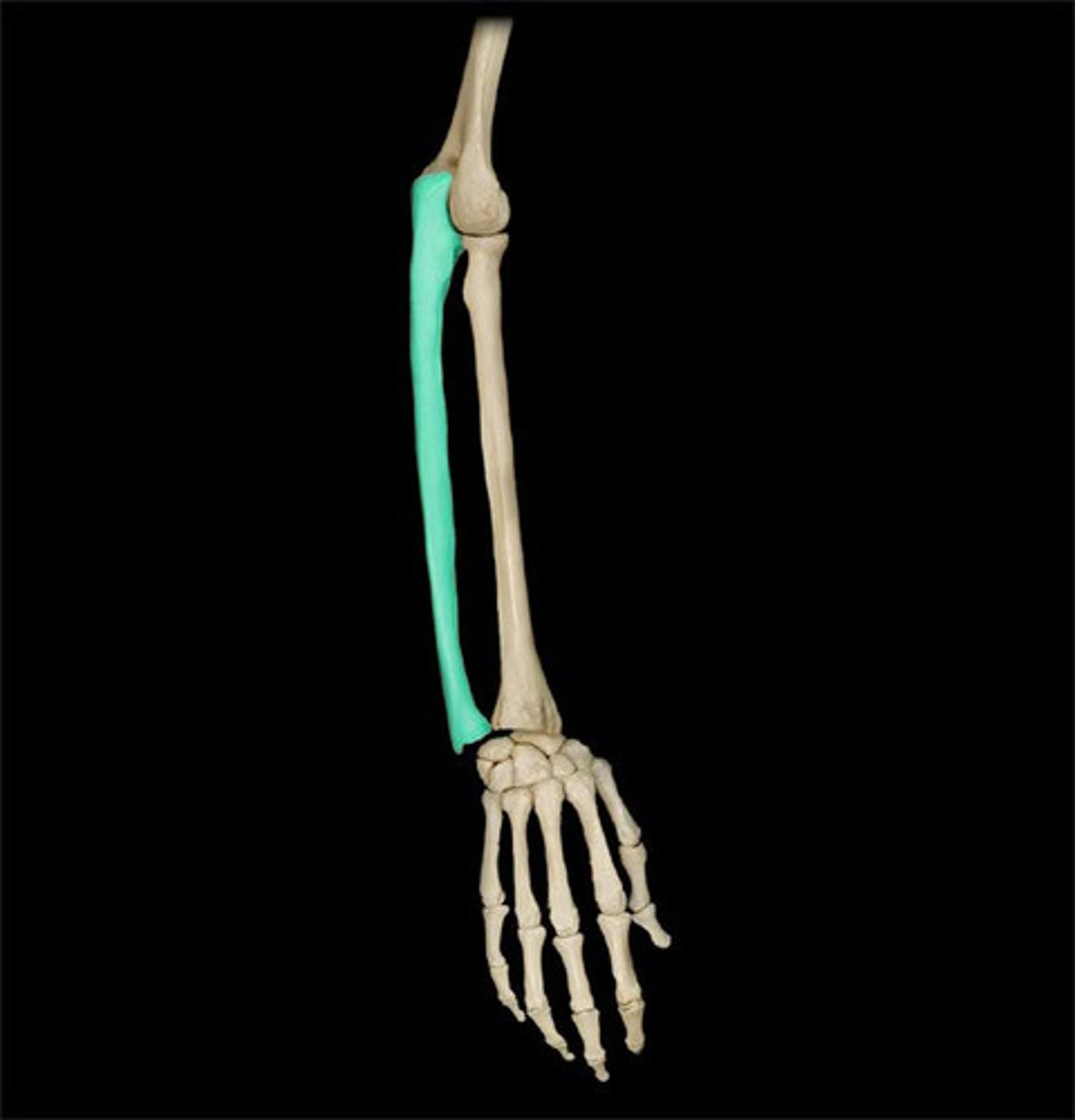
radius
lateral bone of the forearm
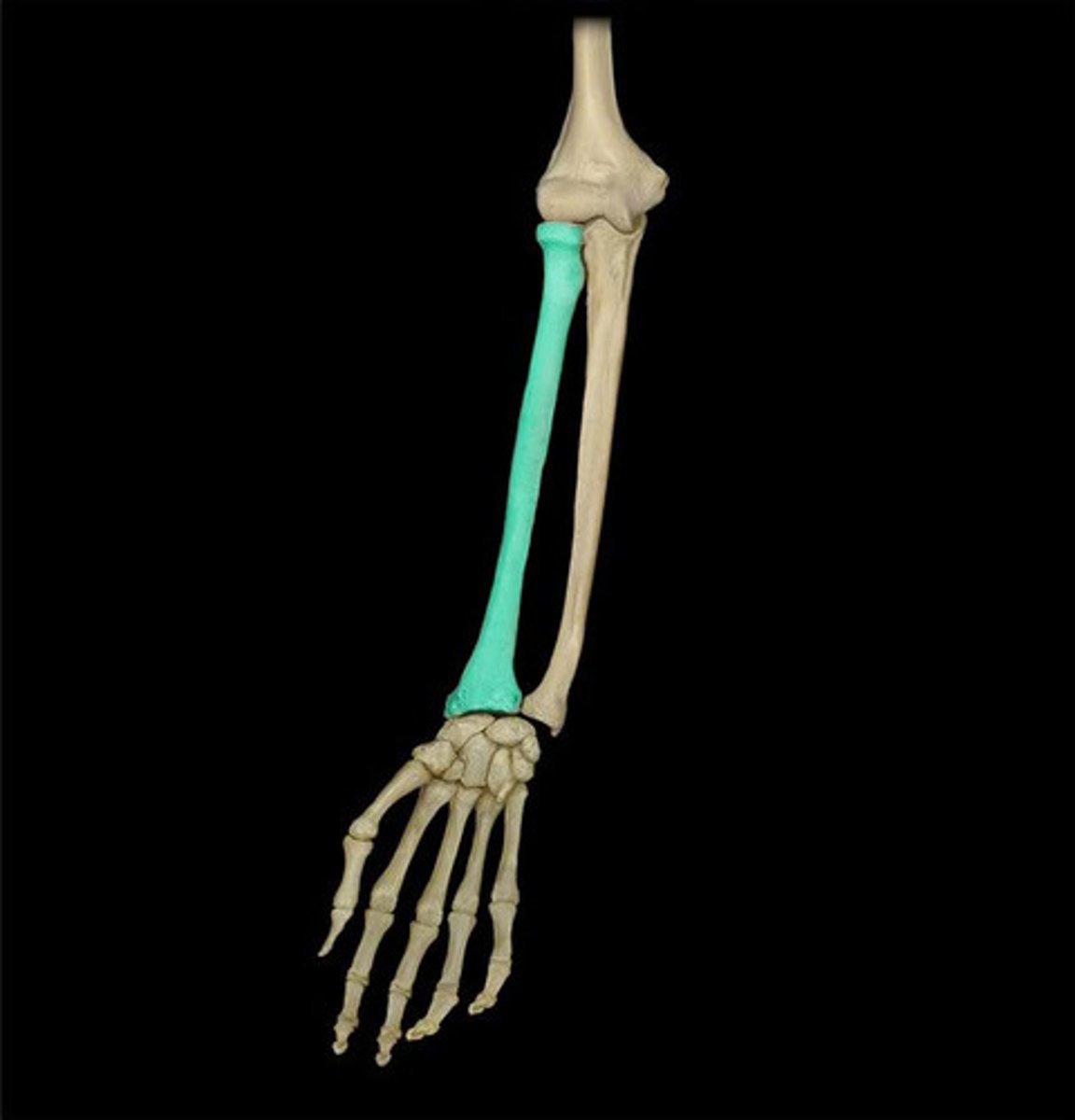
carpals
wrist bones
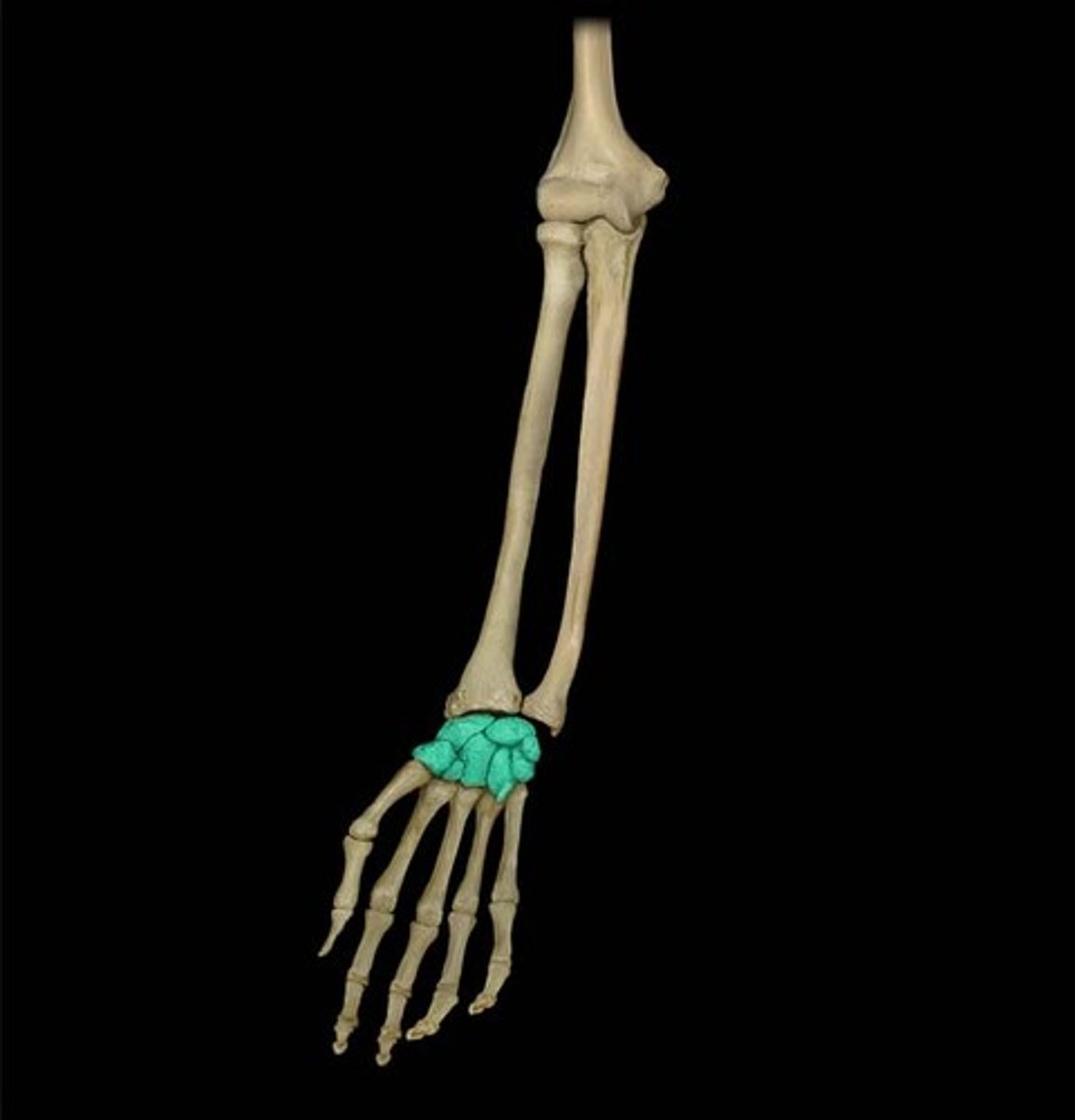
Metacarpals
hand bones
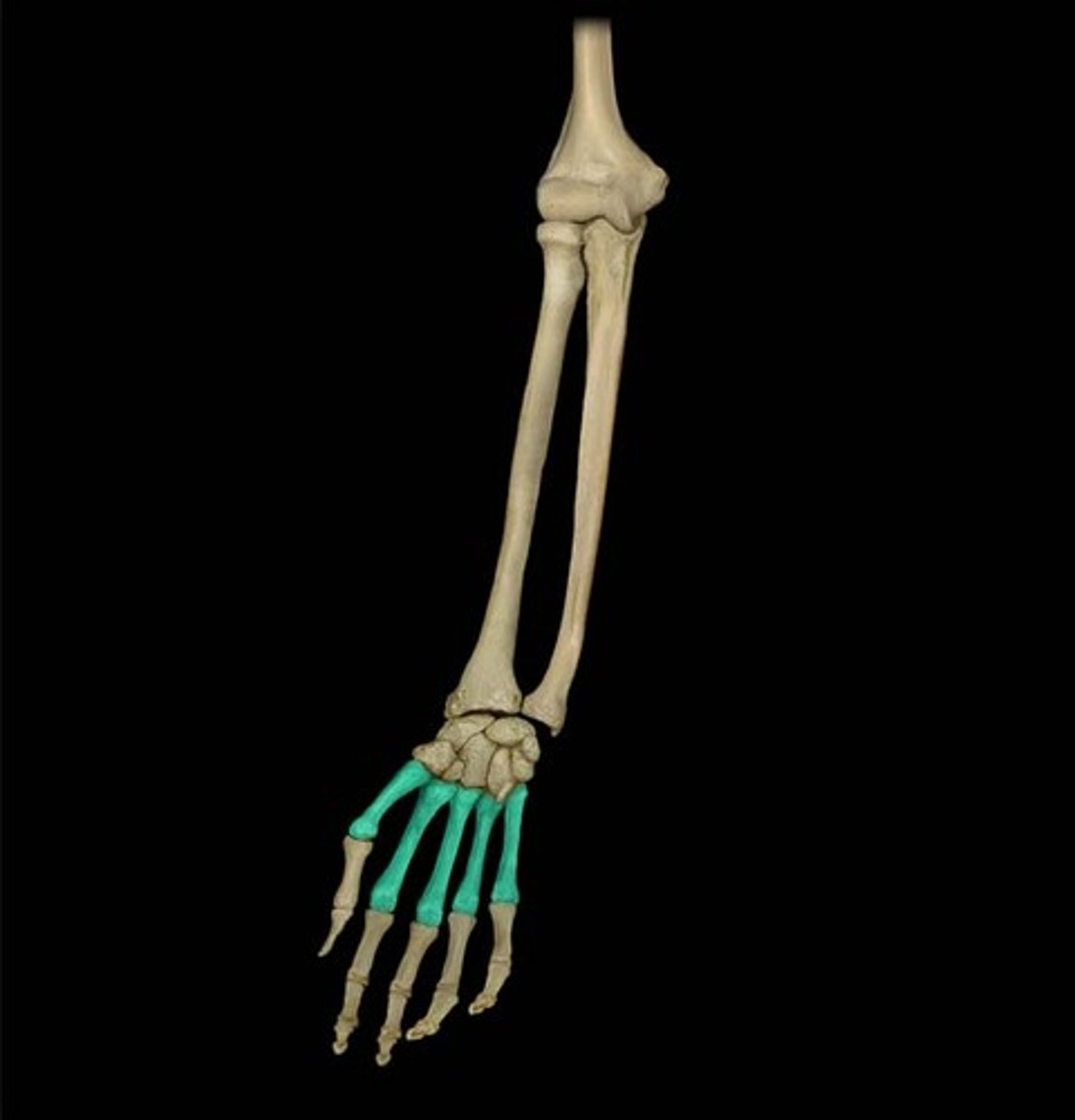
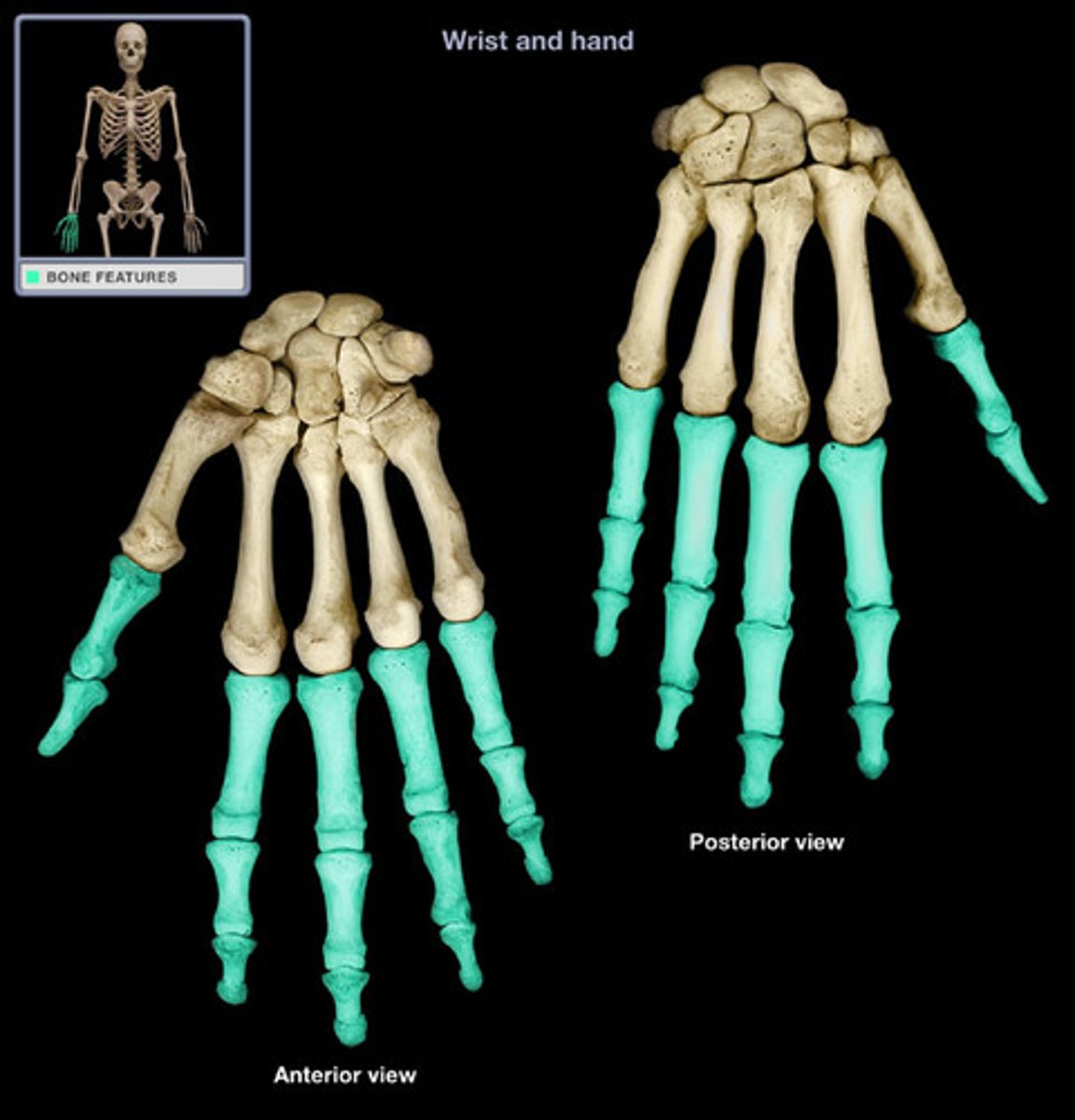
phalanges
fingers
pelvis
hip bone
femur
thigh bone
patella
kneecap
tibia
shin bone
fibula
calf bone
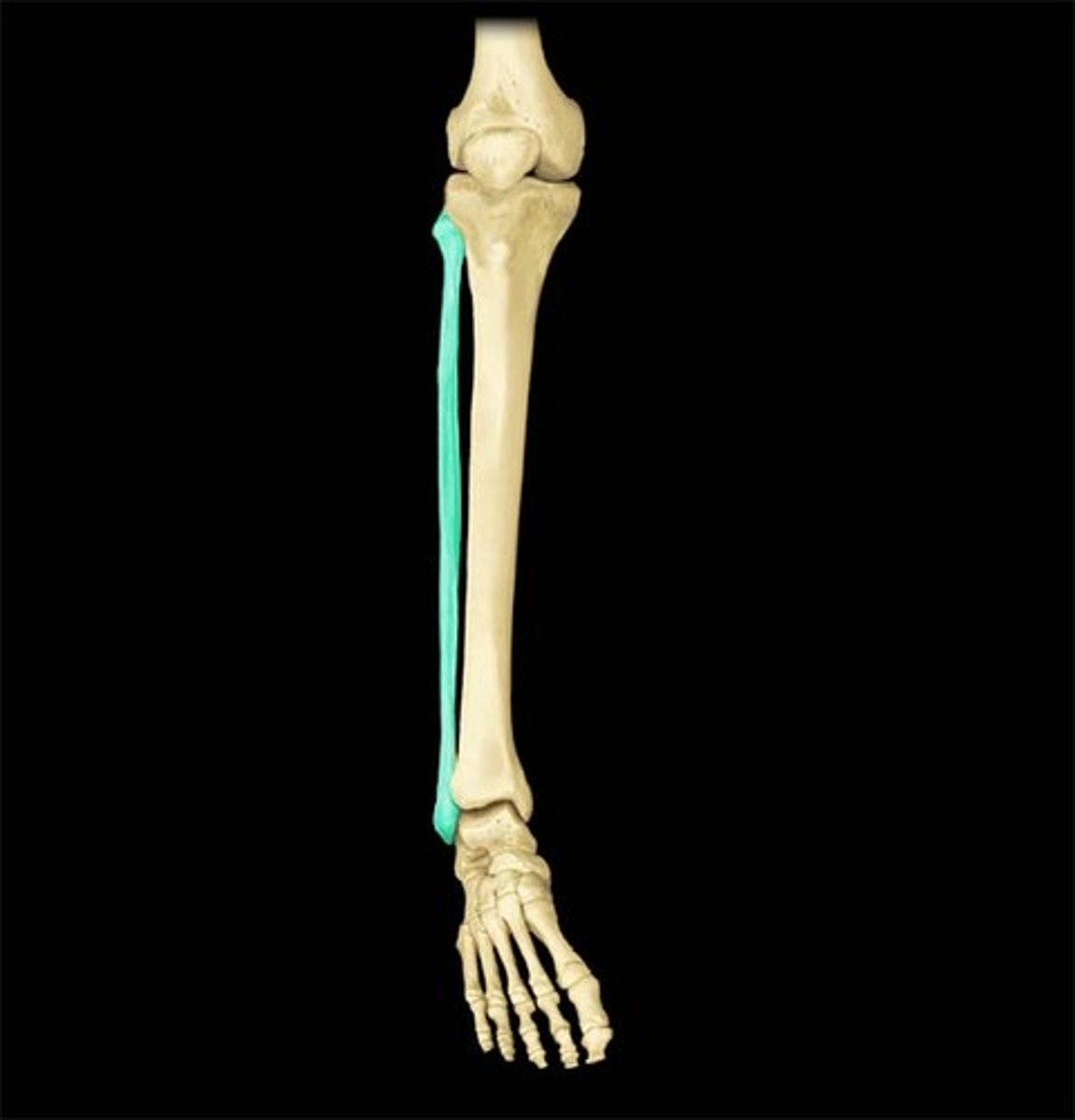
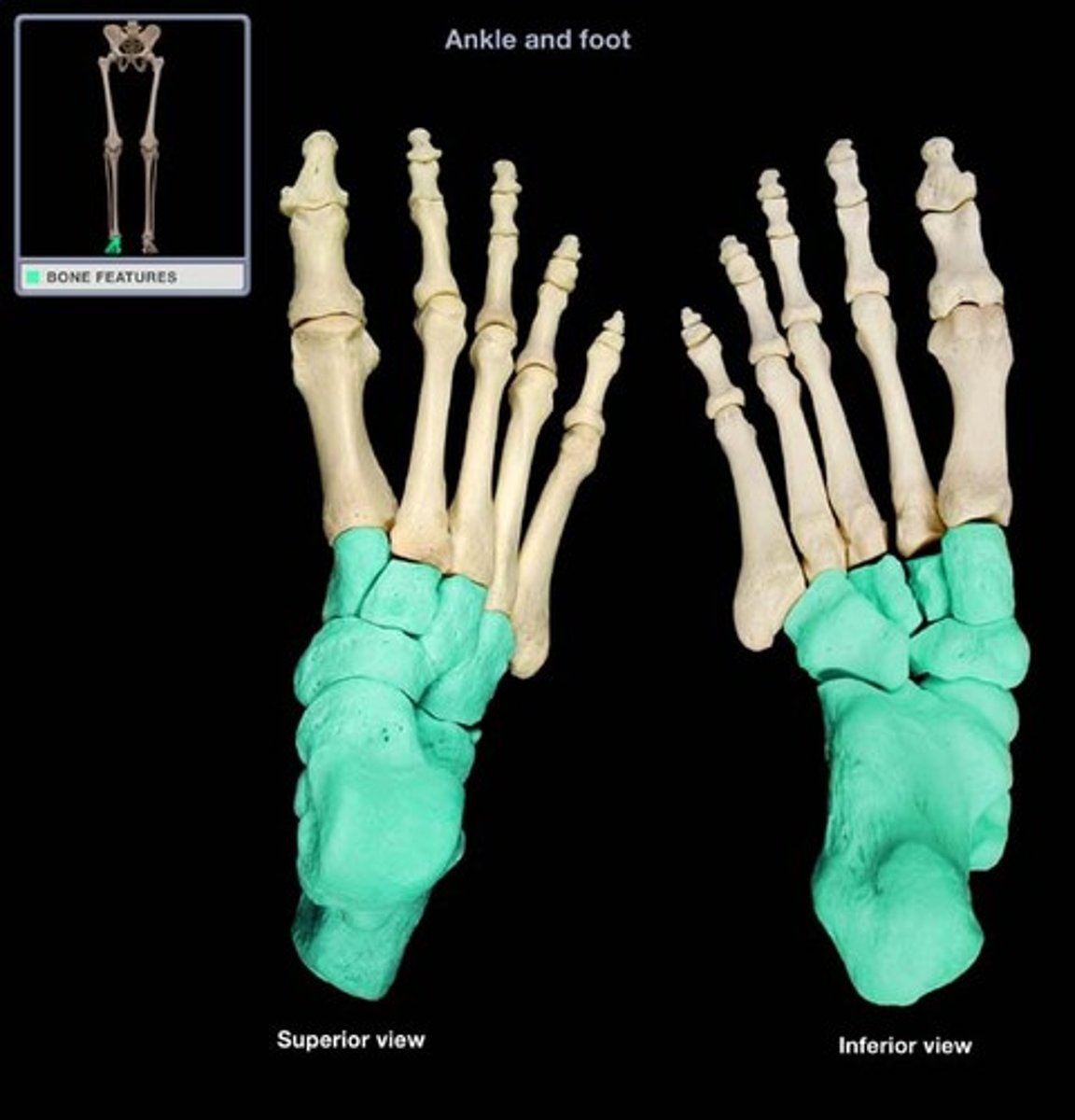
Tarsals
ankle bones
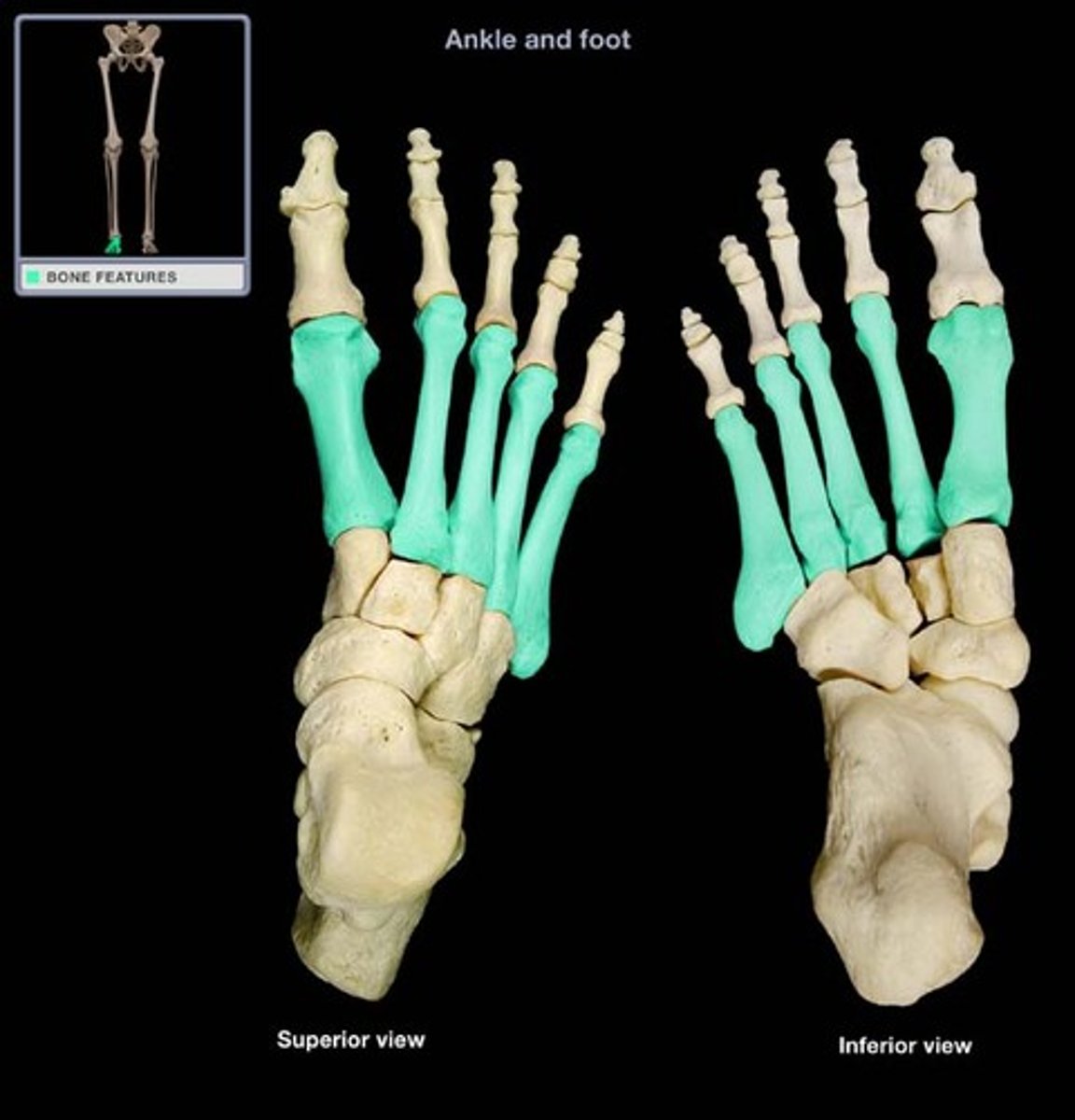
Metatarsals
foot bones
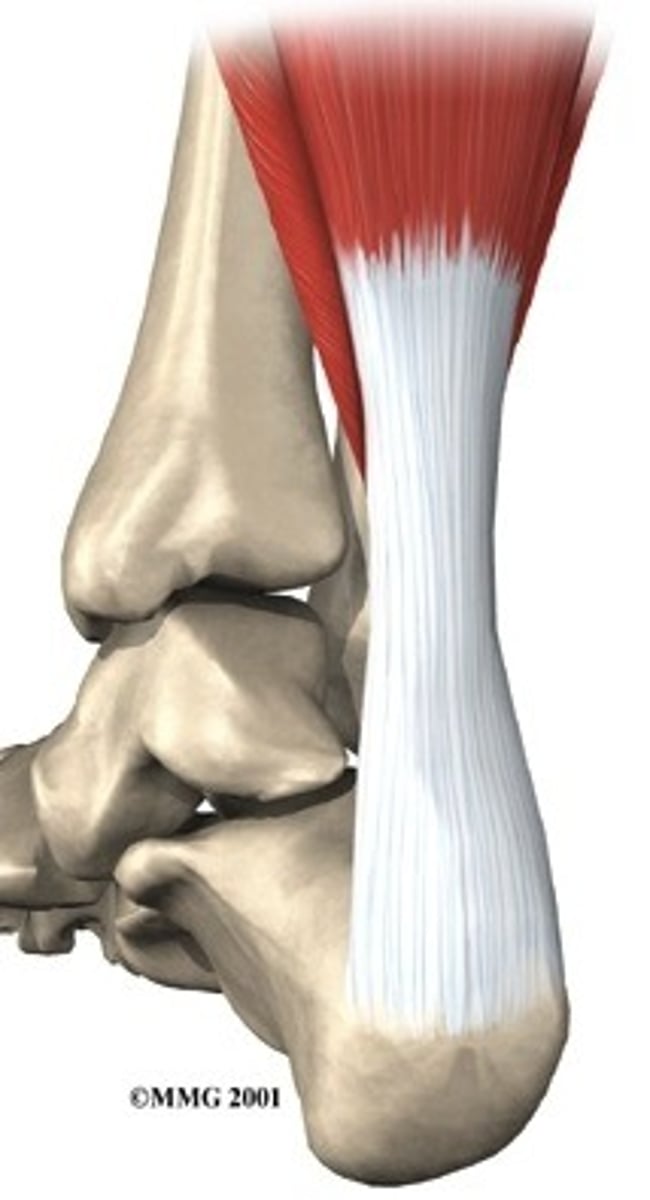
tendons
attach muscle to bone;flexible and shock absorbent
ligaments
Connect bone to bone
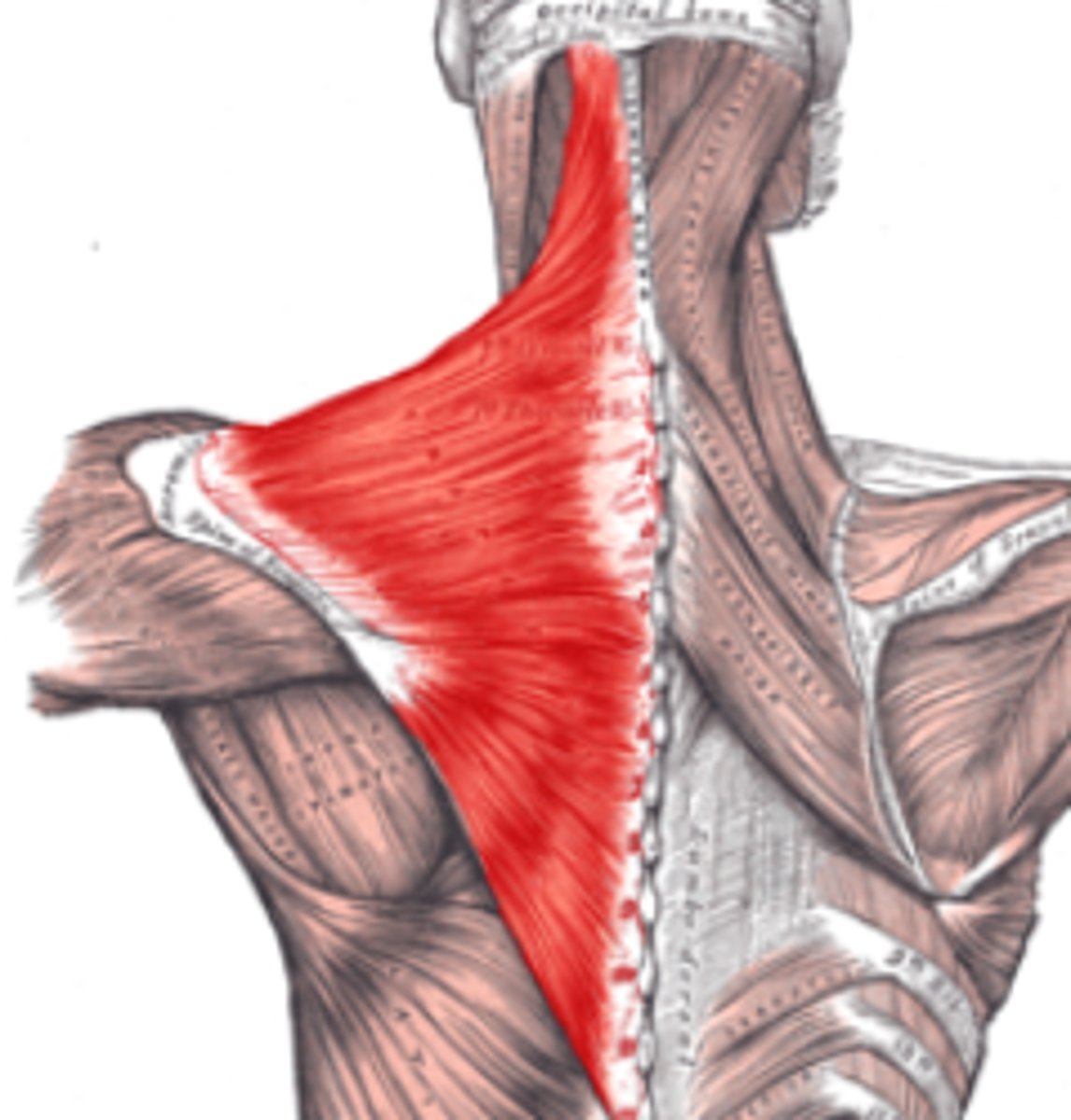
trapezius
Elevates, depresses (depends on area of muscle being activated), adducts and upwardly rotates the scapulae
agonist
prime mover muscle
Antagonist
opposes the prime mover
synergists
assist with movement
fixators
hold a bone firmly so agonist has a stable base on which to move a body part
origin of a muscle
end of muscle attached to bone that does not move during contraction
insertion of a muscle
muscle end attached to the bone that moves when the muscle contracts
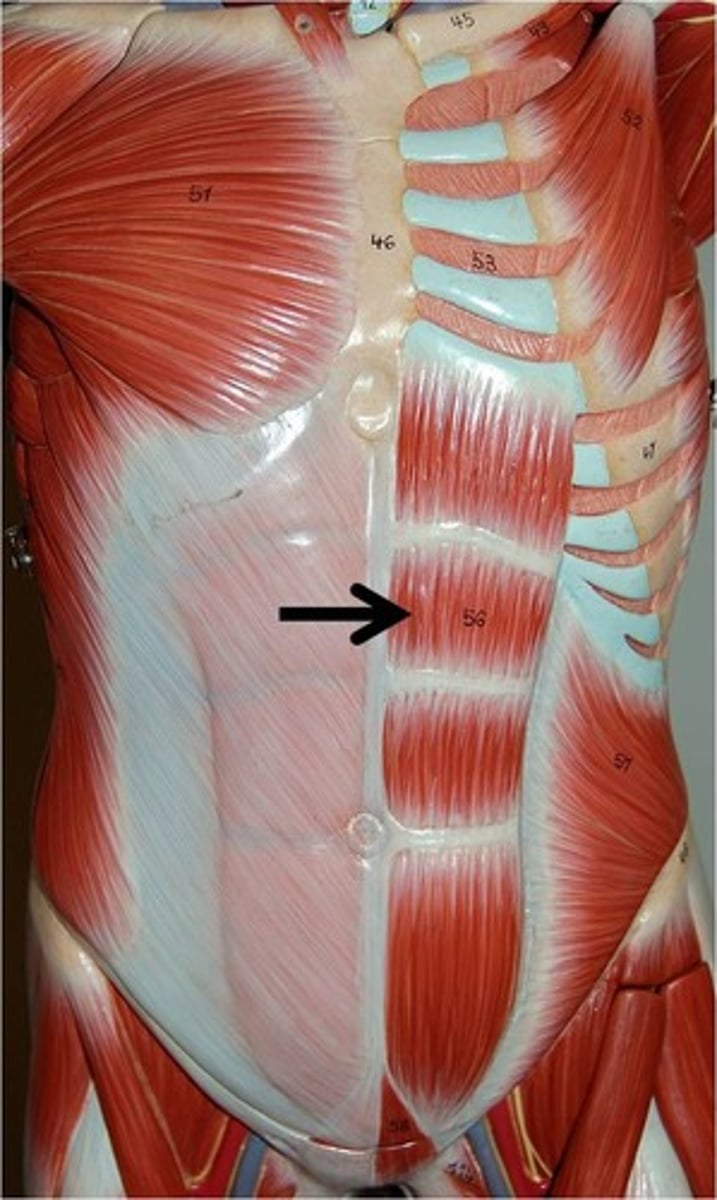
rectus abdominis
flexion and lateral flexion of the trunk
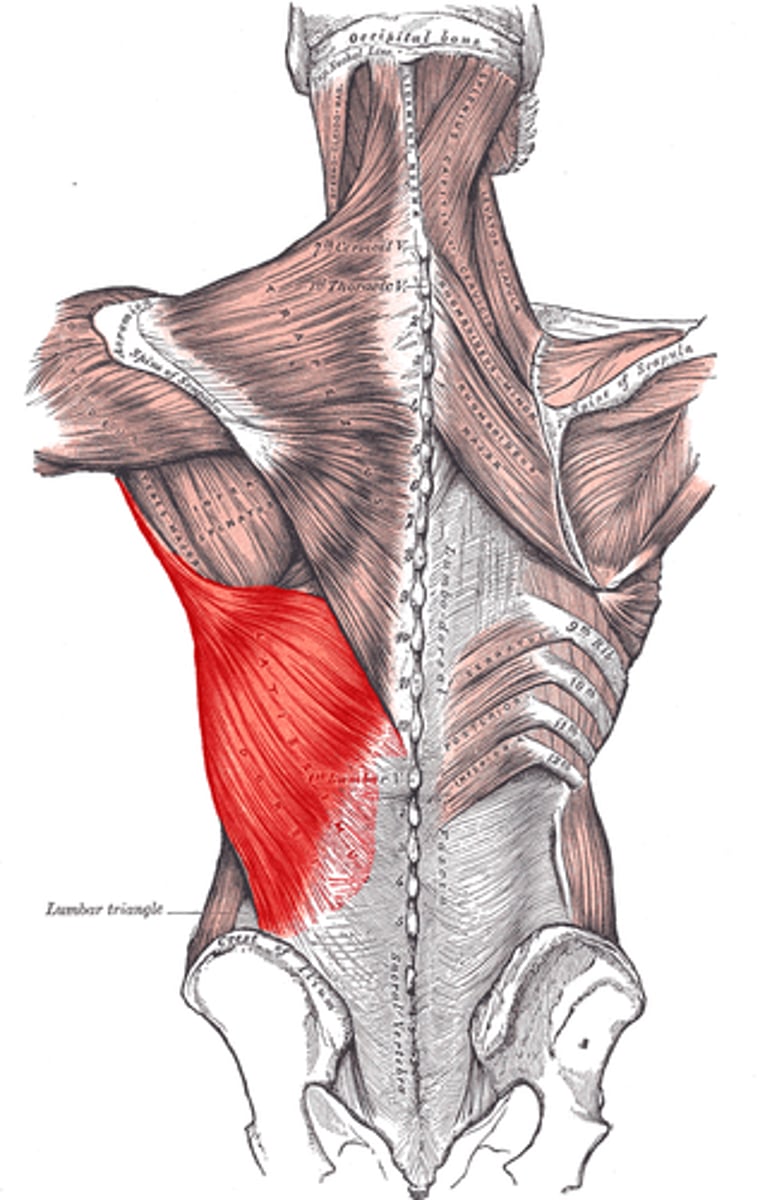
Latissimus dorsi
Adducts, extends, internally rotates, and horizontally abducts the arm
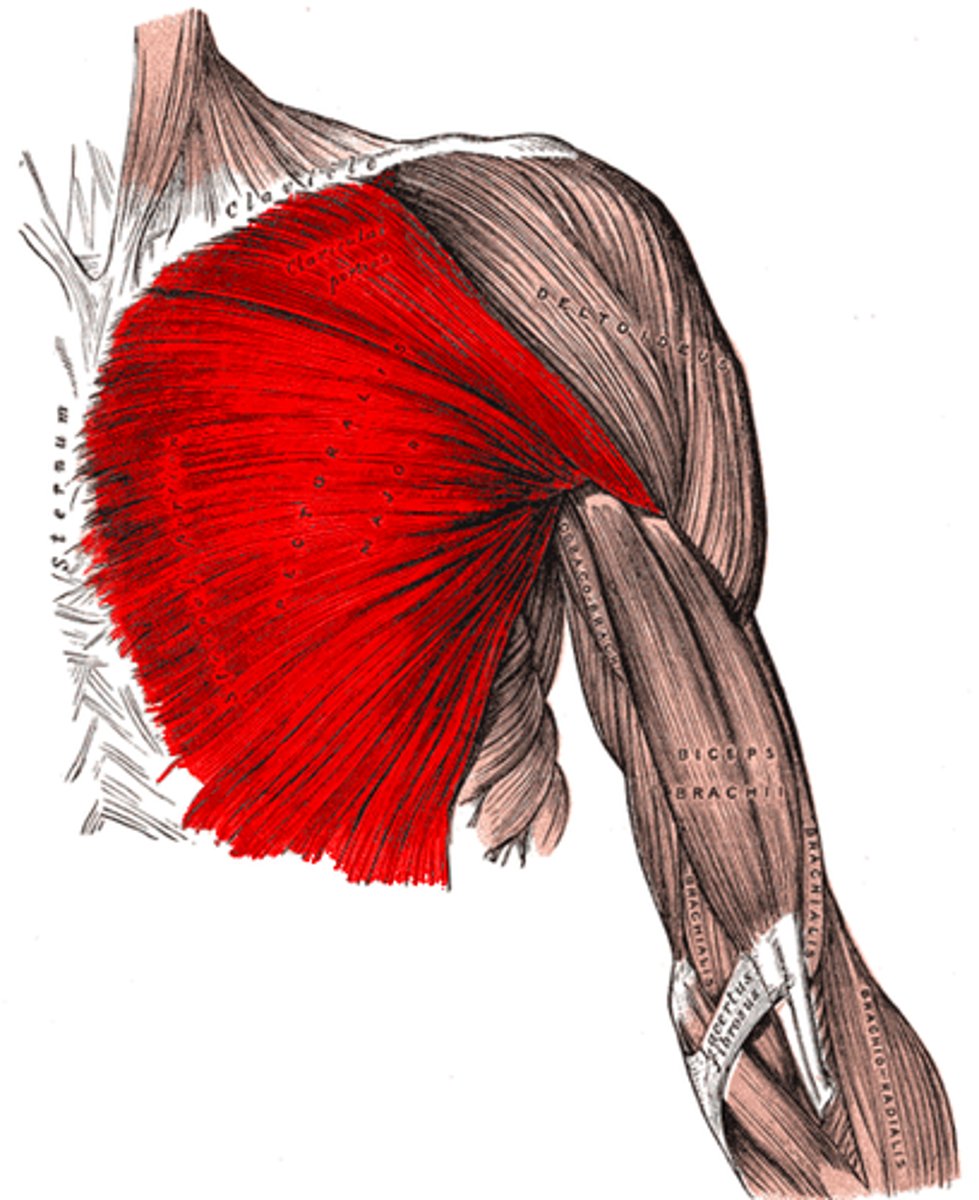
Pectoralis major
Adducts, flexes, extends (depends on fibers being recruited), internally rotates and horizontally adducts the arm
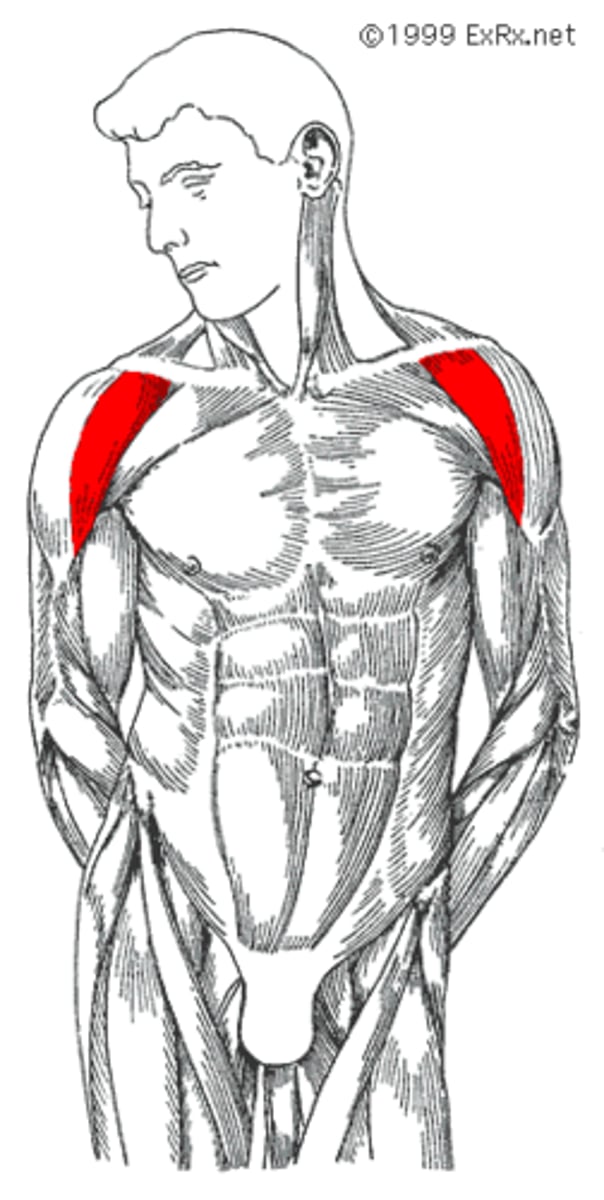
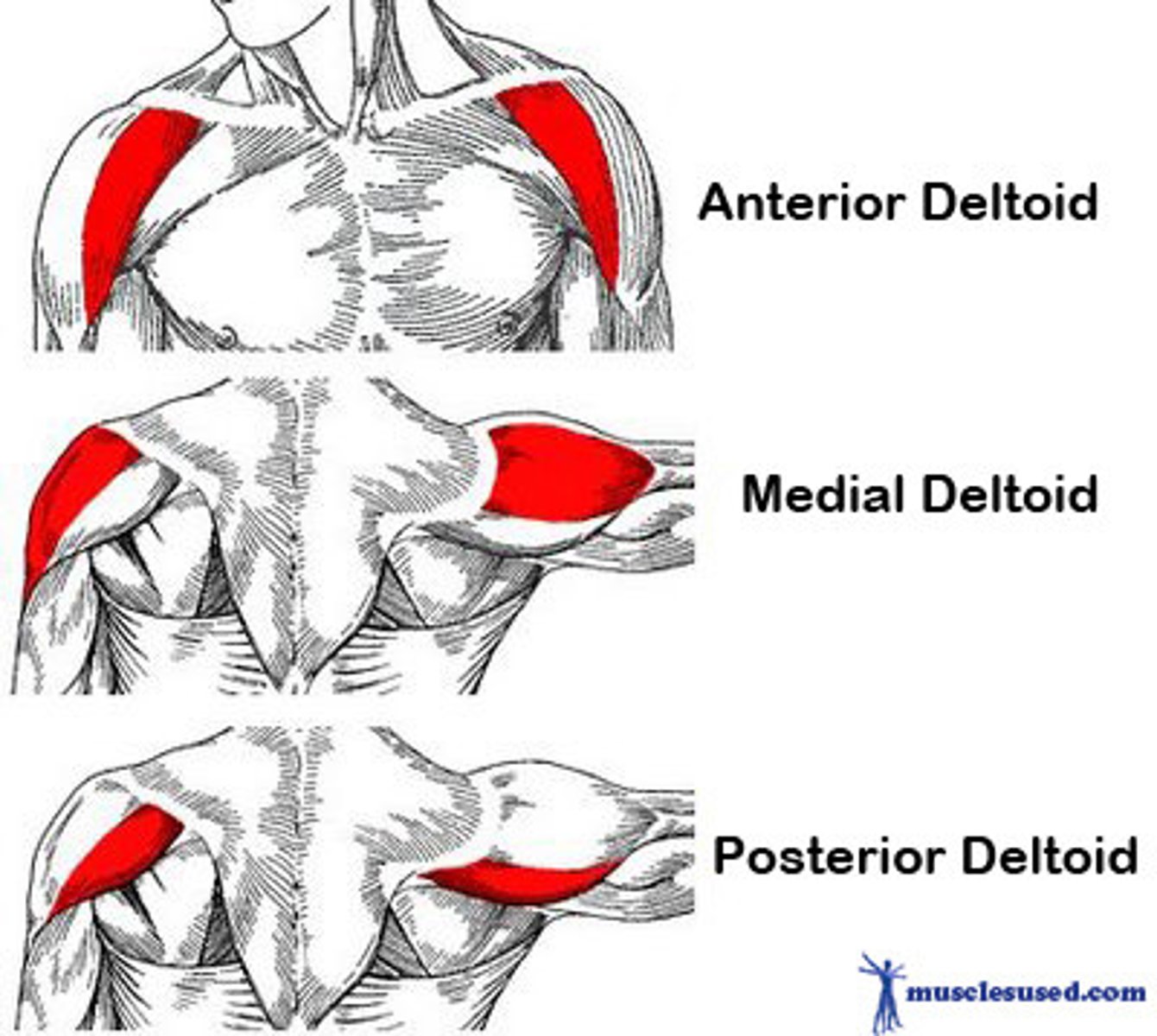
Deltoid Anterior
Abducts, flexion, internally rotates and horizontally adducts the arm
Deltoid Medial
Abducts the arm
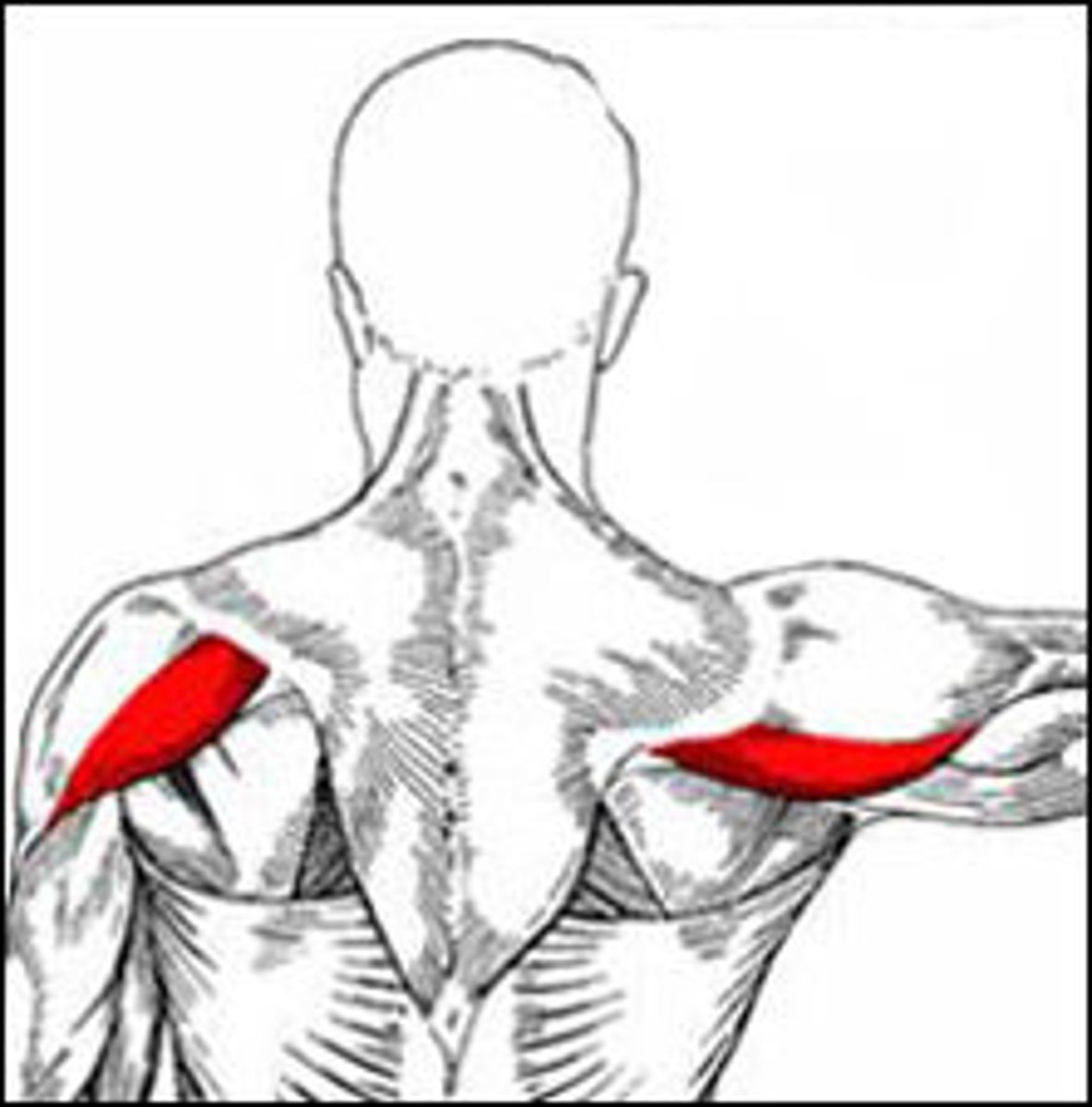
Deltoid Posterior
Abducts, extends, externally rotates and horizontally abducts the arm
Biceps brachii
Flexion of the elbow and shoulder, supination of the forearm
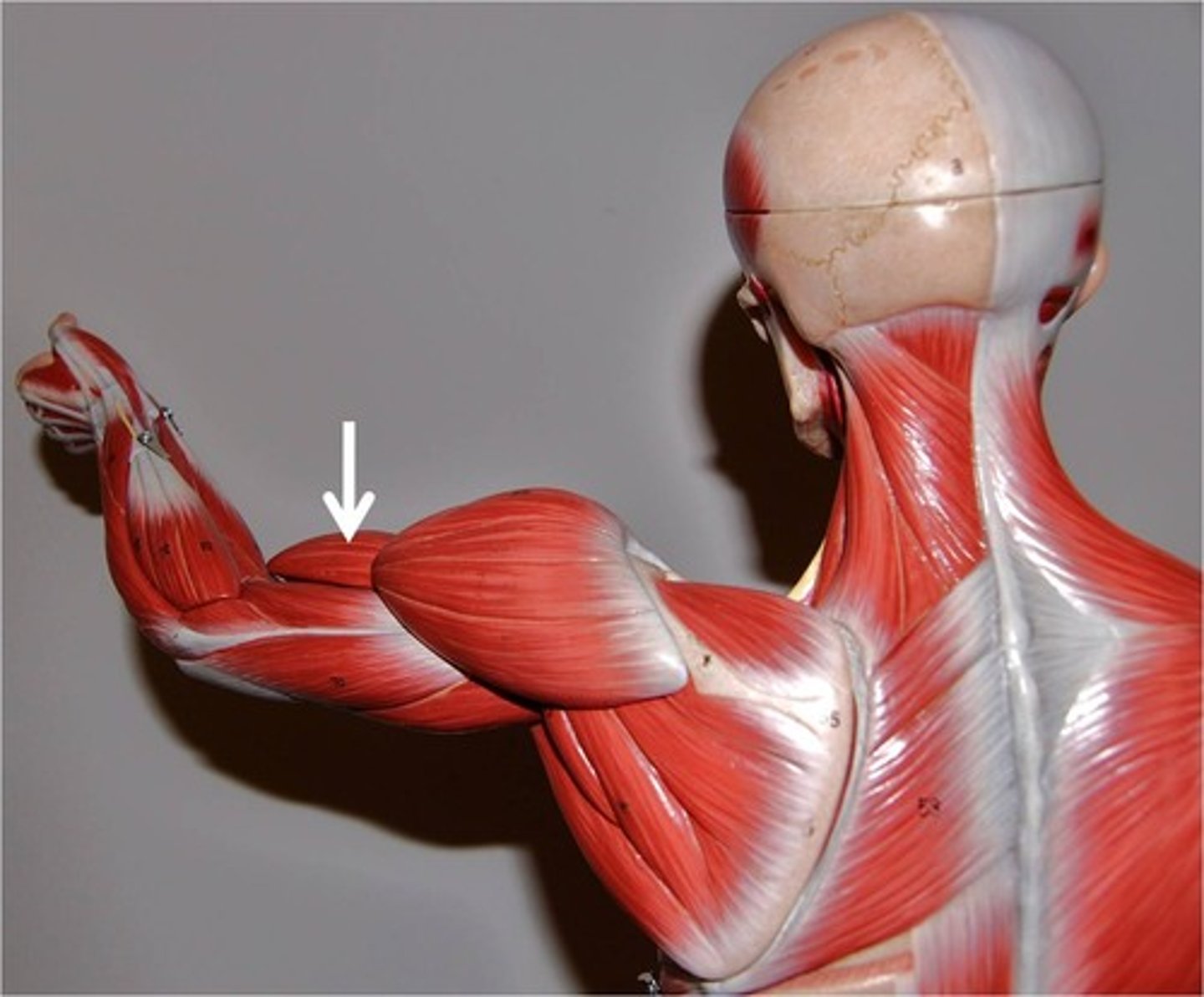
Triceps brachii
Extends the elbow, adducts and extends the shoulder (long head
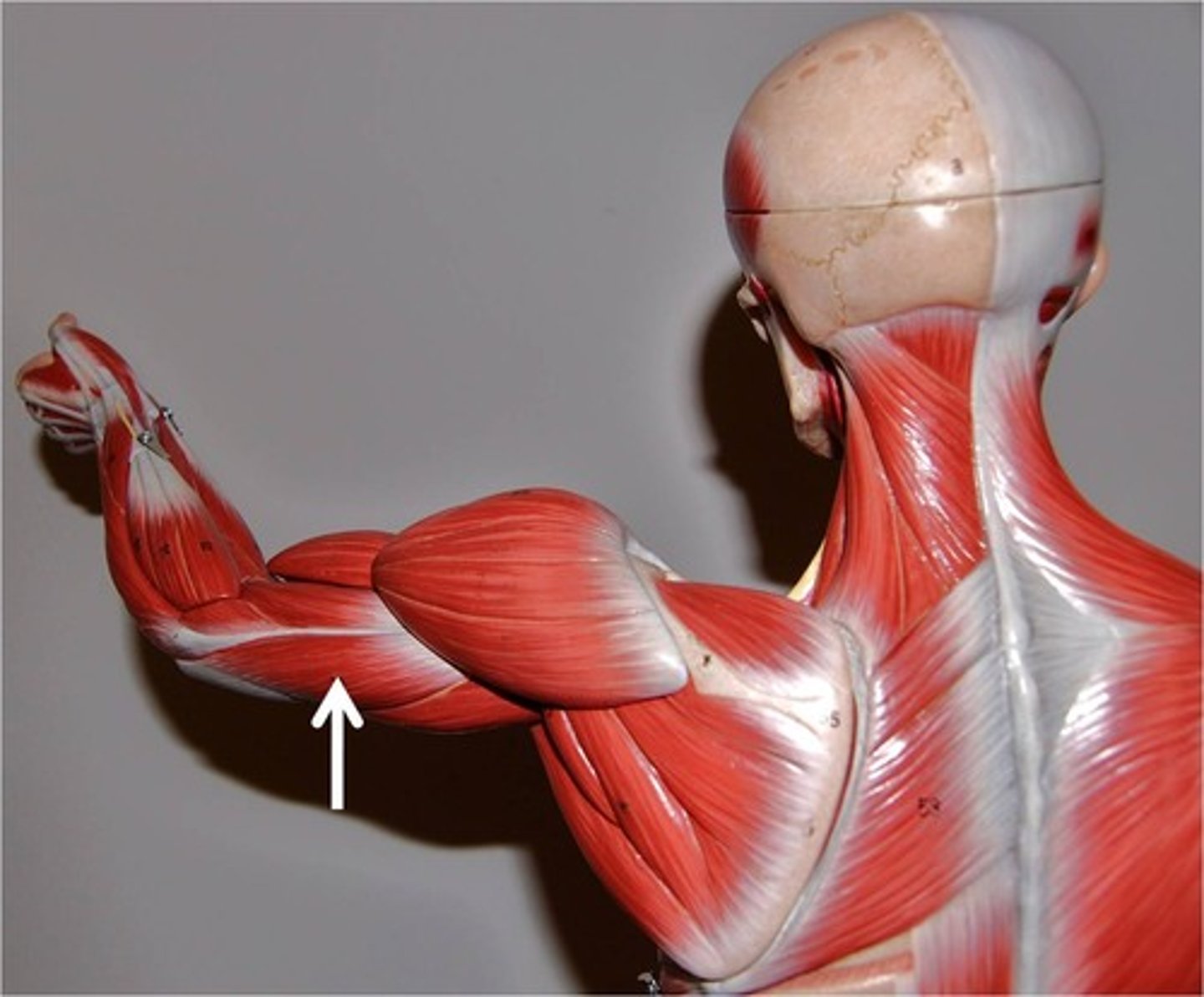
Brachialis
Flexion of the elbow
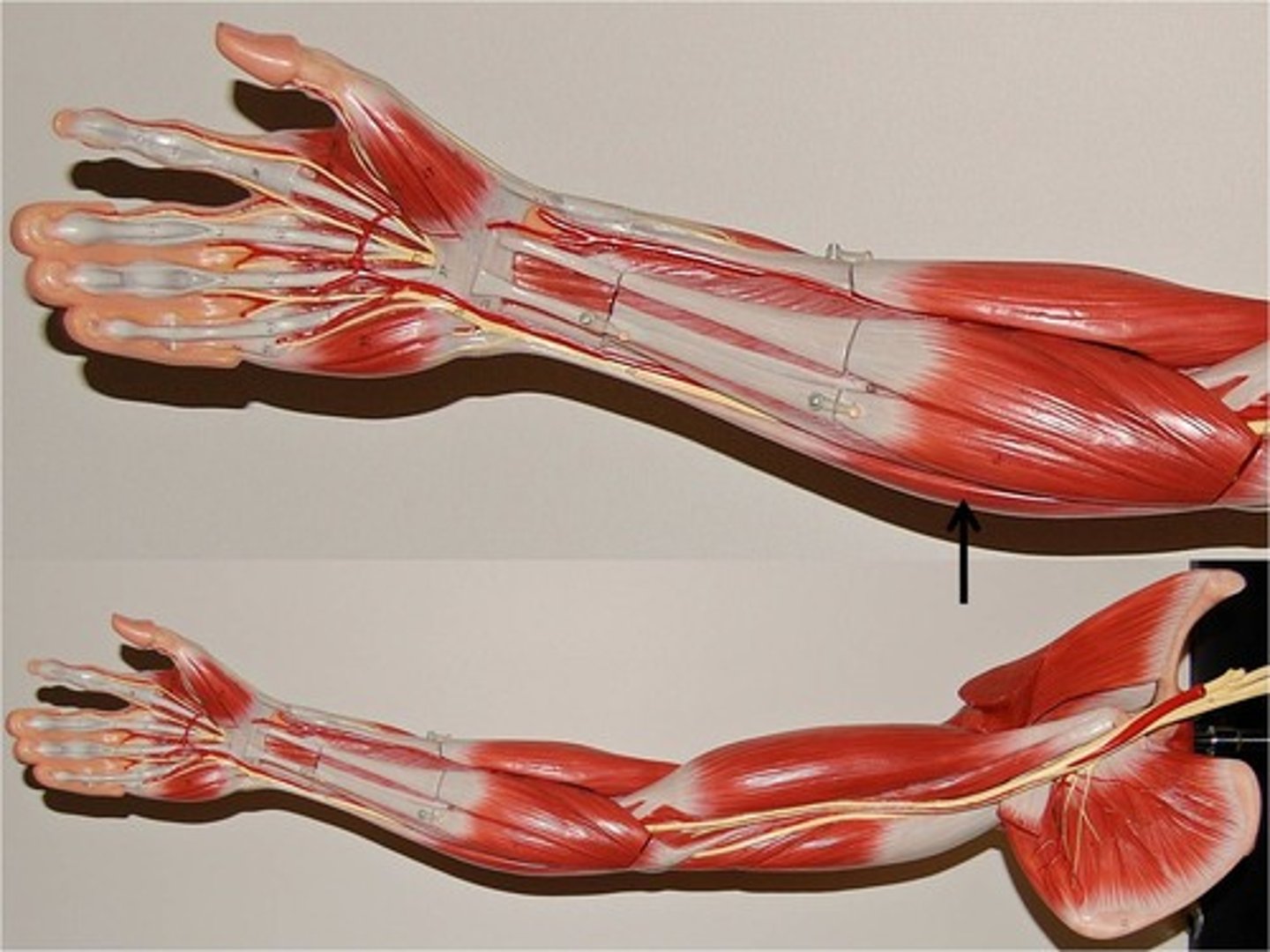
flexor carpi radialis
flexes and abducts wrist
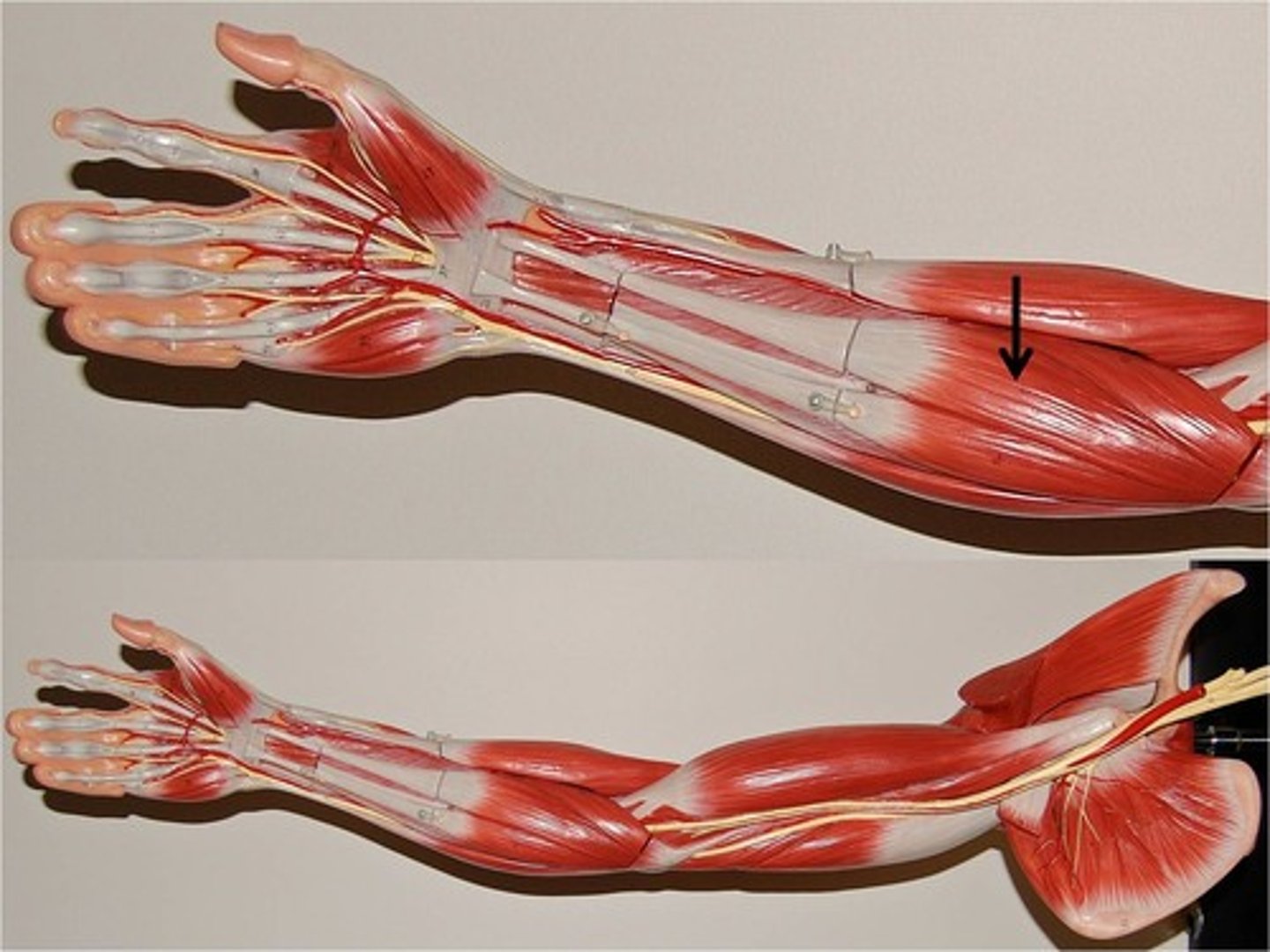
flexor carpi ulnaris
Flexes and adducts wrist
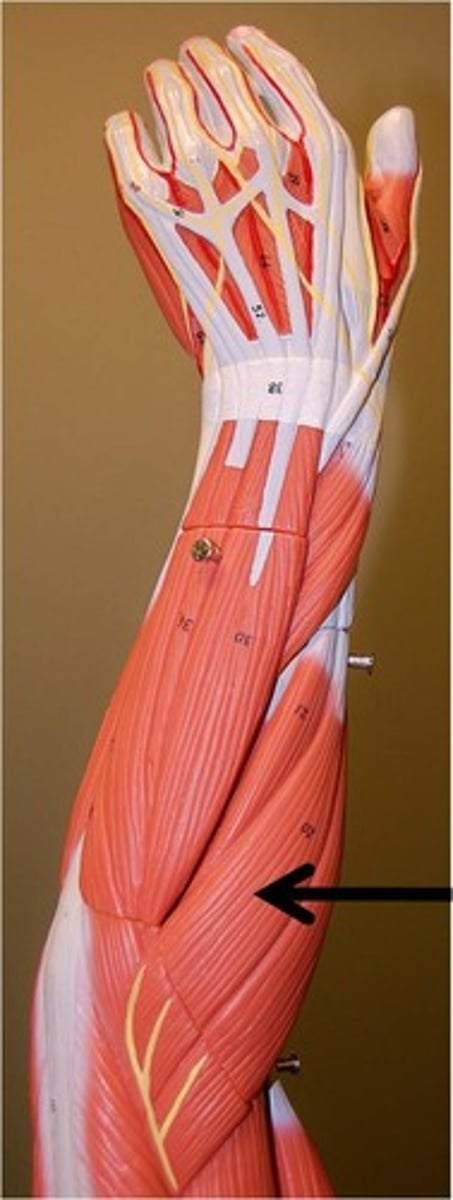
Extensor carpi radialis longus
Extends and adducts the wrist
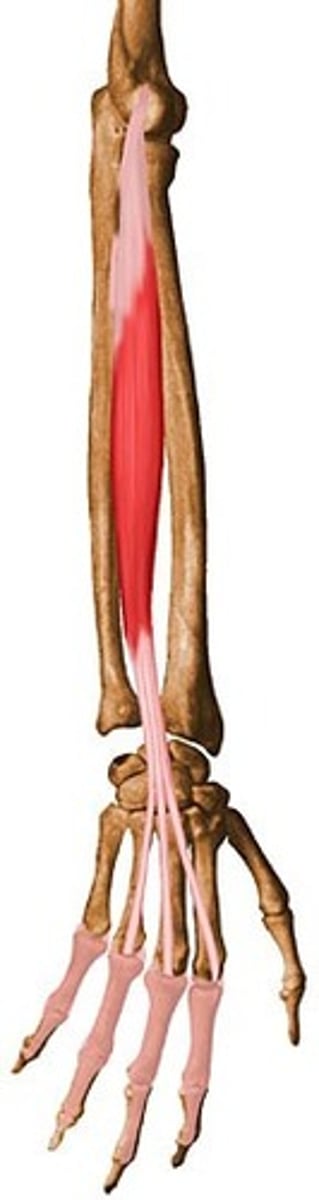
Extensor digitorum
Extends the wrist
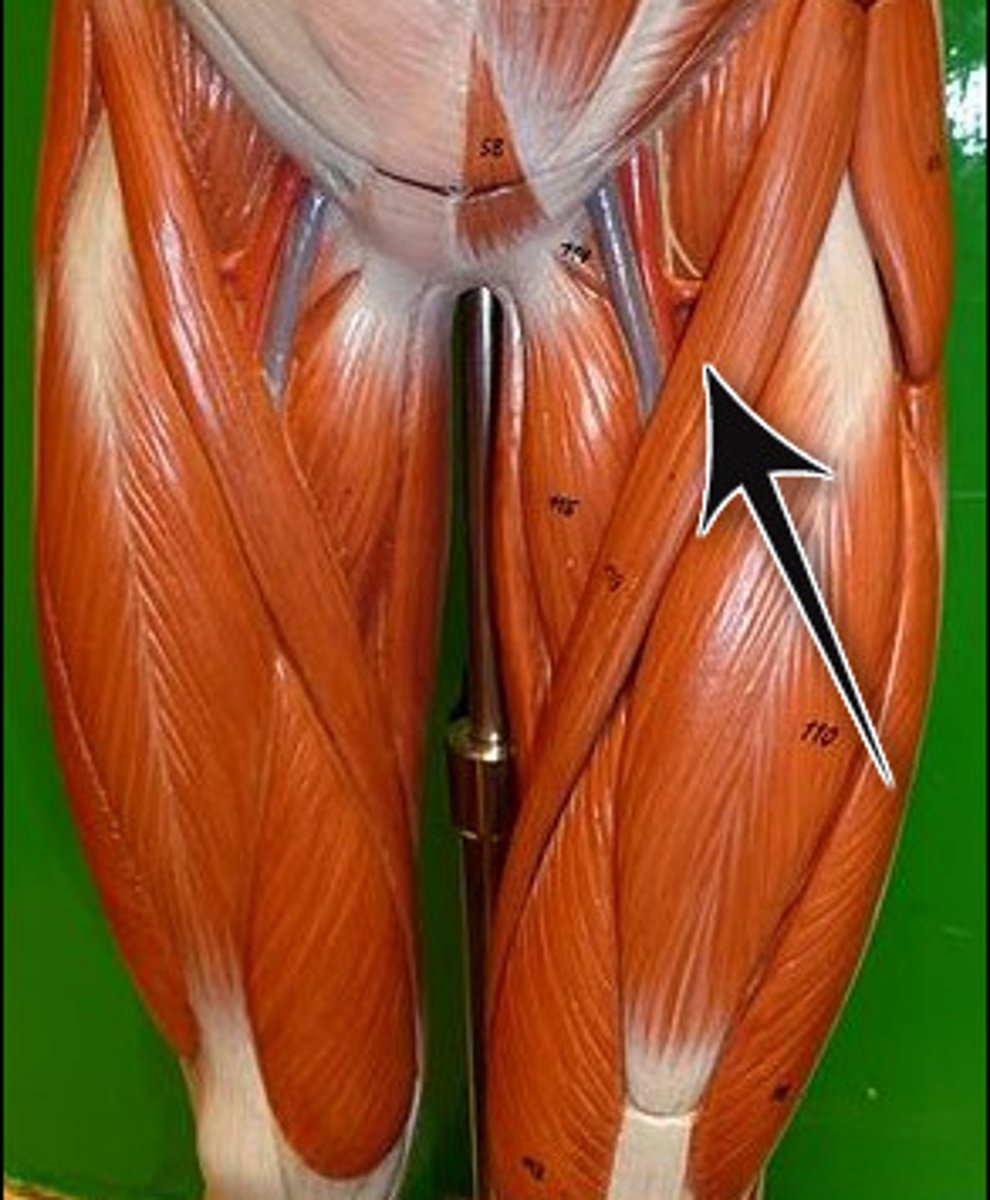
Sartorius
flexion, external rotation, and abduction at the hip, flexion and internal rotation at the knee
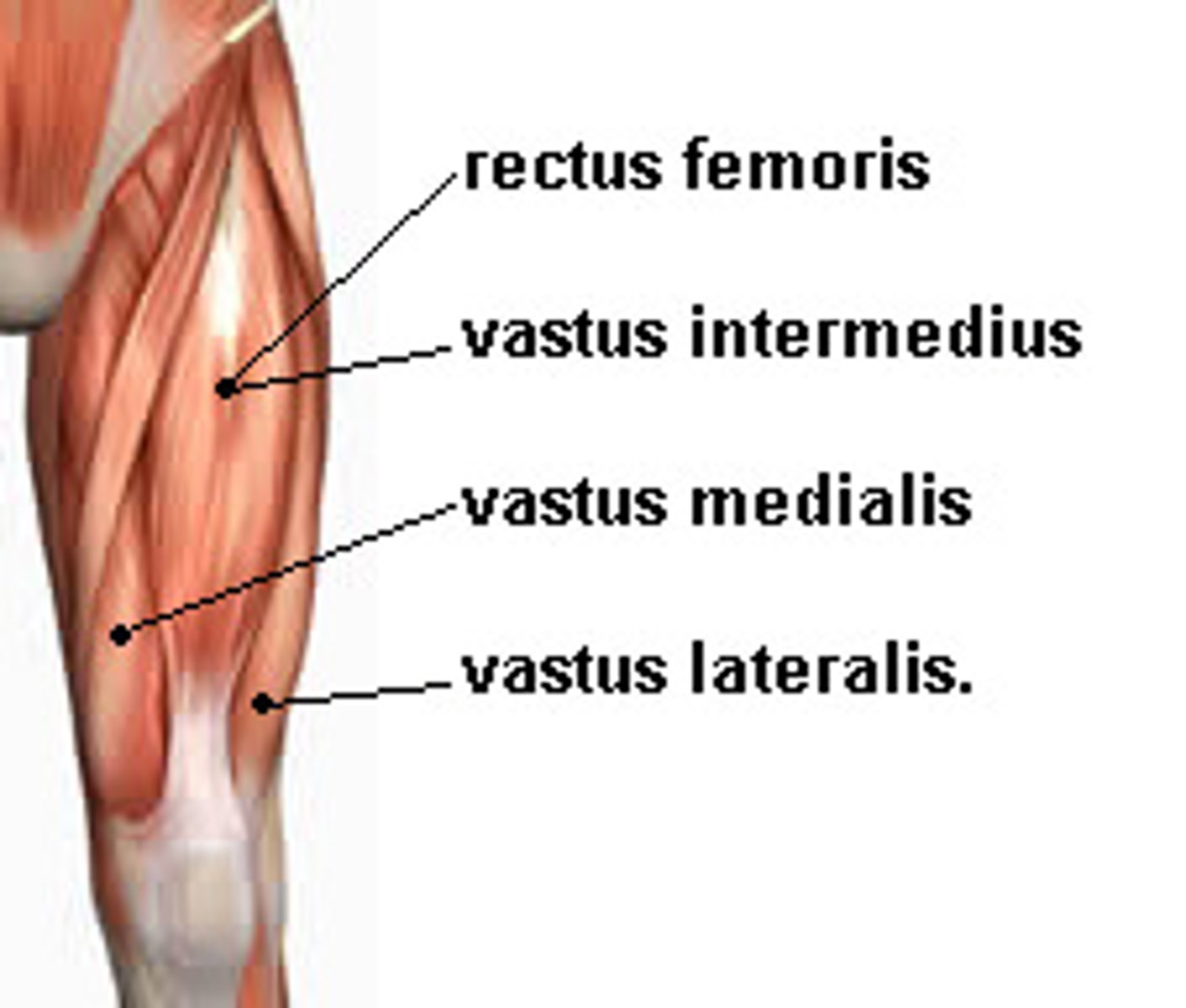
Rectus femoris (portion of quadriceps)
hip flexion and knee extension
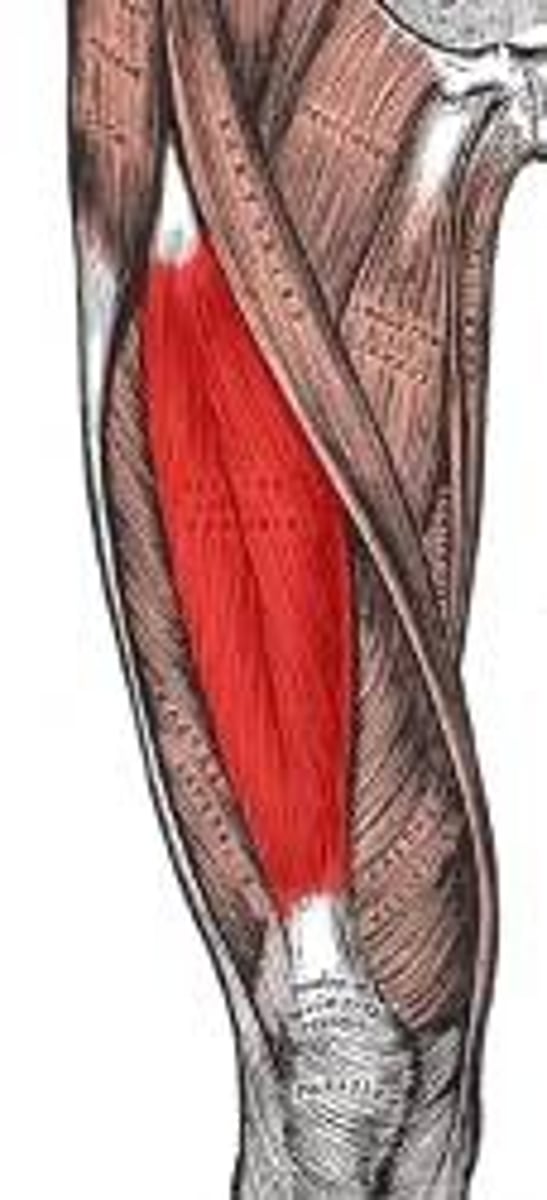
Semimembranosus (hamstrings)
extension at the hip, and flexion and internal rotation at the knee
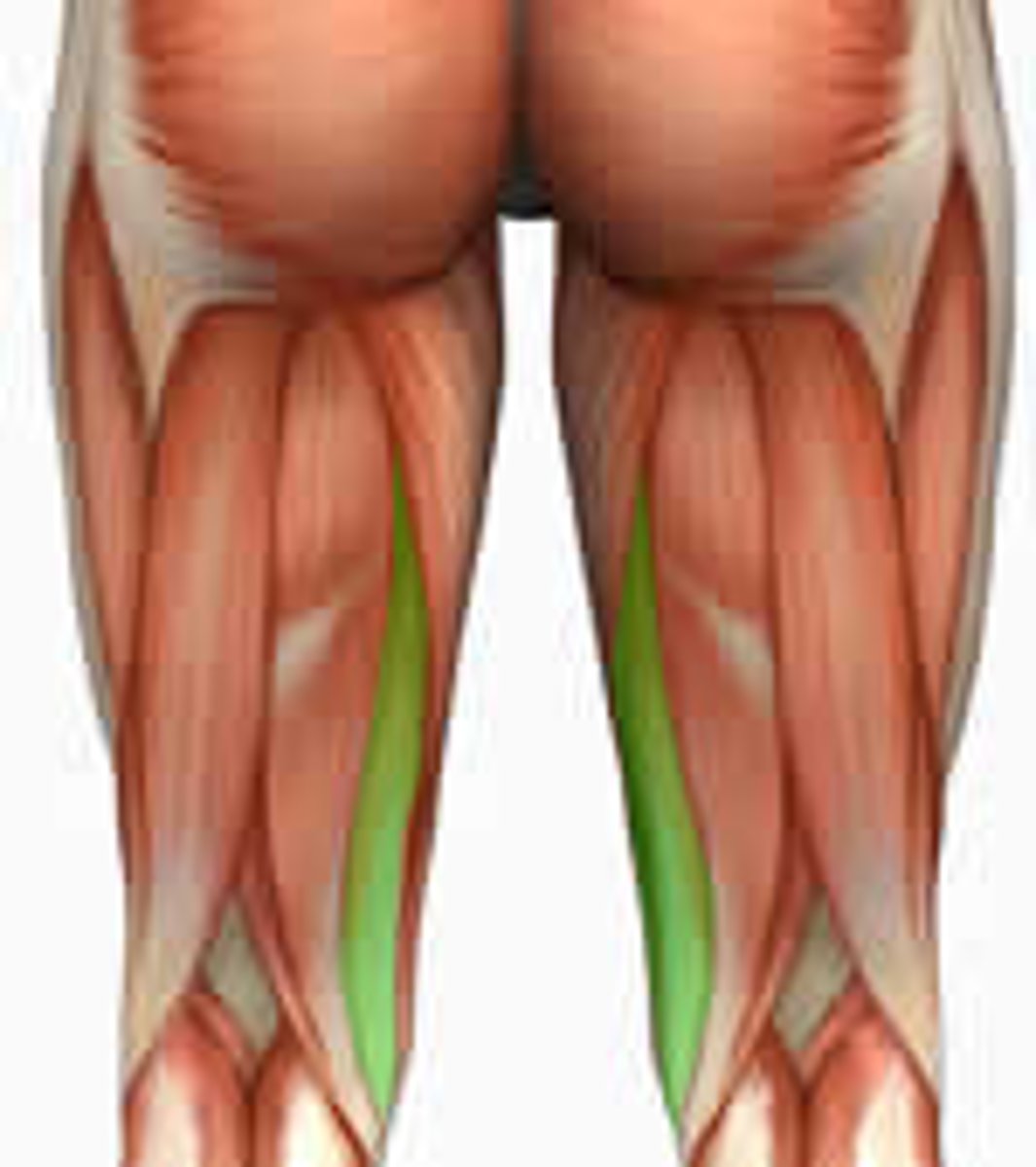
Semitendinosus (hamstrings)
extension and internal rotation at the hip, flexion and internal rotation at the knee
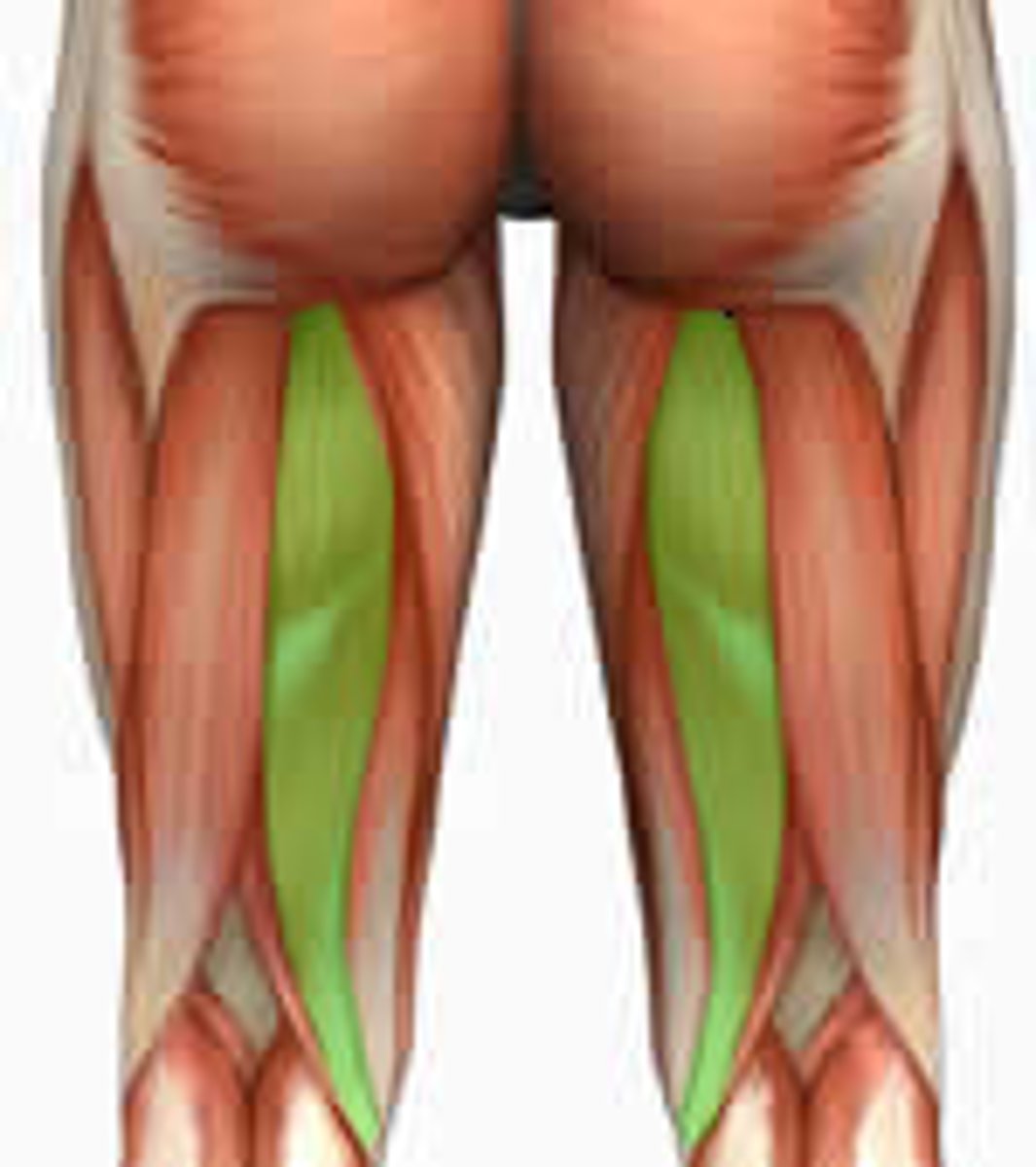
Biceps femoris (hamstrings)
extension at the hip, external rotation and flexion at the knee
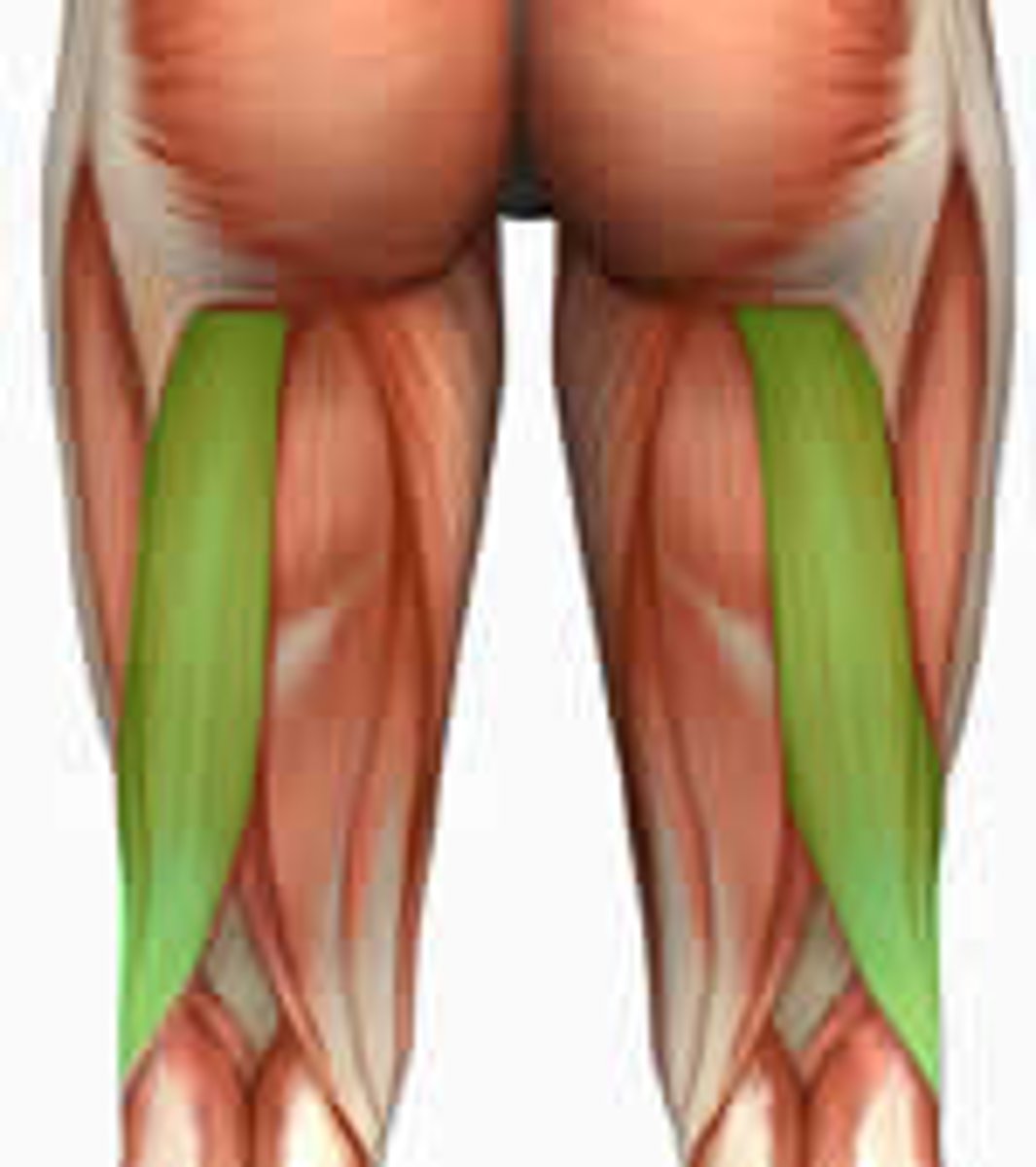
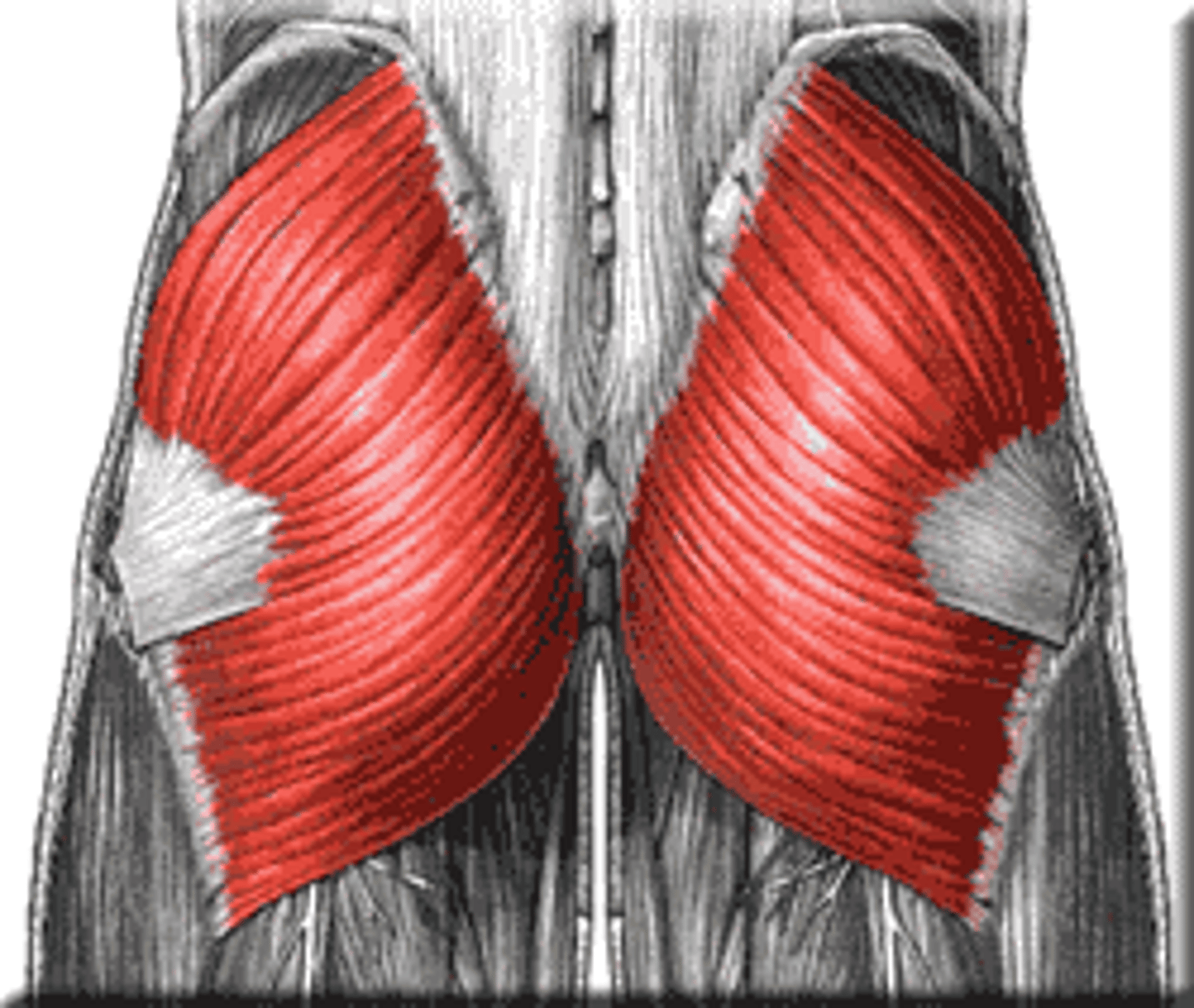
Gluteus maximus
extension, external rotation
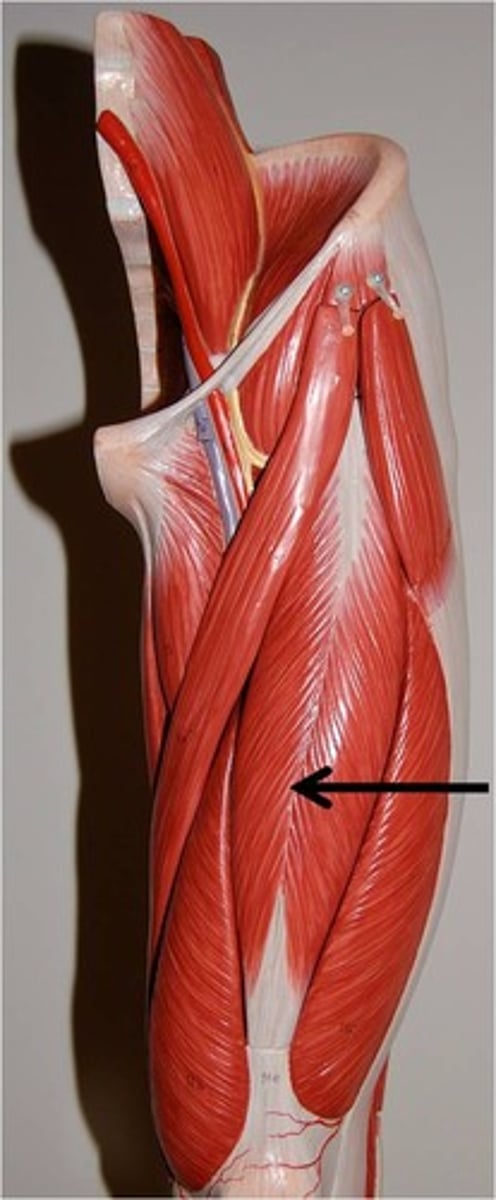
Rectus femoris (quadriceps)
hip flexion and knee extension
Vastus lateralis (quadriceps)
knee extension
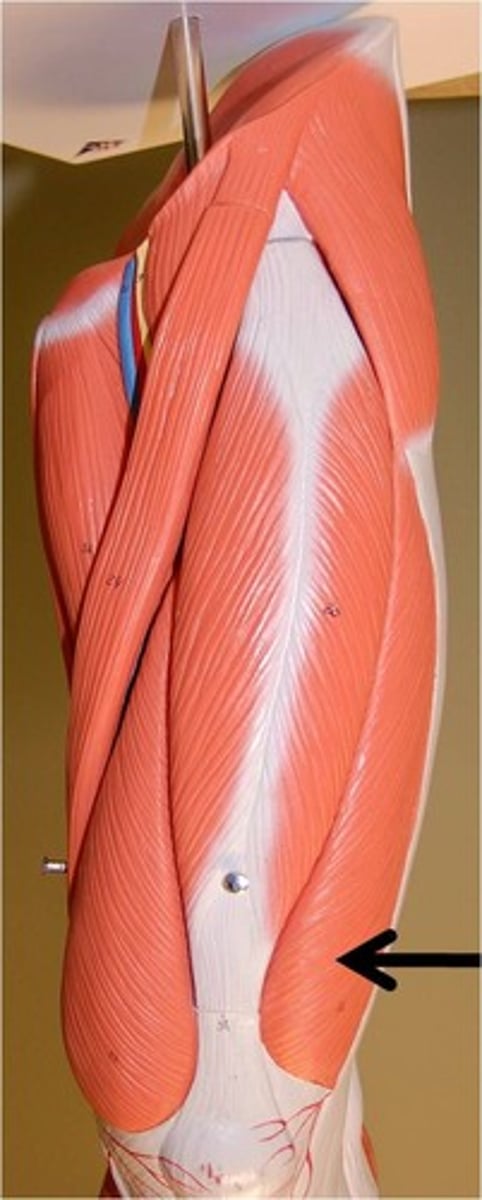
Vastus medialis (quadriceps)
knee extension
Vastus Intermedius (quadriceps)
knee extension
Tibialis anterior
dorsiflexion and inversion of the foot
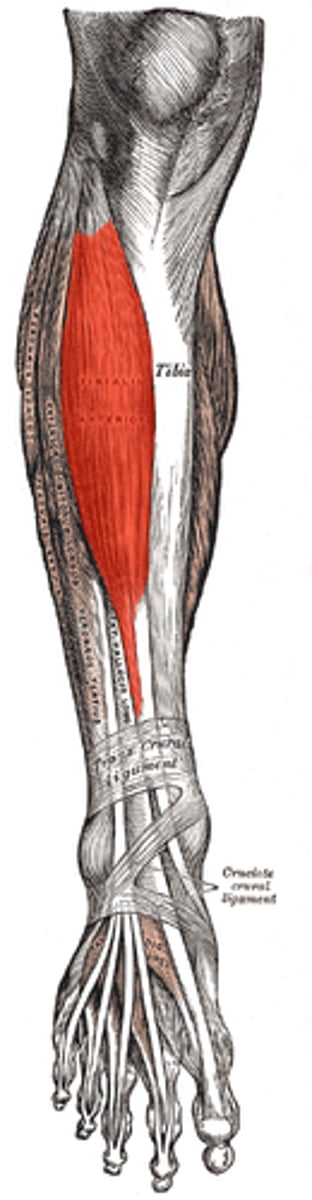
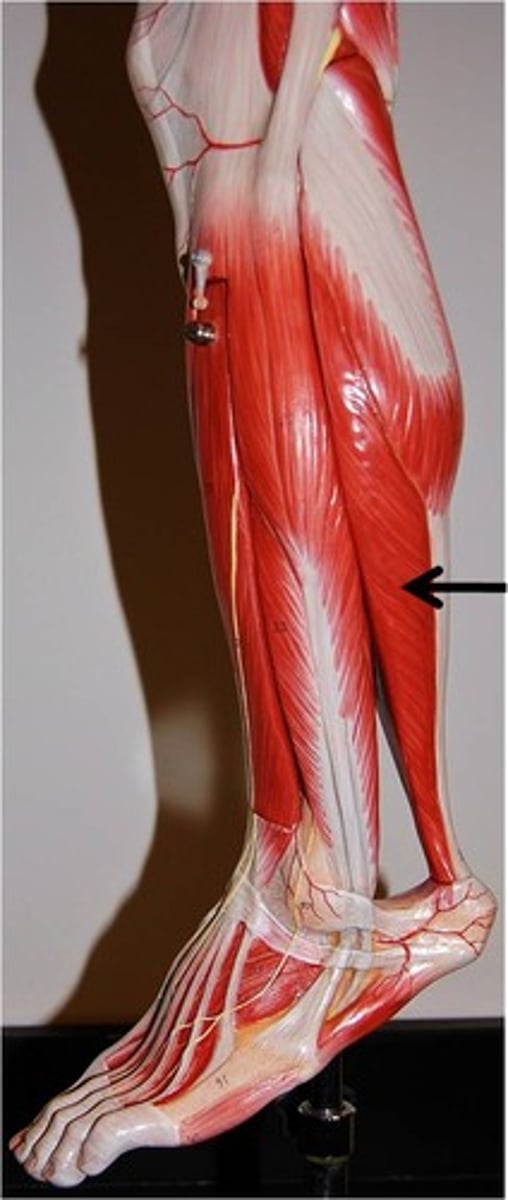
Soleus
plantarflexion
bone mechanical functions
support body
provide lever system
provide protection
bone physiological functions
where blood cells form
storage reservoir for calcium
store minerals
organic matrix (collagen)
15% of bone tissue
water
20% bone tissue
mineral (calcium and phosphate)
65% bone tissue
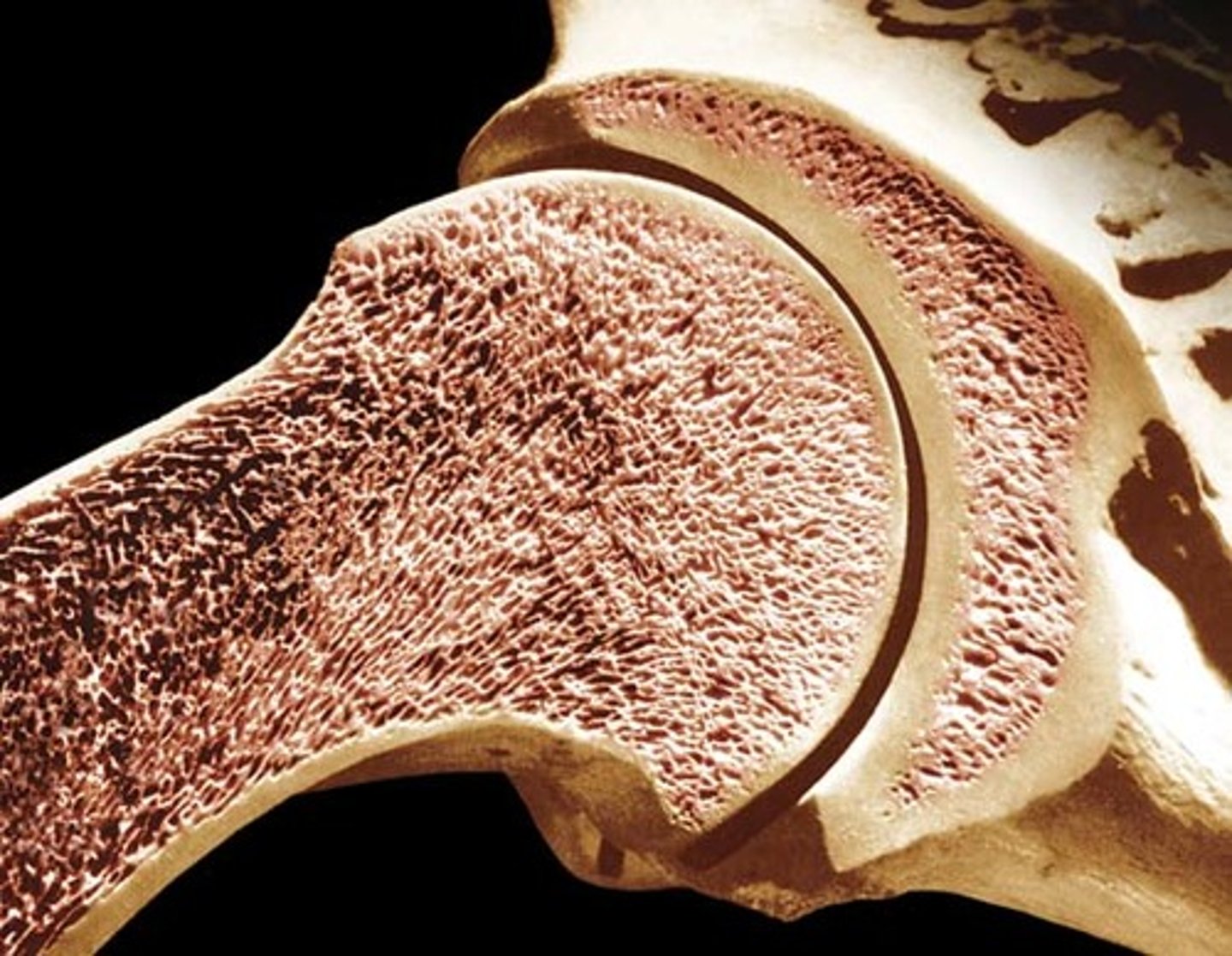
cortical bone
hard, dense, strong bone that forms the outer layer of bone; also called compact bone; ARRANGED IN OSTEONS
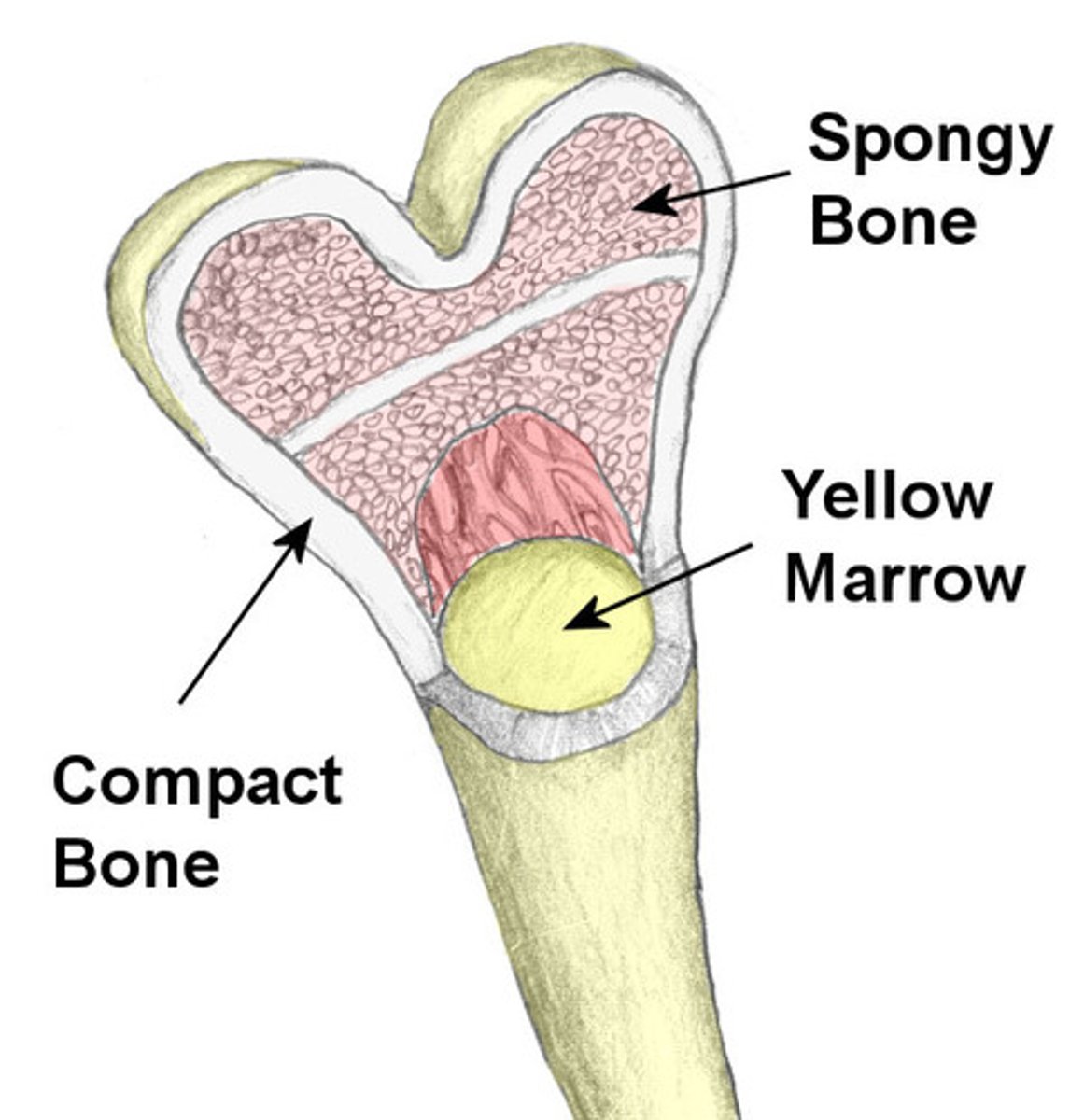
cancellous bone
spongy, porous, bone tissue in the inner part of a bone; NO OSTEONS, ARRANGED IN TRABECULAE
osteon
basic structural unit of compact bone
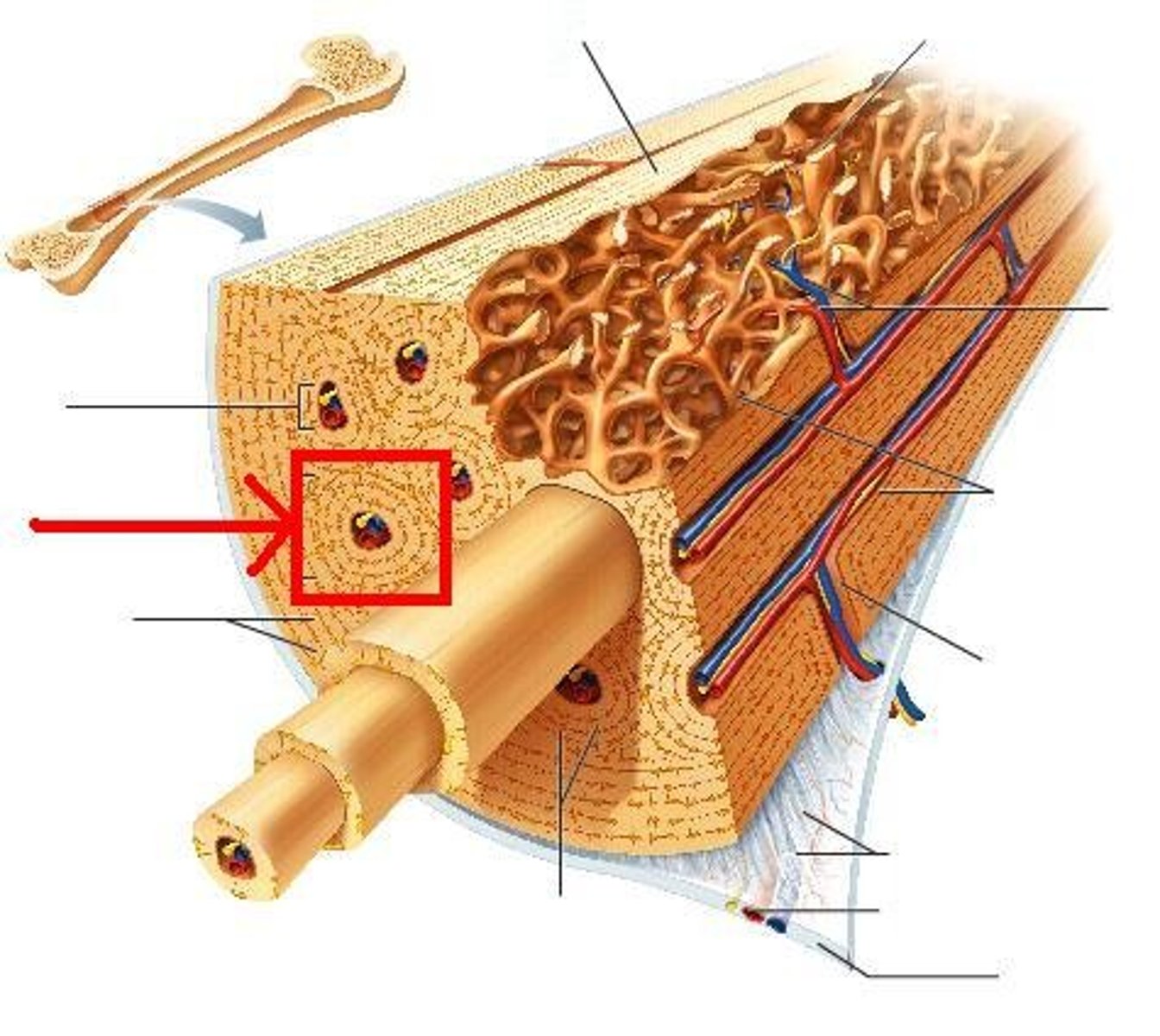
periosteum
A dense fibrous membrane covering the surface of bones (except at their extremities) and serving as an attachment for tendons and muscles.
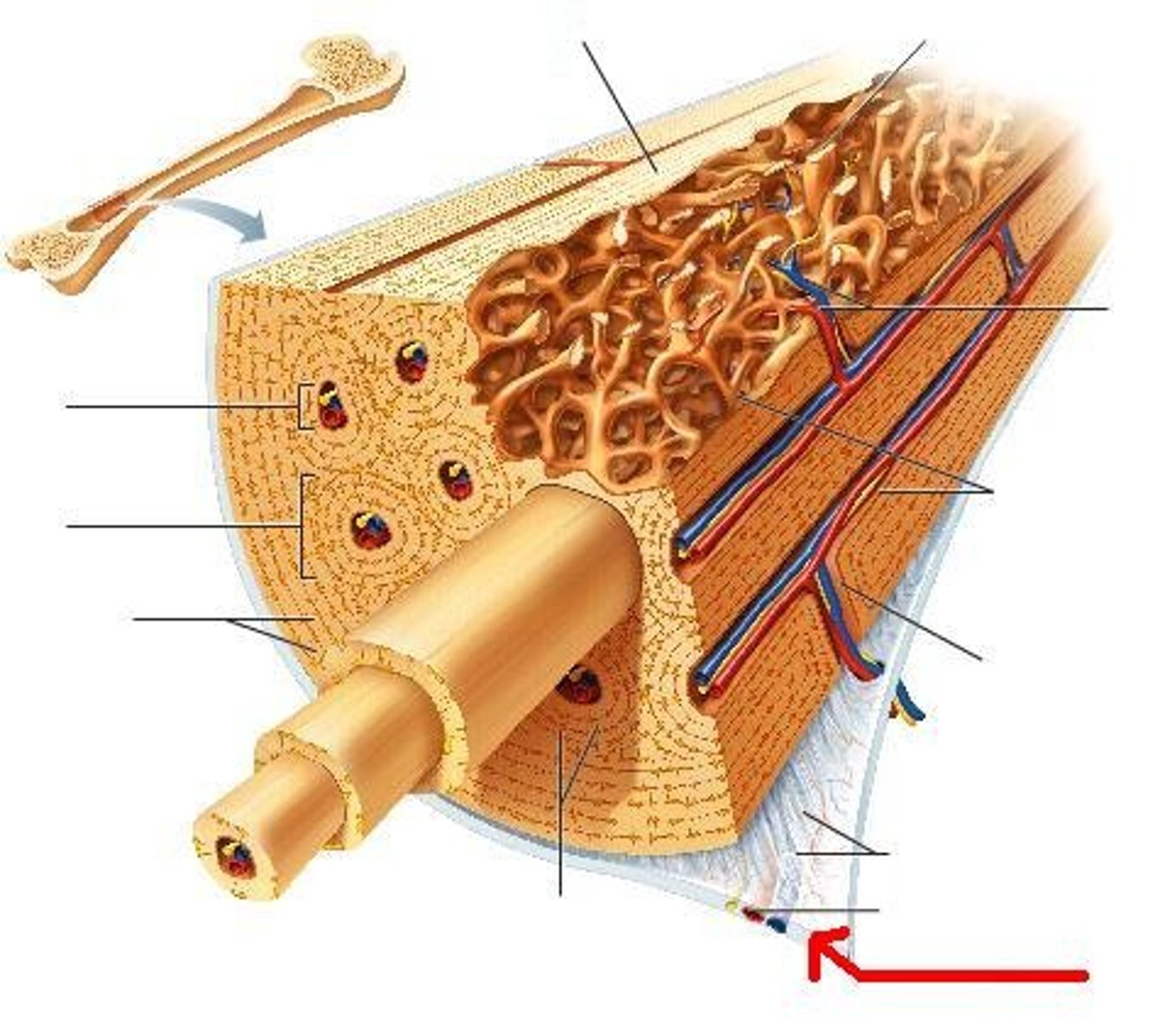
bone lacunae
a small cavity within the bone matrix, containing an osteocyte
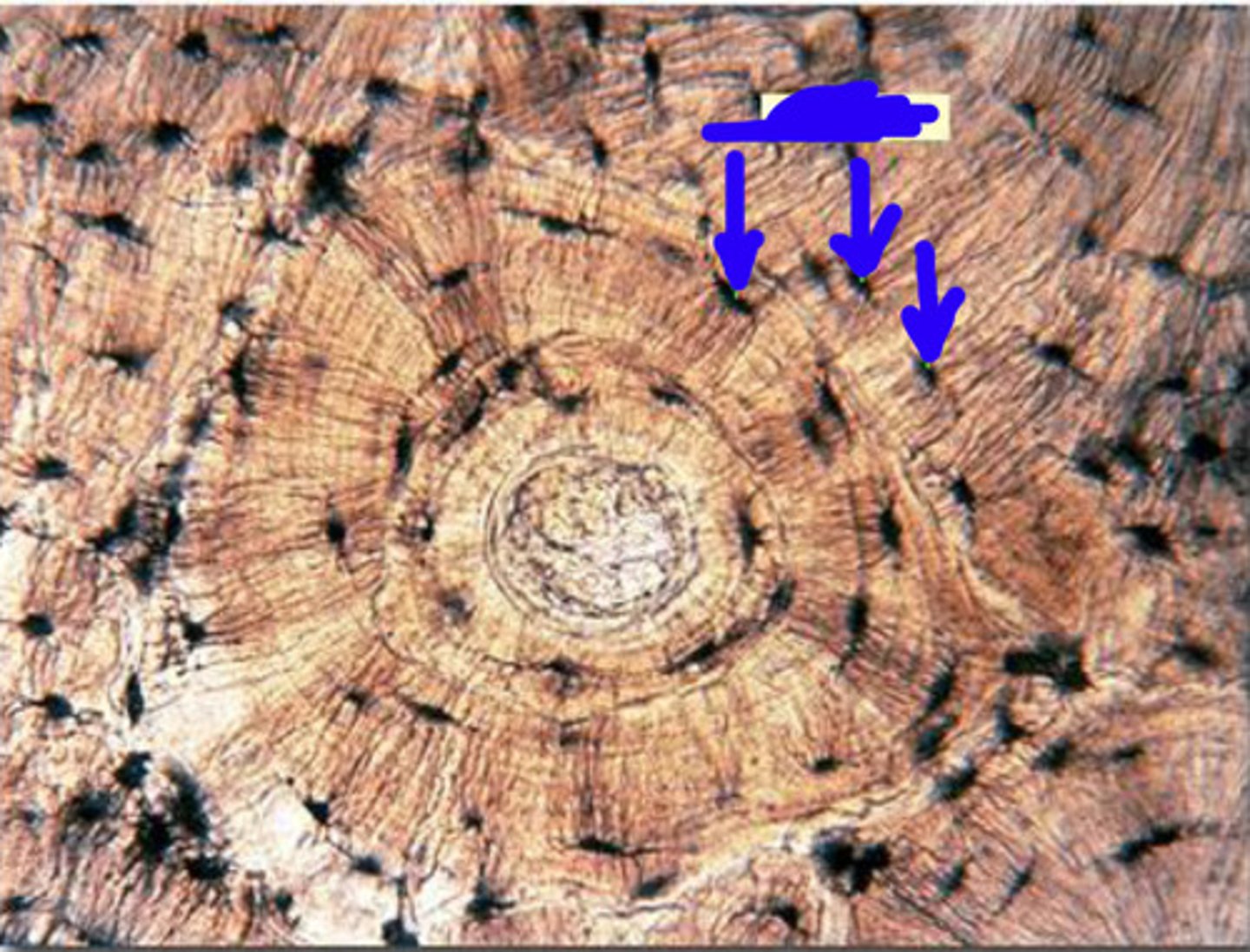

osteocyte
mature bone cell
bone assumptions
bone is isotropic, homogeneous, and elastic
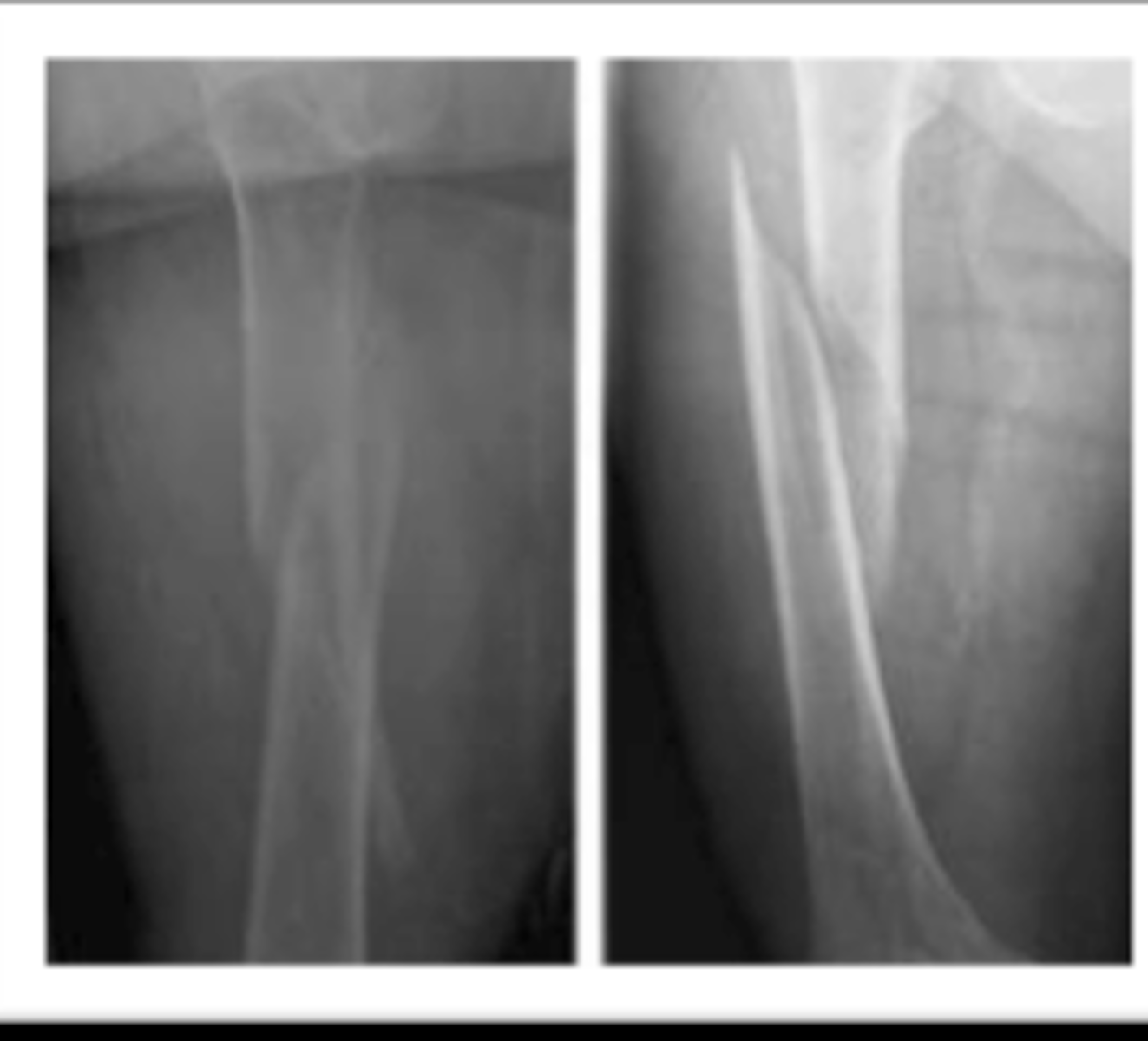
transverse fracture
tension
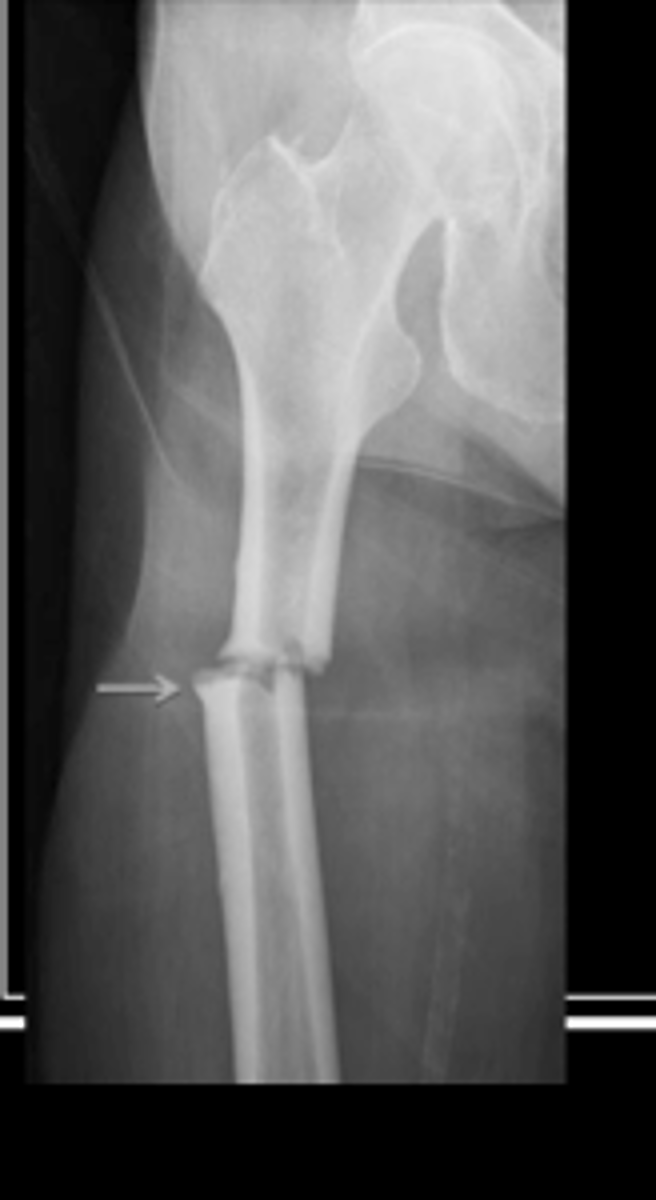
oblique fracture
compression
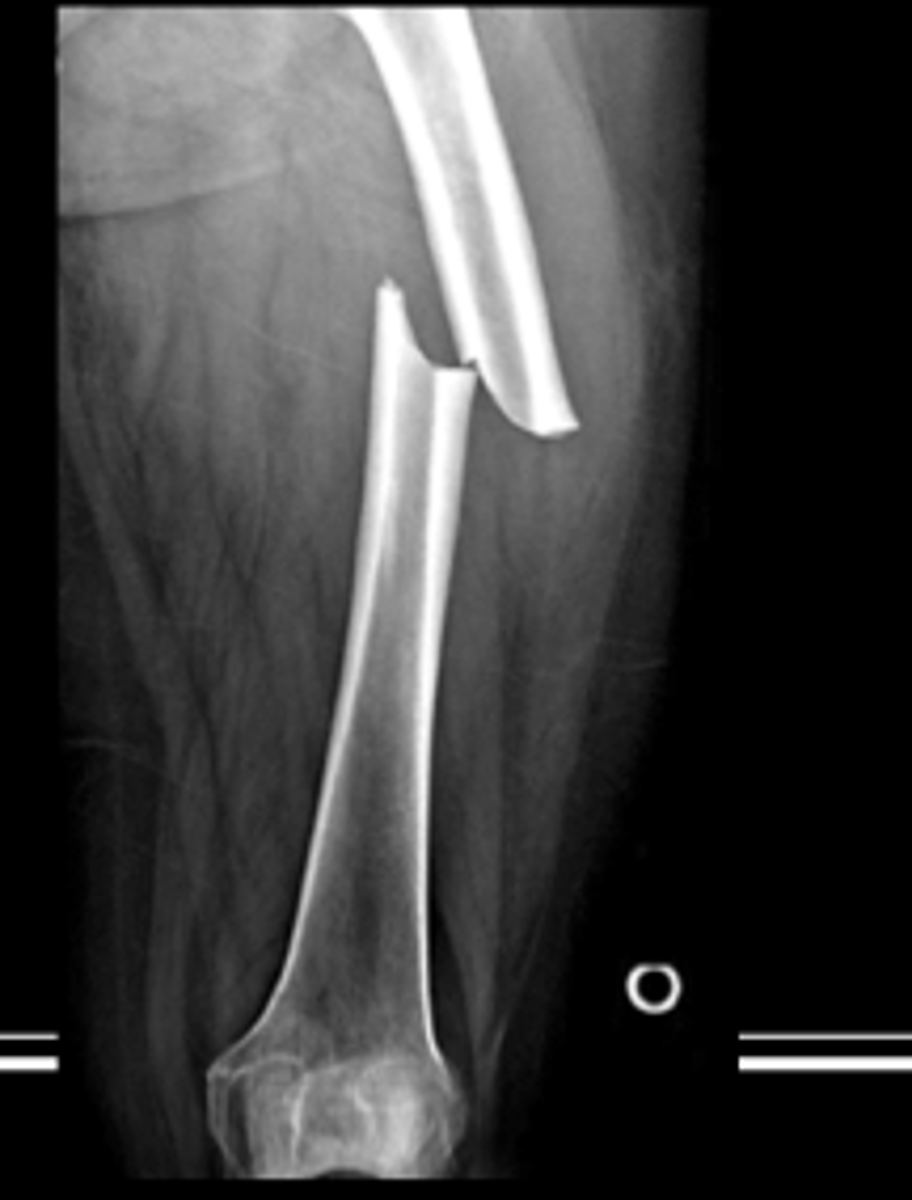
butterfly fracture
bending
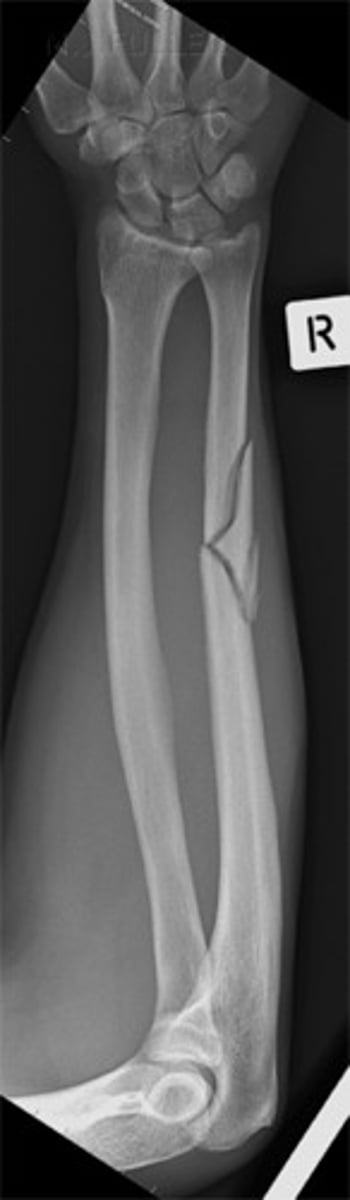
spiral fracture
torsion
primary bone
First bone to be produced by either ossification method; requires cartilage
secondary bone
product of resorption of previously existing bone tissue and the deposition of new bone to replace it
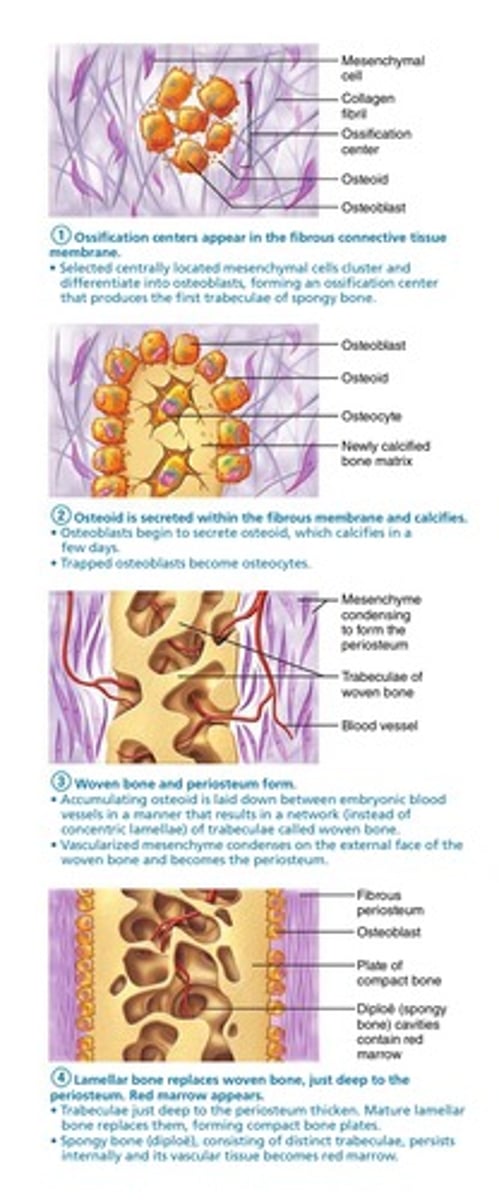
intramembranous ossification
process by which bone forms directly from mesenchymal cell: ossification center appears>woven bone and periosteum form>osteoid forms>bone collar and marrow form