Ap Pysch Unit 1 Test vocab
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
central nervous system (CNS)
consists of brain and spinal chord. Main processing center of the nervous system
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
The nervous system outside the brain and spinal chord
Automatic Nervous System (ANS)
a part of the nervous system that controls involuntary bodily functions. Ex: breathing, heartbeat, etc.
Somatic Nervous System (SNS)
a part of the nervous system that controls voluntary bodily functions. Ex: moving arms
Sympathetic Nervous System (SNS)
A network of nerves that prepare the body for physical activity, stress and danger. Often referred to as the “fight of flight” response.
Parasympathetic Nervous System (PSNS)
a network of nerves that help the body relax and restore homeostasis after periods of stress or danger
Neurons
A type of cell that receives and sends messages from the body to the brain and back to the body
Soma
The cell body
Axon
Passes messages away from the cell body to other neurons, muscles, or glands
Dendrites
Receive messages from other cells
Terminal Buttons
The small knobs at the end of an axon that releases chemicals called neurotransmitters
Low Serotonin
Depression
Myasthenia Gravis
A condition where certain muscles have difficulty contracting
Low levels of dopamine
Linked to parkinsons
High levels of dopamine
Linked to schizophrenia
Ach
Responsible for learning and memory
Norepinephrine
Neurotransmitter that controls alertness, mode, and attention
Serotonin
A neurotransmitter that regulates sleep, mood, and body temperature
Dopmaine
A neurotransmitter involved in mood, movement, and attention
Glutamate
The main excitatory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system; important for learning and memory
Glial cells
Cells that support and protect nerve cells in the central and peripheral nervous systems
Inter motor neurons
Carry information between sensory and motor neurons
Agonists
Drugs that mimic a particular neurotransmitter
Antagonists
Drugs that block a particular neurotransmitter from activating its recepters
Action potential
The electrical impulse sent along an axon when the dendrites of a neuron fire
Synapse
The small gap between the axon and the dendrite
Inhibitory
Describes a neurotransmitters causes postsynaptic neuron to propagate fewer action potentials
Substance P
Regulates bone metabolism, cartilage metabolism, and fracture healing
Gamma - aminobutyric acid (GABA)
neurotransmitters that slows down the brain by blocking signals in the central nervous system
Neurotransmitter
A chemical substance that is released by the end of a nerve by the arrival of a nerve impulse and diffuses across the synapse
Right Hemisphere
Controls left side of the body, creativity, emotions, spatial reasoning
Left Hemisphere
controls right side of the body, logical, language
Corpus Callosum
allows 2 hemi-sphere to communicate
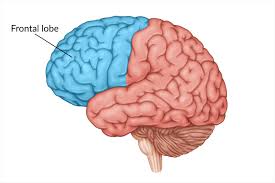
Frontal lobes
personality, working memory, critical thinking, emotions, speech
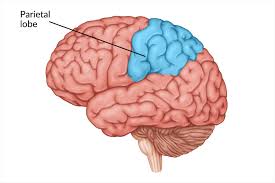
Parietal lobes
process sense of touch, stimulates movement, and body control
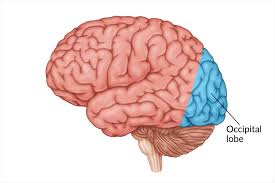
Occipital lobes
process visual info, visual cortex, does NOT identify people or objects
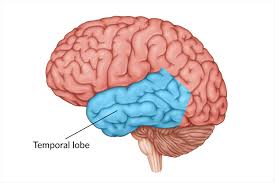
Temporal lobes
processes hearing and language
Cerebellum
balance, coordination, memory, motor movement, processes sensory input, balance, non-verbal learning,
Medulla
controls heartbeat, breathing, digestion, and blood pressure
reticular activating system (RAS)
relays information to the brain through routes, stimulates arousal and alertness
Thalamus
brain sensory control center, receives information from all senses except smell
Hypothalamus
notifies body of hunger, thirst, body temperature (shivering and sweating), sexual behavior, controls all glands
Amygdala
enables aggression and fear
Hippocampus
converts short-term memories into long term ones, involved with spatial awareness, memory, and learning
pre-fontal cortex
processes tasks, memory, critical thinking, and emotions
Broca’s Area
left hemisphere in the frontal lobe
produces speech
motor cortex
back of the frontal lobe
sense of movement
somatic sensory cortex
processes which area is most sensitive to detecting pain
auditory cortex
helps you understand spoken language
insomnia
linked to low GABA and pineal gland
limbic system
HAH! hypothalamus, amygdala, hippocampus
ach
linked with alzeimers
basal ganglia
voluntary movements, routine behaviors, linked with parkinson’s and dopamine levels